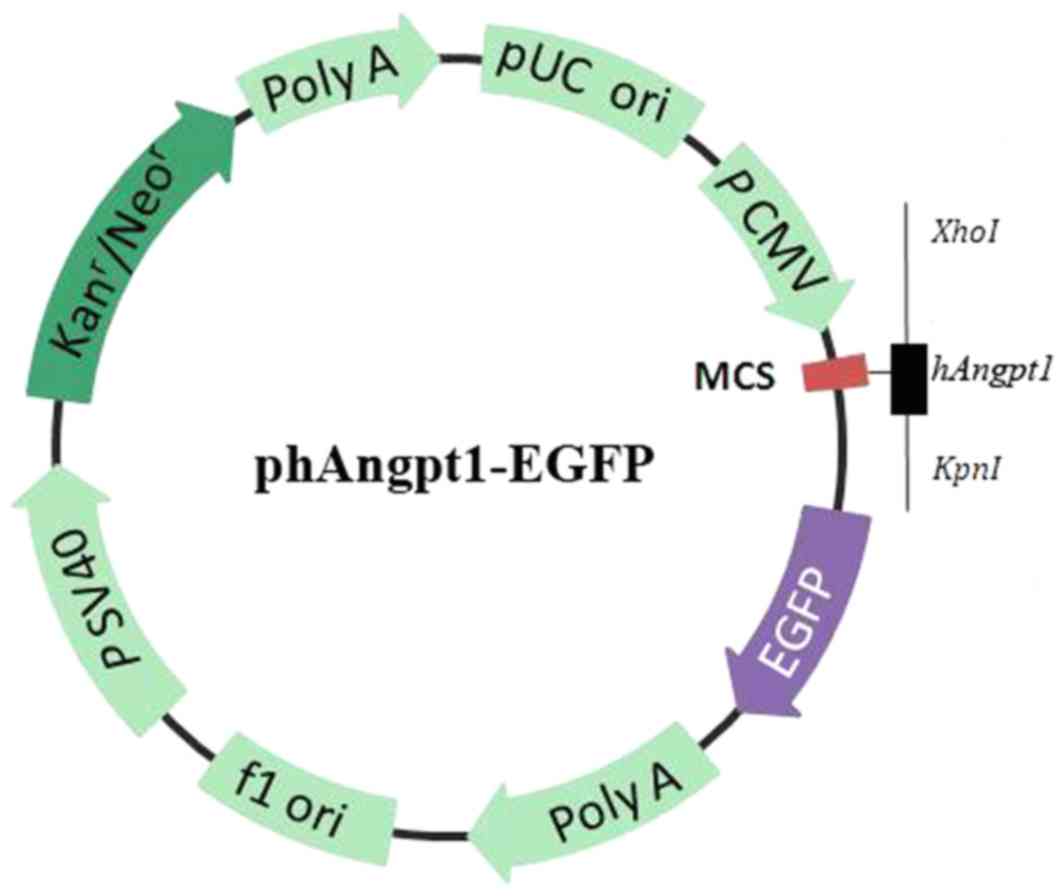
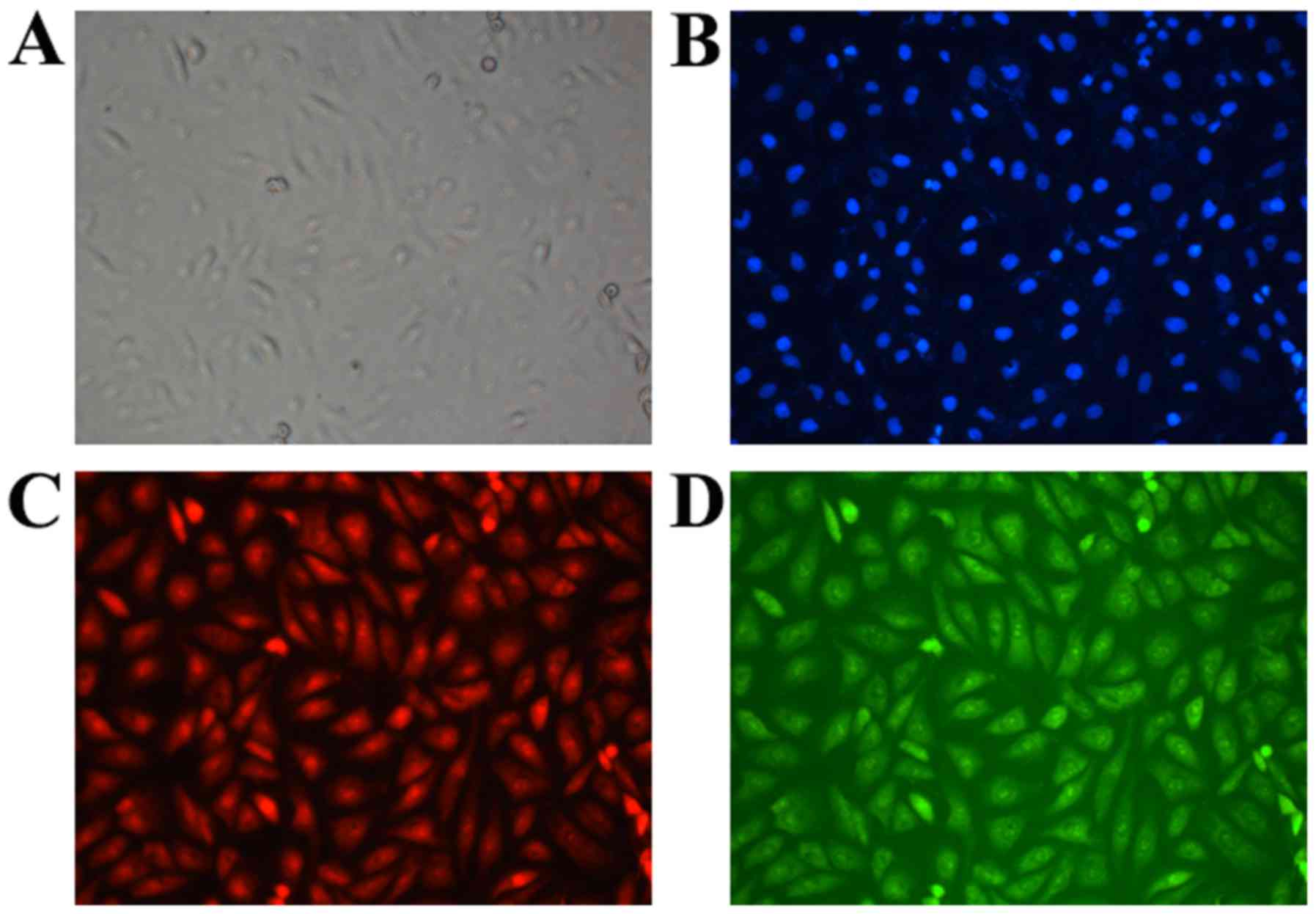
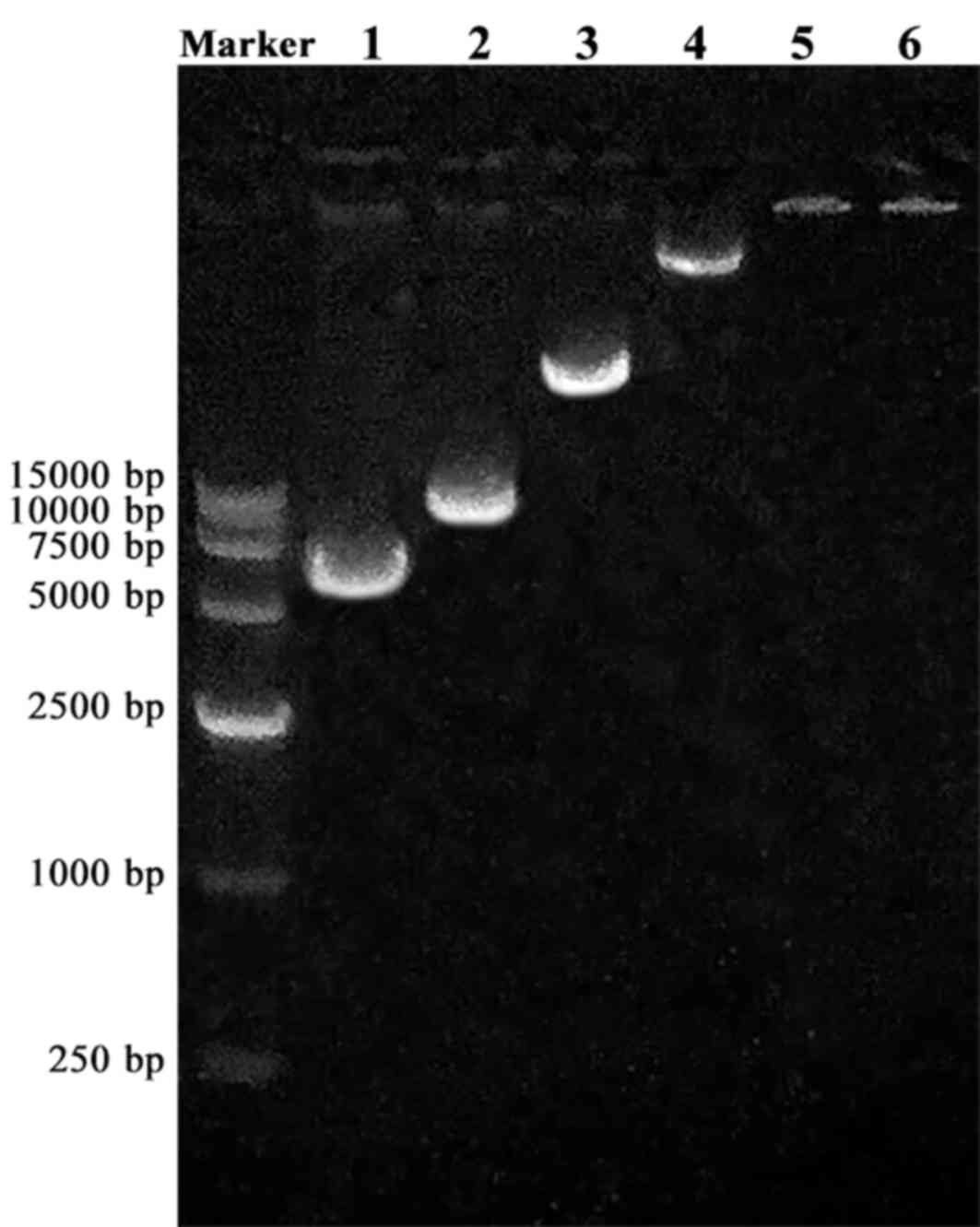
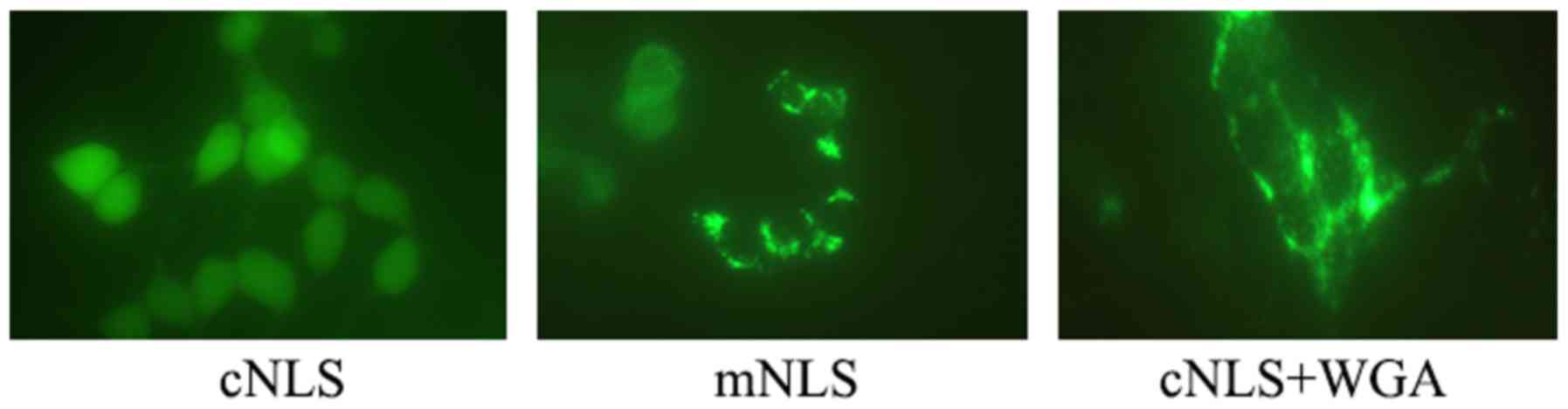
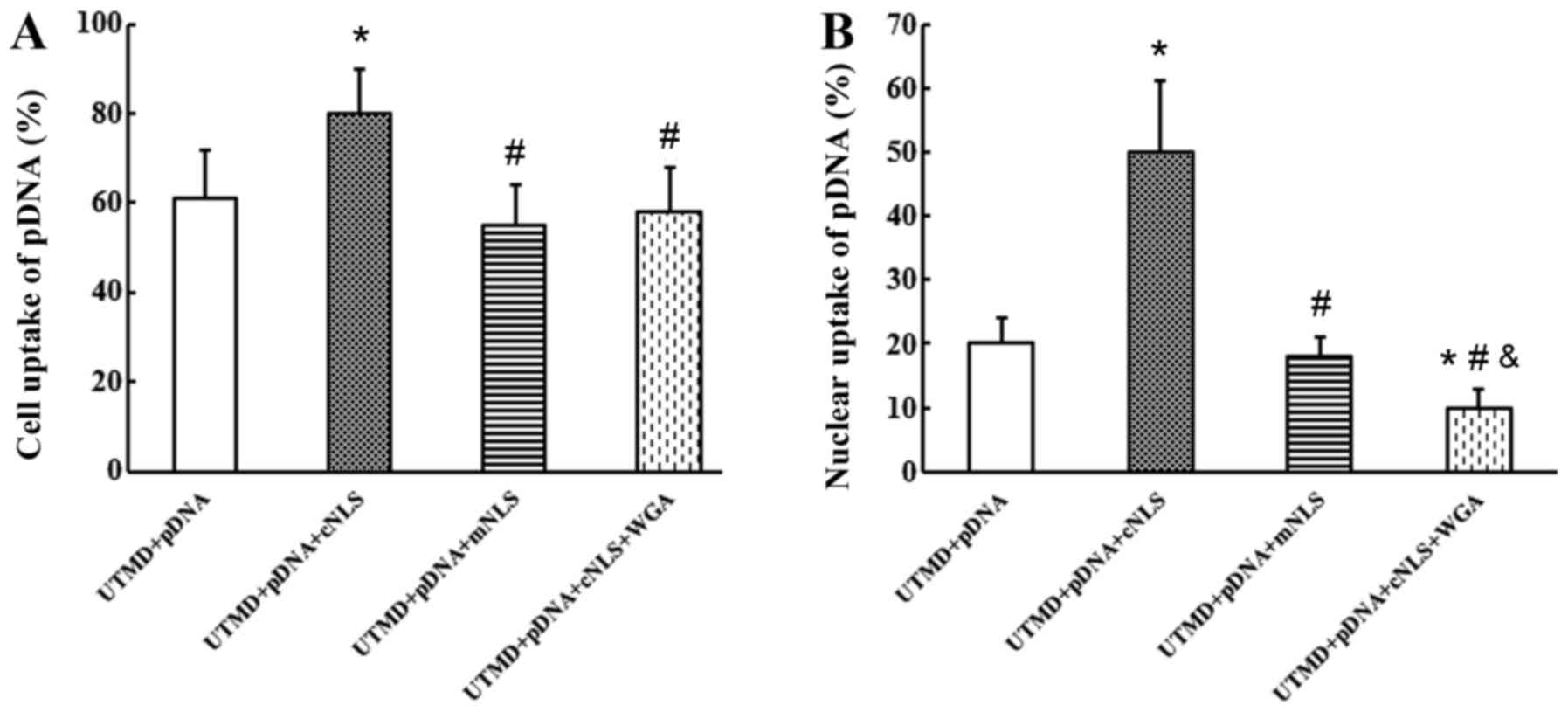
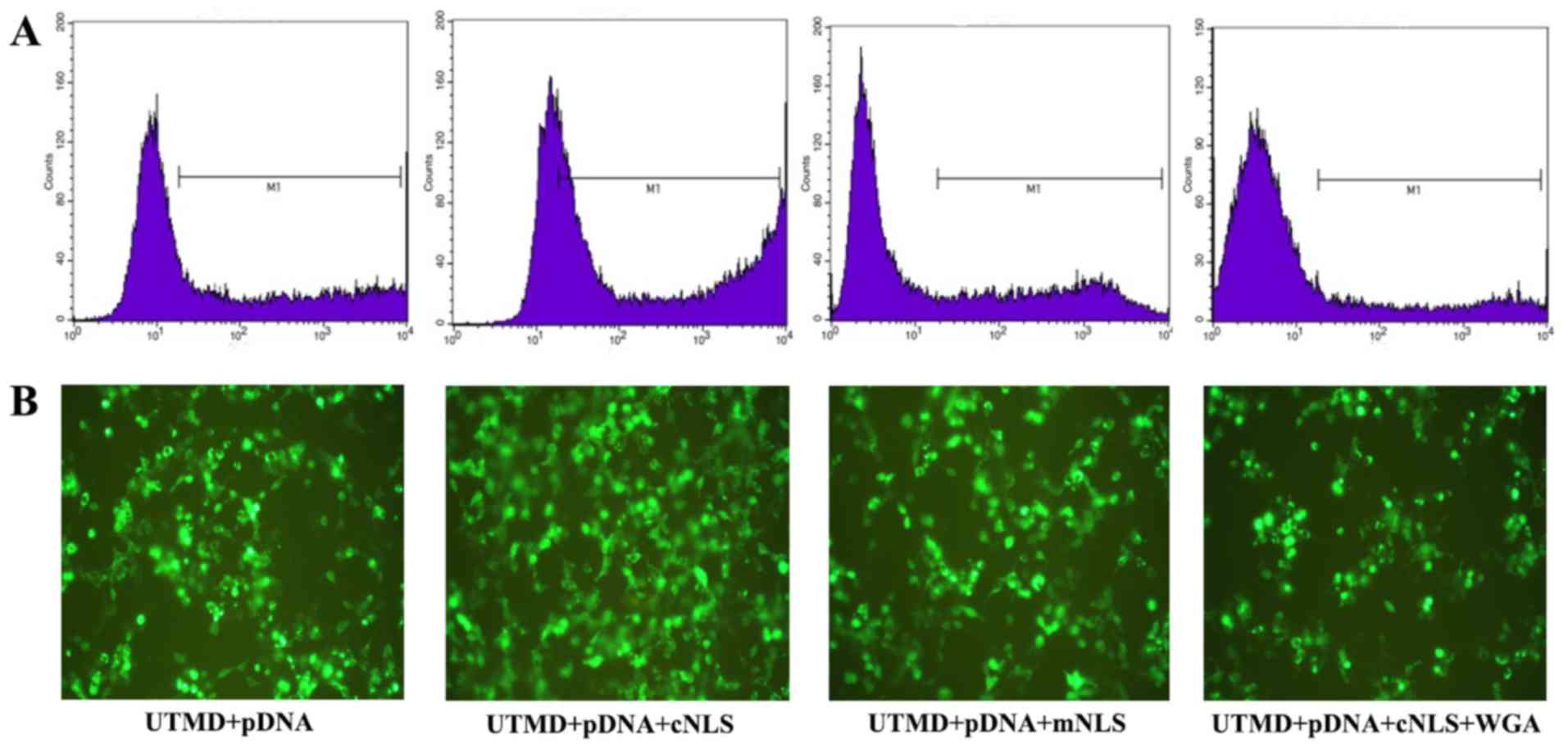
|
1
|
Noble ML, Kuhr CS, Graves SS, Loeb KR, Sun
SS, Keilman GW, Morrison KP, Paun M, Storb RF and Miao CH:
Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-mediated gene delivery
into canine livers. Mol Ther. 21:1687–1694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hernot S and Klibanov AL: Microbubbles in
ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
60:1153–1166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fan Z, Chen D and Deng CX: Improving
ultrasound gene transfection efficiency by controlling ultrasound
excitation of microbubbles. J Control Release. 170:401–413. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Teulon JM, Delcuze Y, Odorico M, Chen SW,
Parot P and Pellequer JL: Single and multiple bonds in
(strept)avidin-biotin interactions. J Mol Recognit. 24:490–502.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kocbek P, Obermajer N, Cegnar M, Kos J and
Kristl J: Targeting cancer cells using PLGA nanoparticles surface
modified with monoclonal antibody. J Control Release. 120:18–26.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Laing ST and McPherson DD: Cardiovascular
therapeutic uses of targeted ultrasound contrast agents. Cardiovasc
Res. 83:626–635. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Suzuki R, Oda Y, Utoguchi N and Maruyama
K: Progress in the development of ultrasound-mediated gene delivery
systems utilizing nano- and microbubbles. J Control Release.
149:36–41. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mannell H, Pircher J, Fochler F, Stampnik
Y, Räthel T, Gleich B, Plank C, Mykhaylyk O, Dahmani C, Wörnle M,
et al: Site directed vascular gene delivery in vivo by ultrasonic
destruction of magnetic nanoparticle coated microbubbles.
Nanomedicine. 8:1309–1318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meinema AC, Poolman B and Veenhoff LM: The
transport of integral membrane proteins across the nuclear pore
complex. Nucleus. 3:322–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marfori M, Mynott A, Ellis JJ, Mehdi AM,
Saunders NFW, Curmi PM, Forwood JK, Bodén M and Kobe B: Molecular
basis for specificity of nuclear import and prediction of nuclear
localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1562–1577. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lupberger J, Schaedler S, Peiran A and
Hildt E: Identification and characterization of a novel bipartite
nuclear localization signal in the hepatitis B virus polymerase.
World J Gastroenterol. 19:8000–8010. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Adam SA, Lobl TJ, Mitchell MA and Gerace
L: Identification of specific binding proteins for a nuclear
location sequence. Nature. 337:276–279. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Collins E, Birchall JC, Williams JL and
Gumbleton M: Nuclear localisation and pDNA condensation in
non-viral gene delivery. J Gene Med. 9:265–274. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yoo HS and Jeong SY: Nuclear targeting of
non-viral gene carriers using psoralen-nuclear localization signal
(NLS) conjugates. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 66:28–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Finlay DR, Newmeyer DD, Price TM and
Forbes DJ: Inhibition of in vitro nuclear transport by a lectin
that binds to nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 104:189–200. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deng P, Gong X and Jiang Y: A novel method
for studying nuclear localization signal-mediated nuclear
translocation. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 32:1148–1150.
2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deng Q, Chen JL, Zhou Q, Hu B, Chen Q,
Huang J and Guo RQ: Ultrasound microbubbles combined with the NFκB
binding motif increase transfection efficiency by enhancing the
cytoplasmic and nuclear import of plasmid DNA. Mol Med Rep.
8:1439–1445. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Villanueva FS: Getting good vibes: The
therapeutic power of microbubbles and ultrasound. JACC Cardiovasc
Imaging. 5:1263–1266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kooiman K, Emmer M, Foppen-Harteveld M,
van Wamel A and de Jong N: Increasing the endothelial layer
permeability through ultrasound-activated microbubbles. IEEE Trans
Biomed Eng. 57:29–32. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meijering BDM, Juffermans LJ, van Wamel A,
Henning RH, Zuhorn IS, Emmer M, Versteilen AM, Paulus WJ, van Gilst
WH, Kooiman K, et al: Ultrasound and microbubble targeted delivery
of macromolecules is regulated by induction of endocytosis and pore
formation. Circ Res. 104:679–687. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bekeredjian R, Kroll RD, Fein E, Tinkov S,
Coester C, Winter G, Katus HA and Kulaksiz H: Ultrasound targeted
microbubble destruction increases capillary permeability in
hepatomas. Ultrasound Med Biol. 33:1592–1598. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li P, Gao Y, Liu Z, Tan K, Zuo Z, Xia H,
Yang D, Zhang Y and Lu D: DNA transfection of bone marrow stromal
cells using microbubble-mediated ultrasound and polyethylenimine:
An in vitro study. Cell Biochem Biophys. 66:775–786. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Werth S, Urban-Klein B, Dai L, Höbel S,
Grzelinski M, Bakowsky U, Czubayko F and Aigner A: A low molecular
weight fraction of polyethylenimine (PEI) displays increased
transfection efficiency of DNA and siRNA in fresh or lyophilized
complexes. J Control Release. 112:257–270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim BK, Kang H, Doh KO, Lee SH, Park JW,
Lee SJ and Lee TJ: Homodimeric SV40 NLS peptide formed by disulfide
bond as enhancer for gene delivery. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
22:5415–5418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Duvshan-Eshet M, Keren H, Oz S,
Radzishevsky IS, Mor A and Machluf M: Effect of peptides bearing
nuclear localization signals on therapeutic ultrasound mediated
gene delivery. J Gene Med. 10:1150–1159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yi WJ, Yang J, Li C, Wang HY, Liu CW, Tao
L, Cheng SX, Zhuo RX and Zhang XZ: Enhanced nuclear import and
transfection efficiency of TAT peptide-based gene delivery systems
modified by additional nuclear localization signals. Bioconjug
Chem. 23:125–134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Duvshan-Eshet M, Haber T and Machluf M:
Insight concerning the mechanism of therapeutic ultrasound
facilitating gene delivery: Increasing cell membrane permeability
or interfering with intracellular pathways? Hum Gene Ther.
25:156–164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Opanasopit P, Rojanarata T, Apirakaramwong
A, Ngawhirunpat T and Ruktanonchai U: Nuclear localization signal
peptides enhance transfection efficiency of chitosan/DNA complexes.
Int J Pharm. 382:291–295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kawazu T, Kanzaki H, Uno A, Azuma H and
Nagasaki T: HVJ-E/importin-β hybrid vector for overcoming
cytoplasmic and nuclear membranes as double barrier for non-viral
gene delivery. Biomed Pharmacother. 66:519–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stock K, Nolden L, Edenhofer F, Quandel T
and Brüstle O: Transcription factor-based modulation of neural stem
cell differentiation using direct protein transduction. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 67:2439–2449. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Arenal A, Pimentel R, García C, Pimentel E
and Aleström P: The SV40 T antigen nuclear localization sequence
enhances nuclear import of vector DNA in embryos of a crustacean
(Litopenaeus schmitti). Gene. 337:71–77. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|