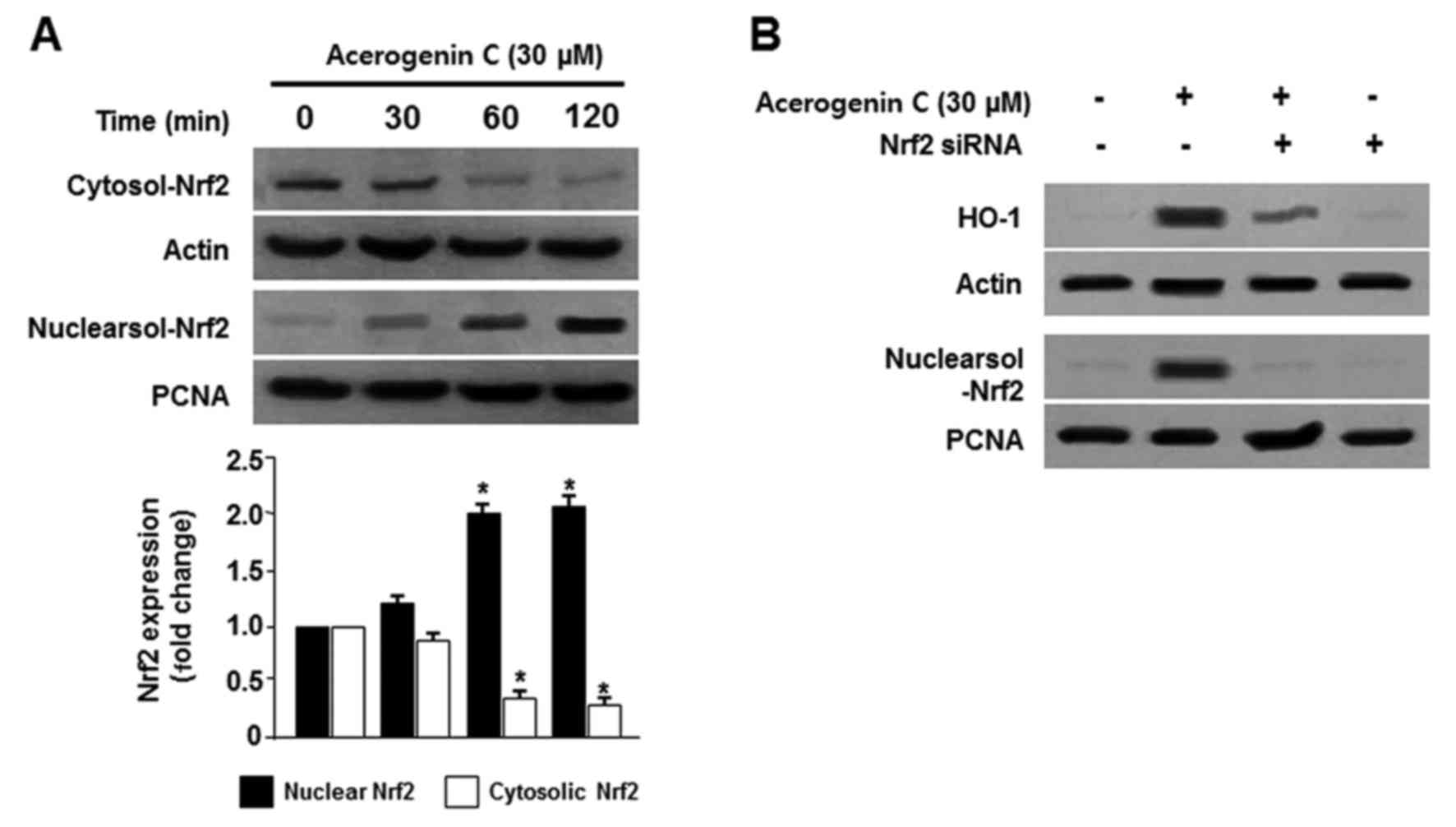
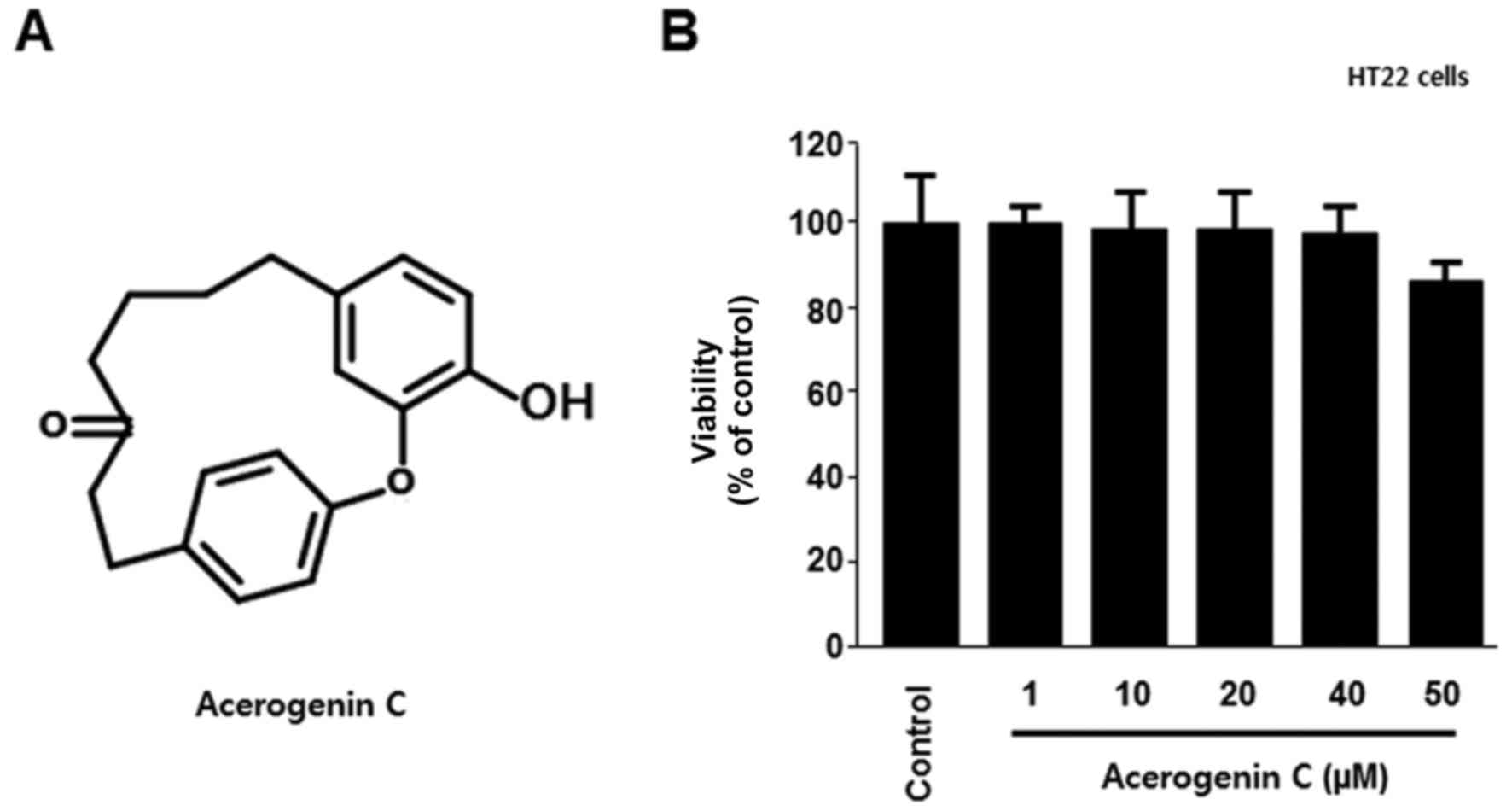
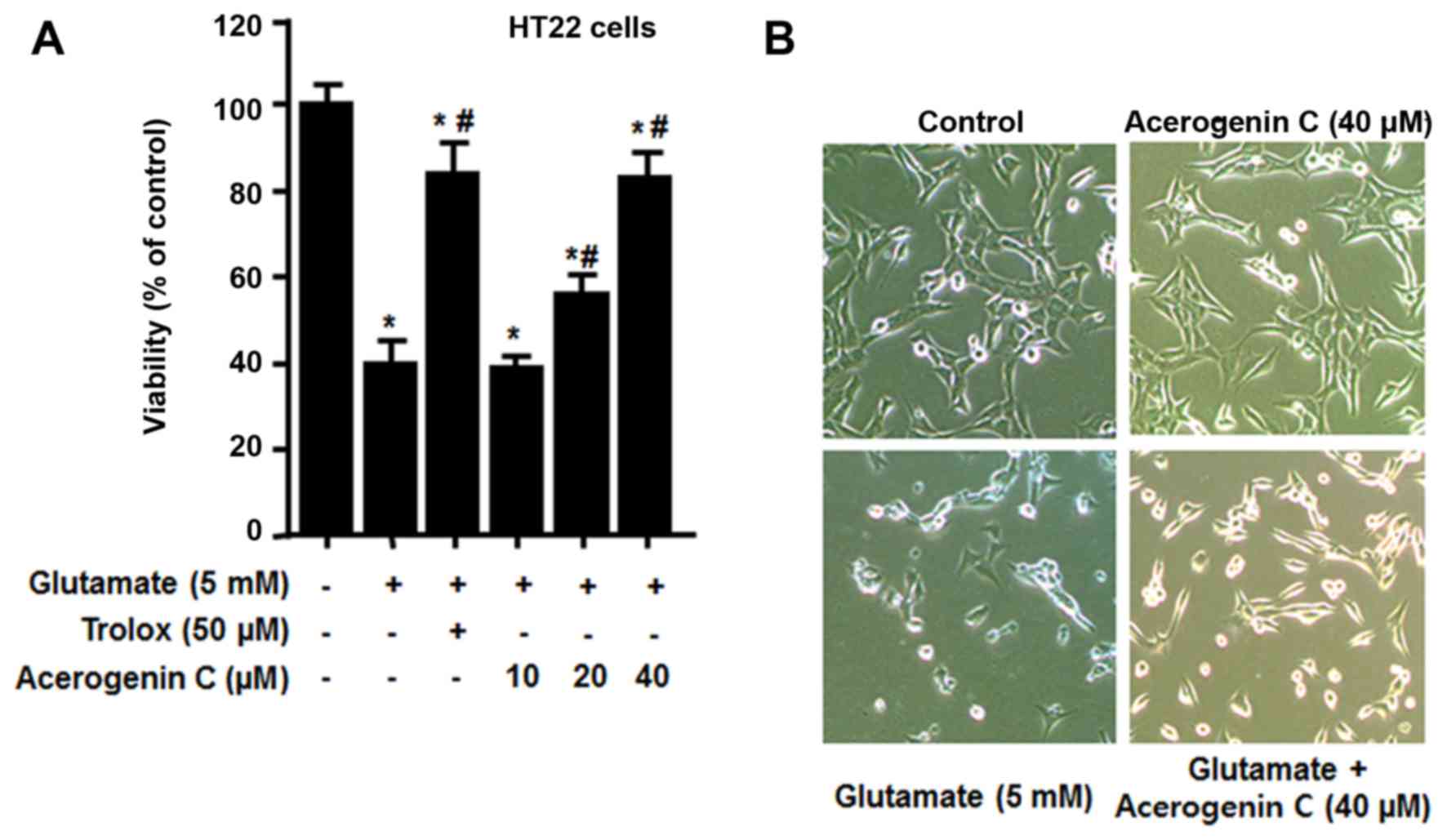
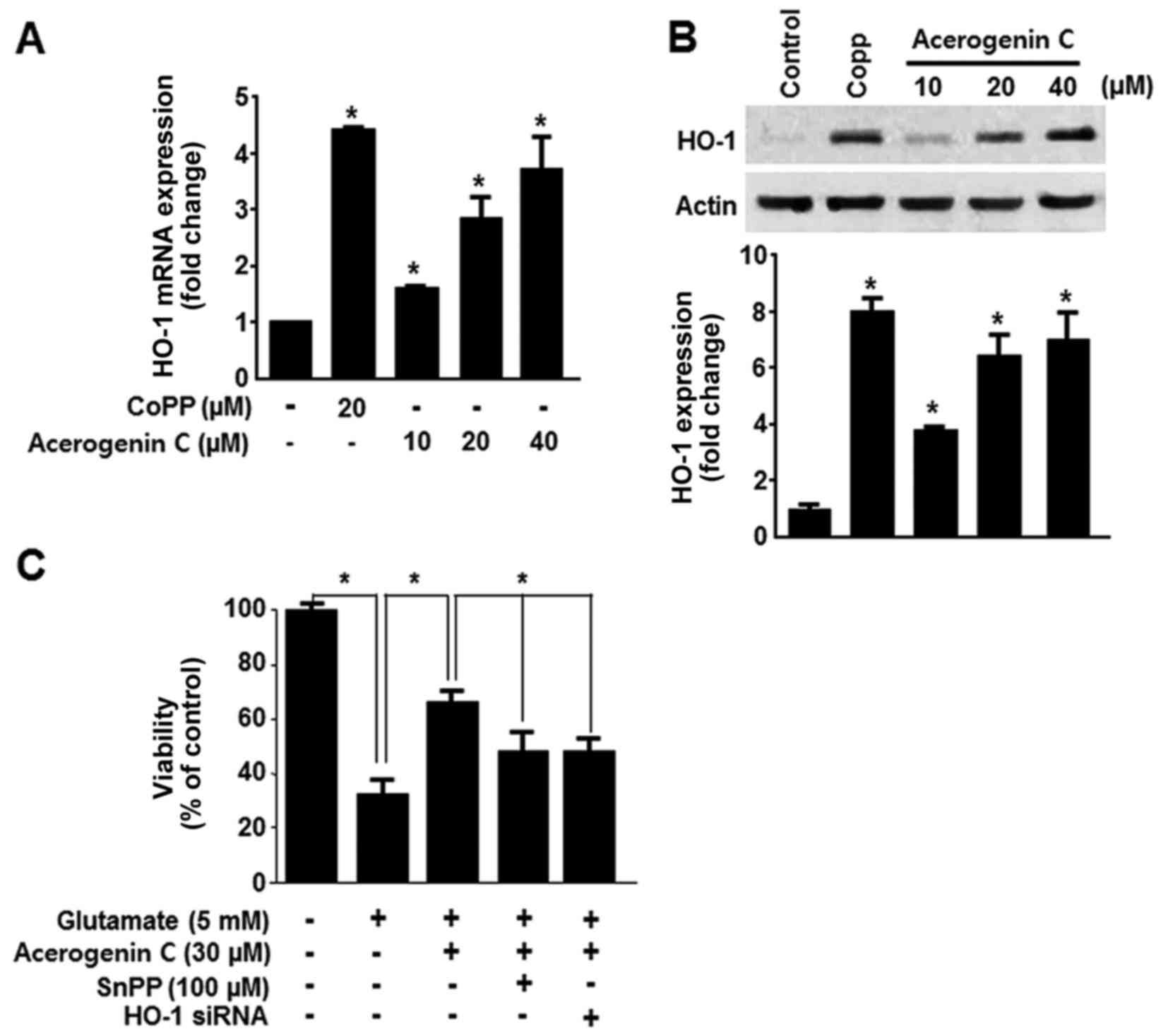
|
1
|
Jazwa A and Cuadrado A: Targeting heme
oxygenase-1 for neuroprotection and neuroinflammation in
neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 11:1517–1531. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mosley RL, Benner EJ, Kadiu I, Thomas M,
Boska MD, Hasan K, Laurie C and Gendelman HE: Neuroinflammation,
Oxidative Stress and the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease. Clin
Neurosci Res. 6:261–281. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Caceres LG, Aon Bertolino L, Saraceno GE,
Zubilete MA Zorrilla, Uran SL, Capani F and Guelman LR:
Hippocampal-related memory deficits and histological damage induced
by neonatal ionizing radiation exposure. Role of oxidative status.
Brain Res. 1312:67–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Conrad M and Sato H: The oxidative
stress-inducible cystine/glutamate antiporter, system × (c) (−):
Cystine supplier and beyond. Amino Acids. 42:231–246. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lim JL, Wilhelmus MM, de Vries HE,
Drukarch B, Hoozemans JJ and van Horssen J: Antioxidative defense
mechanisms controlled by Nrf2: State-of-the-art and clinical
perspectives in neurodegenerative diseases. Arch Toxicol.
88:1773–1786. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ouyang Y, Chen Z, Tan M, Liu A, Chen M,
Liu J, Pi R and Fang J: Carvedilol, a third-generation β-blocker
prevents oxidative stress-induced neuronal death and activates
Nrf2/ARE pathway in HT22 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
441:917–922. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haines DD, Lekli I, Teissier P, Bak I and
Tosaki A: Role of haeme oxygenase-1 in resolution of oxidative
stress-related pathologies: Focus on cardiovascular, lung,
neurological and kidney disorders. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 204:487–501.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ryter SW, Otterbein LE, Morse D and Choi
AM: Heme oxygenase/carbon monoxide signaling pathways: Regulation
and functional significance. Mol Cell Biochem 234–235. 249–263.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kim DC, Cho KH, Ko W, Yoon CS, Sohn JH,
Yim JH, Kim YC and Oh H: Anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective
effects of TMC-256C1 from marine-derived Fungus Aspergillus sp.
SF-6354 via up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 in murine hippocampal
and microglial cell lines. Int J Mol Sci. 17:5292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee DS, Cha BY, Woo JT, Kim YC and Jang
JH: Acerogenin A from Acer nikoense Maxim prevents oxidative
stress-induced neuronal cell death through Nrf2-mediated heme
oxygenase-1 expression in mouse hippocampal HT22 cell line.
Molecules. 20:12545–12557. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nagai M, Kubo M, Fujita M, Inoue T and
Matsuo M: Studies on the constituents of Aceraceae plants. II.
Structure of aceroside I, a glucoside of a novel cyclic
diarylheptanoid from Acer nikoense Maxim. Chem Pharm Bull.
26:2805–2810. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Morikawa T, Tao J, Ueda K, Matsuda H and
Yoshikawa M: Medicinal foodstuffs. XXXI. Structures of new aromatic
constituents and inhibitors of degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells from
a Japanese folk medicine, the stem bark of Acer nikoense. Chem
Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 51:62–67. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Inoue T, Ishidate Y, Fujita M, Kubo M,
Fukushima M and Nagai M: Studies on the constituents of Aceraceae
plants. I. Constituents in the leaves and the stem bark of Acer
nikoense Maxim. Yakugaku Zasshi. 98:41–46. 1978.(In Japanese).
|
|
14
|
Furukawa N, Nagumo S, Inoue T and Nagai M:
Studies on the constituents of aceraceae plants VII.
Coumarinolignans from the wood of Acer nikoense. Shoyakugaku
Zasshi. 42:163–165. 1988.
|
|
15
|
Morita H, Deguchi J, Motegi Y, Sato S,
Aoyama C, Takeo J, Shiro M and Hirasawa Y: Cyclic diarylheptanoids
as Na+-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitors from Acer nikoense.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 20:1070–1074. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deguchi J, Motegi Y, Nakata A, Hosoya T
and Morita H: Cyclic diarylheptanoids as inhibitors of NO
production from Acer nikoense. J Nat Med. 67:234–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Akazawa H, Akihisa T, Taguchi Y, Banno N,
Yoneima R and Yasukawa K: Melanogenesis inhibitory and free radical
scavenging activities of diarylheptanoids and other phenolic
compounds from the bark of Acer nikoense. Biol Pharm Bull.
29:1970–1972. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Inoue T: Constituents of Acer nikoense and
Myrica rubra. On diarylheptanoids. Yakugaku Zasshi. 113:181–197.
1993.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shinoda M, Ohta S, Kumasaka M, Fujita M,
Nagai M and Inoue T: Protective effect of the bark of Acer nikoense
on hepatic injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats.
Shoyakugaku Zasshi. 40:177–181. 1986.
|
|
20
|
Kihara T, Ichikawa S, Yonezawa T, Lee JW,
Akihisa T, Woo JT, Michi Y, Amagasa T and Yamaguchi A: Acerogenin
A, a natural compound isolated from Acer nikoense Maxim, stimulates
osteoblast differentiation through bone morphogenetic protein
action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 406:211–217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cha BY, Wen LS, Kotaro W, Takayuki Y,
Toshiaki T, Kiyotake K, Yuichi I, Shigeru N, Kazuo N and Woo JT:
Antiproliferative activity of acerogenin C, a
macrocyclicdiarylheptanoid, on PDGF-induced human aortic smooth
muscle cells proliferation. Sci Res Publ. 6:47–55. 2015.
|
|
22
|
Kim JS, Kim HJ, Jung CL, Nam DH, Lim JS,
Han MY and Hong YS: Estrogenic activity of acerogenin C isolated
from Acer nikoense Maxim. FASEB J. 25:771.102011.
|
|
23
|
Litvak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)). Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Martin D, Rojo AI, Salinas M, Diaz R,
Gallardo G, Alam J, De Galarreta CM and Cuadrado A: Regulation of
heme oxygenase-1 expression through the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt pathway and the Nrf2 transcription factor in response
to the antioxidant phytochemical carnosol. J Biol Chem.
279:8919–8929. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koehn FE and Carter GT: Rediscovering
natural products as a source of new drugs. Discov Med. 5:159–164.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hald A and Lotharius J: Oxidative stress
and inflammation in Parkinson's disease: Is there a causal link?
Exp Neurol. 193:279–290. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee DS, Jeong GS, Li B, Park H and Kim YC:
Anti-inflammatory effects of sulfuretin from Rhus verniciflua
Stokes via the induction of heme oxygenase-1 expression in murine
macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 10:850–858. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee DS and Jeong GS: Arylbenzofuran
isolated from Dalbergia odorifera suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse BV2 microglial cell activation,
which protects mouse hippocampal HT22 cells death from
neuroinflammation-mediated toxicity. Eur J Pharmacol. 728:1–8.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liao G, Li R, Chen X, Zhang W, Du S and
Yuan Y: Sodium valproate prevents radiation-induced injury in
hippocampal neurons via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
Neuroscience. 331:40–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang B, Liu H, Yue L, Li X, Zhao L, Yang
X, Wang X, Yang Y and Qu Y: Neuroprotective effects of
pterostilbene against oxidative stress injury: Involvement of
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 pathway. Brain Res.
1643:70–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li B, Jeong GS, Kang DG, Lee HS and Kim
YC: Cytoprotective effects of lindenenyl acetate isolated from
Lindera strychnifolia on mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 614:58–65. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee DS, Ko W, Kim DC, Kim YC and Jeong GS:
Cudarflavone B provides neuroprotection against glutamate-induced
mouse hippocampal HT22 cell damage through the Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt
signaling pathways. Molecules. 19:10818–10831. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang B, Liu H, Yue L, Li X, Zhao L, Yang
X, Wang X, Yang Y and Qu Y: Neuroprotective effects of
pterostilbene against oxidative stress injury: Involvement of
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 pathway. Brain Res.
1643:70–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sandberg M, Patil J, D'Angelo B, Weber SG
and Mallard C: NRF2-regulation in brain health and disease:
Implication of cerebral inflammation. Neuropharmacology.
79:298–306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mann GE: Nrf2-mediated redox signalling in
vascular health and disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 75 Suppl
1:S12014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Krajka-Kuźniak V, Paluszczak J and
Baer-Dubowska W: Xanthohumol induces phase II enzymes via Nrf2 in
human hepatocytes in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 27:149–156. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saw CL, Guo Y, Yang AY, Paredes-Gonzalez
X, Ramirez C, Pung D and Kong AN: The berry constituents quercetin,
kaempferol, and pterostilbene synergistically attenuate reactive
oxygen species: Involvement of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Food
Chem Toxicol. 72:303–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Oh GS, Pae HO, Lee BS, Kim BN, Kim JM, Kim
HR, Jeon SB, Jeon WK, Chae HJ and Chung HT: Hydrogen sulfide
inhibits nitric oxide production and nuclear factor-kappaB via heme
oxygenase-1 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated with
lipopolysaccharide. Free Radic Biol Med. 41:106–119. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Alam J, Stewart D, Touchard C, Boinapally
S, Choi AM and Cook JL: Nrf2, a Cap'n'Collar transcription factor,
regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J Biol Chem.
274:26071–26078. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Elbirt KK, Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ and
Bonkovsky HL: Mechanism of sodium arsenite-mediated induction of
heme oxygenase-1 in hepatoma cells. Role of mitogen-activated
protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 273:8922–8931. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|