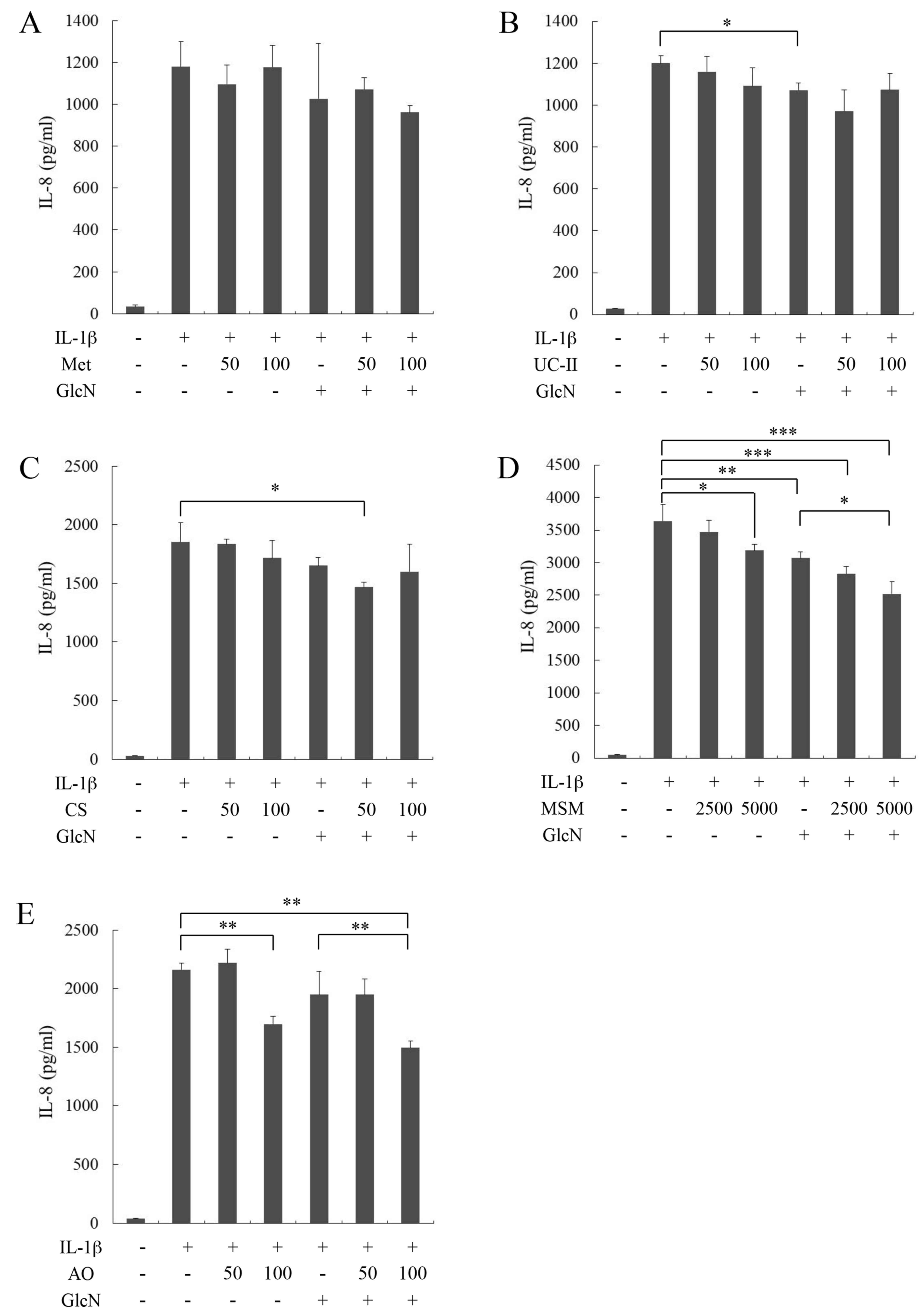
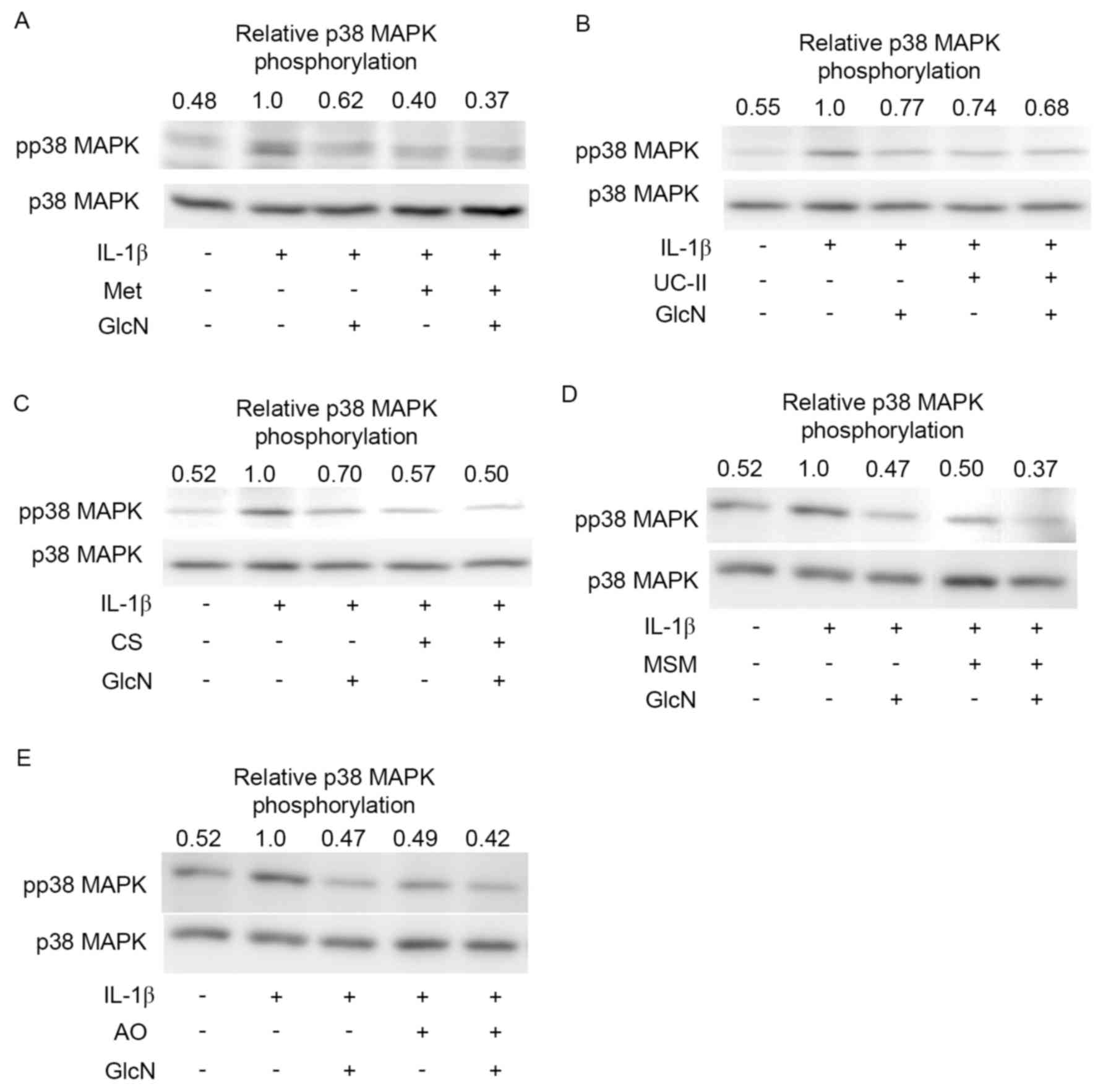
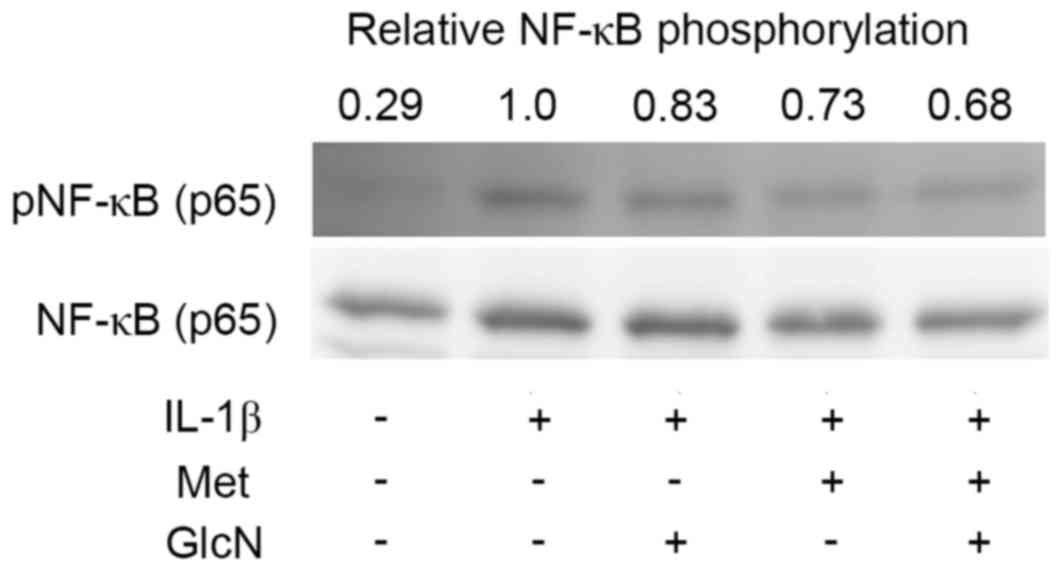
|
1
|
Fenton JI, Chlebec-Brown KA, Peters TL,
Caron JP and Orth MW: Glucosamine HCl reduces equine articular
cartilage degradation in explants culture. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 8:258–265. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oegema TR Jr, Deloria LB, Sandy JD and
Hart DA: Effect of oral glucosamine on cartilage and meniscus in
normal and chymopapain-injected knees of young rabbits. Arthritis
Rheum. 46:2495–2503. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gouze JN, Bordji K, Gulberti S, Terlain B,
Netter P, Magdalou J, Fournel-Giqleux S and Ouzzine M:
Interleukin-1beta down-regulates the expression of
glucuronosyltransferase I, a key enzyme priming glycosaminoglycan
biosynthesis: Influence of glucosamine on
Interleukin-1beta-mediated effects in rat chondrocytes. Arthritis
Rheum. 44:351–360. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hua J, Sakamoto K, Kikukawa T, Abe C,
Kurosawa H and Nagaoka I: Evaluation of the suppressive actions of
glucosamine on the interleukin-1beta-mediated activation of
synoviocytes. Inflamm Res. 56:432–438. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nagaoka I: Recent aspects of the
chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory actions of glucosamine, a
functional food. Juntendo Medical J. 60:580–587. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Largo R, Alvarez-Soria MA, Díez-Ortego I,
Sánchez-Pernatute O, Eqido J and Herrero-Beaumont G: Glucosamine
inhibits IL-1beta-induced NFkappaB activation in human
osteoarthritic chondrocyte. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 11:290–298.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rafi MM, Yadav PN and Rossi AO:
Glucosamine inhibits LPS-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression in mouse
macrophage cells (RAW 264.7) by inhibition of p38-MAP kinase and
transcription factor NF-kappaB. Mol Nutr Food Res. 51:587–593.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ju Y, Hua J, Sakamoto K, Ogawa H and
Nagaoka I: Modulaion of TNF-α-induced endothelial cell activation
by glucosamine, a naturally occurring amino monosaccharide. Int J
Mol Med. 22:809–815. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yomogida S, Hua J, Sakamoto K and Nagaoka
I: Glucosamine suppresses interleukin-8 production and
ICAM-1expression by TNF-α-stimulated human colonic epithelial HT-29
cells. Int J Mol Med. 22:205–211. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iouv M, Dumais G and du Souich P:
Anti-inflammatory activity of chondroitin sulfate. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 16 Suppl 3:S14–S18. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim YH, Kim DH, Lim H, Baek DY, Shin HK
and Kim JK: The anti-inflammatory effects of methylsulfonylmethane
on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in murine
macrophages. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:651–656. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ohnogi H, Kudo Y, Hayami S, Mizutani S and
Enoki T: Synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of
agaro-oligosaccharides and glucosamine in vivo and in vitro.
Glucosamine Res. 8:51–56. 2012.(In Japanese).
|
|
13
|
Volpi N: Anti-inflammatory activity of
chondroitin sulphate: New functions from an old natural
macromolecule. Inflammopharmacology. 19:299–306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hasegawa T, Ueno S and Kumamoto S:
Suppressive effect of methylsulphonylmethane (MSM) on type II
collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice. Jpn Pharmacol Ther.
32:421–427. 2004.
|
|
15
|
Yamagishi Y, Igarashi M, Suzuki A, Suguro
S, Hirano SI and Nagaoka I: Evaluation of the effect of methionine
and glucosamine on adjuvant arthritis in rats. Exp Ther Med.
4:640–644. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lugo JP, Saiyed ZM and Lane NE: Efficacy
and tolerability of an undenatured type II collagen supplement in
modulating knee osteoarthritis symptoms: A multicenter randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr J. 15:142016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoshimura S, Asano K and Nakane A:
Attenuation of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by salmon
proteoglycan. Biomed Res Int. 2014:4064532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tobetto K, Yasui T, Ando T, Hayashi M,
Motohashi N, Shinogi M and Mori I: Inhibitort effects of hyaluronan
on [14C]arachidonic acid release from labeled human synovial
fibroblast. Jap J Pharmacol. 60:79–84. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Isaka S, Someya A, Nakamura S, Naito K,
Nozawa M, Inoue N, Sugihara F, Nagaoka I and Kaneko K: Evaluation
of the effect of oral administration of collagen peptides on an
experimental rat osteoarthritis model. Exp Ther Med. (In press).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ohara H, Matsumoto H, Ito K, Iwai K and
Sato K: Comparison of quantity and structures of
Hydroxyproline-containing peptides in human blood after oral
ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates from different sources. J Agric
Food Chem. 55:1532–1535. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gong D, Geng C, Jiang L, Wang L, Yoshimura
H and Zhong L: Mechanisms of olive leaf extract-ameliorated rat
arthritis caused by kaolin and carrageenan. Phytother Res.
26:397–402. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee TY, Lee KC, Chen SY and Chang HH:
6-Gingerol inhibits ROS and iNOS through the suppression of
PKC-alpha and NF-kappaB pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
mouse macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 382:134–139. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Catanzaro D, Rancan S, Orso G, Dall'Acqua
S, Brun P, Giron MC, Carrara M, Castagliuolo I, Ragazzi E,
Caparrotta L and Montopoli M: Boswellia serrata Preserves
Intestinal Epithelial Barrier from Oxidative and Inflammatory
Damage. PLoS One. 10:e01253752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fiebich BL, Muñoz E, Rose T, Weiss G and
McGregor GP: Molecular targets of the antiinflammatory
Harpagophytum procumbens (devil's claw): Inhibition of TNFα and
COX-2 gene expression by preventing activation of AP-1. Phytother
Res. 26:806–811. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang F, Yang F, Zhao H and An Y: Curcumin
alleviates lung injury in diabetic rats by inhibiting NF-κB
pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hua J, Suguro S, Sakamoto K and Nagaoka I:
Preventive actions of a high dose of glucosamine on adjuvant
arthritis in rats. Inflamm Res. 54:127–132. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Naito K, Watari T, Furuhata A, Yomogida S,
Sakamoto K, Kurosawa H, Kaneko K and Nagaoka I: Evaluation of the
effect of glucosamine on an experimental rat osteoarthritis model.
Life Sci. 86:538–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Enoki T, Okuda S, Kudo Y, Takshima F,
Sagawa H and Kato I: Oligosaccharides from agar inhibit
pro-inflammatory mediator release by inducing heme oxygenase 1.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 74:766–770. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoshinari O, Shiojima Y, Moriyama H,
Shinozaki J, Nakane T, Masuda K and Bagchi M: Water-soluble
undenaturated type II collagen ameliorates collagen-induced
arthritis in mice. J Med Food. 16:1039–1045. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Parhar K, Ray A, Steinbrecher U, Nelson C
and Salh B: The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates
interleukin-1beta-induced IL-8 expression via an effect on the IL-8
promoter in intestinal epithelial cells. Immunology. 108:502–512.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu DN, Chen M, Zhang DY, Ye F, McCormick
SA and Chan CC: Interleukin-1beta increases baseline expression and
secretion of interleukin-6 by human uveal melanocytes in vitro via
the p38 MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
52:3767–3774. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wells L, Vosseller K and Hart GW:
Glycosylation of nucleocytoplasmic proteins: Signal transduction
and O-GlcNAc. Science. 291:2376–2378. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hanover JA: Glycan-dependent signaling:
O-linled N-acetylglucosamine. FASEB J. 15:1865–1876. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|