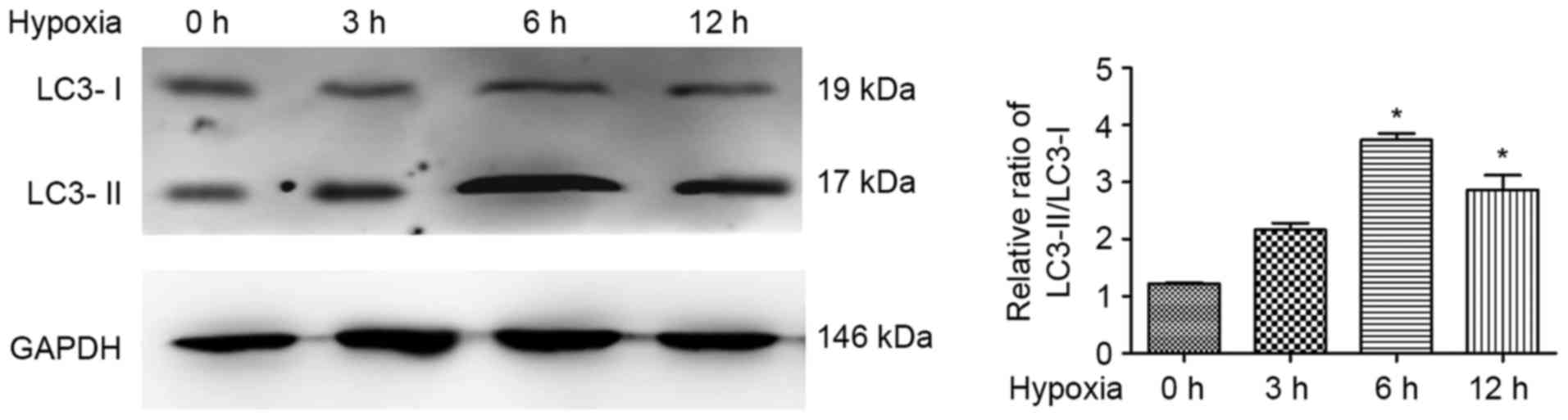
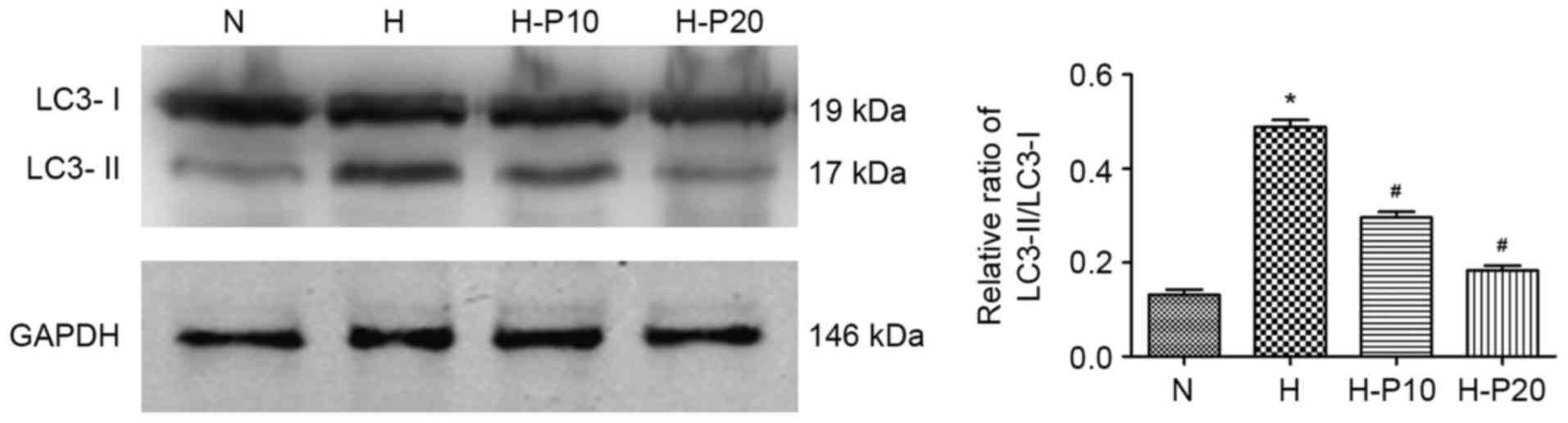
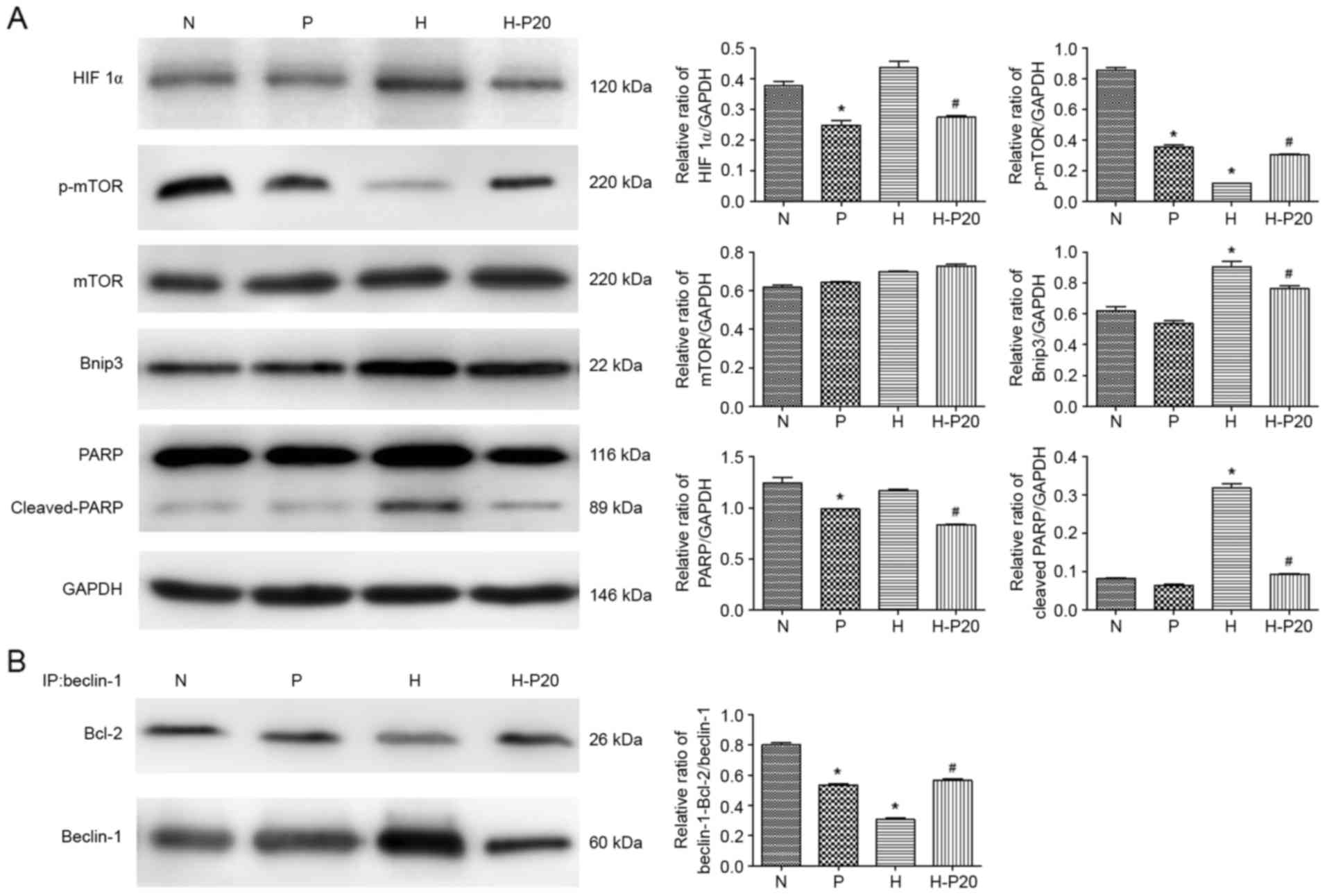
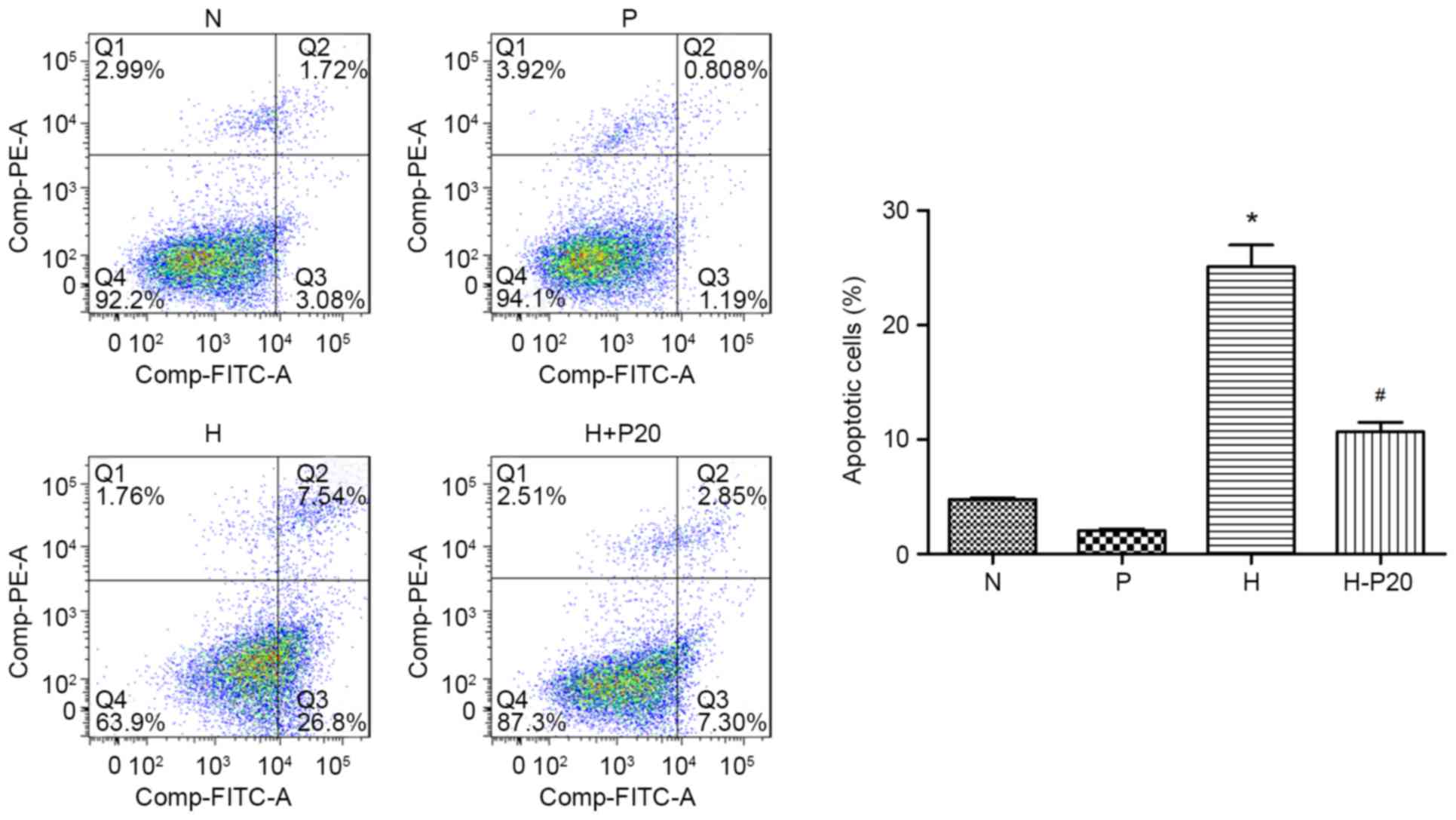
|
1
|
Li C, Xu M, Wu Y, Li YS, Huang WQ and Liu
KX: Limb remote ischemic preconditioning attenuates lung injury
after pulmonary resection under propofol-remifentanil anesthesia: A
randomized controlled study. Anesthesiology. 121:249–259. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bae HB, Li M, Lee SH, Jeong CW, Kim SJ,
Kim HS, Chung SS and Kwak SH: Propofol attenuates pulmonary injury
induced by collapse and reventilation of lung in rabbits.
Inflammation. 36:680–688. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yao W, Luo G, Zhu G, Chi X, Zhang A, Xia Z
and Hei Z: Propofol activation of the Nrf2 pathway is associated
with amelioration of acute lung injury in a rat liver
transplantation model. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:2585672014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hatakeyama N and Matsuda N: Alert cell
strategy: Mechanisms of inflammatory response and organ protection.
Curr Pharm Des. 20:5766–5778. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ma L, Wu XY, Zhang LH, Chen WM, Uchiyama
A, Mashimo T and Fujino Y: Propofol exerts anti-inflammatory
effects in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
by inhibition of CD14 and TLR4 expression. Braz J Med Biol Res.
46:299–305. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei L, Matsumoto H and Yamaguchi H:
Propofol attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 production through p38 MAPK and SAPK/JNK
in alveolar epithelial cells. J Anesth. 27:366–373. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yeh CH, Cho W, So EC, Chu CC, Lin MC, Wang
JJ and Hsing CH: Propofol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced lung
epithelial cell injury by reducing hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
expression. Br J Anaesth. 106:590–599. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsai YC, Huang CC, Chu LM and Liu YC:
Differential influence of propofol on different cell types in terms
of the expression of various oxidative stress-related enzymes in an
experimental endotoxemia model. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan.
50:159–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heberlein W, Wodopia R, Bärtsch P and
Mairbäurl H: Possible role of ROS as mediators of hypoxia-induced
ion transport inhibition of alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 278:L640–L648. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matthay MA, Folkesson HG and Clerici C:
Lung epithelial fluid transport and the resolution of pulmonary
edema. Physiol Rev. 82:569–600. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Clegg GR, Tyrrell C, McKechnie SR, Beers
MF, Harrison D and McElroy MC: Coexpression of RTI40 with alveolar
epithelial type II cell proteins in lungs following injury:
Identification of alveolar intermediate cell types. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 289:L382–L390. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ghosh MC, Gorantla V, Makena PS, Luellen
C, Sinclair SE, Schwingshackl A and Waters CM: Insulin-like growth
factor-I stimulates differentiation of ATII cells to ATI-like cells
through activation of Wnt5a. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
305:L222–L228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He XY, Shi XY, Yuan HB, Xu HT, Li YK and
Zou Z: Propofol attenuates hypoxia-induced apoptosis in alveolar
epithelial type II cells through down-regulating hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α. Injury. 43:279–283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rabinowitz JD and White E: Autophagy and
metabolism. Science. 330:1344–1348. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun Y, Xing X, Liu Q, Wang Z, Xin Y, Zhang
P, Hu C and Liu Y: Hypoxia-induced autophagy reduces
radiosensitivity by the HIF-1α/miR-210/Bcl-2 pathway in colon
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 46:750–756. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yousefi S and Simon HU: Apoptosis
regulation by autophagy gene 5. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 63:241–244.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo XG, Ji TX, Xia Y and Ma YY: Autophagy
protects type II alveolar epithelial cells from Mycobacterium
tuberculosis infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 432:308–313.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thorburn J, Horita H, Redzic J, Hansen K,
Frankel AE and Thorburn A: Autophagy regulates selective HMGB1
release in tumor cells that are destined to die. Cell Death Differ.
16:175–183. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cui DR, Wang L, Jiang W, Qi AH, Zhou QH
and Zhang XL: Propofol prevents cerebral ischemia-triggered
autophagy activation and cell death in the rat hippocampus through
the NF-κB/p53 signaling pathway. Neuroscience. 246:117–132. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen Z, Hu Z, Lu Z, Cai S, Gu X, Zhuang H,
Ruan Z, Xia Z, Irwin MG, Feng D and Zhang L: Differential microRNA
profiling in a cellular hypoxia reoxygenation model upon
posthypoxic propofol treatment reveals alterations in autophagy
signaling network. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:3784842013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dobbs LG, Gonzalez R and Williams MC: An
improved method for isolating type II cells in high yield and
purity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 134:141–145. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu YL, Jahangiri A, De Lay M and Aghi MK:
Hypoxia-induced tumor cell autophagy mediates resistance to
anti-angiogenic therapy. Autophagy. 8:979–981. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mizushima N: Methods for monitoring
autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2491–2502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P,
Chiche J, Roux D, Pouysségur J and Mazure NM: Hypoxia-induced
autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of
BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2570–2581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang J and Ney PA: Role of BNIP3 and NIX
in cell death, autophagy, and mitophagy. Cell Death Differ.
16:939–946. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jung CH, Jun CB, Ro SH, Kim YM, Otto NM,
Cao J, Kundu M and Kim DH: ULK-Atg13-FIP200 complexes mediate mTOR
signaling to the autophagy machinery. Mol Biol Cell. 20:1992–2003.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Noh HS, Shin IW, Ha JH, Hah YS, Baek SM
and Kim DR: Propofol protects the autophagic cell death induced by
the ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Cells. 30:455–460.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Wang Y, Kim E, Beemiller P, Wang CY,
Swanson J, You M and Guan KL: Bnip3 mediates the hypoxia-induced
inhibition on mammalian target of rapamycin by interacting with
Rheb. J Biol Chem. 282:35803–35813. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wirth M, Joachim J and Tooze SA:
Autophagosome formation-the role of ULK1 and Beclin1-PI3KC3
complexes in setting the stage. Semin Cancer Biol. 23:301–309.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen SH, Kwan AL, Chen YY and Wang ZX:
Effect of silencing HIF-1α on proliferation, invasion and migration
of glioblastoma U87 cells. Neurol Sci. 34:365–371. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhuonan Z, Sen G, Zhipeng J, Maoyou Z,
Linglan Y, Gangping W, Cheng J, Zhongliang M, Tian J, Peijian Z and
Kesen X: Hypoxia preconditioning induced HIF-1α promotes glucose
metabolism and protects mitochondria in liver I/R injury. Clin Res
Hepatol Gastroenterol. 39:610–619. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Y, Nie H, Zhang K, Ma D, Yang G, Zheng
Z, Liu K, Yu B, Zhai C and Yang S: A feedback regulatory loop
between HIF-1α and miR-21 in response to hypoxia in cardiomyocytes.
FEBS Lett. 588:3137–3146. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Krick S, Eul BG, Hänze J, Savai R,
Grimminger F, Seeger W and Rose F: Role of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha in hypoxia-induced apoptosis of primary alveolar
epithelial type II cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 32:395–403.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|