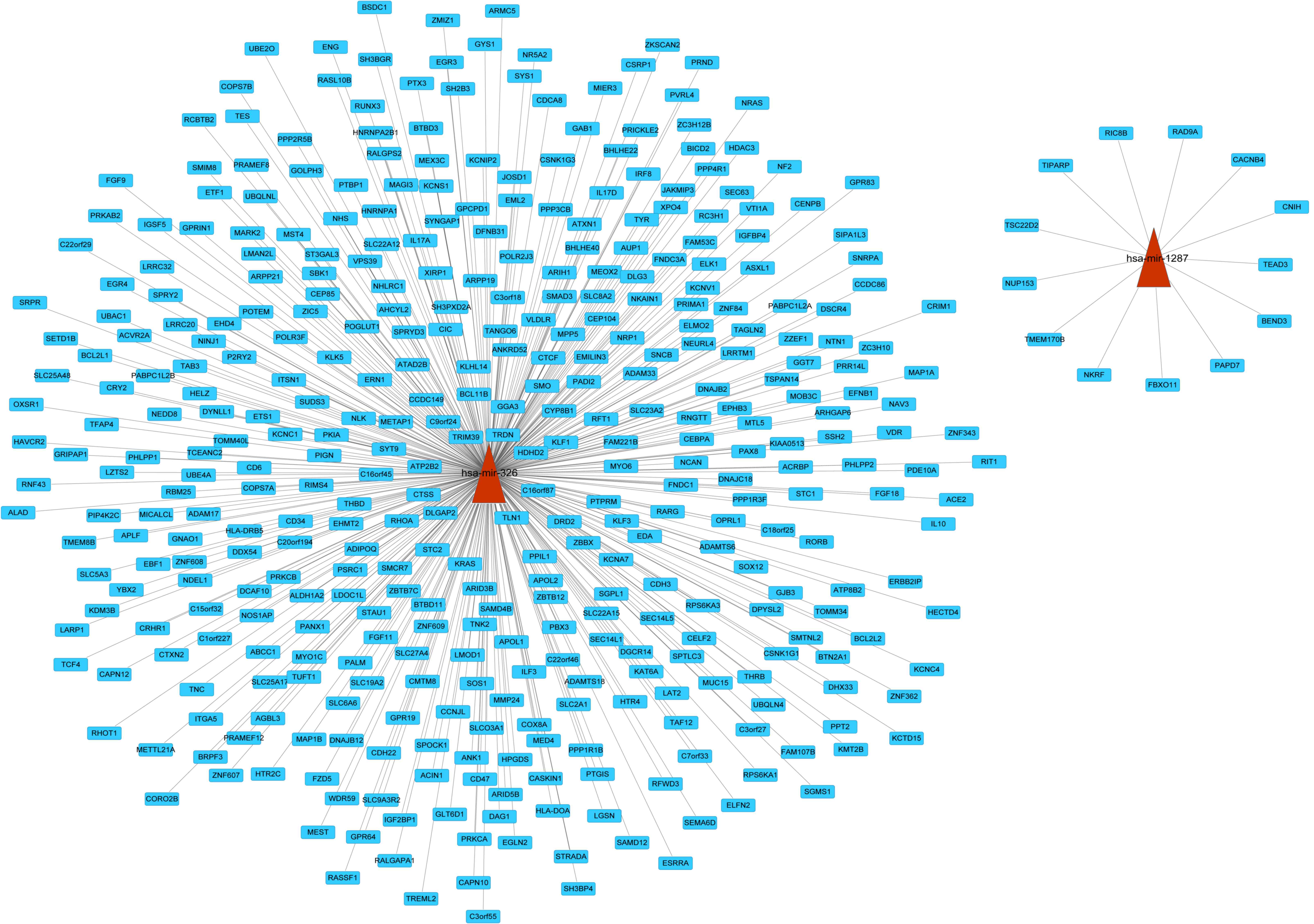
|
1
|
Cavaliere R, Lopes MB and Schiff D:
Low-grade gliomas: An update on pathology and therapy. Lancet
Neurol. 4:760–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giovannetti E, van der Velde A, Funel N,
Vasile E, Perrone V, Leon LG, de Lio N, Avan A, Caponi S, Pollina
LE, et al: High-throughput microRNA (miRNAs) arrays unravel the
prognostic role of MiR-211 in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One.
7:e491452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Markou A, Tsaroucha EG, Kaklamanis L,
Fotinou M, Georgoulias V and Lianidou ES: Prognostic value of
mature microRNA-21 and microRNA-205 overexpression in non-small
cell lung cancer by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Clin Chem.
54:1696–1704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu X, Macdonald DM, Huettner PC, Feng Z,
El Naqa IM, Schwarz JK, Mutch DG, Grigsby PW, Powell SN and Wang X:
A miR-200 microRNA cluster as prognostic marker in advanced ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 114:457–464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huse JT, Brennan C, Hambardzumyan D, Wee
B, Pena J, Rouhanifard SH, Sohn-Lee C, le Sage C, Agami R, Tuschl T
and Holland EC: The PTEN-regulating microRNA miR-26a is amplified
in high-grade glioma and facilitates gliomagenesis in vivo. Genes
Dev. 23:1327–1337. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA, Schrier M,
Mesman E, Mangiola A, Anile C, Maira G, Mercatelli N, Ciafrè SA, et
al: Regulation of the p27(Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and
miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 26:3699–3708.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kefas B, Godlewski J, Comeau L, Li Y,
Abounader R, Hawkinson M, Lee J, Fine H, Chiocca EA, Lawler S and
Purow B: microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor
and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer
Res. 68:3566–3572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hou SX, Ding BJ, Li HZ, Wang L, Xia F, Du
F, Liu LJ, Liu YH, Liu XD, Jia JF, et al: Identification of
microRNA-205 as a potential prognostic indicator for human glioma.
J Clin Neurosci. 20:933–937. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang C, Zhang J, Hao J, Shi Z, Wang Y,
Han L, Yu S, You Y, Jiang T, Wang J, et al: High level of
miR-221/222 confers increased cell invasion and poor prognosis in
glioma. J Transl Med. 10:1192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Therneau TM and Grambsch PM: Modeling
survival data: Extending the Cox model. Springer; 2000, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Original by Klein, Moeschberger and
modifications by. Jun Yan: 2012.KMsurv: Data sets from Klein and
Moeschberger (1997), Survival Analysis. R package version
0.1–5.
|
|
17
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:D105–D110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in drosophila. Genome Biol.
5:R12003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X and El Naqa IM: Prediction of both
conserved and nonconserved microRNA targets in animals.
Bioinformatics. 24:325–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li C: iSubpathwayMiner: The package can
implement the graph-based reconstruction and analyses of the KEGG
pathways. R package version 3.0. 2012.
|
|
30
|
Kefas B, Comeau L, Floyd DH, Seleverstov
O, Godlewski J, Schmittgen T, Jiang J, diPierro CG, Li Y, Chiocca
EA, et al: The neuronal microRNA miR-326 acts in a feedback loop
with notch and has therapeutic potential against brain tumors. J
Neurosci. 29:15161–15168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wong JW: MicroRNA-induced silencing of
glioma progression. J Neurosci. 30:3868–3869. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gureasko J, Galush WJ, Boykevisch S,
Sondermann H, Bar-Sagi D, Groves JT and Kuriyan J:
Membrane-dependent signal integration by the Ras activator Son of
sevenless. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 15:452–461. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Downward J: Targeting RAS signalling
pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Goffin JR and Zbuk K: Epidermal growth
factor receptor: Pathway, therapies, and pipeline. Clin Ther.
35:1282–1303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nico B, Mangieri D, Benagiano V,
Crivellato E and Ribatti D: Nerve growth factor as an angiogenic
factor. Microvasc Res. 75:135–141. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eyles DW, Smith S, Kinobe R, Hewison M and
McGrath JJ: Distribution of the vitamin D receptor and 1
alpha-hydroxylase in human brain. J Chem Neuroanat. 29:21–30. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hansen CM, Binderup L, Hamberg KJ and
Carlberg C: Vitamin D and cancer: Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 and its
analogs on growth control and tumorigenesis. Front Biosci.
6:D820–D848. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Conery AR, Cao Y, Thompson EA, Townsend CM
Jr, Ko TC and Luo K: Akt interacts directly with Smad3 to regulate
the sensitivity to TGF-beta induced apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol.
6:366–372. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hjelmeland AB, Hjelmeland MD, Shi Q, Hart
JL, Bigner DD, Wang XF, Kontos CD and Rich JN: Loss of phosphatase
and tensin homologue increases transforming growth factor
beta-mediated invasion with enhanced SMAD3 transcriptional
activity. Cancer Res. 65:11276–11281. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tafesse FG, Ternes P and Holthuis JC: The
multigenic sphingomyelin synthase family. J Biol Chem.
281:29421–29425. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zeidan YH and Hannun YA: Translational
aspects of sphingolipid metabolism. Trends Mol Med. 13:327–336.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Oskouian B and Saba JD: Cancer treatment
strategies targeting sphingolipid metabolismSphingolipids as
Signaling and Regulatory Molecules. Springer; pp. 185–205. 2010,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Pidgeon GP, Lysaght J, Krishnamoorthy S,
Reynolds JV, O'Byrne K, Nie D and Honn KV: Lipoxygenase metabolism:
Roles in tumor progression and survival. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:503–524. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang WG, Douglas-Jones A and Mansel RE:
Levels of expression of lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenase-2 in human
breast cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids.
69:275–281. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hoque A, Lippman SM, Wu TT, Xu Y, Liang
ZD, Swisher S, Zhang H, Cao L, Ajani JA and Xu XC: Increased
5-lipoxygenase expression and induction of apoptosis by its
inhibitors in esophageal cancer: A potential target for prevention.
Carcinogenesis. 26:785–791. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Leung HW, Yang WH, Lai MY, Lin CJ and Lee
HZ: Inhibition of 12-lipoxygenase during baicalein-induced human
lung nonsmall carcinoma H460 cell apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol.
45:403–411. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|