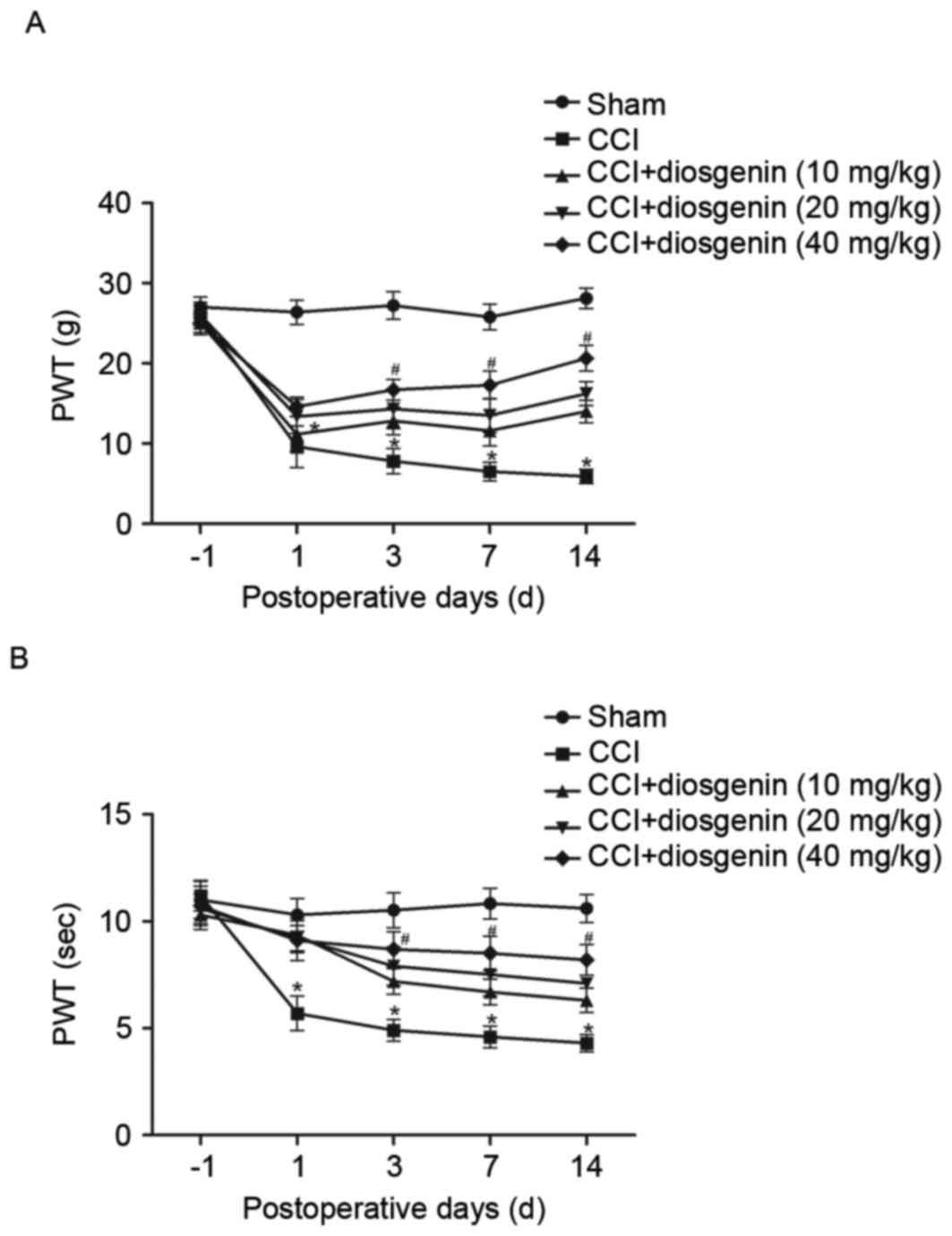
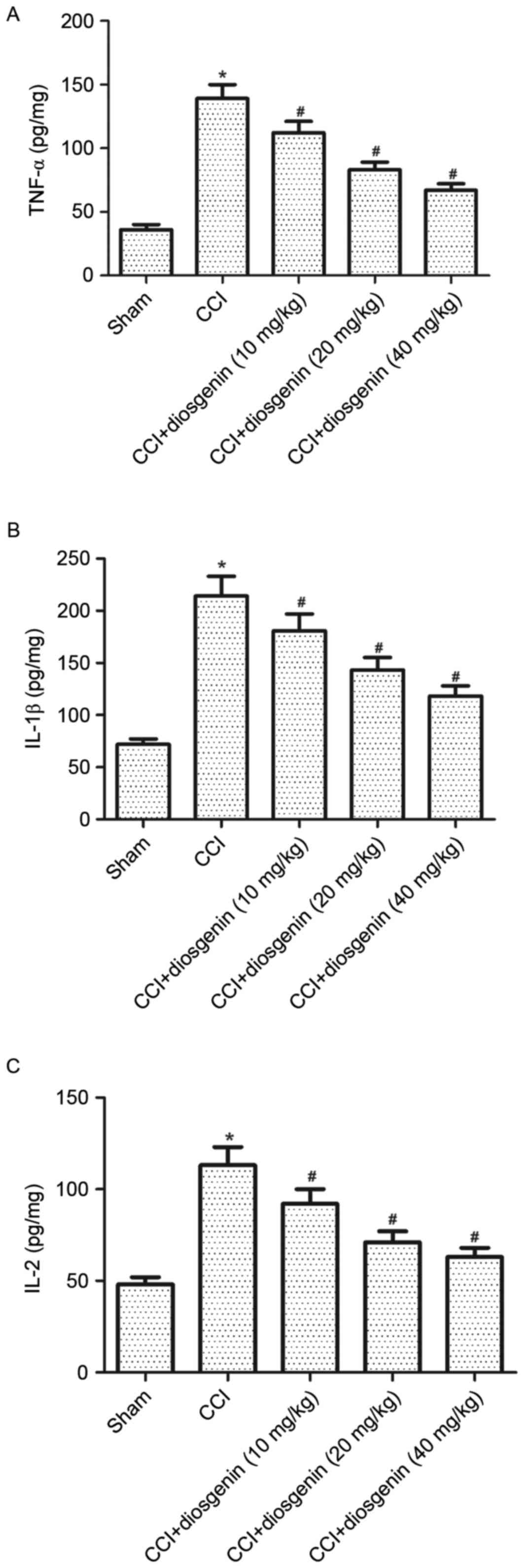
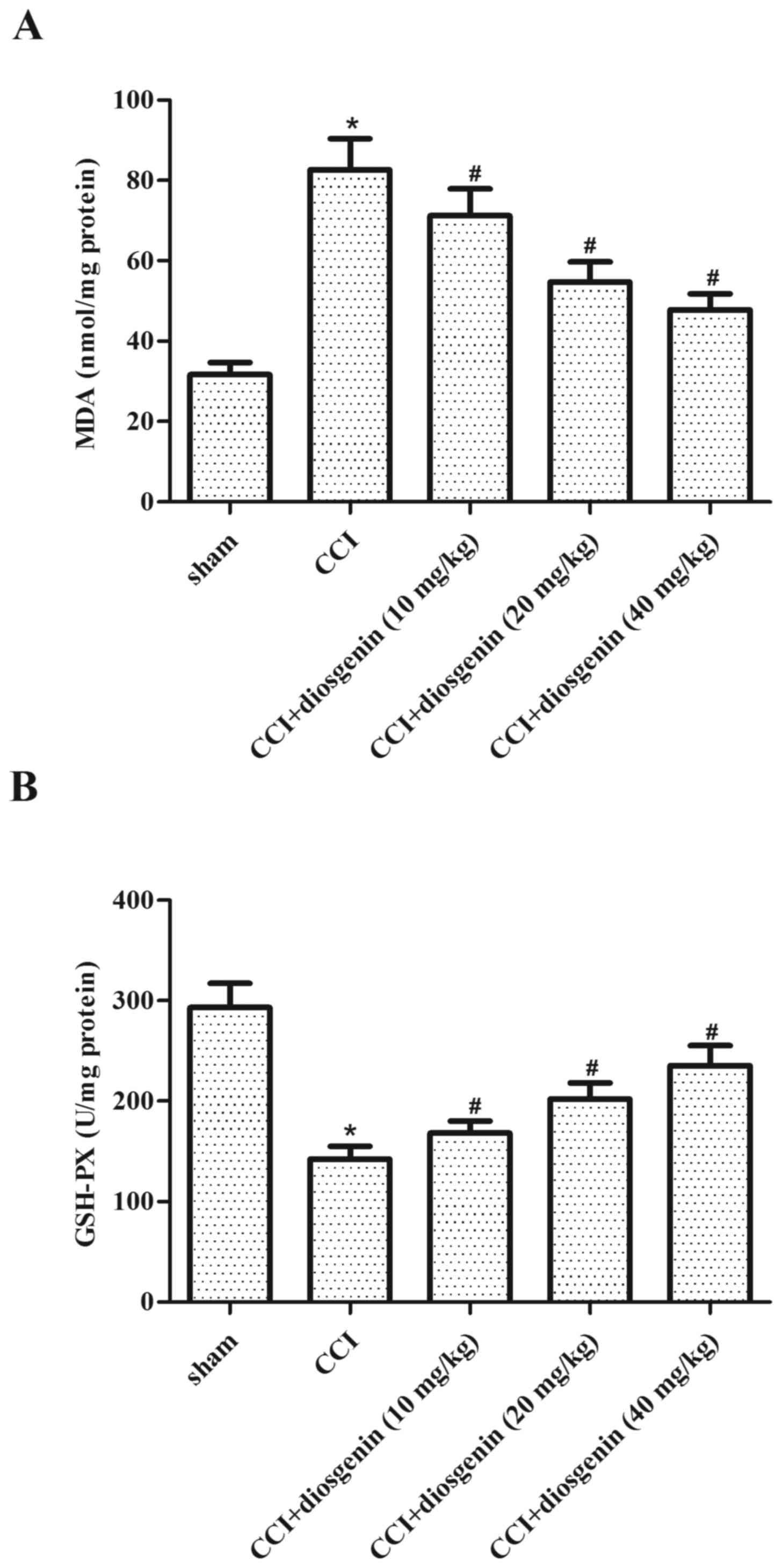
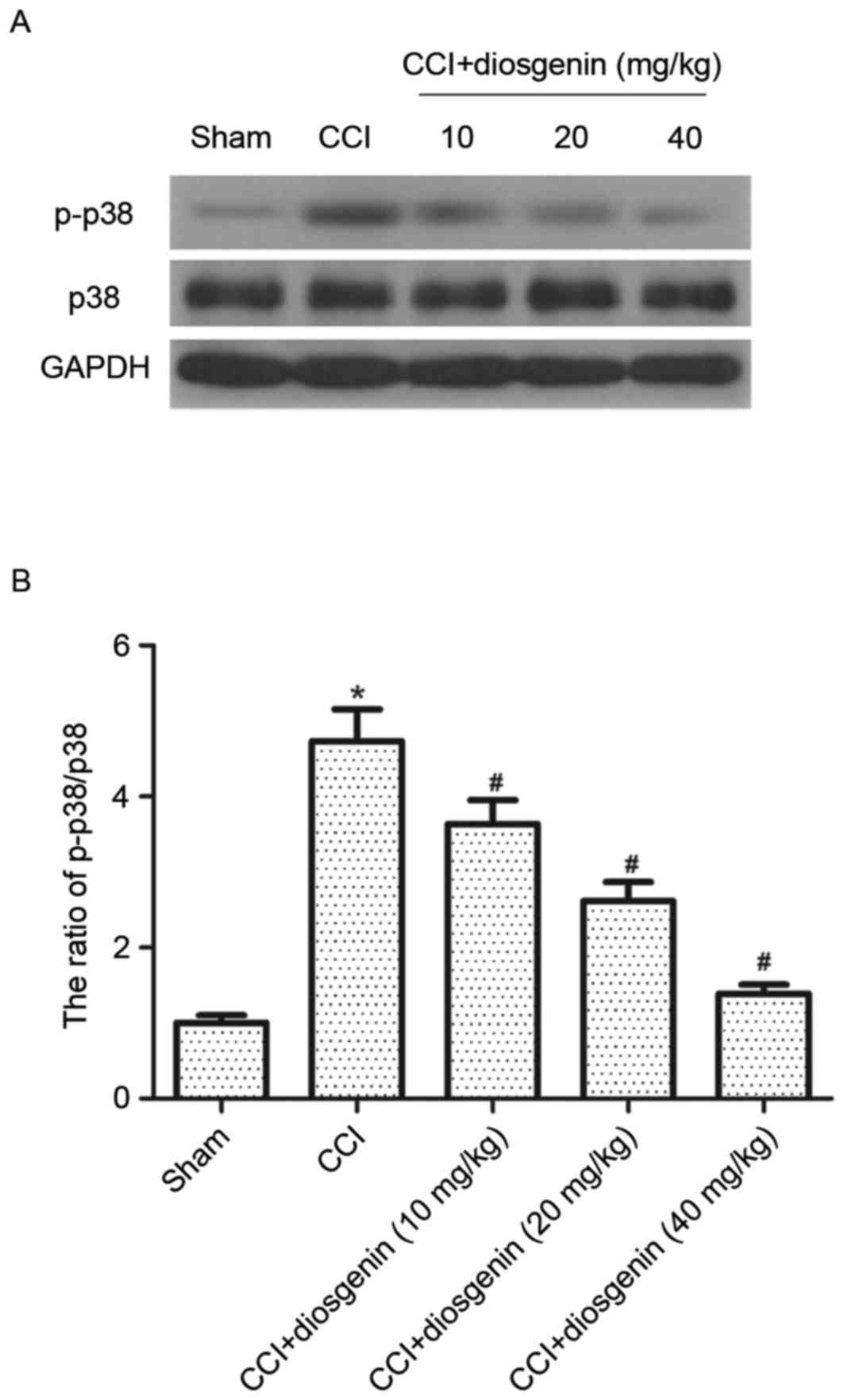
|
1
|
Rowbotham MC: Mechanisms of neuropathic
pain and their implications for the design of clinical trials.
Neurology. 65 12 Suppl 4:S66–S73. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Neville A, Peleg R, Singer Y, Sherf M and
Shvartzman P: Chronic pain: A population-based study. Isr Med Assoc
J. 10:676–680. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baastrup C and Finnerup NB:
Pharmacological management of neuropathic pain following spinal
cord injury. CNS Drugs. 22:455–475. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Finnerup NB, Otto M, McQuay H, Jensen TS
and Sindrup SH: Algorithm for neuropathic pain treatment: An
evidence based proposal. Pain. 118:289–305. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dray A: Inflammatory mediators of pain.
Brit J Anaesth. 75:125–131. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
DeLeo JA and Yezierski RP: The role of
neuroinflammation and neuroimmune activation in persistent pain.
Pain. 90:1–6. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim HK, Park SK, Zhou JL, Taglialatela G,
Chung K, Coggeshall RE and Chung JM: Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
play an important role in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain.
111:116–124. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Moriya H and Myers
RR: TNF-alpha and TNF-alpha receptor type 1 upregulation in glia
and neurons after peripheral nerve injury: Studies in murine DRG
and spinal cord. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 29:1082–1088. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Taves S, Berta T, Chen G and Ji RR:
Microglia and spinal cord synaptic plasticity in persistent pain.
Neural Plast. 2013:7536562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma W and Bisby MA: Increased activation of
nuclear factor kappa B in rat lumbar dorsal root ganglion neurons
following partial sciatic nerve injuries. Brain Res. 797:243–254.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jung DH, Park HJ, Byun HE, Park YM, Kim
TW, Kim BO, Um SH and Pyo S: Diosgenin inhibits macrophage-derived
inflammatory mediators through downregulation of CK2, JNK,
NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 10:1047–1054.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Son IS, Kim JH, Sohn HY, Son KH, Kim JS
and Kwon CS: Antioxidative and hypolipidemic effects of diosgenin,
a steroidal saponin of yam (Dioscorea spp.), on high-cholesterol
fed rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 71:3063–3071. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moalic S, Liagre B, Corbière C, Bianchi A,
Dauça M, Bordji K and Beneytout JL: A plant steroid, diosgenin,
induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and COX activity in
osteosarcoma cells. FEBS Lett. 506:225–230. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tohda C, Urano T, Umezaki M, Nemere I and
Kuboyama T: Diosgenin is an exogenous activator of 1,
25D3-MARRS/Pdia3/ERp57 and improves Alzheimer's disease pathologies
in 5XFAD mice. Sci Rep. 2:5352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bennett GJ and Xie YK: A peripheral
mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation
like those seen in man. Pain. 33:87–107. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JM, Chung JM
and Yaksh TL: Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the
rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 53:55–63. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C
and Joris J: A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal
nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 32:77–88. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jaggi AS, Jain V and Singh N: Animal
models of neuropathic pain. Fund Clin Pharmacol. 25:1–28. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nadeau S, Filali M, Zhang J, Kerr BJ,
Rivest S, Soulet D, Iwakura Y, de Rivero Vaccari JP, Keane RW and
Lacroix S: Functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury is
dependent on the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF:
Implications for neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. 31:12533–12542.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Detloff MR, Fisher LC, McGaughy V,
Longbrake EE, Popovich PG and Basso DM: Remote activation of
microglia and pro-inflammatory cytokines predict the onset and
severity of below-level neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury
in rats. Exp Neurol. 212:337–347. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang JM and An J: Cytokines,
inflammation, and pain. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 45:27–37. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zanella JM, Burright EN, Hildebrand K,
Hobot C, Cox M, Christoferson L and McKay WF: Effect of etanercept,
a tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor, on neuropathic pain in the
rat chronic constriction injury model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
33:227–234. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
del Rey A, Yau HJ, Randolf A, Centeno MV,
Wildmann J, Martina M, Besedovsky HO and Apkarian AV: Chronic
neuropathic pain-like behavior correlates with IL-1β expression and
disrupts cytokine interactions in the hippocampus. Pain.
152:2827–2835. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park ES, Gao X, Chung JM and Chung K:
Levels of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species increase in rat
neuropathic spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett. 391:108–111.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Navarro SA, Serafim KG, Mizokami SS,
Hohmann MS, Casagrande R and Verri WA Jr: Analgesic activity of
piracetam: Effect on cytokine production and oxidative stress.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 105:183–192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Twining CM, Sloane EM, Milligan ED, Chacur
M, Martin D, Poole S, Marsh H, Maier SF and Watkins LR:
Peri-sciatic proinflammatory cytokines, reactive oxygen species and
complement induce mirror-image neuropathic pain in rats. Pain.
110:299–309. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ji RR and Suter MR: p38 MAPK, microglial
signaling, and neuropathic pain. Mol Pain. 3:332007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhuang ZY, Kawasaki Y, Tan PH, Wen YR,
Huang J and Ji RR: Role of the CX3CR1/p38 MAPK pathway in spinal
microglia for the development of neuropathic pain following nerve
injury-induced cleavage of fractalkine. Brain Behav Immun.
21:642–651. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hua XY, Svensson CI, Matsui T, Fitzsimmons
B, Yaksh TL and Webb M: Intrathecal minocycline attenuates
peripheral inflammation-induced hyperalgesia by inhibiting p38 MAPK
in spinal microglia. Eur J Neurosci. 22:2431–2440. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tsuda M, Mizokoshi A, Shigemoto-Mogami Y,
Koizumi S and Inoue K: Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase in spinal hyperactive microglia contributes to pain
hypersensitivity following peripheral nerve injury. Glia. 45:89–95.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun T, Song WG, Fu ZJ, Liu ZH, Liu YM and
Yao SL: Alleviation of neuropathic pain by intrathecal injection of
antisense oligonucleotides to p65 subunit of NF-kappaB. Brit J
Anaesth. 97:553–558. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tegeder I, Niederberger E, Schmidt R, Kunz
S, Gühring H, Ritzeler O, Michaelis M and Geisslinger G: Specific
inhibition of IkappaB kinase reduces hyperalgesia in inflammatory
and neuropathic pain models in rats. J Neurosci. 24:1637–1645.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee KM, Jeon SM and Cho HJ: Tumor necrosis
factor receptor 1 induces interleukin-6 upregulation through
NF-kappaB in a rat neuropathic pain model. Eur J Pain. 13:794–806.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wei XH, Yang T, Wu Q, Xin WJ, Wu JL, Wang
YQ, Zang Y, Wang J, Li YY and Liu XG: Peri-sciatic administration
of recombinant rat IL-1β induces mechanical allodynia by activation
of src-family kinases in spinal microglia in rats. Exp Neurol.
234:389–397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|