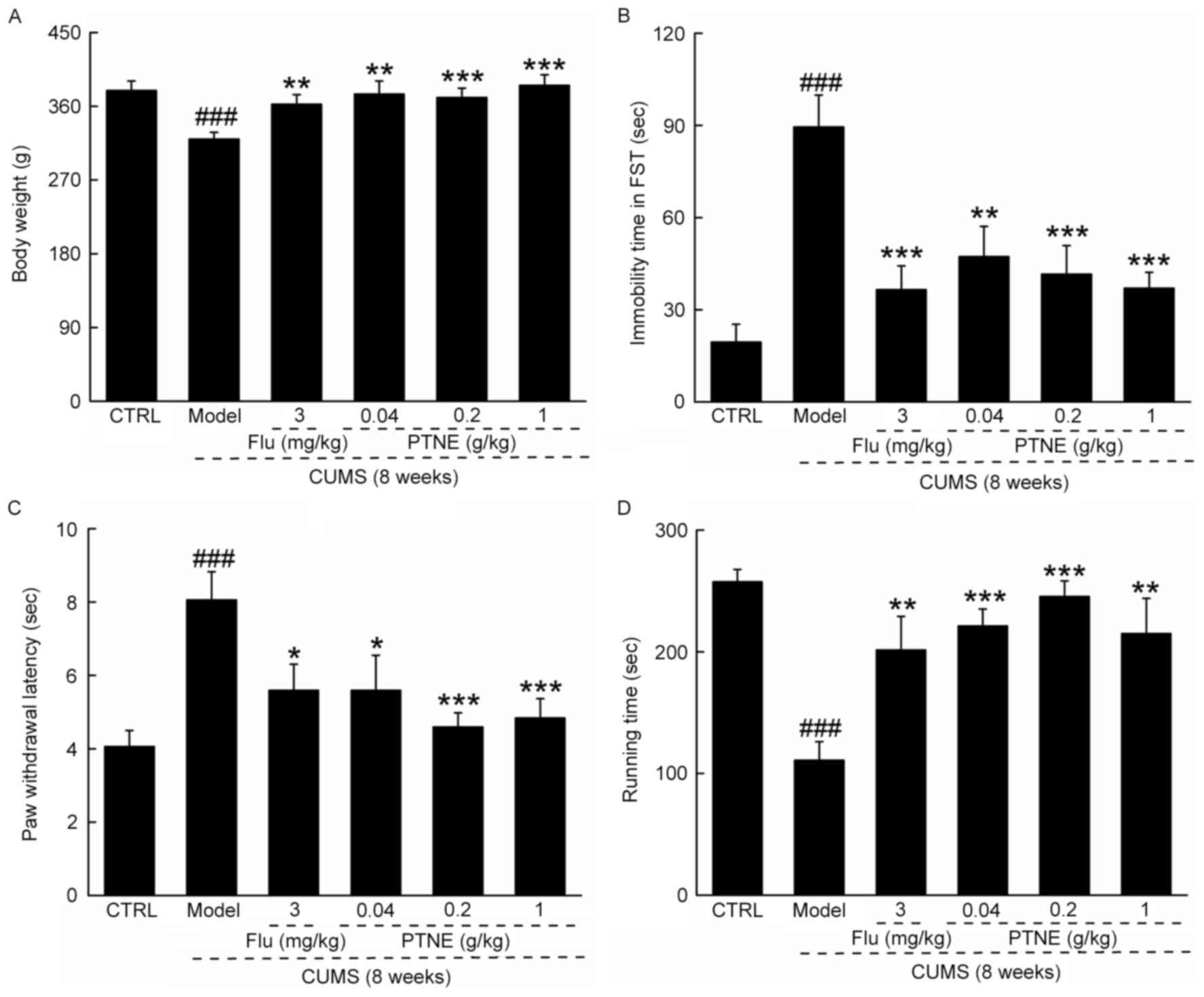
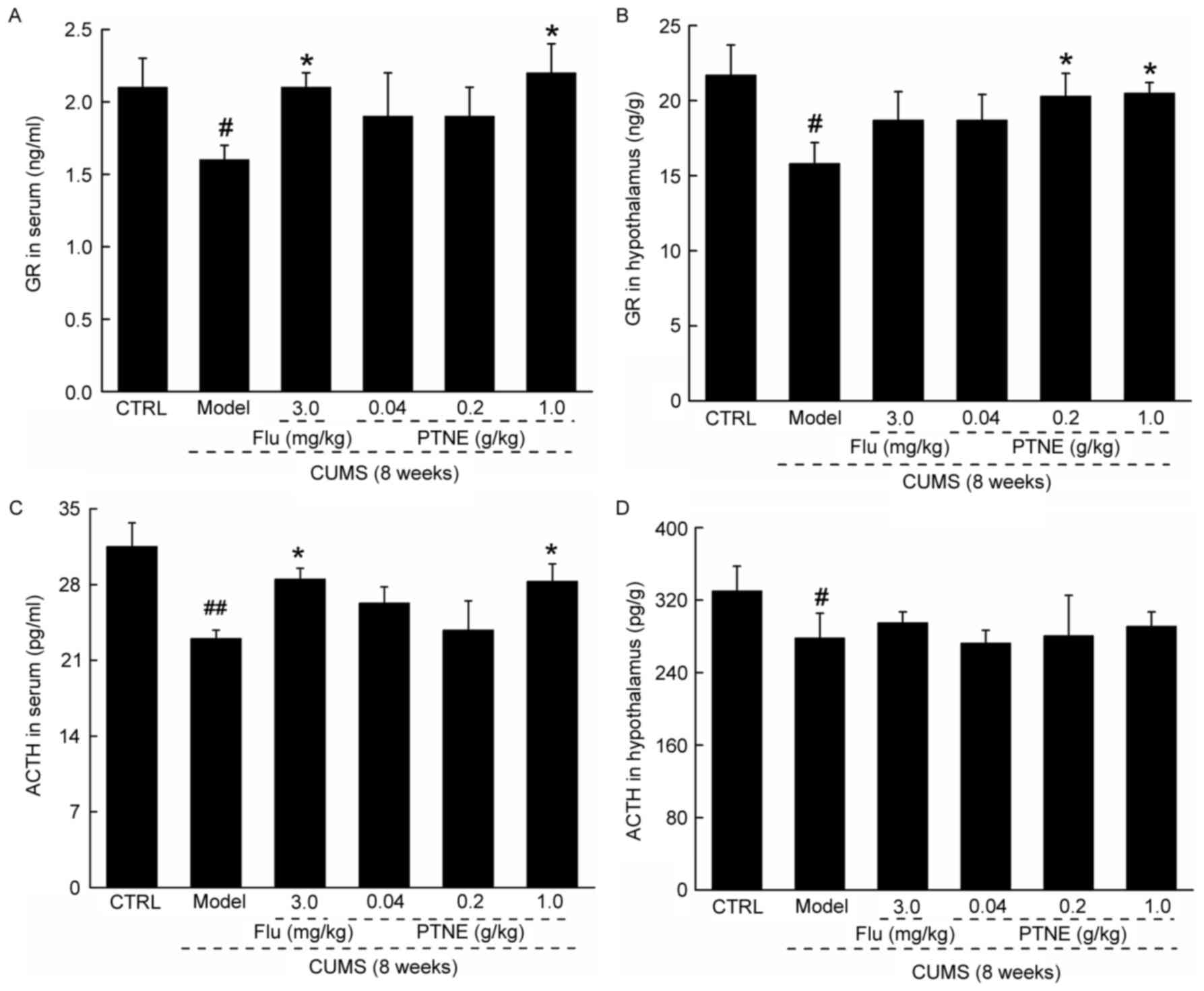
|
1
|
Kessler RC: The costs of depression.
Psychiat Clin N Am. 35:12012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mathers CD and Loncar D: Projections of
global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med.
3:e4422006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Luppa M, Heinrich S, Angermeyer MC, König
HH and Riedel-Heller SG: Cost-of-illness studies of depression: A
systematic review. J Affect Disord. 98:29–43. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krishnan V and Nestler EJ: The molecular
neurobiology of depression. Nature. 455:894–902. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li X, Li L, Shen LL, Qian Y, Cao YX and
Zhu DN: Changes of adrenomedullin and its receptor components mRNAs
expression in the brain stem and hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal
axis of stress-induced hypertensive rats. Sheng Li Xue Bao.
56:723–729. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sartori SB, Whittle N, Hetzenauer A and
Singewald N: Magnesium deficiency induces anxiety and HPA axis
dysregulation: Modulation by therapeutic drug treatment.
Neuropharmacology. 62:304–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou XJ, Liu M, Yan JJ, Cao Y and Liu P:
Antidepressant-like effect of the extracted of Kai Xin San, a
traditional Chinese herbal prescription, is explained by modulation
of the central monoaminergic neurotransmitter system in mouse. J
Ethnopharmacol. 139:422–428. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma Z, Ji W, Qu R, Wang M, Yang W, Zhan Z,
Fu Q and Ma S: Metabonomic study on the antidepressant-like effects
of banxia houpu decoction and its action mechanism. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:2137392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kang A, Hao H, Zheng X, Liang Y, Xie Y,
Xie T, Dai C, Zhao Q, Wu X, Xie L and Wang G: Peripheral
anti-inflammatory effects explain the ginsenosides paradox between
poor brain distribution and anti-depression efficacy. J
Neuroinflammation. 8:1002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cui M, Li Q, Zhang M, Zhao YJ, Huang F and
Chen YJ: Long-term curcumin treatment antagonizes masseter muscle
alterations induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in rats.
Arch Oral Biol. 59:258–267. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thachil AF, Mohan R and Bhugra D: The
evidence base of complementary and alternative therapies in
depression. J Affect Disorders. 97:23–35. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee DH, Park T and Kim HW: Induction of
apoptosis by disturbing mitochondrial-membrane potential and
cleaving PARP in Jurkat T cells through treatment with
acetoxyscirpenol mycotoxins. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:648–654. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kan H, Ming L, Li C, Kan H, Sun B and
Liang Y: Antidepressant effect of bioactive compounds from
Paecilomyces tenuipes in mice and rats. Neural Regen Res.
5:1568–1572. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Yin YY, Ming L, Zheng LF, Kan HW, Li CR
and Li WP: Bioactive compounds from Paecilomyces tenuipes
regulating the function of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system axis
in chronic unpredictable stress rats. Chin Med J (Engl).
120:1088–1092. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang Y, Qi X, Gao K, Liu W, Li N, Cheng
N, Ding G, Huang W, Wang Z and Xiao W: Relationship between
molecular weight, monosaccharide composition and immunobiologic
activity of Astragalus polysaccharides. Glycoconj J. 33:755–761.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li SP, Yang FQ and Tsim KW: Quality
control of Cordyceps sinensis, a valued traditional Chinese
medicine. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 41:1571–1584. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakagawasai O, Yamada K, Nemoto W,
Fukahori M, Tadano T and Tan-No K: Liver hydrolysate assists in the
recovery from physical fatigue in a mouse model. J Pharmacol Sci.
123:328–335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Espejo EF and Mir D: Structure of the
rat's behaviour in the hot plate test. Behav Brain Res. 56:171–176.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Overstreet DH and Steiner M: Genetic and
environmental models of stress-induced depression in rats. Stress
Med. 14:261–268. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ji WW, Li RP, Li M, Wang SY, Zhang X, Niu
XX, Li W, Yan L, Wang Y, Fu Q and Ma SP: Antidepressant-like effect
of essential oil of Perilla frutescens in a chronic, unpredictable,
mild stress-induced depression model mice. Chin J Nat Med.
12:753–759. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan WJ, Tan YC, Xu JC, Tang XP, Zhang C,
Zhang PB and Ren ZQ: Protective effects of silibinin and its
possible mechanism of action in mice exposed to chronic
unpredictable mild stress. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 23:245–250. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bjørnebekk A, Mathé AA and Brené S:
Running has differential effects on NPY, opiates, and cell
proliferation in an animal model of depression and controls.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 31:256–264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Burke NN, Hayes E, Calpin P, Kerr DM,
Moriarty O, Finn DP and Roche M: Enhanced nociceptive responding in
two rat models of depression is associated with alterations in
monoamine levels in discrete brain regions. Neuroscience.
171:1300–1313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Detke MJ, Rickels M and Lucki I: Active
behaviors in the rat forced swimming test differentially produced
by serotonergic and noradrenergic antidepressants.
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 121:66–72. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B and Simon P:
The tail suspension test: A new method for screening
antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 85:367–370.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mohammad-Zadeh LF, Moses L and
Gwaltney-Brant SM: Serotonin: A review. J Vet Pharmacol Ther.
31:187–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang ZJ, Wang D, Man SC, Ng R, McAlonan
GM, Wong HK, Wong W, Lee J and Tan QR: Platelet 5-HT(1A) receptor
correlates with major depressive disorder in drug-free patients.
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 53:74–79. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gobbi G, Murphy DL, Lesch KP and Blier P:
Modifications of the serotonergic system in mice lacking serotonin
transporters: An in vivo electrophysiological study. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 296:987–995. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chrousos GP: Stress and disorders of the
stress system. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 5:374–381. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lambert G, Johansson M, Agren H and
Friberg P: Reduced brain norepinephrine and dopamine release in
treatment-refractory depressive illness: Evidence in support of the
catecholamine hypothesis of mood disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry.
57:787–793. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Di Giovanni G, Strac D Svob, Sole M,
Unzeta M, Tipton KF, Mück-Šeler D, Bolea I, Corte L Della, Perkovic
M Nikolac, Pivac N, et al: Monoaminergic and histaminergic
strategies and treatments in brain diseases. Front Neurosci.
10:5412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ainsworth K, Smith SE, Zetterström TS, Pei
Q, Franklin M and Sharp T: Effect of antidepressant drugs on
dopamine D1 and D2 receptor expression and dopamine release in the
nucleus accumbens of the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl).
140:470–477. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pirke KM: Central and peripheral
noradrenalin regulation in eating disorders. Psychiat Res.
62:43–49. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gareri P, Castagna A, Cotroneo AM,
Putignano D, Conforti R, Santamaria F, Marino S and Putignano S:
The Citicholinage Study: Citicoline plus cholinesterase inhibitors
in aged patients affected with Alzheimer's disease study. J
Alzheimers Dis. 56:557–565. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brown RE, Stevens DR and Haas HL: The
physiology of brain histamine. Prog Neurobiol. 63:637–672. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Geller HM, Springfield SA and Tiberio AR:
Electrophysiological actions of histamine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
62:715–719. 1984. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Deuschle M, Bode L, Schnitzler P,
Meyding-Lamadé U, Plesch A, Ludwig H, Hamann B and Heuser I:
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) system activity in depression
and infection with Borna disease virus and Chlamydia pneumoniae.
Mol Psychiatry. 8:469–470. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Varghese FP and Brown ES: The
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in major depressive disorder: A
brief primer for primary care physicians. Prim Care Companion J
Clin Psychiatry. 3:151–155. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mason BL and Pariante CM: The effects of
antidepressants on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Drug
News Perspect. 19:603–608. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bao L, Yao XS, Zhao L, Lu YQ and Kurihara
H: Correlation between changes of central neurotransmitter
expression and stress response in mice-A restraint time-course
analysis. Neural Regeneration Res. 3:167–171. 2008.
|
|
41
|
Wu J, Du J, Xu C, Le J, Xu Y, Liu B and
Dong J: Icariin attenuates social defeat-induced down-regulation of
glucocorticoid receptor in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.
98:273–278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Song J, Xing G, Cao J and Teng L, Li C,
Meng Q, Lu J, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Wang D and Teng L: Investigation of
the antidepressant effects of exopolysaccharides obtained from
Marasmius androsaceus fermentation in a mouse model. Mol Med Rep.
13:939–946. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|