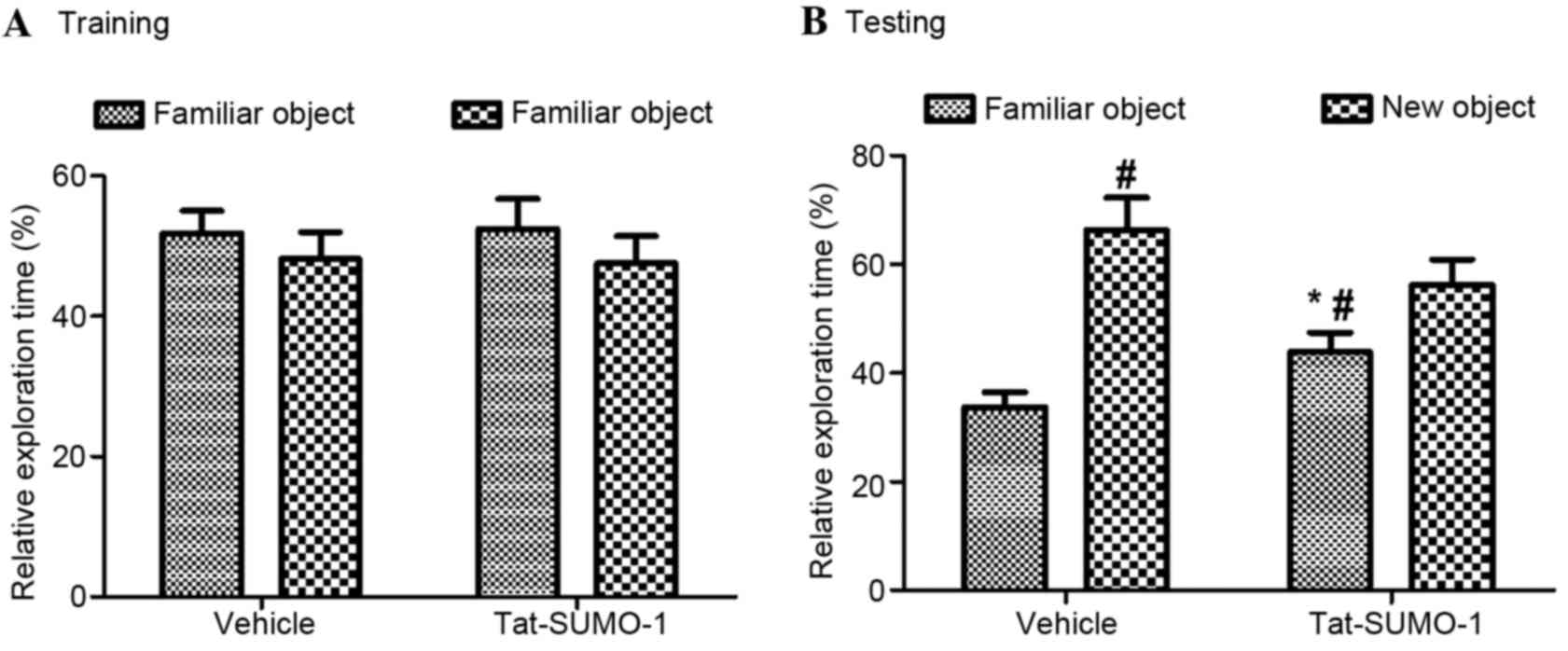
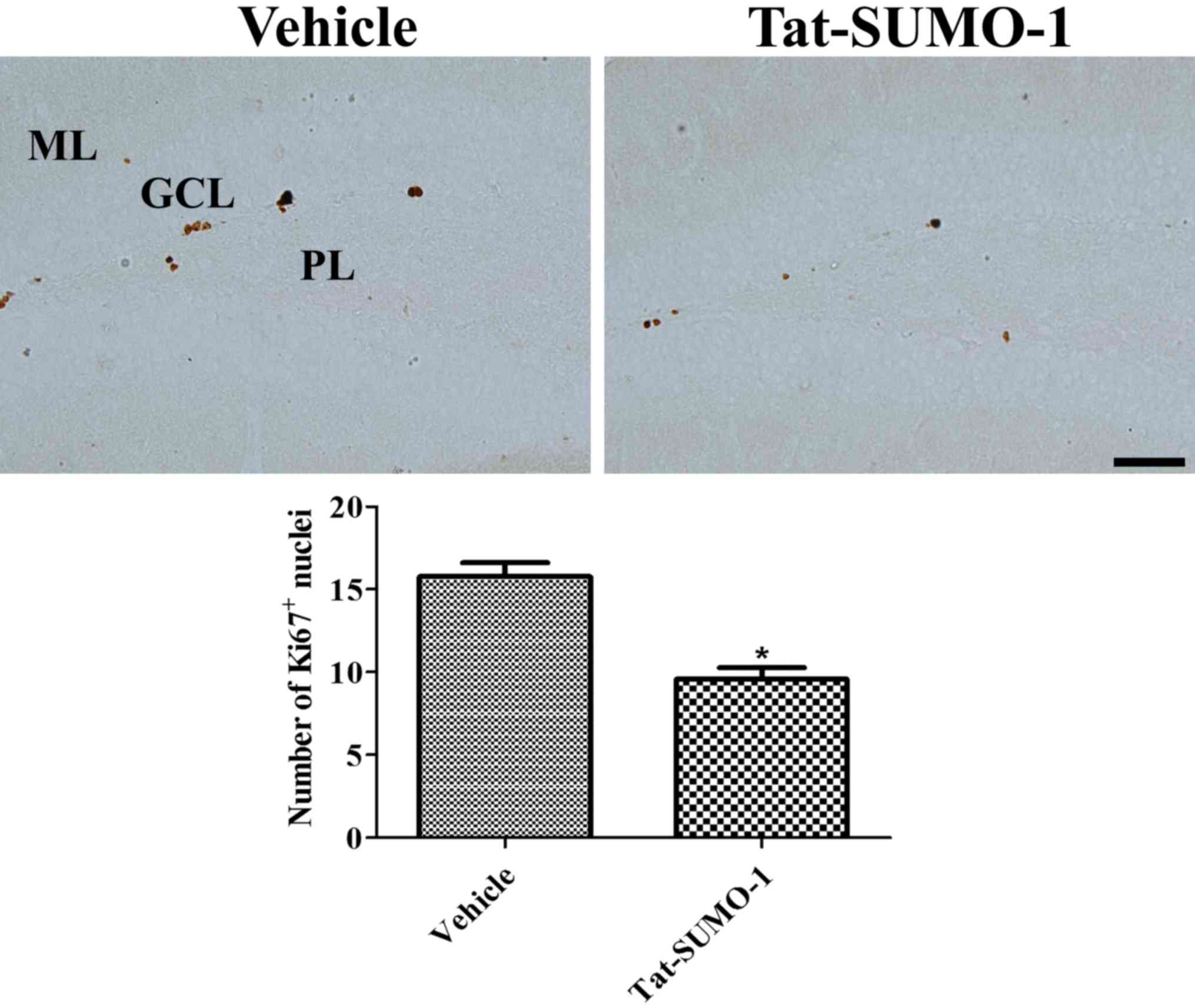
|
1
|
Gwizdek C, Cassé F and Martin S: Protein
sumoylation in brain development, neuronal morphology and
spinogenesis. Neuromolecular Med. 15:677–691. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luo J, Ashikaga E, Rubin PP, Heimann MJ,
Hildick KL, Bishop P, Girach F, Josa-Prado F, Tang LT, Carmichael
RE, et al: Receptor trafficking and the regulation of synaptic
plasticity by SUMO. Neuromolecular Med. 15:692–706. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cho Y and Cavalli V: HDAC signaling in
neuronal development and axon regeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol.
27:118–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Santos AI, Martínez-Ruiz AI and Araújo IM:
S-nitrosation and neuronal plasticity. Br J Pharmacol.
172:1468–1478. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Soderling TR and Derkach VA: Postsynaptic
protein phosphorylation and LTP. Trends Neurosci. 23:75–80. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
DiAntonio A and Hicke L:
Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of the synapse. Annu Rev Neurosci.
27:223–246. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fukata Y and Fukata M: Protein
palmitoylation in neuronal development and synaptic plasticity. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 11:161–175. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Routtenberg A and Rekart JL:
Post-translational protein modification as the substrate for
long-lasting memory. Trends Neurosci. 28:12–19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Droescher M, Chaugule VK and Pichler A:
SUMO rules: Regulatory concepts and their implication in neurologic
functions. Neuromolecular Med. 15:639–660. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saitoh H and Hinchey J: Functional
heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1
versus SUMO-2/3. J Biol Chem. 275:6252–6258. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moser MB and Moser EI: Functional
differentiation in the hippocampus. Hippocampus. 8:608–619. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schmajuk NA: Role of the hippocampus in
temporal and spatial navigation: An adaptive neural network. Behav
Brain Res. 39:205–229. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gage FH, Kempermann G, Palmer TD, Peterson
DA and Ray J: Multipotent progenitor cells in the adult dentate
gyrus. J Neurobiol. 36:249–266. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Andreou AM and Tavernarakis N: Roles for
SUMO modification during senescence. Adv Exp Med Biol. 694:160–171.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lomelí H and Vázquez M: Emerging roles of
the SUMO pathway in development. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:4045–4064.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martin S, Wilkinson KA, Nishimune A and
Henley JM: Emerging extranuclear roles of protein SUMOylation in
neuronal function and dysfunction. Nat Rev Neurosci. 8:948–959.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Craig TJ and Henley JM: Protein
SUMOylation in spine structure and function. Curr Opin Neurobiol.
22:480–487. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wilkinson KA, Nakamura Y and Henley JM:
Targets and consequences of protein SUMOylation in neurons. Brain
Res Rev. 64:195–212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Plant LD, Dowdell EJ, Dementieva IS, Marks
JD and Goldstein SA: SUMO modification of cell surface Kv2.1
potassium channels regulates the activity of rat hippocampal
neurons. J Gen Physiol. 137:441–454. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ballabh P, Braun A and Nedergaard M: The
blood-brain barrier: An overview: Structure, regulation and
clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis. 16:1–13. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kilic E, Kilic U and Hermann DM: TAT
fusion proteins against ischemic stroke: Current status and future
perspectives. Front Biosci. 11:1716–1721. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fonseca SB, Pereira MP and Kelley SO:
Recent advances in the use of cell-penetrating peptides for medical
and biological applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 61:953–964. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stalmans S, Bracke N, Wynendaele E,
Gevaert B, Peremans K, Burvenich C, Polis I and De Spiegeleer B:
Cell-penetrating peptides selectively cross the blood-brain barrier
in vivo. PLoS One. 10:e01396522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Eum WS, Kim DW, Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Kang TC,
Jang SH, Choi HS, Choi SH, Kim YH, Kim SY, et al: In vivo protein
transduction: Biologically active intact pep-1-superoxide dismutase
fusion protein efficiently protects against ischemic insult. Free
Radic Biol Med. 37:1656–1669. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee L, Dale E, Staniszewski A, Zhang H,
Saeed F, Sakurai M, Fa' M, Orozco I, Michelassi F, Akpan N, et al:
Regulation of synaptic plasticity and cognition by SUMO in normal
physiology and Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep. 4:71902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kwon HY, Eum WS, Jang HW, Kang JH, Ryu J,
Lee B Ryong, Jin LH, Park J and Choi SY: Transduction of Cu,
Zn-superoxide dismutase mediated by an HIV-1 Tat protein basic
domain into mammalian cells. FEBS Lett. 485:163–167. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brown JP, Couillard-Després S, Cooper-Kuhn
CM, Winkler J, Aigner L and Kuhn HG: Transient expression of
doublecortin during adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 467:1–10.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Couillard-Despres S, Winner B, Schaubeck
S, Aigner R, Vroemen M, Weidner N, Bogdahn U, Winkler J, Kuhn HG
and Aigner L: Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect
neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci. 21:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Franklin KBJ and Paxinos G: The Mouse
Brain In Stereotaxic Coordinates. 3rd. San Diego: Academic Press;
1997
|
|
31
|
Chamberlain SE, González-González IM,
Wilkinson KA, Konopacki FA, Kantamneni S, Henley JM and Mellor JR:
SUMOylation and phosphorylation of GluK2 regulate kainate receptor
trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 15:845–852.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Martin S, Nishimune A, Mellor JR and
Henley JM: SUMOylation regulates kainate-receptor-mediated synaptic
transmission. Nature. 447:321–325. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Georgopoulou N, McLaughlin M, McFarlane I
and Breen KC: The role of post-translational modification in
beta-amyloid precursor protein processing. Biochem Soc Symp. 23–36.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Marcus JN and Schachter J: Targeting
post-translational modifications on tau as a therapeutic strategy
for Alzheimer's disease. J Neurogenet. 25:127–133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nisticò R, Ferraina C, Marconi V, Blandini
F, Negri L, Egebjerg J and Feligioni M: Age-related changes of
protein SUMOylation balance in the AβPP Tg2576 mouse model of
Alzheimer's disease. Front Pharmacol. 5:632014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yun SM, Cho SJ, Song JC, Song SY, Jo SA,
Jo C, Yoon K, Tanzi RE, Choi EJ and Koh YH: SUMO1 modulates Aβ
generation via BACE1 accumulation. Neurobiol Aging. 34:650–662.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cho SJ, Yun SM, Lee DH, Jo C, Park M Ho,
Han C and Koh Y Ho: Plasma SUMO1 protein is elevated in Alzheimer's
disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 47:639–643. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Squire LR, Wixted JT and Clark RE:
Recognition memory and the medial temporal lobe: A new perspective.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 8:872–883. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Leuner B and Gould E: Structural
plasticity and hippocampal function. Annu Rev Psychol. 61:111–140.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Matsuzaki S, Lee L, Knock E, Srikumar T,
Sakurai M, Hazrati LN, Katayama T, Staniszewski A, Raught B,
Arancio O and Fraser PE: SUMO1 affects synaptic function, spine
density and memory. Sci Rep. 5:107302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang L, Rodriguiz RM, Wetsel WC, Sheng H,
Zhao S, Liu X, Paschen W and Yang W: Neuron-specific Sumo1-3
knockdown in mice impairs episodic and fear memories. J Psychiatry
Neurosci. 39:259–266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|