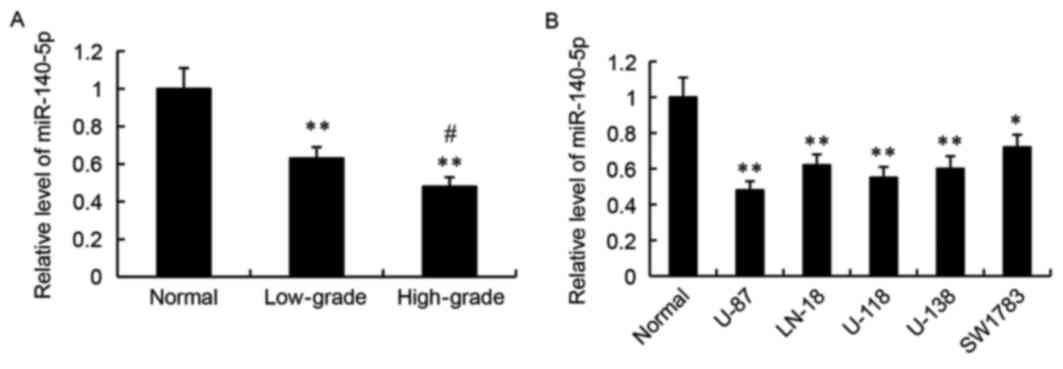
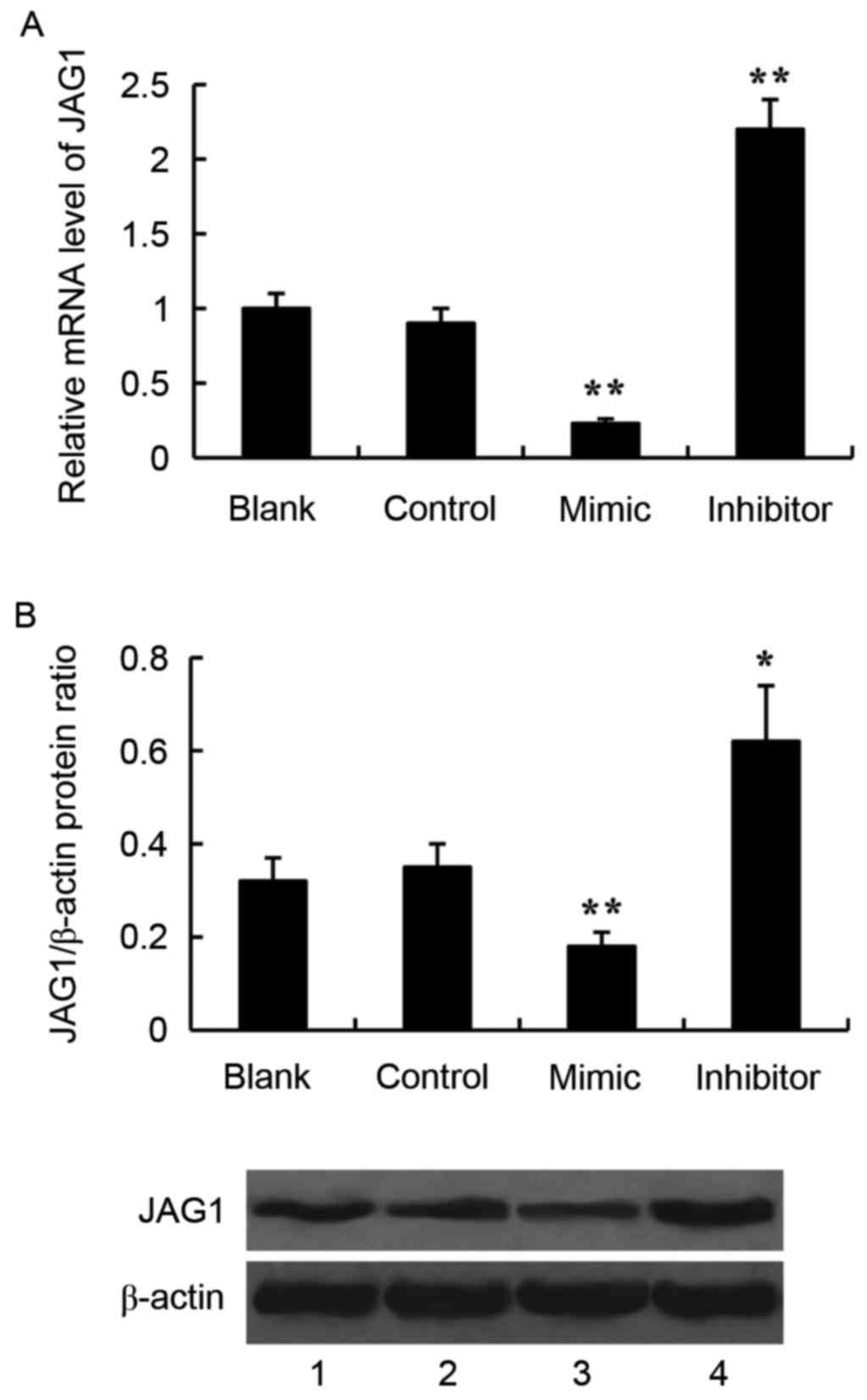
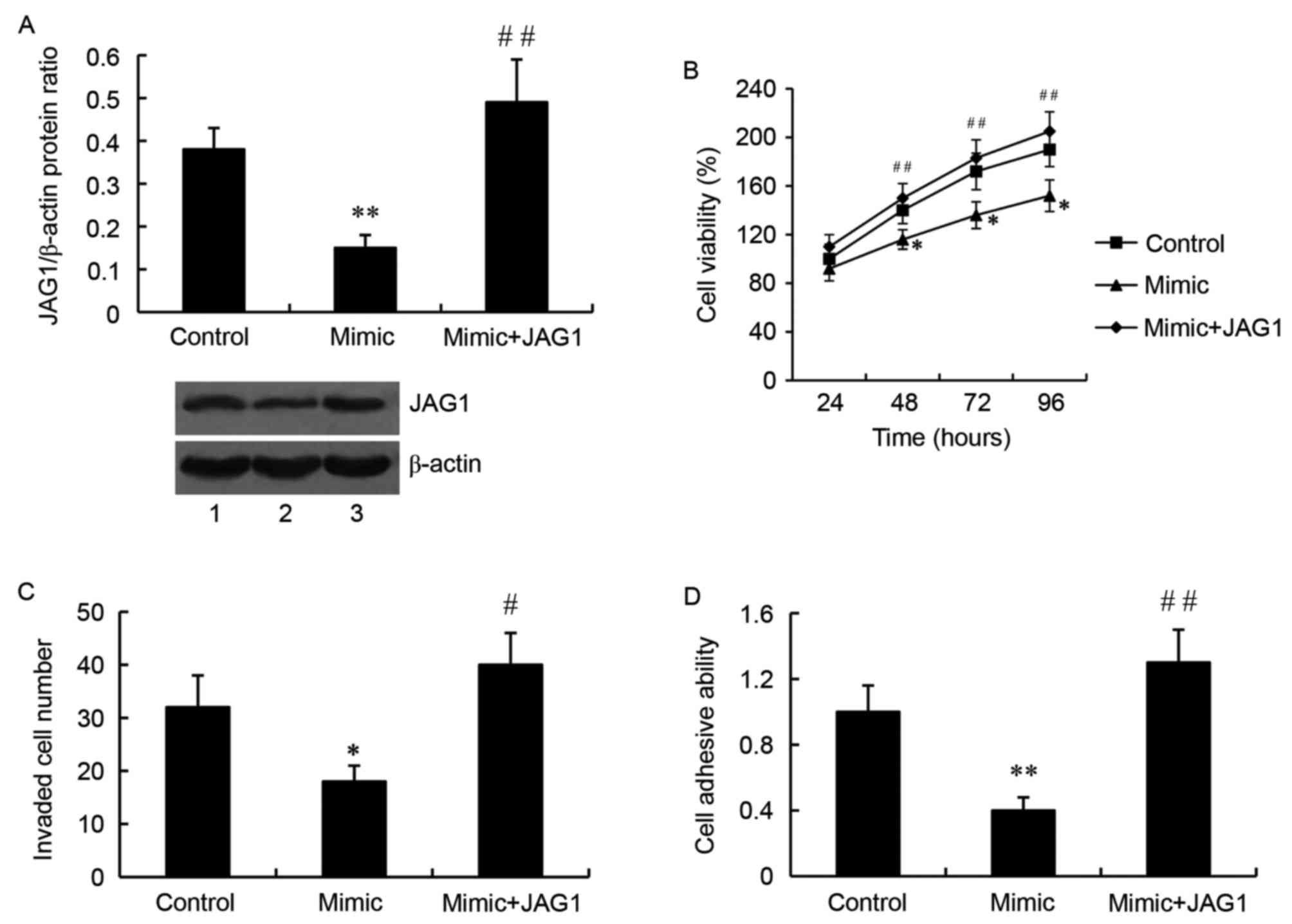
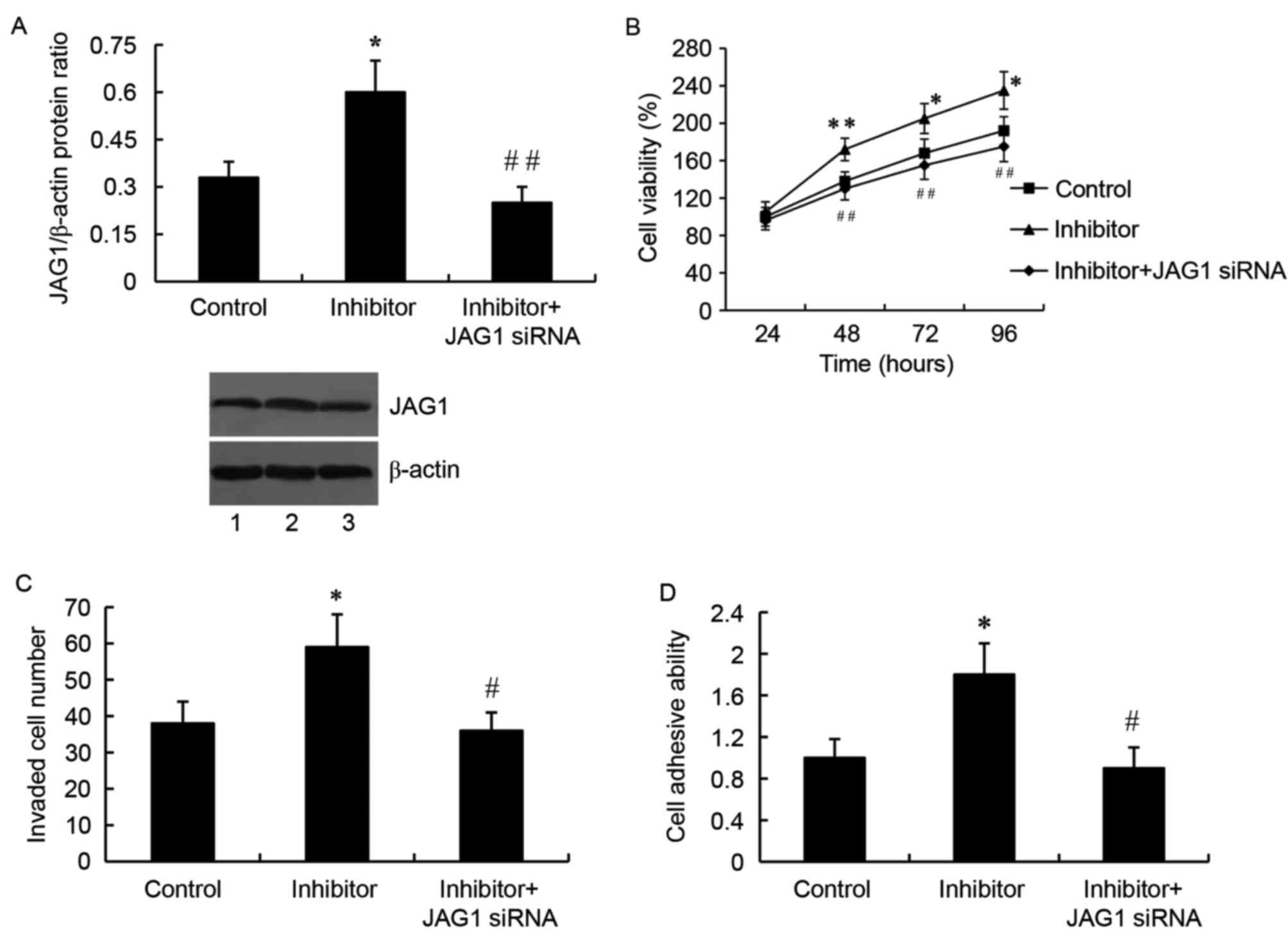
|
1
|
Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup NE and
Kruchko C: CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central
nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005–2009.
Neuro Oncol. 14:(Suppl 5). v1–v49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chi Y and Zhou D: MicroRNAs in colorectal
carcinoma-from pathogenesis to therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li Y and Sarkar FH: MicroRNA targeted
therapeutic approach for pancreatic cancer. Int J Biol Sci.
12:326–337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kuninty PR, Schnittert J, Storm G and
Prakash J: MicroRNA targeting to modulate tumor microenvironment.
Front Oncol. 6:32016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun W, Li YS Julie, Huang HD, Shyy JY and
Chien S: microRNA: A master regulator of cellular processes for
bioengineering systems. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 12:1–27. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD and Welch DR:
Metastamir: The field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is
spreading. Cancer Res. 69:7495–7498. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics.
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 4:143–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Manrique-Guzmán S: Biomarkers in
high-grade gliomas: A systematic review. Gac Med Mex. 152:87–93.
2016.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Silber J, James CD and Hodgson JG:
microRNAs in gliomas: Small regulators of a big problem.
Neuromolecular Med. 11:208–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wong JW: MicroRNA-induced silencing of
glioma progression. J Neurosci. 30:3868–3869. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang HW, Xing H and Johnson MD: A major
role for microRNAs in glioblastoma cancer stem-like cells. Arch
Pharm Res. 38:423–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Costa PM, Cardoso AL, Mano M and de Lima
MC: MicroRNAs in glioblastoma: Role in pathogenesis and
opportunities for targeted therapies. CNS Neurol Disord Drug
Targets. 14:222–238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang H, Fang F, Chang R and Yang L:
MicroRNA-140-5p suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by targeting
transforming growth factor β receptor 1 and fibroblast growth
factor 9 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 58:205–217. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kai Y, Peng W, Ling W, Jiebing H and Zhuan
B: Reciprocal effects between microRNA-140-5p and ADAM10 suppress
migration and invasion of human tongue cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 448:308–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li W and He F: Monocyte to macrophage
differentiation-associated (MMD) targeted by miR-140-5p regulates
tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 450:844–850. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhai H, Fesler A, Ba Y, Wu S and Ju J:
Inhibition of colorectal cancer stem cell survival and invasive
potential by hsa-miR-140-5p mediated suppression of Smad2 and
autophagy. Oncotarget. 6:19735–19746. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li WB, Chen HY, Zhang W, Yan W, Shi R, Li
SW and Jiang T: Relationship between magnetic resonance imaging
features and miRNA gene expression in patients with glioblastoma
multiforme. Chin Med J (Engl). 126:2881–2885. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiao YF, Yong X, Tang B, Qin Y, Zhang JW,
Zhang D, Xie R and Yang SM: Notch and Wnt signaling pathway in
cancer: Crucial role and potential therapeutic targets (Review).
Int J Oncol. 48:437–449. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shimizu K, Chiba S, Saito T, Kumano K and
Hirai H: Physical interaction of Delta1, Jagged1, and Jagged2 with
Notch1 and Notch3 receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
276:385–389. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu TS, Costello MA, Talsma CE, Flack CG,
Crowley JG, Hamm LL, He X, Hervey-Jumper SL, Heth JA, Muraszko KM,
et al: Endothelial cells create a stem cell niche in glioblastoma
by providing NOTCH ligands that nurture self-renewal of cancer
stem-like cells. Cancer Res. 71:6061–6072. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jeon HM, Kim SH, Jin X, Park JB, Kim SH,
Joshi K, Nakano I and Kim H: Crosstalk between glioma-initiating
cells and endothelial cells drives tumor progression. Cancer Res.
74:4482–4492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Purow BW, Haque RM, Noel MW, Su Q, Burdick
MJ, Lee J, Sundaresan T, Pastorino S, Park JK, Mikolaenko I, et al:
Expression of Notch-1 and its ligands, Delta-like-1 and Jagged-1,
is critical for glioma cell survival and proliferation. Cancer Res.
65:2353–2363. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jubb AM, Browning L, Campo L, Turley H,
Steers G, Thurston G, Harris AL and Ansorge O: Expression of
vascular Notch ligands Delta-like 4 and Jagged-1 in glioblastoma.
Histopathology. 60:740–747. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang W, Zou C, Pan L, Xu Y, Qi W, Ma G,
Hou Y and Jiang P: MicroRNA-140-5p inhibits the progression of
colorectal cancer by targeting VEGFA. Cell Physiol Biochem.
37:1123–1133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jing P, Sa N, Liu X, Liu X and Xu W:
MicroR-140-5p suppresses tumor cell migration and invasion by
targeting ADAM10-mediated Notch1 signaling pathway in
hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol.
100:132–138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen X, Stoeck A, Lee SJ, Shih IeM, Wang
MM and Wang TL: Jagged1 expression regulated by Notch3 and
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget.
1:210–218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamamoto M, Taguchi Y, Ito-Kureha T, Semba
K, Yamaguchi N and Inoue J: NF-κB non-cell-autonomously regulates
cancer stem cell populations in the basal-like breast cancer
subtype. Nat Commun. 4:22992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Choi K, Ahn YH, Gibbons DL, Tran HT,
Creighton CJ, Girard L, Minna JD, Qin FX and Kurie JM: Distinct
biological roles for the notch ligands Jagged-1 and Jagged-2. J
Biol Chem. 284:17766–17774. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Banerjee S, Kong D, Ahmad A,
Nogueira V, Hay N and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of Notch-1 and
Jagged-1 inhibits prostate cancer cell growth, migration and
invasion, and induces apoptosis via inactivation of Akt, mTOR and
NF-kappaB signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem. 109:726–736.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zeng Q, Li S, Chepeha DB, Giordano TJ, Li
J, Zhang H, Polverini PJ, Nor J, Kitajewski J and Wang CY:
Crosstalk between tumor and endothelial cells promotes tumor
angiogenesis by MAPK activation of Notch signaling. Cancer Cell.
8:13–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zavadil J, Cermak L, Soto-Nieves N and
Böttinger EP: Integration of TGF-beta/Smad and Jagged1/Notch
signalling in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. EMBO J.
23:1155–1165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li D, Masiero M, Banham AH and Harris AL:
The notch ligand JAGGED1 as a target for anti-tumor therapy. Front
Oncol. 4:2542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fiaschetti G, Schroeder C, Castelletti D,
Arcaro A, Westermann F, Baumgartner M, Shalaby T and Grotzer MA:
NOTCH ligands JAG1 and JAG2 as critical pro-survival factors in
childhood medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2:392014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|