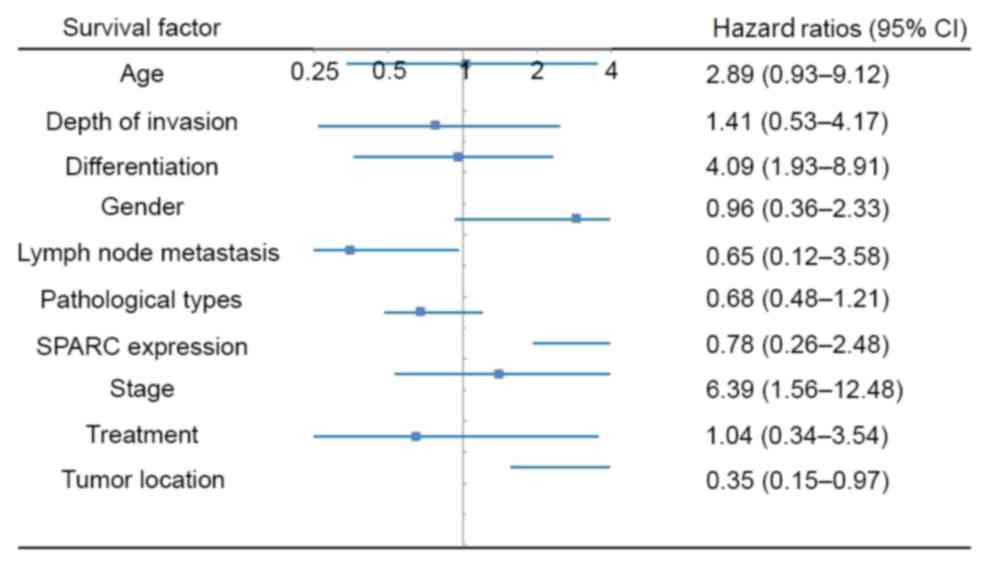
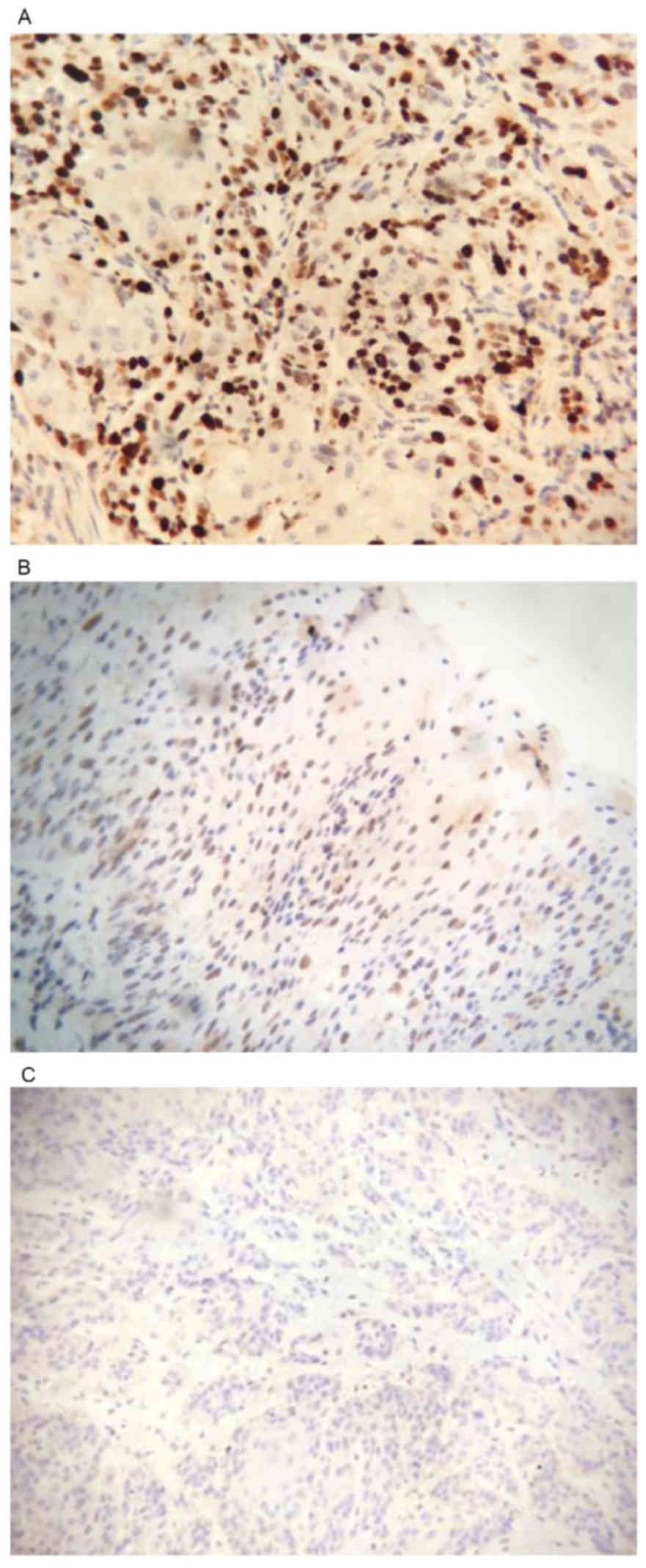
|
1
|
Tustumi F, Takeda FR, Kimura CM, Sallum
RA, Ribeiro U Junior and Cecconello I: Esophageal carcinoma: Is
squamous cell carcinoma different disease compared to
adenocarcinoma? A transversal study in a quaternary high volume
hospital in Brazil. Arq Gastroenterol. 53:44–48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu YM, Zhang H, Ni S, Wang J, Li DZ and
Liu SY: Multi-disciplinary treatment increases the survival rate of
late stage pharyngeal, laryngeal or cervical esophageal cancers
treated by free jejunal flap reconstruction after cancer resection.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 38:389–394. 2016.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang XE, Wang L, Ji ZQ, Liu MY, Qian T
and Li L: Safety of lienal polypeptide injection combined with
chemotherapy in treating patients with advanced cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:7837–7841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jia X, Liu P, Zhang M, Feng T, Tang H,
Tang Z, Zhao H and Jin T: Genetic variants at 6p21, 10q23, 16q21
and 22q12 are associated with esophageal cancer risk in a Chinese
Han population. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:19381–19387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang J, Jiang Y, Wu C, Cai S, Wang R,
Zhen Y, Chen S, Zhao K, Huang Y, Luketich J and Chen H: Comparison
of clinicopathologic features and survival between eastern and
western population with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J
Thorac Dis. 7:1780–1786. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nakamura R, Omori T, Takeuchi H, Kawakubo
H, Takahashi T, Wada N, Saikawa Y and Kitagawa Y: Salvage
endoscopic resection as a treatment for locoregional failure or
recurrence following chemoradiotherapy or radiotherapy for
esophageal cancer. Oncol Lett. 11:3631–3636. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gamboa AM, Kim S, Force SD, Staley CA,
Woods KE, Kooby DA, Maithel SK, Luke JA, Shaffer KM, Dacha S, et
al: Treatment allocation in patients with early-stage esophageal
adenocarcinoma: Prevalence and predictors of lymph node
involvement. Cancer. 122:2150–2157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cho JW: The role of endosonography in the
staging of gastrointestinal cancers. Clin Endosc. 48:297–301. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anandarajah EM, Ditgen D, Hansmann J,
Erttmann KD, Liebau E and Brattig NW: SPARC (secreted protein
acidic and rich in cysteine) of the intestinal nematode
Strongyloides ratti is involved in mucosa-associated parasite-host
interaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 207:75–83. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi D, Jiang K, Fu Y, Fang R, Liu XI and
Chen J: Overexpression of SPARC correlates with poor prognosis in
patients with cervical carcinoma and regulates cancer cell
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Lett. 11:3251–3258.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rossi MK, Gnanamony M and Gondi CS: The
‘SPARC’ of life: Analysis of the role of osteonectin/SPARC in
pancreatic cancer (Review). Int J Oncol. 48:1765–7871.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rosset EM and Bradshaw AD:
SPARC/osteonectin in mineralized tissue. Matrix Biol. 52–54:78–87.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Notaro A, Sabella S, Pellerito O, Vento R,
Calvaruso G and Giuliano M: The secreted protein acidic and rich in
cysteine is a critical mediator of cell death program induced by
WIN/TRAIL combined treatment in osteosarcoma cells. Int J Oncol.
48:1039–1044. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tseng C and Kolonin MG: Proteolytic
Isoforms of SPARC induce adipose stromal cell mobilization in
obesity. Stem Cells. 34:174–190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim H, Samuel S, Lopez-Casas P, Grizzle W,
Hidalgo M, Kovar J, Oelschlager D, Zinn K, Warram J and Buchsbaum
D: SPARC-independent delivery of Nab-Paclitaxel without depleting
tumor stroma in patient-derived pancreatic cancer xenografts. Mol
Cancer Ther. 15:680–688. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vaz J, Ansari D, Sasor A and Andersson R:
SPARC: A potential prognostic and therapeutic target in pancreatic
cancer. Pancreas. 44:1024–1035. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mattina J, MacKinnon N, Henderson VC,
Fergusson D and Kimmelman J: Design and reporting of targeted
anticancer preclinical studies: A meta-analysis of animal studies
investigating sorafenib antitumor efficacy. Cancer Res.
76:4627–4636. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huo Y, Su T, Cai Q and Macara IG: An in
vivo gain-of-function screen identifies the Williams-Beuren
Syndrome Gene GTF2IRD1 as a mammary tumor promoter. Cell Rep.
15:2089–2096. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee J, Katzenmaier EM, Kopitz J and Gebert
J: Reconstitution of TGFBR2 in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells
causes increased LFNG expression and enhanced
N-acetyl-d-glucosamine incorporation into Notch1. Cell Signal.
28:1105–1113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao R, Ma LQ, Du X, Zhang TT, Zhao L, Liu
L, Liu JC, Guo F, Cheng Z and Huang H: Rnf25/AO7 positively
regulates wnt signaling via disrupting Nkd1-Axin inhibitory complex
independent of its ubiquitin ligase activity. Oncotarget.
7:23850–23859. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fang M, Yuan J, Peng C and Li Y: Collagen
as a double-edged sword in tumor progression. Tumour Biol.
35:2871–2882. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bai J, Zhang X, Hu K, Liu B, Wang H, Li A,
Lin F, Zhang L, Sun X, Du Z and Song J: Silencing DNA
methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) inhibits proliferation, metastasis and
invasion in ESCC by suppressing methylation of RASSF1A and DAPK.
Oncotarget. 7:44129–44141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu JY, Lu JB and Xu Y: MicroRNA-153
inhibits the proliferation and invasion of human laryngeal squamous
cell carcinoma by targeting KLF5. Exp Ther Med. 11:2503–2508.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin W, Zhong M, Yin H, Chen Y, Cao Q, Wang
C and Ling C: Emodin induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell
apoptosis through MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways in vitro and
in vivo. Oncol Rep. 36:961–967. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Che Y, Luo A, Wang H, Qi J, Guo J and Liu
Z: The differential expression of SPARC in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 17:1027–1033. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xue LY, Zou SM, Zheng S, Liu XY, Wen P,
Yuan YL, Lin DM and Lu N: Expressions of the γ2 chain of laminin-5
and secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma and their relation to prognosis. Chin J
Cancer. 30:69–78. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nagaraju GP and Sharma D: Anti-cancer role
of SPARC, an inhibitor of adipogenesis. Cancer Treat Rev.
37:559–566. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zinovyeva MV, Monastyrskaya GS, Kopantzev
EP, Vinogradova TV, Kostina MB, Sass AV, Filyukova OB, Uspenskaya
NY, Sukhikh GT and Sverdlov ED: Identification of some human genes
oppositely regulated during esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
formation and human embryonic esophagus development. Dis Esophagus.
23:260–270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jakharia A, Borkakoty B and Singh S:
Expression of SPARC like protein 1 (SPARCL1), extracellular
matrix-associated protein is down regulated in gastric
adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Oncol. 7:278–283. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Porte H, Triboulet JP, Kotelevets L,
Carrat F, Prévot S, Nordlinger B, DiGioia Y, Wurtz A, Comoglio P,
Gespach C and Chastre E: Overexpression of stromelysin-3,
BM-40/SPARC, and MET genes in human esophageal carcinoma:
Implications for prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 4:1375–1382.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hong Y, Zhang J, Zhang H, Li X, Qu J, Zhai
J, Zhang L, Chen F and Li T: Heterozygous PTCH1 mutations impact
the bone metabolism in patients with nevoid basal cell carcinoma
syndrome likely by regulating SPARC expression. J Bone Miner Res.
31:1413–1428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kao SC, Kirschner MB, Cooper WA, Tran T,
Burgers S, Wright C, Korse T, van den Broek D, Edelman J, Vallely
M, et al: A proteomics-based approach identifies secreted protein
acidic and rich in cysteine as a prognostic biomarker in malignant
pleural mesothelioma. Br J Cancer. 114:524–531. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Slusser-Nore A, Larson-Casey JL, Zhang R,
Zhou XD, Somji S, Garrett SH, Sens DA and Dunlevy JR: SPARC
expression is selectively suppressed in tumor initiating urospheres
isolated from As+3- and Cd+2-transformed human urothelial cells
(UROtsa) stably transfected with SPARC. PLoS One. 11:e01473622016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|