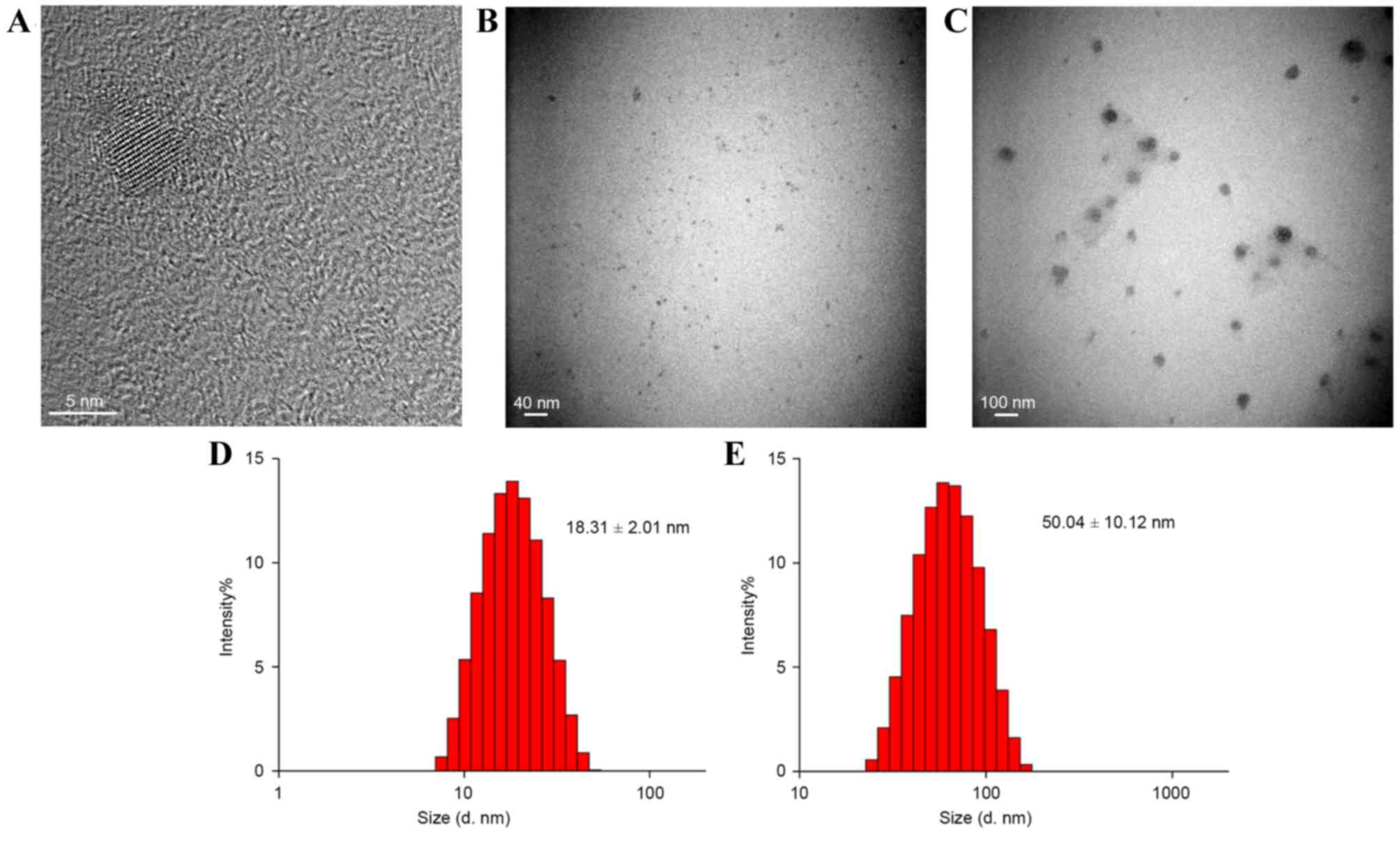
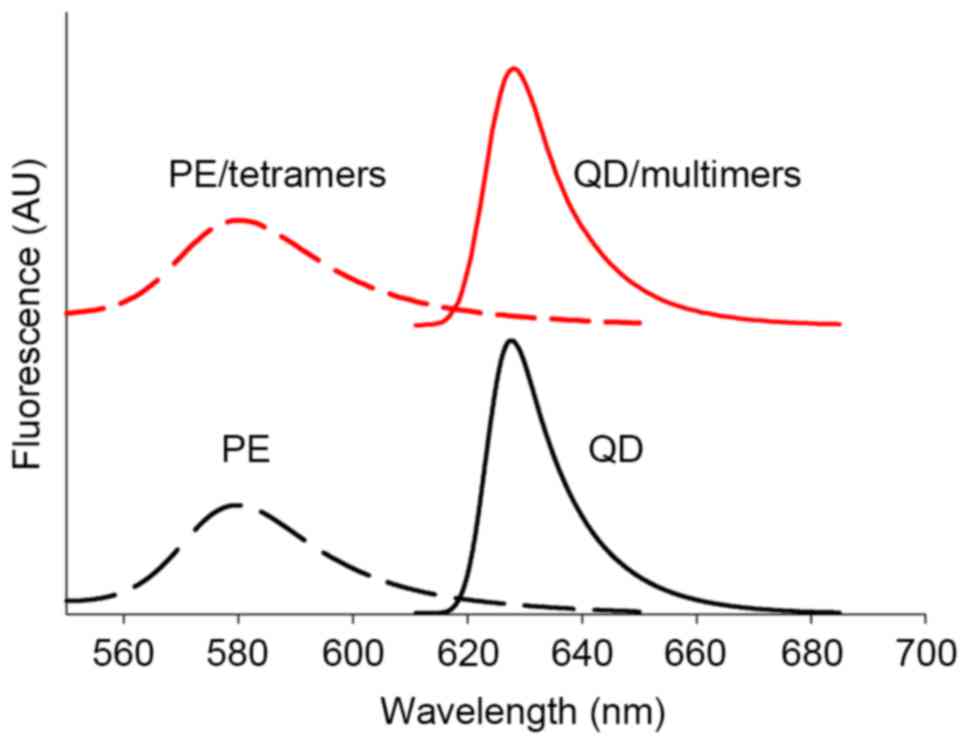
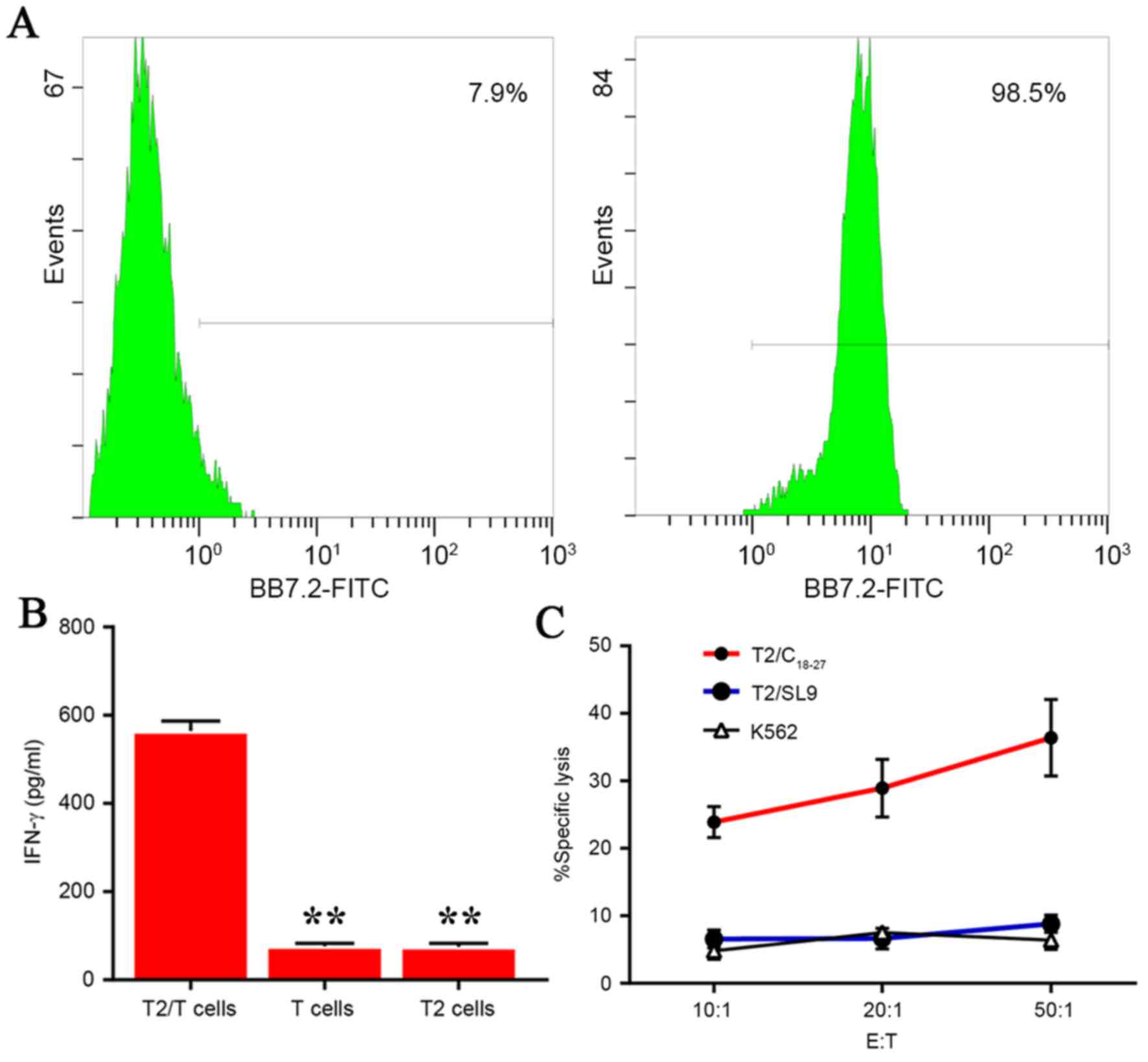
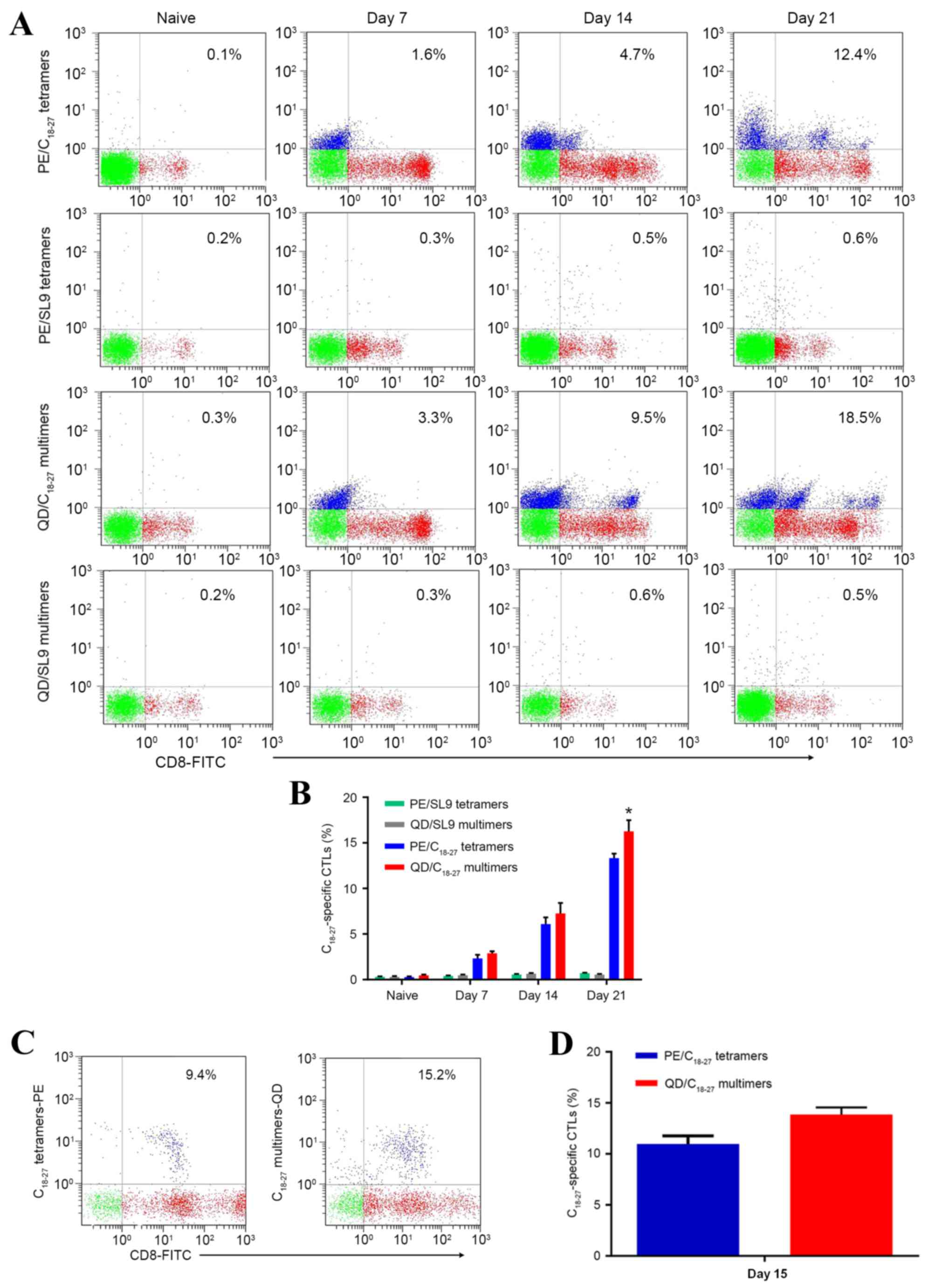
|
1
|
Chisari FV and Ferrari C: Hepatitis B
virus immunopathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 13:29–60. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beasley RP, Hwang LY, Lin CC and Chien CS:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study
of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 2:1129–1133. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Noordeen F: Hepatitis B virus infection:
An insight into infection outcomes and recent treatment options.
Virusdisease. 26:1–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guidotti LG and Chisari FV: Immunobiology
and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu Rev Pathol. 1:23–61.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wherry EJ and Ahmed R: Memory CD8 T-cell
differentiation during viral infection. J Virol. 78:5535–5545.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Virgin HW, Wherry EJ and Ahmed R:
Redefining chronic viral infection. Cell. 138:30–50. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Belyakov IM and Ahlers JD: What role does
the route of immunization play in the generation of protective
immunity against mucosal pathogens? J Immunol. 183:6883–6892. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Varela-Rohena A, Molloy PE, Dunn SM, Li Y,
Suhoski MM, Carroll RG, Milicic A, Mahon T, Sutton DH, Laugel B, et
al: Control of HIV-1 immune escape by CD8 T cells expressing
enhanced T-cell receptor. Nat Med. 14:1390–1395. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bertoletti A and Gehring AJ: The immune
response during hepatitis B virus infection. J Gen Virol.
87:1439–1449. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Engler OB, Dai WJ, Sette A, Hunziker IP,
Reichen J, Pichler WJ and Cerny A: Peptide vaccines against
hepatitis B virus: From animal model to human studies. Mol Immunol.
38:457–465. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu J, Chen KY and Ren EC: Structural
insights into the binding of hepatitis B virus core peptide to
HLA-A2 alleles: Towards designing better vaccines. Eur J Immunol.
41:2097–2106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hobeika AC, Morse MA, Osada T, Ghanayem M,
Niedzwiecki D, Barrier R, Lyerly HK and Clay TM: Enumerating
antigen-specific T-cell responses in peripheral blood: A comparison
of peptide MHC Tetramer, ELISpot, and intracellular cytokine
analysis. J Immunother. 28:63–72. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dolton G, Lissina A, Skowera A, Ladell K,
Tungatt K, Jones E, Kronenberg-Versteeg D, Akpovwa H, Pentier JM,
Holland CJ, et al: Comparison of peptide-major histocompatibility
complex tetramers and dextramers for the identification of
antigen-specific T cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 177:47–63. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meidenbauer N, Hoffmann TK and Donnenberg
AD: Direct visualization of antigen-specific T cells using
peptide-MHC-class I tetrameric complexes. Methods. 31:160–171.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sims S, Willberg C and Klenerman P:
MHC-peptide tetramers for the analysis of antigen-specific T cells.
Expert Rev Vaccines. 9:765–774. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reguzova AY, Karpenko LI, Mechetina LV and
Belyakov IM: Peptide-MHC multimer-based monitoring of CD8 T-cells
in HIV-1 infection and AIDS vaccine development. Expert Rev
Vaccines. 14:69–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bilan R, Fleury F, Nabiev I and Sukhanova
A: Quantum dot surface chemistry and functionalization for cell
targeting and imaging. Bioconjug Chem. 26:609–624. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Altman JD, Moss PA, Goulder PJ, Barouch
DH, McHeyzer-Williams MG, Bell JI, McMichael AJ and Davis MM:
Phenotypic analysis of antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Science.
274:94–96. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hines MA and Guyot-Sionnest P: Synthesis
and characterization of strongly luminescing ZnS-capped CdSe
nanocrystals. J Phys Chem. 100:468–471. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sukhanova A, Devy J, Venteo L, Kaplan H,
Artemyev M, Oleinikov V, Klinov D, Pluot M, Cohen JH and Nabiev I:
Biocompatible fluorescent nanocrystals for immunolabeling of
membrane proteins and cells. Anal Biochem. 324:60–67. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Samir TM, Mansour MM, Kazmierczak SC and
Azzazy HM: Quantum dots: Heralding a brighter future for clinical
diagnostics. Nanomedicine (Lond). 7:1755–1769. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER and
Mattoussi H: Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and
sensing. Nat Mater. 4:435–446. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chattopadhyay PK, Price DA, Harper TF,
Betts MR, Yu J, Gostick E, Perfetto SP, Goepfert P, Koup RA, De
Rosa SC, et al: Quantum dot semiconductor nanocrystals for
immunophenotyping by polychromatic flow cytometry. Nat Med.
12:972–977. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Andersen RS, Kvistborg P, Frøsig TM,
Pedersen NW, Lyngaa R, Bakker AH, Shu CJ, Straten Pt, Schumacher TN
and Hadrup SR: Parallel detection of antigen-specific T cell
responses by combinatorial encoding of MHC multimers. Nat Protoc.
7:891–902. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Howarth M, Chinnapen DJ, Gerrow K,
Dorrestein PC, Grandy MR, Kelleher NL, El-Husseini A and Ting AY: A
monovalent streptavidin with a single femtomolar biotin binding
site. Nat Methods. 3:267–273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu C, Liu J, Zhang P, Li J, Ji H, Yang X
and Wang K: A recognition-before-labeling strategy for sensitive
detection of lung cancer cells with a quantum dot-aptamer complex.
Analyst. 140:6100–6107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pinaud F, King D, Moore HP and Weiss S:
Bioactivation and cell targeting of semiconductor CdSe/ZnS
nanocrystals with phytochelatin-related peptides. J Am Chem Soc.
126:6115–6123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hainfeld JF, Liu W, Halsey CM, Freimuth P
and Powell RD: Ni-NTA-gold clusters target His-tagged proteins. J
Struct Biol. 127:185–198. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Akerman ME, Chan WC, Laakkonen P, Bhatia
SN and Ruoslahti E: Nanocrystal targeting in vivo. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 99:pp. 12617–12621. 2002; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goldman ER, Medintz IL, Whitley JL,
Hayhurst A, Clapp AR, Uyeda HT, Deschamps JR, Lassman ME and
Mattoussi H: A hybrid quantum dot-antibody fragment fluorescence
resonance energy transfer-based TNT sensor. J Am Chem Soc.
127:6744–6751. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Medintz IL, Berti L, Pons T, Grimes AF,
English DS, Alessandrini A, Facci P and Mattoussi H: A reactive
peptidic linker for self-assembling hybrid quantum dot-DNA
bioconjugates. Nano Lett. 7:1741–1748. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hardman R: A toxicologic review of quantum
dots: Toxicity depends on physicochemical and environmental
factors. Environ Health Perspect. 114:165–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ryman-Rasmussen JP, Riviere JE and
Monteiro-Riviere NA: Surface coatings determine cytotoxicity and
irritation potential of quantum dot nanoparticles in epidermal
keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 127:143–153. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miyamoto T, Min W and Lillehoj HS:
Lymphocyte proliferation response during Eimeria tenella infection
assessed by a new, reliable, nonradioactive colorimetric assay.
Avian Dis. 46:10–16. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hadrup SR and Schumacher TN: MHC-based
detection of antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 59:1425–1433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|