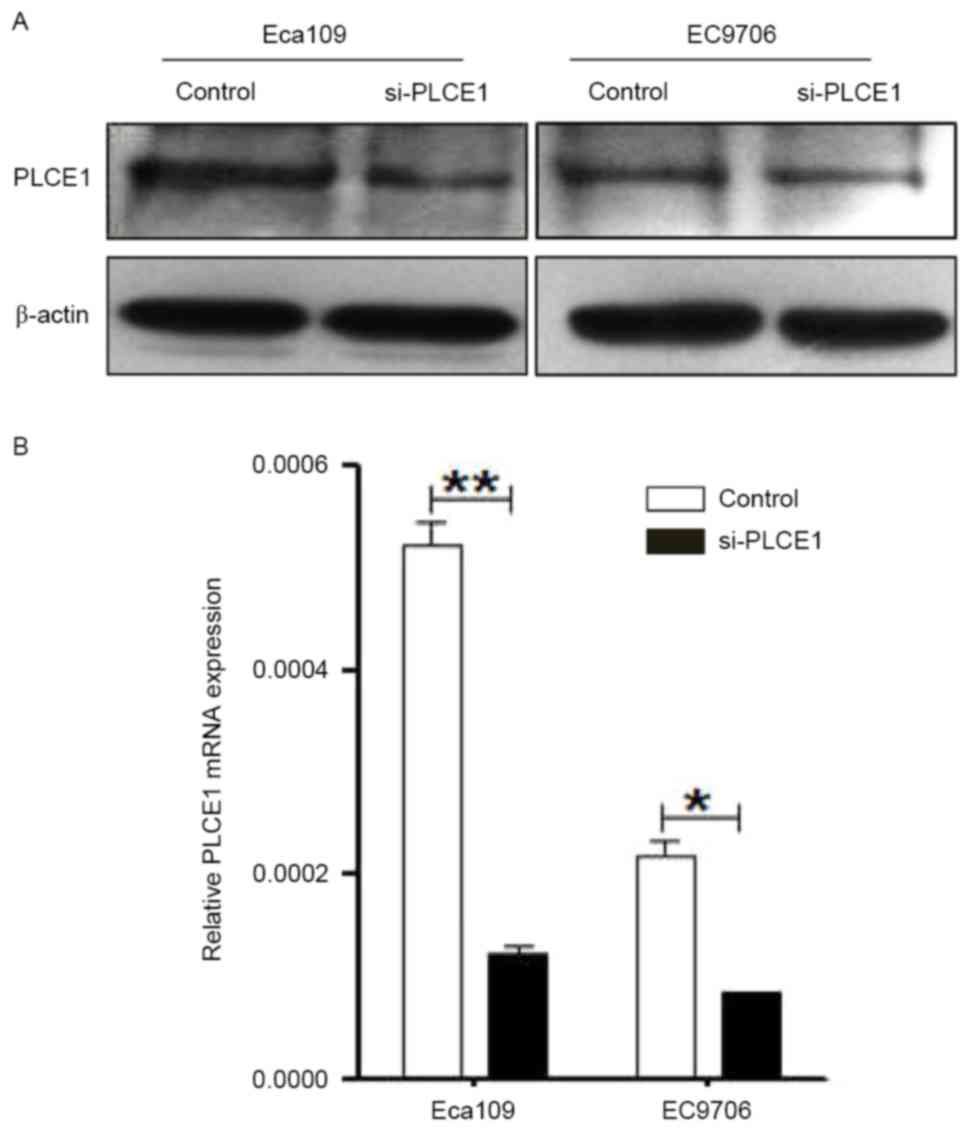
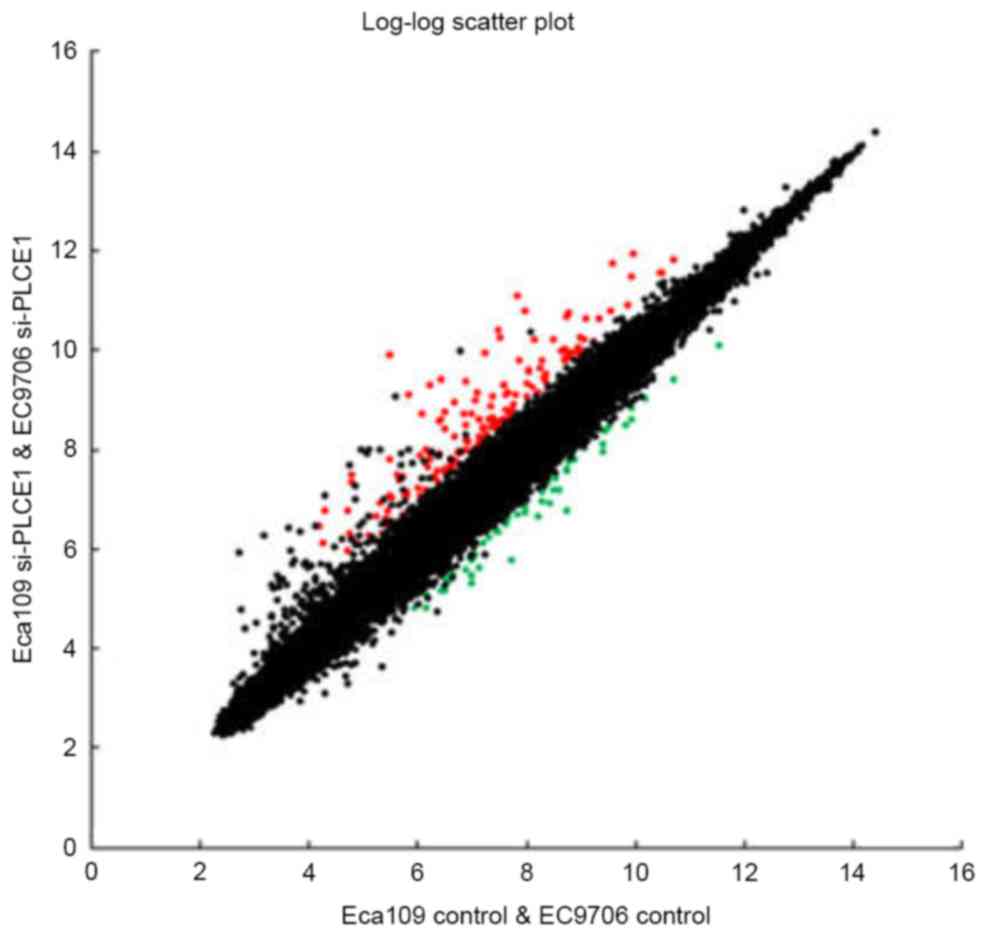
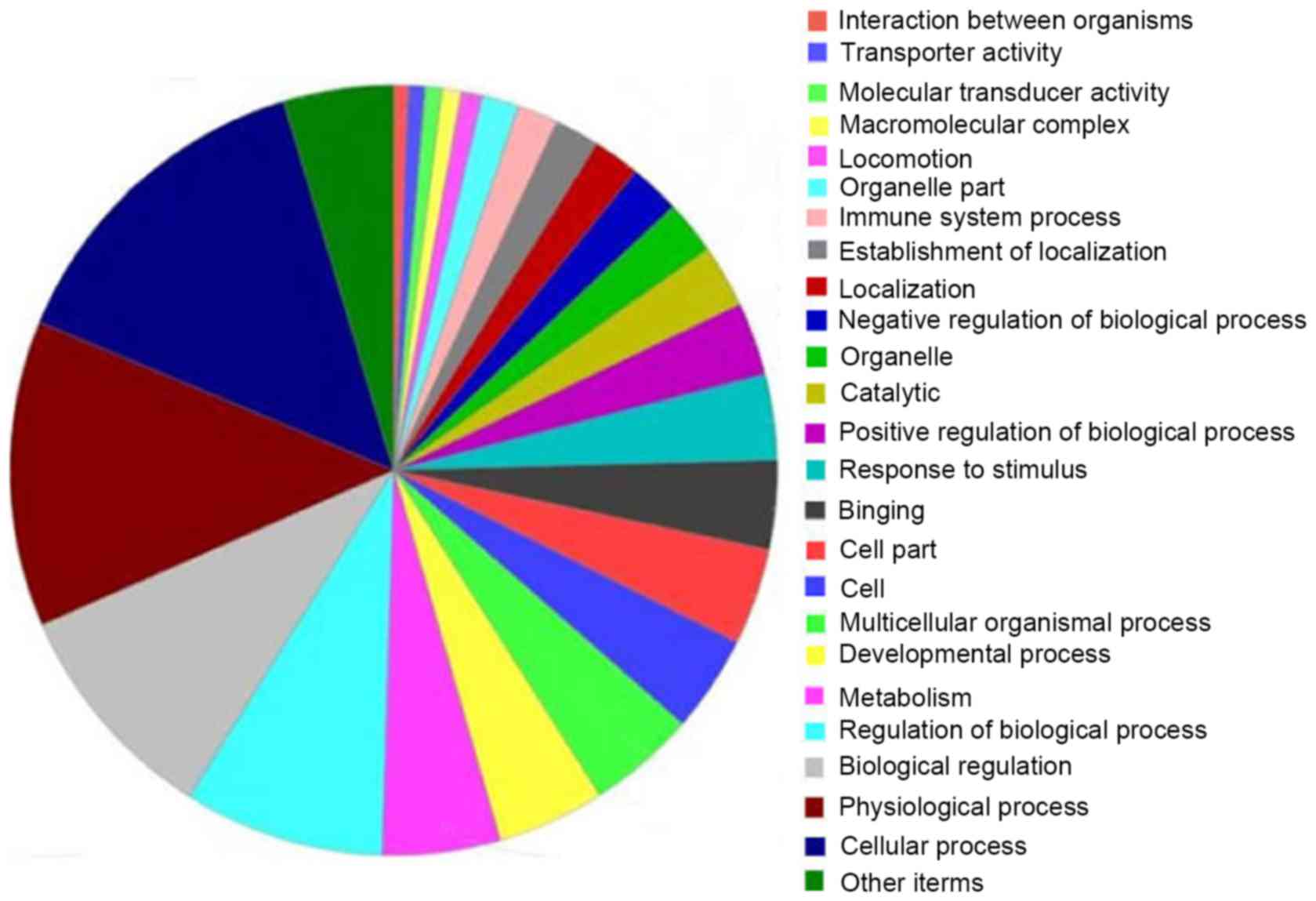
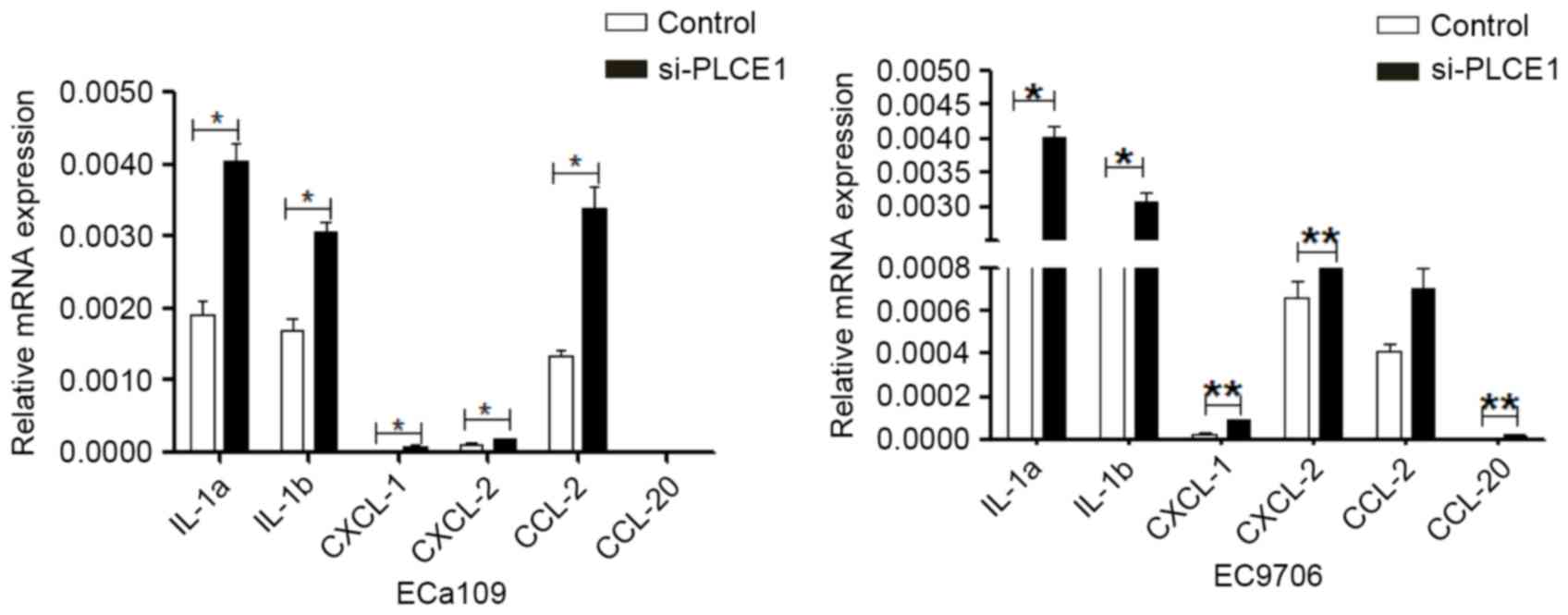
|
1
|
Liu M, Hu Y, Zhang MF, Luo KJ, Xie XY, Wen
J, Fu JH and Yang H: MMP1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 377:97–104. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu M, Liu AM, Kampman E, Zhang ZF, Van't
Veer P, Wu DL, Wang PH, Yang J, Qin Y, Mu LN, et al: Green tea
drinking, high tea temperature and esophageal cancer in high- and
low-risk areas of Jiangsu Province, China: A population-based
case-control study. Int J Cancer. 124:1907–1913. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cui XB, Zhang SM, Xu YX, Dang HW, Liu CX,
Wang LH, Yang L, Hu JM, Liang WH, Jiang JF, et al: PFN2, a novel
marker of unfavorable prognosis, is a potential therapeutic target
involved in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med.
14:1372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cui XB, Li S, Li TT, Peng H, Jin TT, Zhang
SM, Liu CX, Yang L, Shen YY, Li SG, et al: Targeting oncogenic
PLCE1 by miR-145 impairs tumor proliferation and metastasis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:1777–1795. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abnet CC, Freedman ND, Hu N, Wang Z, Yu K,
Shu XO, Yuan JM, Zheng W, Dawsey SM, Dong LM, et al: A shared
susceptibility locus in PLCE1 at 10q23 for gastric adenocarcinoma
and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 42:764–767.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang LD, Zhou FY, Li XM, Sun LD, Song X,
Jin Y, Li JM, Kong GQ, Qi H, Cui J, et al: Genome-wide association
study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54. Nat Genet.
42:759–763. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu C, Hu Z, He Z, Jia W, Wang F, Zhou Y,
Liu Z, Zhan Q, Liu Y, Yu D, et al: Genome-wide association study
identifies three new susceptibility loci for esophageal
squamous-cell carcinoma in Chinese populations. Nat Genet.
43:679–684. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma H, Wang LE, Liu Z, Sturgis EM and Wei
Q: Association between novel PLCE1 variants identified in published
esophageal cancer genome-wide association studies and risk of
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. BMC Cancer.
11:2582011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ou L, Guo Y, Luo C, Wu X, Zhao Y and Cai
X: RNA interference suppressing PLCE1 gene expression decreases
invasive power of human bladder cancer T24 cell line. Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 200:110–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ling Y, Chunli L, Xiaohou W and Qiaoling
Z: Involvement of the PLCε/PKCα pathway in human BIU-87 bladder
cancer cell proliferation. Cell Biol Int. 35:1031–1036. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Yan L, Zhao Y, Ou L, Wu X and Luo
C: Knockdown of phospholipase C-epsilon by short-hairpin
RNA-mediated gene silencing induces apoptosis in human bladder
cancer cell lines. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 28:233–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xue W, Zhu M, Wang Y, He J and Zheng L:
Association between PLCE1 rs2274223 A >G polymorphism and cancer
risk: Proof from a meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 5:79862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yuan J, Li Y, Tian T, Li N, Zhu Y, Zou J,
Gao J and Shen L: Risk prediction for early-onset gastric
carcinoma: A case-control study of polygenic gastric cancer in Han
Chinese with hereditary background. Oncotarget. 7:33608–33615.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oka M, Edamatsu H, Kunisada M, Hu L,
Takenaka N, Dien S, Sakaguchi M, Kitazawa R, Norose K, Kataoka T
and Nishigori C: Enhancement of ultraviolet B-induced skin tumor
development in phospholipase Cε-knockout mice is associated with
decreased cell death. Carcinogenesis. 31:1897–1902. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Wu X, Ou L, Yang X, Wang X, Tang
M, Chen E and Luo C: PLCε knockdown inhibits prostate cancer cell
proliferation via suppression of Notch signalling and nuclear
translocation of the androgen receptor. Cancer Lett. 362:61–69.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen YZ, Cui XB, Hu JM, Zhang WJ, Li SG,
Yang L, Shen XH, Liu CX, Pan QF, Yu SY, et al: Overexpression of
PLCE1 in Kazakh esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Implications in
cancer metastasis and aggressiveness. APMIS. 121:908–918. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cui XB, Pang XL, Li S, Jin J, Hu JM, Yang
L, Liu CX, Li L, Wen SJ, Liang WH, et al: Elevated expression
patterns and tight correlation of the PLCE1 and NF-κB signaling in
Kazakh patients with esophageal carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31:7912014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Zhou C, Qiu G, Yang Y, Yan D, Xing
T, Fan J, Tang H and Peng Z: Phospholipase C epsilon plays a
suppressive role in incidence of colorectal cancer. Med Oncol.
29:1051–1058. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cui X, Li S, Li T, Pang X, Zhang S, Jin J,
Hu J, Liu C, Yang L, Peng H, et al: Significance of elevated ERK
expression and its positive correlation with EGFR in Kazakh
patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:2382–2391. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akl MR, Nagpal P, Ayoub NM, Tai B, Prabhu
SA, Capac CM, Gliksman M, Goy A and Suh KS: Molecular and clinical
significance of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2/bFGF) in
malignancies of solid and hematological cancers for personalized
therapies. Oncotarget. 7:44735–44762. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pierozan P, Biasibetti H, Schmitz F, Ávila
H, Parisi MM, Barbe-Tuana F, Wyse AT and Pessoa-Pureur R:
Quinolinic acid neurotoxicity: Differential roles of astrocytes and
microglia via FGF-2-mediated signaling in redox-linked cytoskeletal
changes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:3001–3014. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He Q, Ren X, Chen J, Li Y, Tang X, Wen X,
Yang X, Zhang J, Wang Y, Ma J and Liu N: miR-16 targets fibroblast
growth factor 2 to inhibit NPC cell proliferation and invasion via
PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways. Oncotarget. 7:3047–3058.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee MN, Kim JW, Oh SH, Jeong BC, Hwang YC
and Koh JT: FGF2 stimulates COUP-TFII expression via the MEK1/2
pathway to inhibit osteoblast differentiation in C3H10T1/2 cells.
PLoS One. 11:e01592342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rios P, Nunes-Xavier CE, Tabernero L, Köhn
M and Pulido R: Dual-specificity phosphatases as molecular targets
for inhibition in human disease. Antioxid Redox Signal.
20:2251–2273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Majumder M, House R, Palanisamy N, Qie S,
Day TA, Neskey D, Diehl JA and Palanisamy V: Correction:
RNA-binding protein FXR1 regulates p21 and TERC RNA to bypass
p53-mediated cellular senescence in OSCC. PLoS Genet.
12:e10064112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, An J, Huang S, Liao H, Weng Y, Cai S
and Zhang J: PLCE1 suppresses p53 expression in esophageal cancer
cells. Cancer Invest. 32:236–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tront JS, Huang Y, Fornace AJ Jr, Hoffman
B and Liebermann DA: Gadd45a functions as a promoter or suppressor
of breast cancer dependent on the oncogenic stress. Cancer Res.
70:9671–9681. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cho JG, Park S, Lim CH, Kim HS, Song SY,
Roh TY, Sung JH, Suh W, Ham SJ, Lim KH and Park SG: ZNF224, Kruppel
like zinc finger protein, induces cell growth and
apoptosis-resistance by down-regulation of p21 and p53 via
miR-663a. Oncotarget. 7:31177–31190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park H, Kim CH, Jeong JH, Park M and Kim
KS: GDF15 contributes to radiation-induced senescence through the
ROS-mediated p16 pathway in human endothelial cells. Oncotarget.
7:9634–9644. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li M, Edamatsu H, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S
and Kataoka T: Phospholipase Cepsilon promotes intestinal
tumorigenesis of Apc(Min/+) mice through augmentation of
inflammation and angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 30:1424–1432. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang X, Ou L, Tang M, Wang Y, Wang X, Chen
E, Diao J, Wu X and Luo C: Knockdown of PLCε inhibits inflammatory
cytokine release via STAT3 phosphorylation in human bladder cancer
cells. Tumour Biol. 36:9723–9732. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oka M, Edamatsu H, Kunisada M, Hu L,
Takenaka N, Sakaguchi M, Kataoka T and Nishigori C: Phospholipase
Cε has a crucial role in ultraviolet B-induced
neutrophil-associated skin inflammation by regulating the
expression of CXCL1/KC. Lab Invest. 91:711–718. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oubaha M, Miloudi K, Dejda A, Guber V,
Mawambo G, Germain MA, Bourdel G, Popovic N, Rezende FA, Kaufman
RJ, et al: Senescence-associated secretory phenotype contributes to
pathological angiogenesis in retinopathy. Sci Transl Med.
8:362ra1442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Freund A, Orjalo AV, Desprez PY and
Campisi J: Inflammatory networks during cellular senescence: Causes
and consequences. Trends Mol Med. 16:238–246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin H, Yan J, Wang Z, Hua F, Yu J, Sun W,
Li K, Liu H, Yang H, Lv Q, et al: Loss of immunity-supported
senescence enhances susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinogenesis
and progression in Toll-like receptor 2-deficient mice. Hepatology.
57:171–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Z, Yan J, Lin H, Hua F, Wang X, Liu
H, Lv X, Yu J, Mi S, Wang J and Hu ZW: Toll-like receptor 4
activity protects against hepatocellular tumorigenesis and
progression by regulating expression of DNA repair protein Ku70 in
mice. Hepatology. 57:1869–1881. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|