|
1
|
European Association For The Study Of The
Liver, . EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of chronic
hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 57:167–185. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Buchmann P, Dembek C, Kuklick L, Jäger C,
Tedjokusumo R, von Freyend MJ, Drebber U, Janowicz Z, Melber K and
Protzer U: A novel therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine induces cellular
and humoral immune responses and breaks tolerance in hepatitis B
virus (HBV) transgenic mice. Vaccine. 31:1197–1203. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maini MK, Boni C, Lee CK, Larrubia JR,
Reignat S, Ogg GS, King AS, Herberg J, Gilson R, Alisa A, et al:
The role of virus-specific CD8(+) cells in liver damage and viral
control during persistent hepatitis B virus infection. J Exp Med.
191:1269–1280. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Michel ML and Loirat D: DNA vaccines for
prophylactic or therapeutic immunization against hepatitis B.
Intervirology. 44:78–87. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li X, Yang X, Jiang Y and Liu J: A novel
HBV DNA vaccine based on T cell epitopes and its potential
therapeutic effect in HBV transgenic mice. Int Immunol.
17:1293–1302. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thermet A, Rollier C, Zoulim F, Trepo C
and Cova L: Progress in DNA vaccine for prophylaxis and therapy of
hepatitis B. Vaccine. 21:659–662. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Banchereau J and Steinman RM: Dendritic
cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 392:245–252. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Beckebaum S, Cicinnati VR, Dworacki G,
Müller-Berghaus J, Stolz D, Harnaha J, Whiteside TL, Thomson AW, Lu
L, Fung JJ and Bonham CA: Reduction in the circulating pDC1/pDC2
ratio and impaired function of ex vivo-generated DC1 in chronic
hepatitis B infection. Clin Immunol. 104:138–150. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kakimi K, Isogawa M, Chung J, Sette A and
Chisari FV: Immunogenicity and tolerogenicity of hepatitis B virus
structural and nonstructural proteins: Implications for
immunotherapy of persistent viral infections. J Virol.
76:8609–8620. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Van Kooten C and Banchereau J: CD40-CD40
ligand. J Leukoc Biol. 67:2–17. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grewal IS and Flavell RA: CD40 and CD154
in cell-mediated immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:111–135. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
O'Sullivan B and Thomas R: CD40 and
dendritic cell function. Crit Rev Immunol. 23:83–107. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Caux C, Massacrier C, Vanbervliet B,
Dubois B, Van Kooten C, Durand I and Banchereau J: Activation of
human dendritic cells through CD40 cross-linking. J Exp Med.
180:1263–1272. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cella M, Scheidegger D, Palmer-Lehmann K,
Lane P, Lanzavecchia A and Alber G: Ligation of CD40 on dendritic
cells triggers production of high levels of interleukin-12 and
enhances T cell stimulatory capacity: T-T help via APC activation.
J Exp Med. 184:747–752. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu JM, Lin XF, Huang ZM and Wu JS:
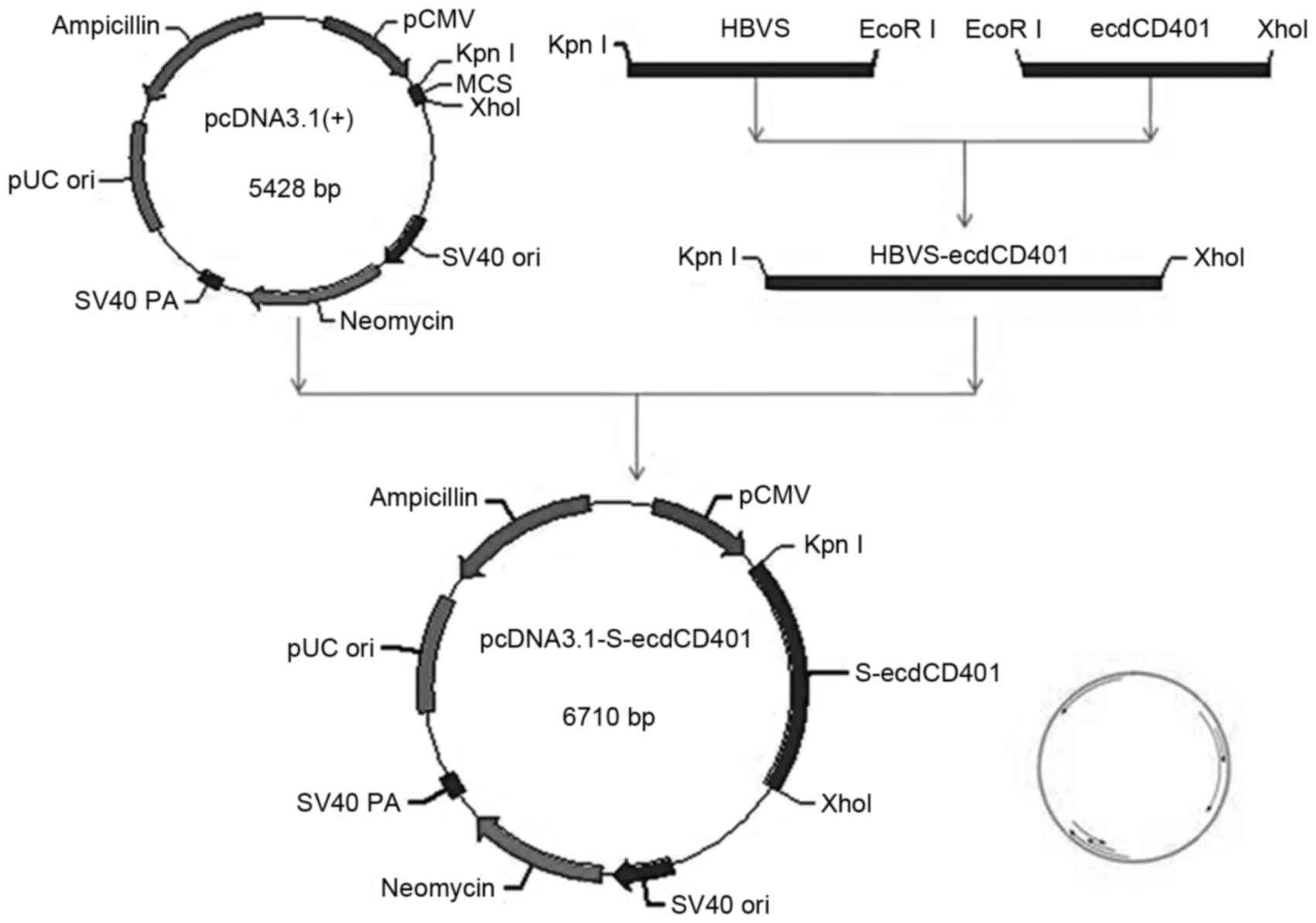
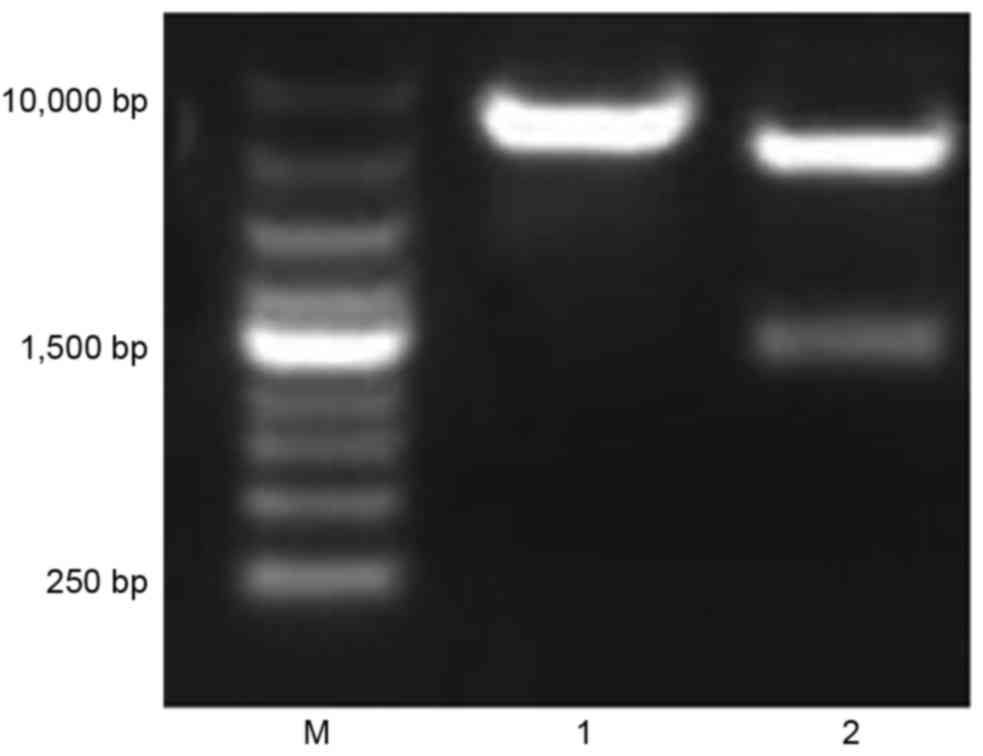
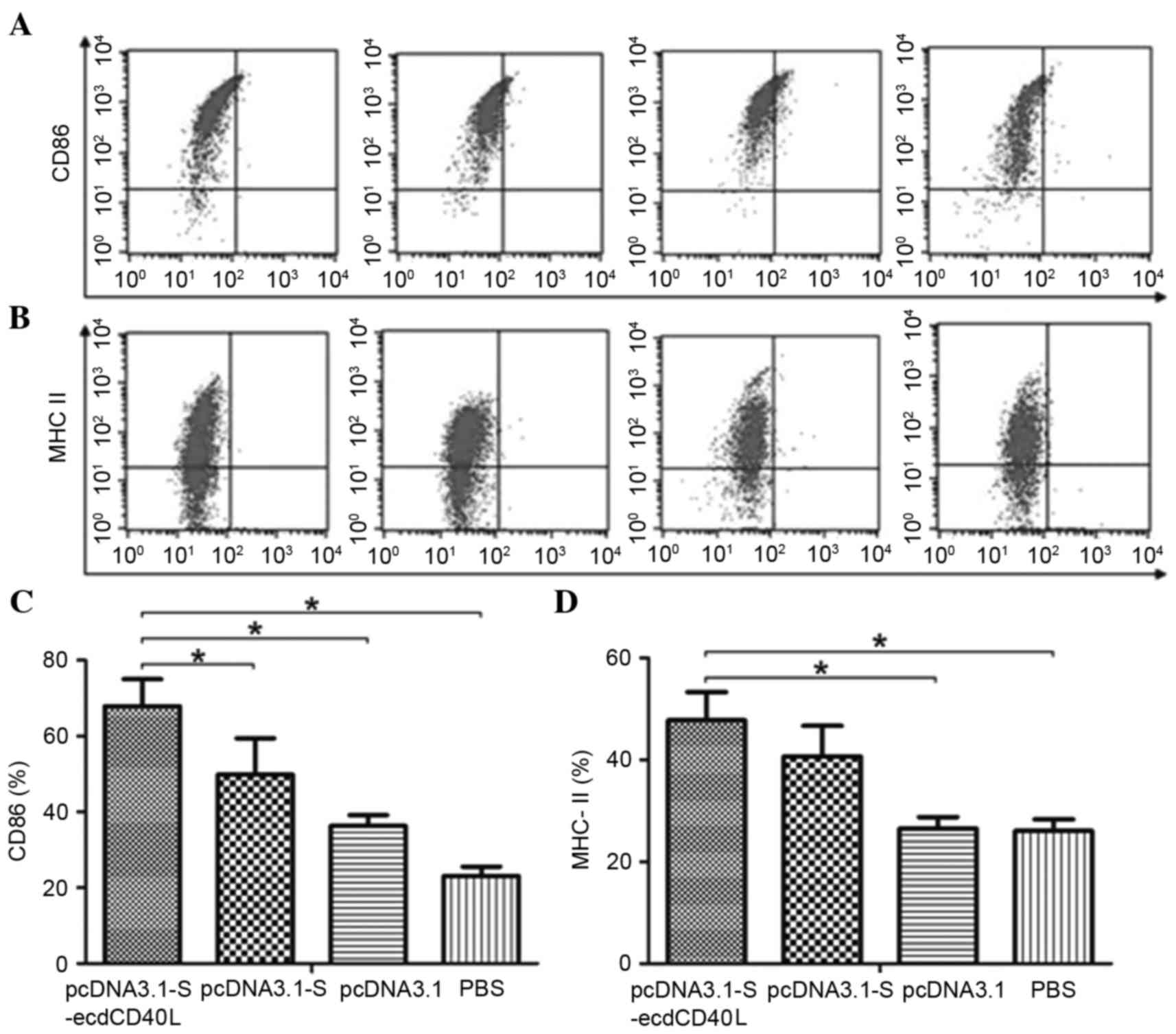
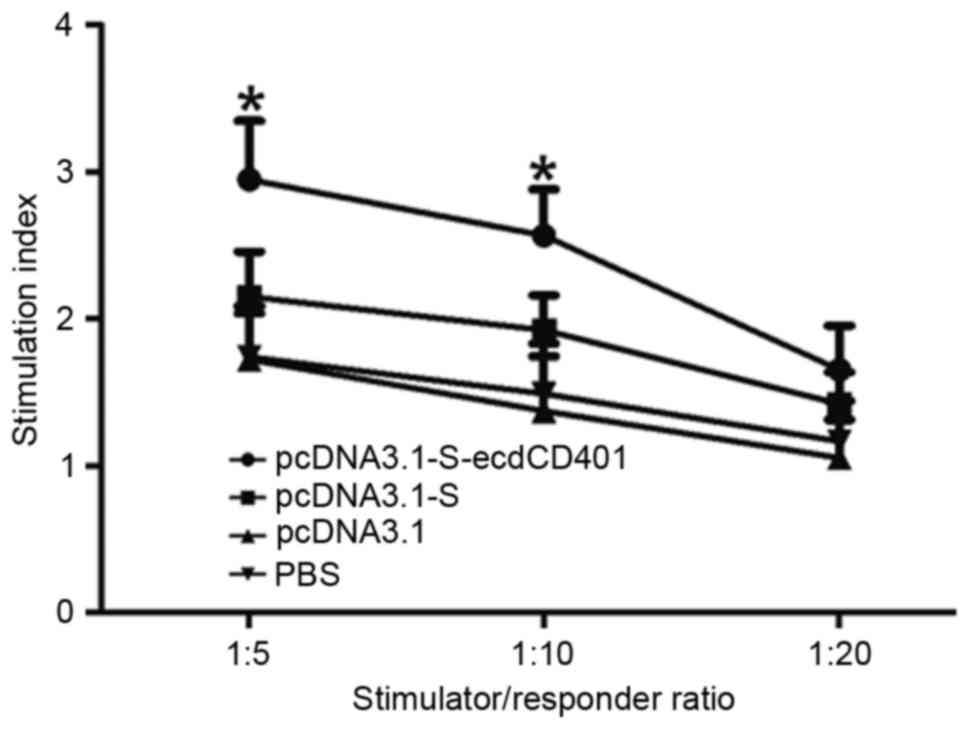
Construction of the HBV S-ecdCD40L fusion gene and effects of HBV
S-ecdCD40L modification on function of dendritic cells. J Viral
Hepat. 18:e461–e467. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu L, Woo J, Rao AS, Li Y, Watkins SC,
Qian S, Starzl TE, Demetris AJ and Thomson AW: Propagation of
dendritic cell progenitors from normal mouse liver using
granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and their
maturational development in the presence of type-1 collagen. J Exp
Med. 179:1823–1834. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao W, Sun Y, Chen S, Zhang J, Kang J,
Wang Y, Wang H, Xia G, Liu Q and Kang Y: Mushroom lectin enhanced
immunogenicity of HBV DNA vaccine in C57BL/6 and HBsAg-transgenic
mice. Vaccine. 31:2273–2280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lavanchy D: Hepatitis B virus
epidemiology, disease burden, treatment and current, and emerging
prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat. 11:97–107. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Geng S, Zhong Y, Wang S, Liu H, Zou Q, Xie
X, Li C, Yu Q, He Z and Wang B: Amiloride enhances antigen specific
CTL by faciliting HBV DNA vaccine entry into cells. PLoS One.
7:e330152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kosinska AD, Zhang E, Lu M and Roggendorf
M: Therapeutic vaccination in chronic hepatitis B: Preclinical
studies in the woodchuck. Hepat Res Treat.
2010:8175802010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roy MJ, Wu MS, Barr LJ, Fuller JT, Tussey
LG, Speller S, Culp J, Burkholder JK, Swain WF, Dixon RM, et al:
Induction of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells, T helper cells, and
protective levels of antibody in humans by particle-mediated
administration of a hepatitis B virus DNA vaccine. Vaccine.
19:764–778. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Su WJ, Wang J, Bai XF, Huang CX
and Lian JQ: A fusion DNA vaccine encoding middle version of HBV
envelope protein fused to interleukin-21 did not enhance
HBV-specific immune response in mice. Viral Immunol. 27:430–437.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoon SK, Seo YB, Im SJ, Bae SH, Song MJ,
You CR, Jang JW, Yang SH, Suh YS, Song JS, et al: Safety and
immunogenicity of therapeutic DNA vaccine with antiviral drug in
chronic HBV patients and its immunogenicity in mice. Liver Int.
35:805–815. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mishra S, Lavelle BJ, Desrosiers J, Ardito
MT, Terry F, Martin WD, De Groot AS and Gregory SH: Dendritic
cell-mediated, DNA-based vaccination against hepatitis C induces
the multi-epitope-specific response of humanized, HLA transgenic
mice. PLoS One. 9:e1046062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Burgdorf S, Kautz A, Böhnert V, Knolle PA
and Kurts C: Distinct pathways of antigen uptake and intracellular
routing in CD4 and CD8 T cell activation. Science. 316:612–616.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sato K and Fujita S: Dendritic cells:
Nature and classification. Allergol Int. 56:183–191. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Tang Y, Akbulut H, Zelterman D,
Linton PJ and Deisseroth AB: An adenoviral vector cancer vaccine
that delivers a tumor-associated antigen/CD40-ligand fusion protein
to dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:15101–15106. 2003;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Deisseroth A, Tang Y, Zhang L, Akbulut H
and Habib N: TAA/ecdCD40L adenoviral prime-protein boost vaccine
for cancer and infectious diseases. Cancer Gene Ther. 20:65–69.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pillarisetty VG, Shah AB, Miller G, Bleier
JI and DeMatteo RP: Liver dendritic cells are less immunogenic than
spleen dendritic cells because of differences in subtype
composition. J Immunol. 172:1009–1017. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|