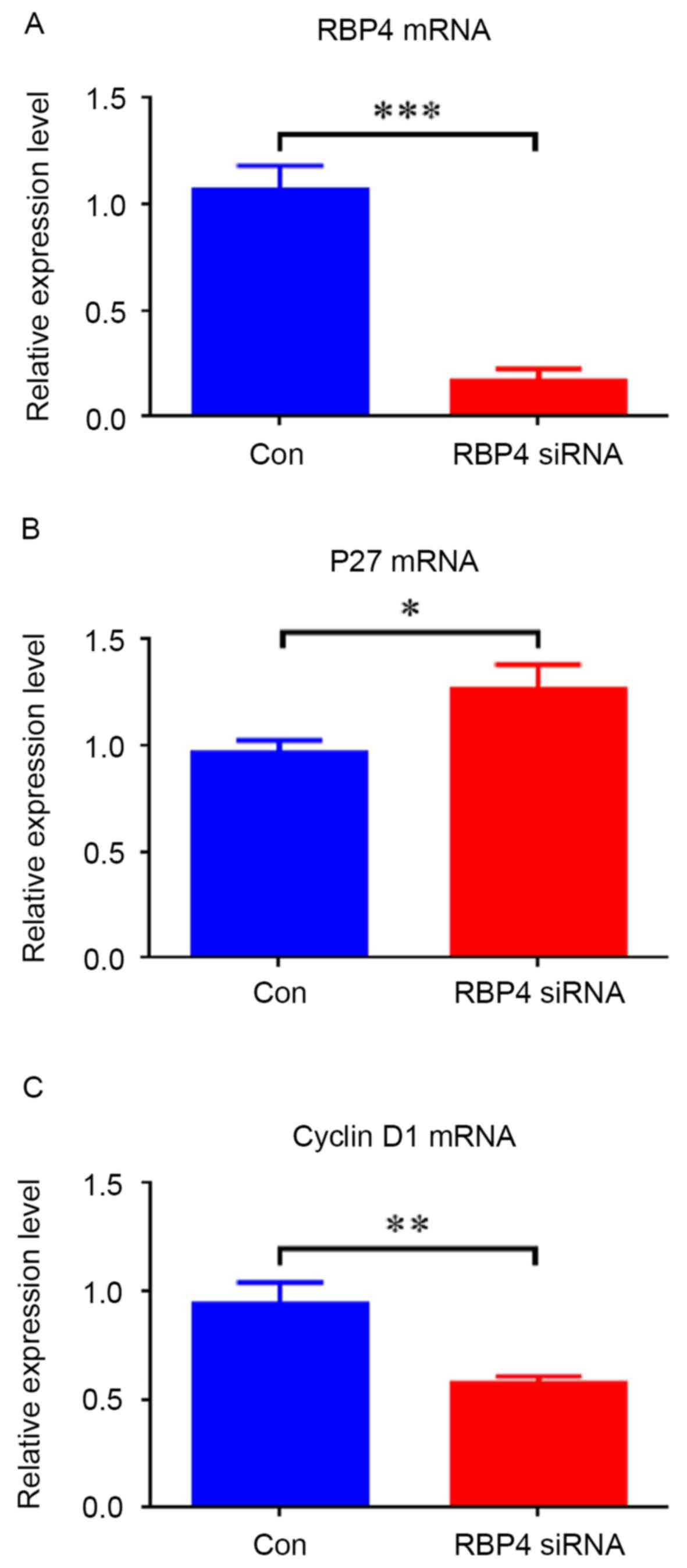
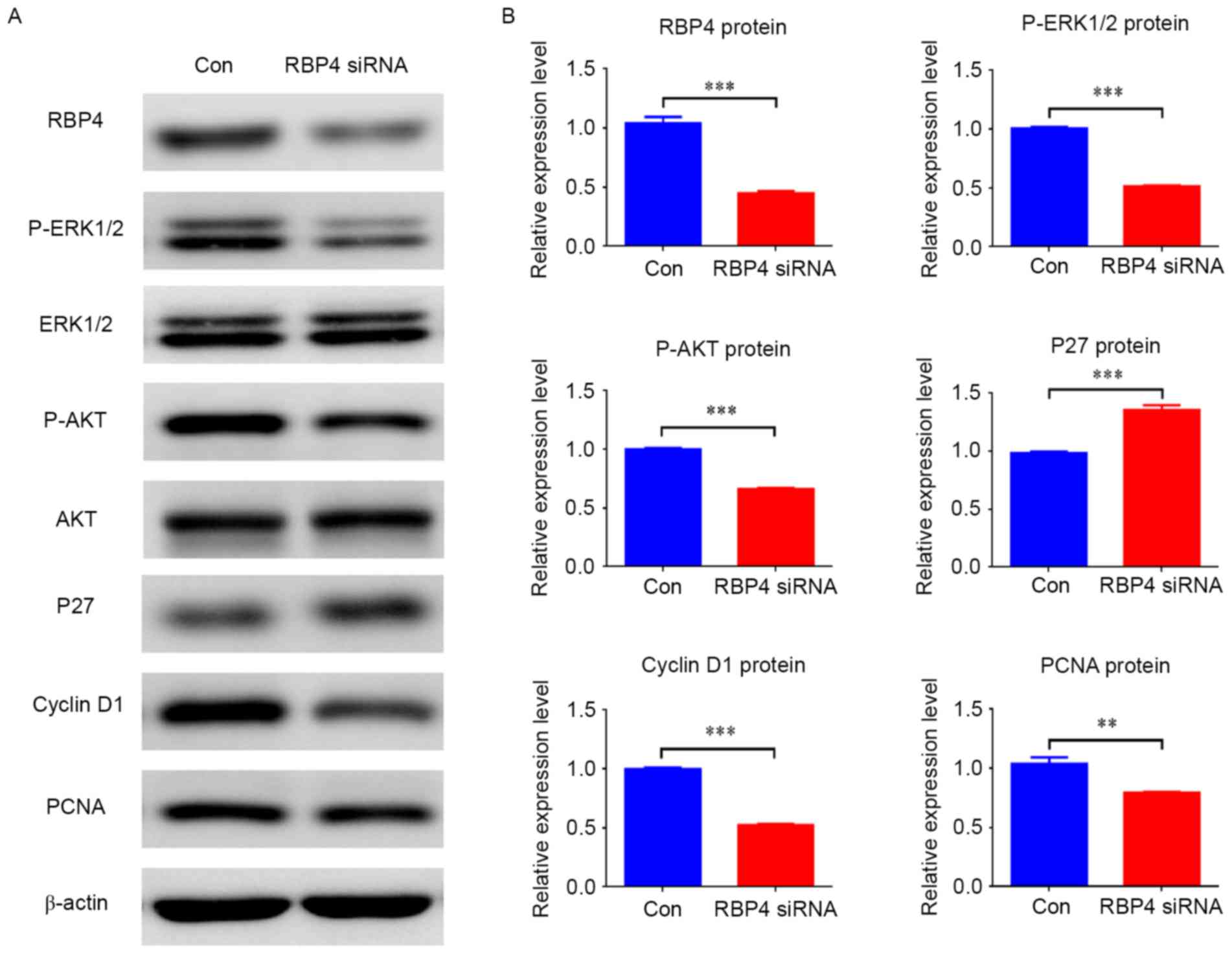
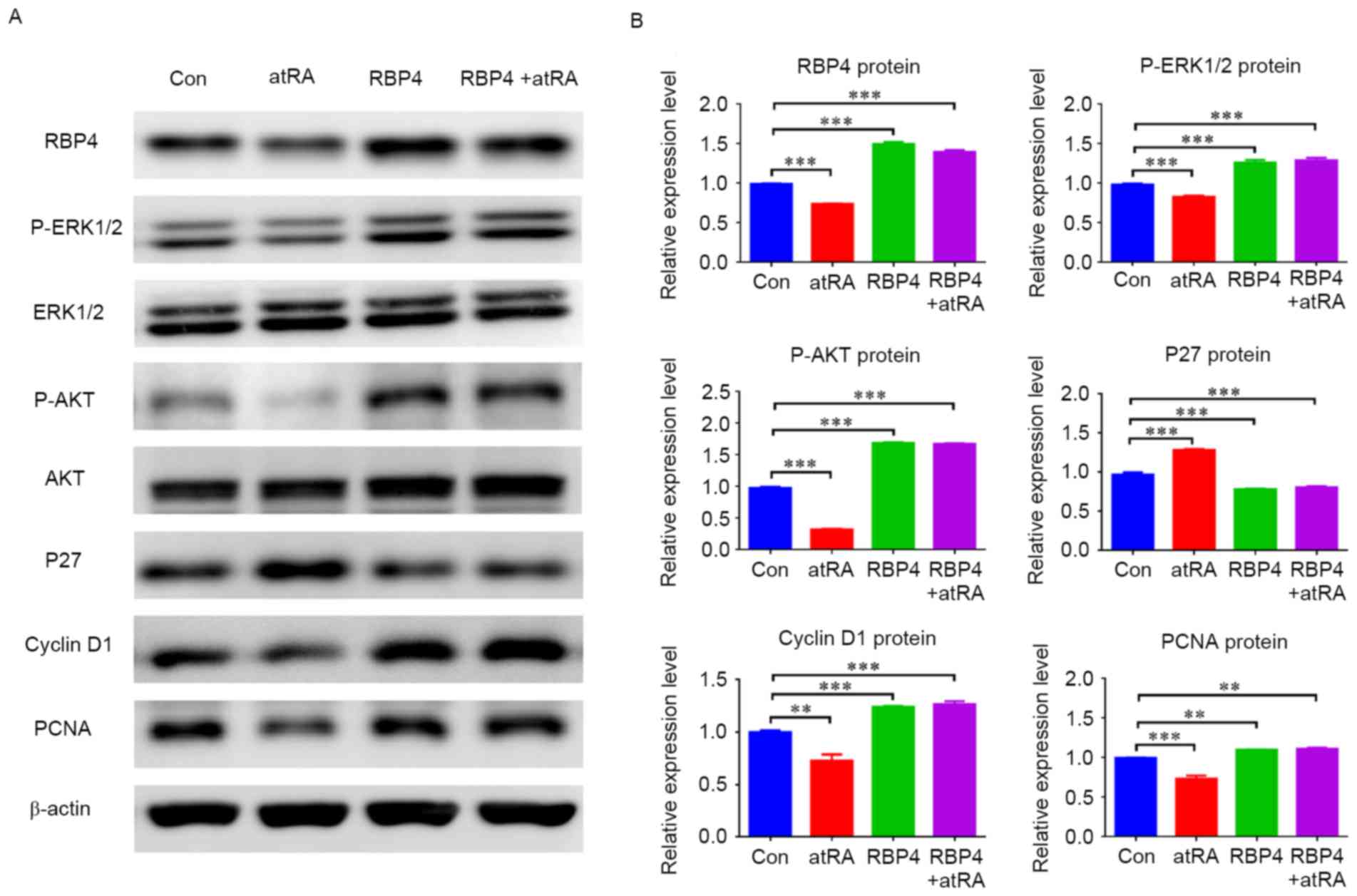
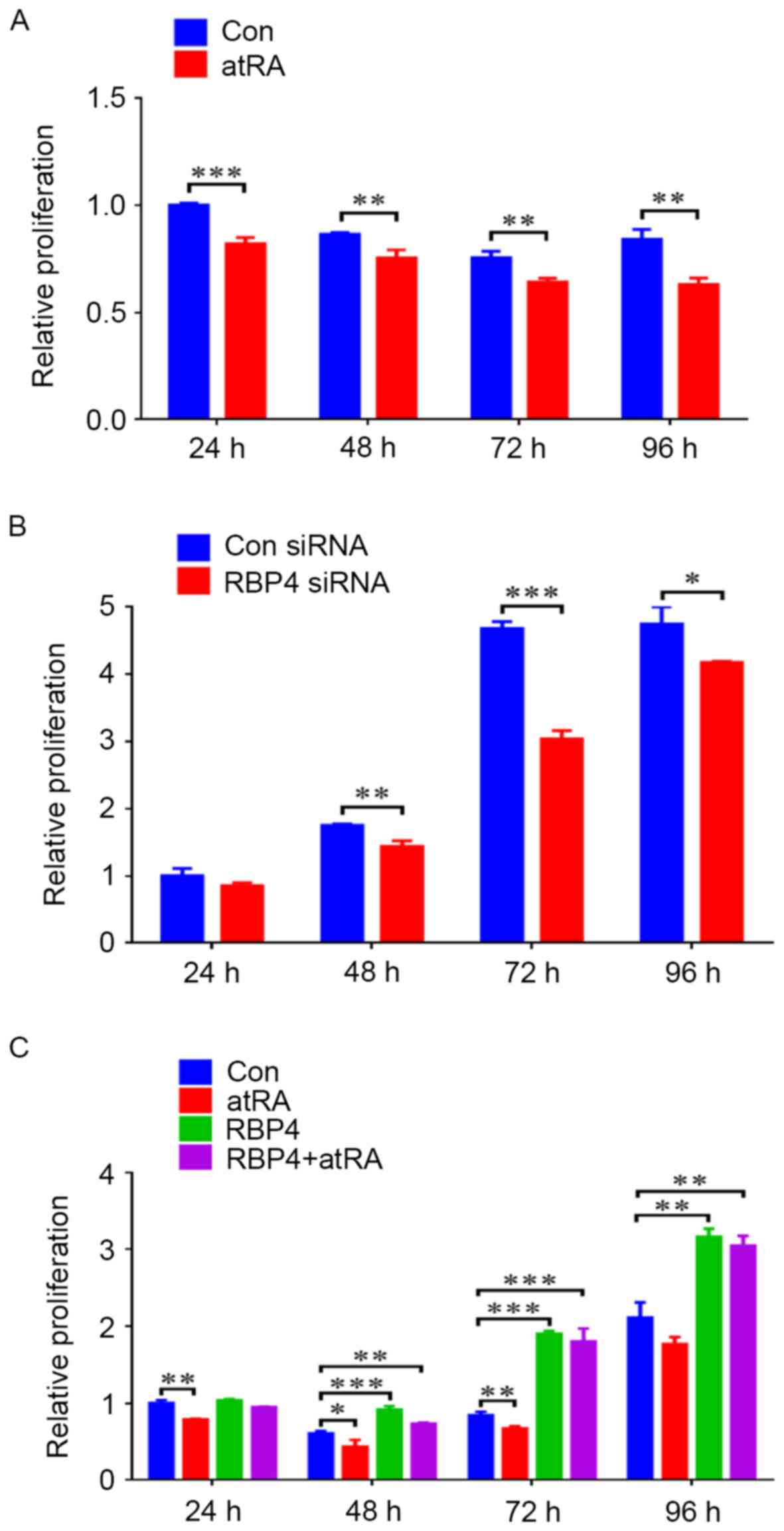
|
1
|
Noy N: Retinoid-binding proteins:
Mediators of retinoid action. Biochem J. 348:481–495. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F,
Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, Kotani K, Quadro L and Kahn BB: Serum
retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in
obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 436:356–362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Munkhtulga L, Nakayama K, Utsumi N,
Yanagisawa Y, Gotoh T, Omi T, Kumada M, Erdenebulgan B, Zolzaya K,
Lkhagvasuren T and Iwamoto S: Identification of a regulatory SNP in
the retinol binding protein 4 gene associated with type 2 diabetes
in Mongolia. Hum Genet. 120:879–888. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chan TF, Tsai YC, Wu CH, Lee CH, Wang SH
and Su JH: The positive correlation between cord serum
retinol-binding protein 4 concentrations and fetal growth. Gynecol
Obstet Invest. 72:98–1028. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hatfield JT, Anderson PJ and Powell BC:
Retinol-binding protein 4 is expressed in chondrocytes of
developing mouse long bones: Implications for a local role in
formation of the secondary ossification center. Histochem Cell
Biol. 139:727–734. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang J, Zhou S, Zhang Q, Feng S, Chen Y,
Zheng H, Wang X, Zhao W, Zhang T, Zhou Y, et al: Proteomic analysis
of RBP4/Vitamin A in children with cleft lip and/or palate. J Dent
Res. 93:547–552. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Quadro L, Hamberger L, Gottesman ME, Wang
F, Colantuoni V, Blaner WS and Mendelsohn CL: Pathways of vitamin A
delivery to the embryo: Insights from a new tunable model of
embryonic vitamin A deficiency. Endocrinology. 146:4479–4490. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marazita ML and Mooney MP: Current
concepts in the embryology and genetics of cleft lip and cleft
palate. Clin Plast Surg. 31:125–140. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wyszynski DF and Beaty TH: Phenotypic
discordance in a family with monozygotic twins and nonsyndromic
cleft lip and palate: Follow-up. Am J Med Genet. 110:182–183. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Murray JC and Schutte BC: Cleft palate:
Players, pathways, and pursuits. J Clin Invest. 113:1676–1678.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Clagett-Dame M and DeLuca HF: The role of
vitamin A in mammalian reproduction and embryonic development. Annu
Rev Nutr. 22:347–381. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Okano J, Suzuki S and Shiota K:
Involvement of apoptotic cell death and cell cycle perturbation in
retinoic acid-induced cleft palate in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
221:42–56. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu Z, Lin J, Xiao Y, Han J, Zhang X, Jia
H, Tang Y and Li Y: Induction of cell-cycle arrest by all-trans
retinoic acid in mouse embryonic palatal mesenchymal (MEPM) cells.
Toxicol Sci. 83:349–354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mercader J, Granados N, Bonet ML and Palou
A: All-trans retinoic acid decreases murine adipose retinol binding
protein 4 production. Cell Physiol Biochem. 22:363–372. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Dong S, Wang W, Wang J, Wang M,
Chen M, Hou J and Huang H: Activation of Notch1 inhibits medial
edge epithelium apoptosis in all-trans retinoic acid-induced cleft
palate in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 477:322–328. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ross SA, McCaffery PJ, Drager UC and De
Luca LM: Retinoids in embryonal development. Physiol Rev.
80:1021–1054. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang M, Huang H and Chen Y: Smad2/3 is
involved in growth inhibition of mouse embryonic palate mesenchymal
cells induced by all-trans retinoic acid. Birth Defects Res A Clin
Mol Teratol. 85:780–790. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abbott BD and Birnbaum LS: Retinoic
acid-induced alterations in the expression of growth factors in
embryonic mouse palatal shelves. Teratology. 42:597–610. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ferguson MW: Palate development.
Development. 103 Suppl:S41–S60. 1988.
|
|
20
|
Campbell JL Jr, Smith MA, Fisher JW and
Warren DA: Dose-response for retinoic acid-induced forelimb
malformations and cleft palate: A comparison of computerized image
analysis and visual inspection. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod
Toxicol. 71:289–295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rocchi M, Covone A, Romeo G, Faraonio R
and Colantuoni V: Regional mapping of RBP4 to 10q23-q24 and RBP1 to
3q21-q22 in man. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 15:185–190. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Blaner WS: Retinol-binding protein: The
serum transport protein for vitamin A. Endocr Rev. 10:308–316.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wolf G: Serum retinol-binding protein: A
link between obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Nutr
Rev. 65:251–256. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vaisbuch E, Romero R, Mazaki-Tovi S, Erez
O, Kim SK, Chaiworapongsa T, Gotsch F, Than NG, Dong Z, Pacora P,
et al: Retinol binding protein 4-a novel association with
early-onset preeclampsia. J Perinat Med. 38:129–139. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Singh AT, Evens AM, Anderson RJ, Beckstead
JA, Sankar N, Sassano A, Bhalla S, Yang S, Platanias LC, Forte TM,
et al: All trans retinoic acid nanodisks enhance retinoic acid
receptor mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in mantle cell
lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 150:158–169. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Radu M, Soprano DR and Soprano KJ: S10
phosphorylation of p27 mediates atRA induced growth arrest in
ovarian carcinoma cell lines. J Cell Physiol. 217:558–568. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang ML, Tao Y, Zhou WQ, Ma PC, Cao YP,
He CD, Wei J and Li LJ: All-trans retinoic acid induces cell-cycle
arrest in human cutaneous squamous carcinoma cells by inhibiting
the mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein 1 pathway.
Clin Exp Dermatol. 39:354–360. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wesley UV, Hatcher JF and Dempsey RJ:
Sphingomyelin synthase 1 regulates Neuro-2a cell proliferation and
cell cycle progression through modulation of p27 expression and Akt
signaling. Mol Neurobiol. 51:1530–1541. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fillies T, Woltering M, Brandt B, Van
Diest JP, Werkmeister R, Joos U and Buerger H: Cell cycle
regulating proteins p21 and p27 in prognosis of oral squamous cell
carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 17:355–359. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dubey RK, Fingerle J, Gillespie DG, Mi Z,
Rosselli M, Imthurn B and Jackson EK: Adenosine attenuates human
coronary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation by inhibiting
multiple signaling pathways that converge on Cyclin D.
Hypertension. 66:1207–1219. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han YH, Gao B, Huang JH, Wang Z, Guo Z,
Jie Q, Yang L and Luo ZJ: Expression of CD147, PCNA, VEGF, MMPs and
their clinical significance in the giant cell tumor of bones. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8446–8452. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen H, Zhou E, Wei X, Fu Z, Niu C, Li Y,
Pan B, Mathew AV, Wang X, Pennathur S, et al: High density
lipoprotein promotes proliferation of adipose-derived stem cells
via S1P1 receptor and Akt, ERK1/2 signal pathways. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 6:952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang XJ and Jia SS: Fisetin inhibits
laryngeal carcinoma through regulation of AKT/NF-κB/mTOR and ERK1/2
signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 83:1164–1174. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li F, Xia K, Sheikh SA, Cheng J, Li C and
Yang T: Involvement of RBP4 in hyperinsulinism-induced vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation. Endocrine. 48:472–482. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li F, Xia K, Sheikh MS, Cheng J, Li C and
Yang T: Retinol binding protein 4 promotes hyperinsulinism-induced
proliferation of rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Mol Med Rep.
9:1634–1640. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Takebayashi K, Sohma R, Aso Y and Inukai
T: Effects of retinol binding protein-4 on vascular endothelial
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 408:58–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|