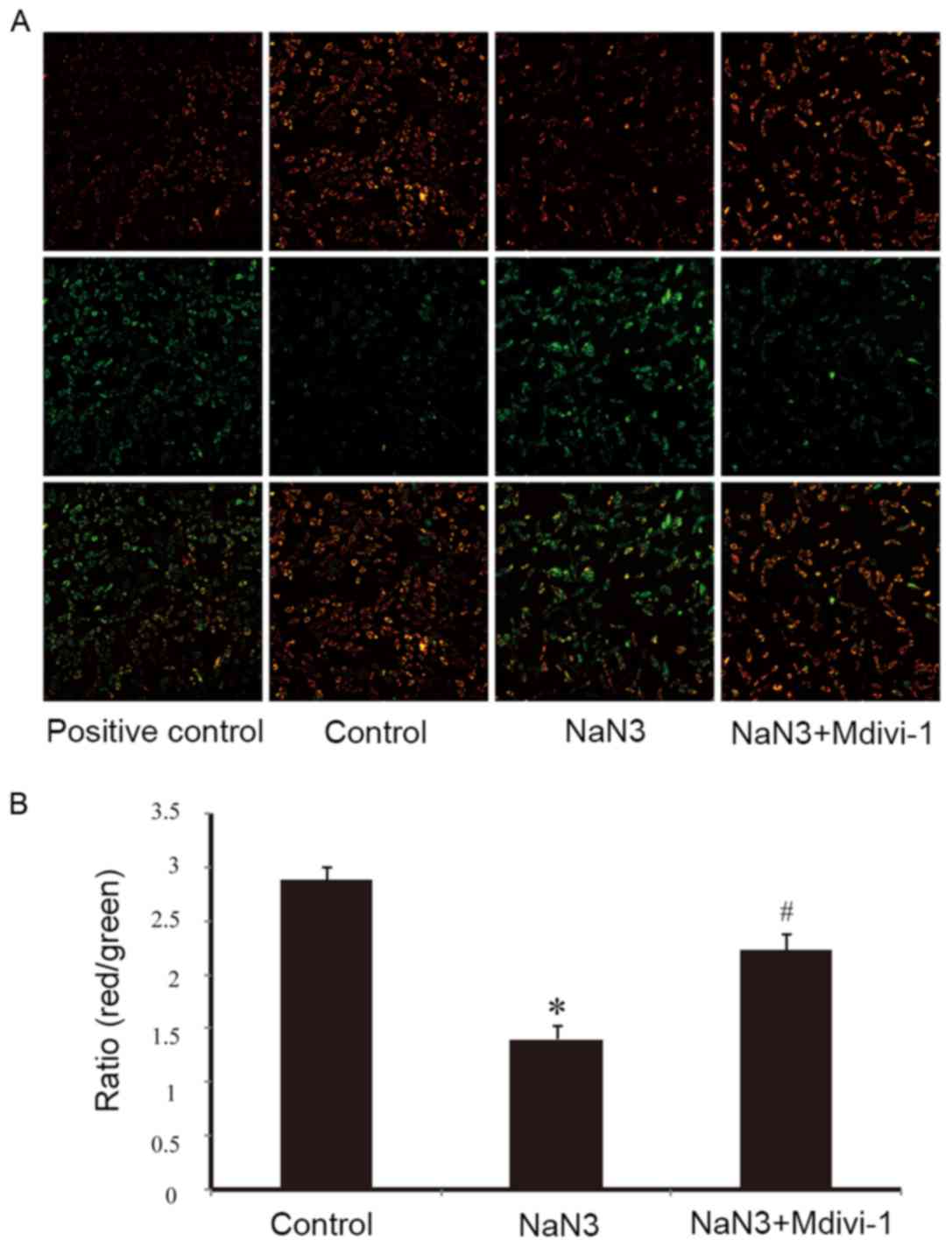
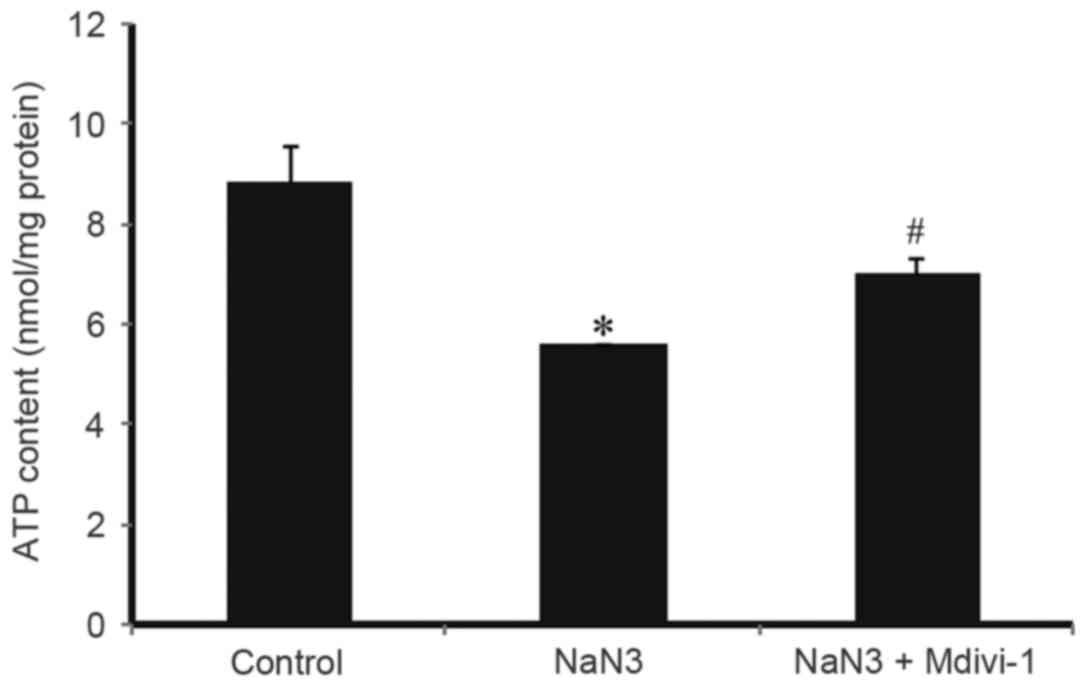
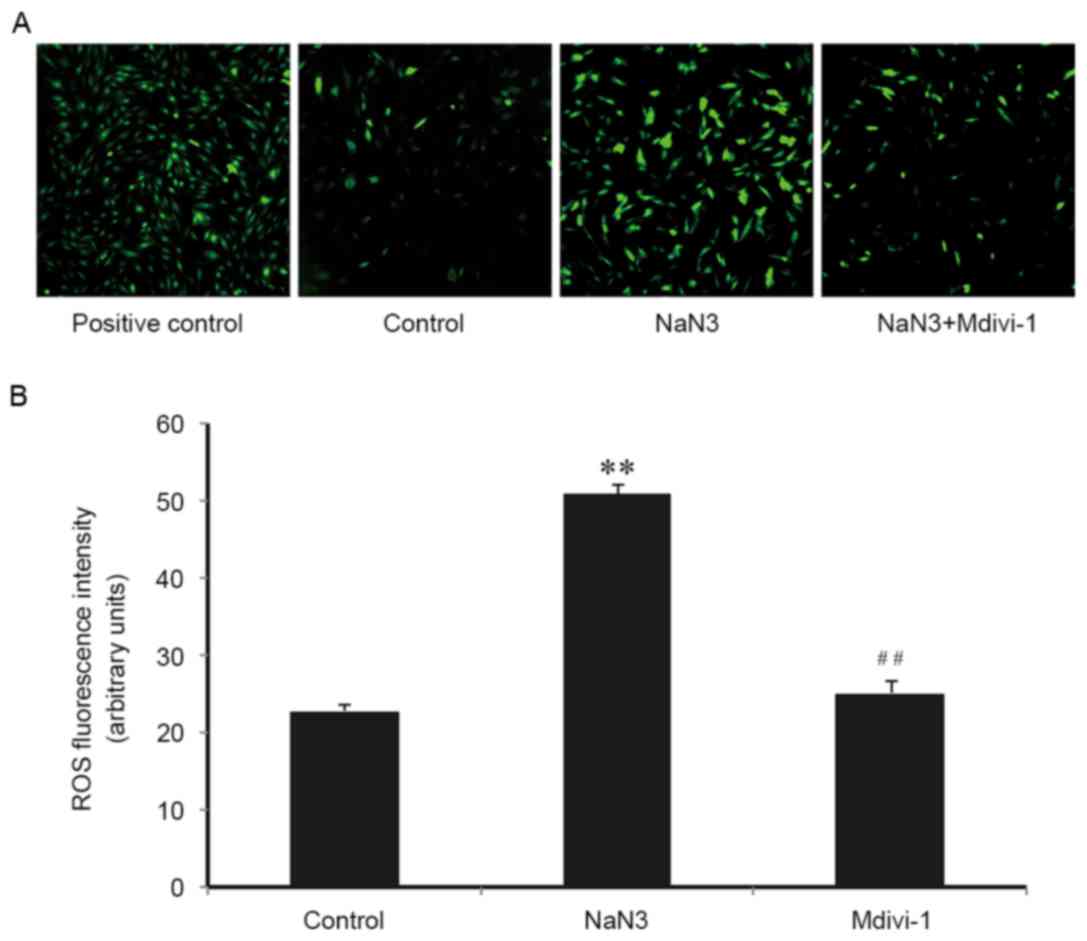
|
1
|
Chang S and Lamm SH: Human health effects
of sodium azide exposure: A literature review and analysis. Int J
Toxicol. 22:175–186. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qamirani E, Razavi HM, Wu X, Davis MJ, Kuo
L and Hein TW: Sodium azide dilates coronary arterioles via
activation of inward rectifier K+ channels and
Na+-K+-ATPase. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 290:H1617–1623. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Shenawy NS, Al-Harbi MS and Hamza RZ:
Effect of vitamin E and selenium separately and in combination on
biochemical, immunological and histological changes induced by
sodium azide in male mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 67:65–76. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Meatherall R and Oleschuk C: Suicidal
fatality from Azide ingestion. J Forensic Sci. 60:1666–1667. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wiergowski M, Galer-Tatarowicz K,
Krzyzanowski M, Jankowski Z and Sein AJ: Suicidal intoxication with
sodium azide-a case report. Przegl Lek. 69:568–571. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mutz S, Meatherall R and Palatnick W:
Fatal intentional sodium azide poisoning. Clin Tox. 47:7132009.
|
|
7
|
Meatherall R and Palatnick W: Convenient
headspace gas chromatographic determination of azide in blood and
plasma. J Anal Toxicol. 33:525–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kikuchi M, Sato M, Ito T and Honda M:
Application of a new analytical method using gas chromatography and
gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the azide ion to human
blood and urine samples of an actual case. J Chromatogr B Biomed
Sci Appl. 752:149–157. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Downes MA, Taliana KE, Muscat TM and Whyte
IM: Sodium azide ingestion and secondary contamination risk in
healthcare workers. Eur J Emerg Med. 23:68–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marino S, Marani L, Nazzaro C, Beani L and
Siniscalchi A: Mechanisms of sodium azide-induced changes in
intracellular calcium concentration in rat primary cortical
neurons. Neurotoxicology. 28:622–629. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen SJ, Bradley ME and Lee TC: Chemical
hypoxia triggers apoptosis of cultured neonatal rat cardiac
myocytes: Modulation by calcium-regulated proteases and protein
kinases. Mol Cell Biochem. 178:141–149. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Szabados T, Dul C, Majtényi K, Hargitai J,
Pénzes Z and Urbanics R: A chronic alzheimer's model evoked by
mitochondrial poison sodium azide for pharmacological
investigations. Behav Brain Res. 154:31–40. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hessel MH, Michielsen EC, Atsma DE,
Schalij MJ, Van Der Valk EJ, Bax WH, Hermens WT, van Dieijen-Visser
MP and van der Laarse A: Release kinetics of intact and degraded
troponin I and T after irreversible cell damage. Exp Mol Pathol.
85:90–95. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Swafford AJ Jr, Bratz IN, Knudson JD,
Rogers PA, Timmerman JM, Tune JD and Dick GM: C-reactive protein
does not relax vascular smooth muscle: Effects mediated by sodium
azide in commercially available preparations. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 288:H1786–H1795. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brooks C, Wei Q, Cho SG and Dong Z:
Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics in acute kidney injury in cell
culture and rodent models. J Clin Invest. 119:1275–1285. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Inomata K and Tanaka H: Protective effect
of benidipine against sodium azide-induced cell death in cultured
neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. J Pharmacol Sci. 93:163–170. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cassidy-Stone A, Chipuk JE, Ingerman E,
Song C, Yoo C, Kuwana T, Kurth MJ, Shaw JT, Hinshaw JE, Green DR
and Nunnari J: Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division
dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak dependent mitochondrial outer
membrane permeabilization. Dev Cell. 14:193–204. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sharp WW, Fang YH, Han M, Zhang HJ, Hong
Z, Banathy A, Morrow E, Ryan JJ and Archer SL: Dynamin-related
protein1 (Drp1)-mediated diastolic dysfunction in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: Therapeutic benefits of Drp1
inhibition to reduce mitochondrial fission. FASEB J. 28:316–326.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang N, Wang S, Li Y, Che L and Zhao Q: A
selective inhibitor of Drp1, Mdivi-1, acts against cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury via an anti-apoptotic pathway in rats.
Neurosci Lett. 535:104–109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu Q, Xia SX, Li QQ, Gao Y, Shen X, Ma L,
Zhang MY, Wang T, Li YS, Wang ZF, et al: Mitochondrial division
inhibitor 1 (Mdivi-1) offers neuroprotection through diminishing
cell death and improving functional outcome in a mouse model of
traatic brain injury. Brain Res. 1630:134–143. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Labrousse AM, Zappaterra MD, Rube DA and
van der Bliek AM: C. Elegans dynamin-related protein DRP-1 controls
severing of the mitochondrial outer membrane. Mol Cell. 4:815–826.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chan DC: Mitochondria: Dynamic organelles
in disease, aging, and development. Cell. 125:1241–1252. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Smirnova E, Griparic L, Shurland DL and
Van der Bliek AM: Dynamin-related protein drp1 is required for
mitochondrial division in mammalian cells. Mol Biol Cell.
12:2245–2256. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boland K, Flanagan L and Prehn JH:
Paracrine control of tissue regeneration and cell proliferation by
caspase-3. Cell Death Dis. 4:e7252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ong SB, Subrayan S, Lim SY, Yellon DM,
Davidson SM and Hausenloy DJ: Inhibiting mitochondrial fission
protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Circulation. 121:2012–2022. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Givvimani S, Munjal C, Tyagi N, Sen U,
Metreveli N and Tyagi SC: Mitochondrial division/mitophagy
inhibitor (Mdivi) ameliorates pressure overload induced heart
failure. PLoS One. 7:e323882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cipolat S, de Brito O Martins, Dal Zilio B
and Scorrano L: OPA1 requires mitofusin 1 to promote mitochondrial
fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:15927–15932. 2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Claycomb WC, Lanson NA Jr, Stallworth BS,
Egeland DB, Delcarpio JB, Bahinski A and Izzo NJ Jr: HL-1 cells: A
cardiac muscle cell line that contracts and retains phenotypic
characteristics of the adult cardiomyocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:2979–2984. 1998; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hom J and Sheu SS: Morphological dynamics
of mitochondria - A special emphasis on cardiac muscle cells. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 46:811–820. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ong SB and Hausenloy DJ: Mitochondrial
morphology and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res. 88:16–29.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ong SB, Hall AR and Hausenloy DJ:
Mitochondrial dynamics in cardiovascular health and disease.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 19:400–414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Wang P, Wei J, Fan R, Zuo Y, Shi M,
Wu H, Zhou M, Lin J, Wu M, et al: Inhibition of DRP1 by Mdivi-1
attenuates cerebral ischemic injury via inhibition
ofthemitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway after cardiac arrest.
Neuroscience. 311:67–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Crompton M: The mitochondrial permeability
transition pore and its role in cell death. Biochem J. 341:233–249.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Di Lisa F and Bernardi P: Mitochondrial
function as a determinant of recovery or death in cell response to
injury. Mol Cell Biochem. 184:379–391. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang ZW, Xu XC, Liu T and Yuan S:
Mitochondrion-permeable antioxidants to treat ROS-burst-mediated
acute diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:68595232016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Giordano FJ: Oxygen, oxidative stress,
hypoxia, and heart failure. J Clin Invest. 115:500–508. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Z, Cheng XR, Juan-Juan HU, Lan S and Du
GH: Neuroprotective effects of hyperoside on sodium azide-induced
apoptosis in pc12 cells. Chin J Nat Med. 9:450–455. 2011.
|
|
39
|
Wang J, Wei Q, Wang CY, Hill WD, Hess DC
and Dong Z: Minocycline up-regulates bcl-2 and protects against
cell death in mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 279:19948–19949. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chao DT and Korsmeyer SJ: BCL-2 family:
Regulators of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:395–419. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schulze K, Dorner A and Schultheiß HP:
Mitochondrial function in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 4:229–244.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Moorjani N, Catarino P, Trabzuni D, Saleh
S, Moorji A, Dzimiri N, Al-Mohanna F, Westaby S and Ahmad M:
Upregulation of bcl-2 proteins during the transition to pressure
overload-induced heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 116:27–33. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|