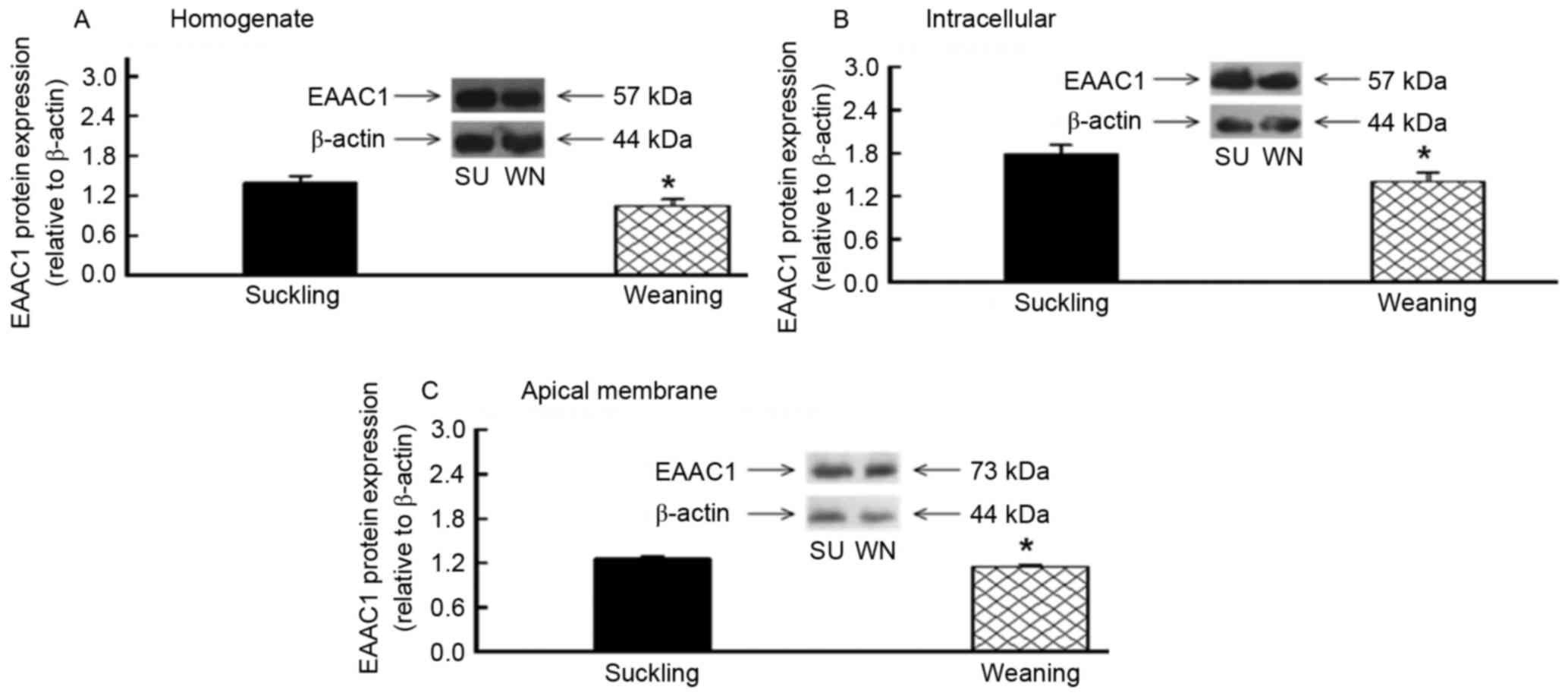
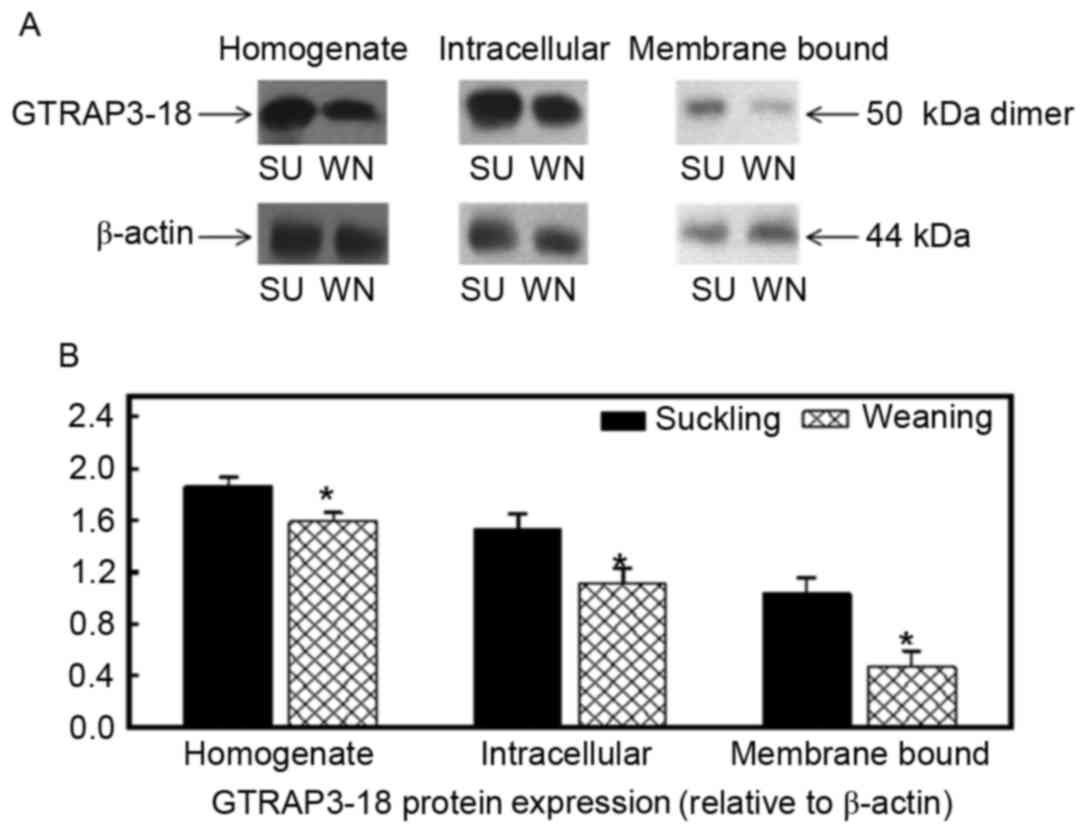
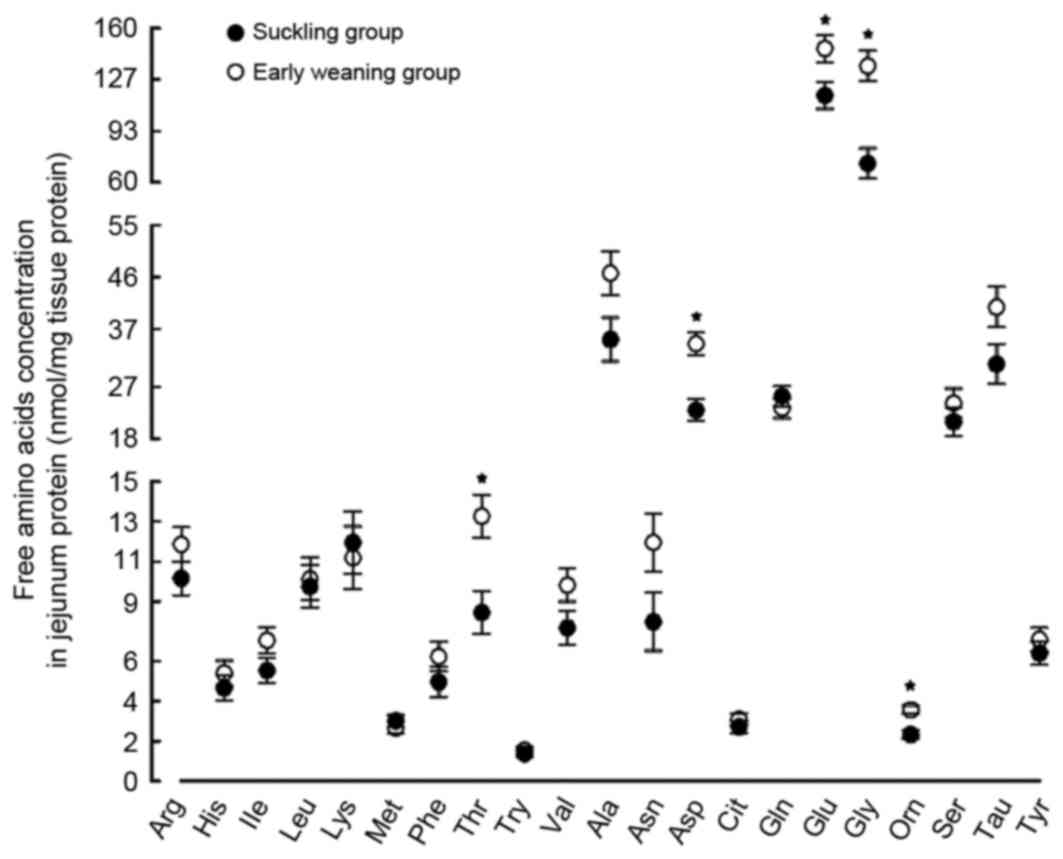
|
1
|
Ruth MR and Field CJ: The immune modifying
effects of amino acids on gut-associated lymphoid tissue. J Anim
Sci Biotechnol. 4:272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bianchi MG, Bardelli D, Chiu M and
Bussolati O: Changes in the expression of the glutamate transporter
EAAT3/EAAC1 in health and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:2001–2015.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aoyama K and Nakaki T: Neuroprotective
properties of the excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1). Amino
Acids. 45:133–142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Butchbach ME, Lai L and Lin CL: Molecular
cloning, gene structure, expression profile and functional
characterization of the mouse glutamate transporter (EAAT3)
interacting protein GTRAP3-18. Gene. 292:81–90. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aoyama K and Nakaki T: Inhibition of
GTRAP3-18 may increase neuroprotective glutathione (GSH) synthesis.
Int J Mol Sci. 13:12017–12035. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jang BG, Won SJ, Kim JH, Choi BY, Lee MW,
Sohn M, Song HK and Suh SW: EAAC1 gene deletion alters zinc
homeostasis and enhances cortical neuronal injury after transient
cerebral ischemia in mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 26:85–88. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aoyama K, Watabe M and Nakaki T:
Modulation of neuronal glutathione synthesis by EAAC1 and its
interacting protein GTRAP3-18. Amino Acids. 42:163–169. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Berman AE, Chan WY, Brennan AM, Reyes RC,
Adler BL, Suh SW, Kauppinen TM, Edling Y and Swanson RA:
N-acetylcysteine prevents loss of dopaminergic neurons in the
EAAC1-/-mouse. Ann Neurol. 69:509–520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Duerson K, Woltjer RL, Mookherjee P,
Leverenz JB, Montine TJ, Bird TD, Pow DV, Rauen T and Cook DG:
Detergent-insoluble EAAC1/EAAT3 aberrantly accumulates in
hippocampal neurons of Alzheimer's disease patients. Brain Pathol.
19:267–278. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fu D, Yang H, Kong X, Blachier F, Wang W
and Yin Y: Molecular cloning and expression profiling of excitatory
amino acid carrier 1 in suckling Huanjiang mini-piglets with large
or small body weight at birth. Mol Biol Rep. 40:3341–3350. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bregendahl K, Yang X, Liu L, Yen JT,
Rideout TC, Shen Y, Werchola G and Fan MZ: Fractional 485 protein
synthesis rates are similar when measured by intraperitoneal or
intravenous flooding 486 doses of L-[ring-2H5]phenylalanine in
combination with a rapid regimen of sampling in piglets. J Nutr.
138:1976–1981. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thiele B, Stein N, Oldiges M and Hofmann
D: Direct analysis of underivatized amino acids in plant extracts
by LC-MS-MS. Methods Mol Biol. 828:317–328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takita M and Kikusui T: Early weaning
influences short-term synaptic plasticity in the medial
prefrontal-anterior basolateral amygdala pathway. Neurosci Res.
103:48–53. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xiong X, Yang H, Tan B, Yang C, Wu M, Liu
G, Kim SW, Li T, Li L, Wang J, et al: Differential expression of
proteins involved in energy production along the crypt-villus axis
in early-weaning pig small intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 309:G229–G237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Candeias EM, Sebastião IC, Cardoso SM,
Correia SC, Carvalho CI, Plácido AI, Santos MS, Oliveira CR,
Moreira PI and Duarte AI: Gut-brain connection: The neuroprotective
effects of the anti-diabetic drug liraglutide. World J Diabetes.
6:807–827. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gu X, Li D and She R: Effect of weaning on
small intestinal structure and function in the piglet. Arch
Tierernahr. 56:275–286. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Watabe M, Aoyama K and Nakaki T: A
dominant role of GTRAP3-18 in neuronal glutathione synthesis. J
Neurosci. 28:9404–9413. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin CI, Orlov I, Ruggiero AM, Dykes-Hoberg
M, Lee A, Jackson M and Rothstein JD: Modulation of the neuronal
glutamate transporter EAAC1 by the interacting protein GTRAP3-18.
Nature. 410:84–88. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Burrin DG and Stoll B: Metabolic fate and
function of dietary glutamate in the gut. Am J Clin Nutr.
90:850S–856S. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fan MZ, Matthews JC, Etienne NM, Stoll B,
Lackeyram D and Burrin DG: Expression of apical membrane
L-glutamate transporters in neonatal porcine epithelial cells along
the small intestinal crypt-villus axis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 287:G385–G398. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|