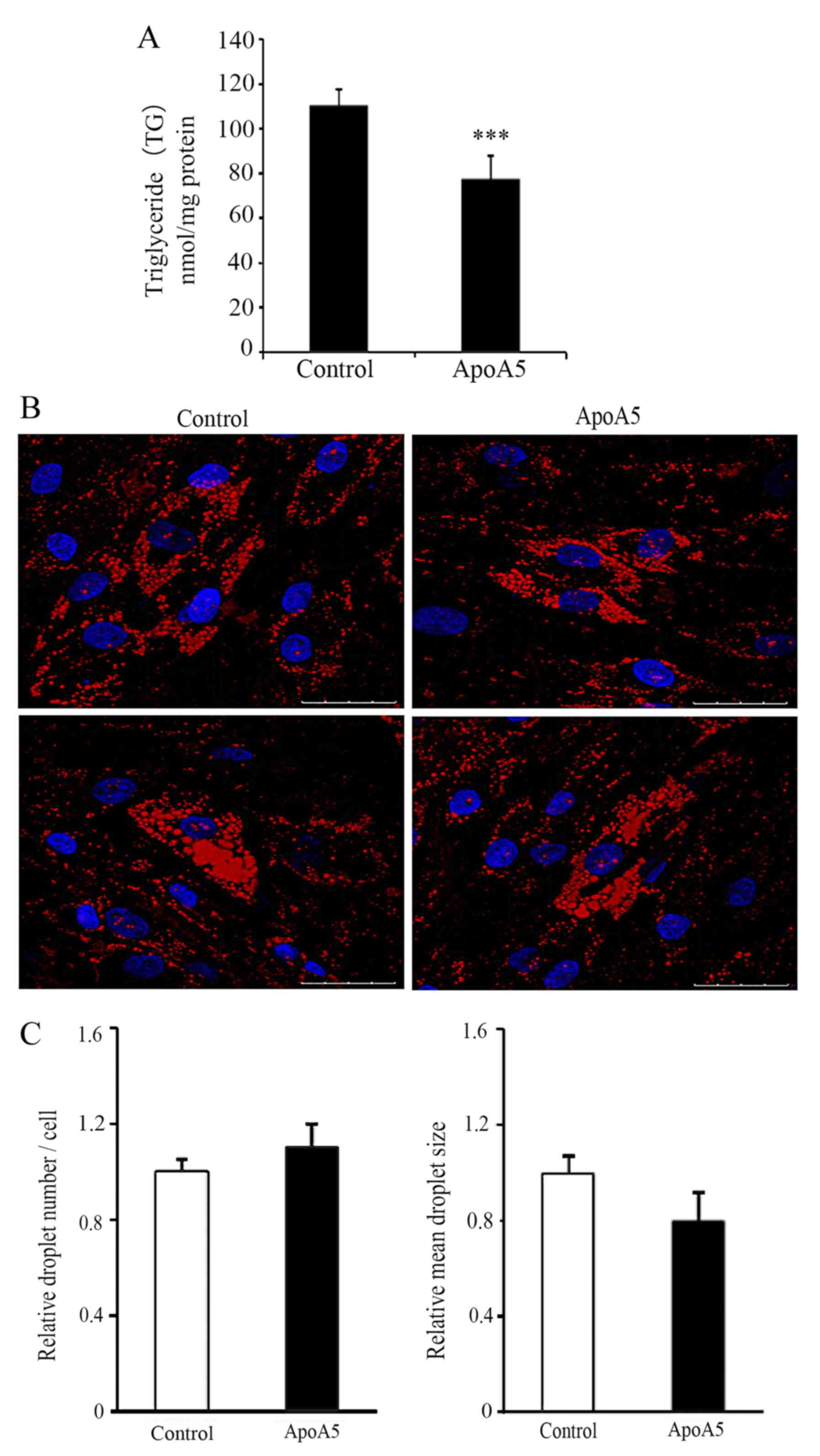
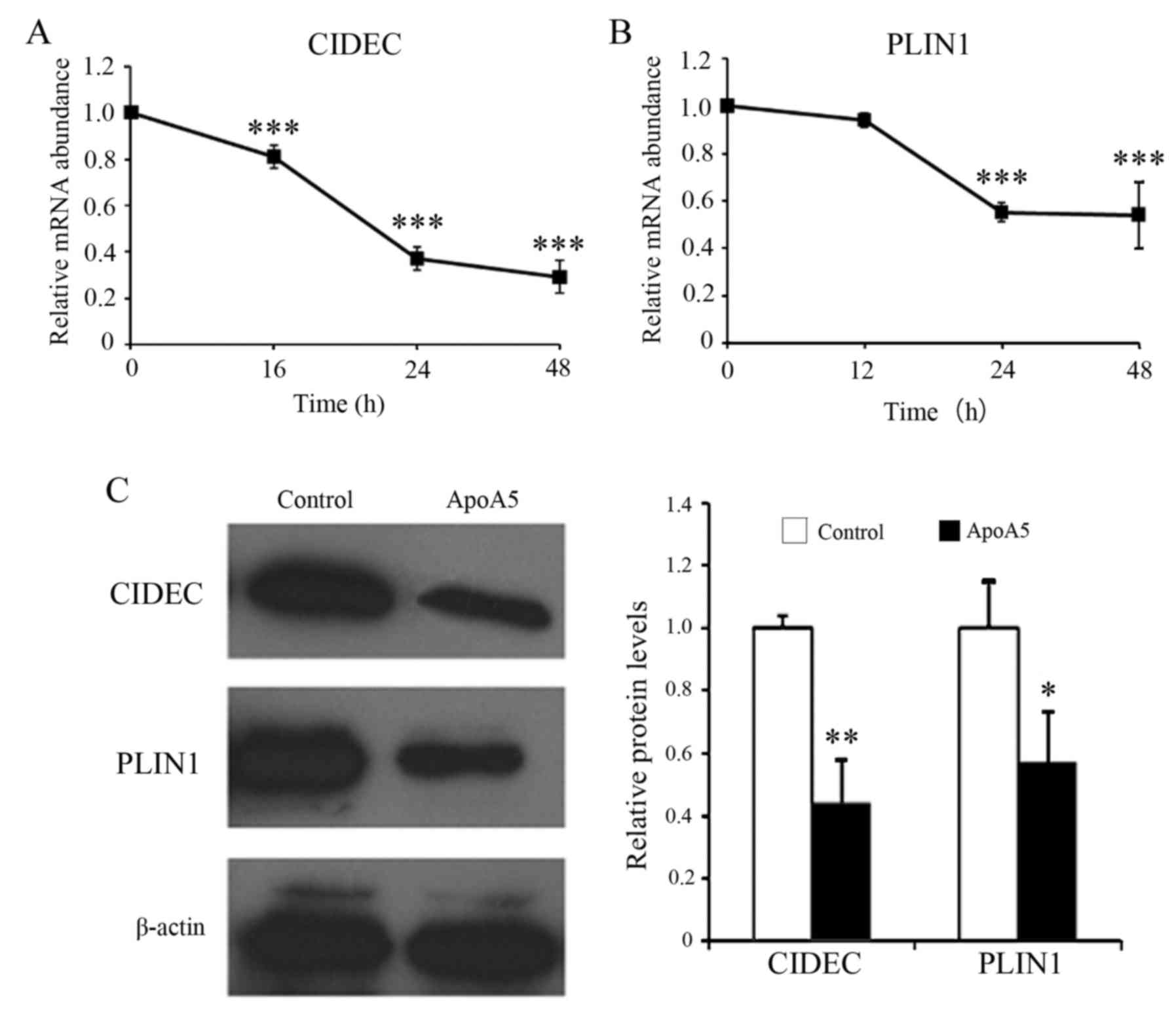
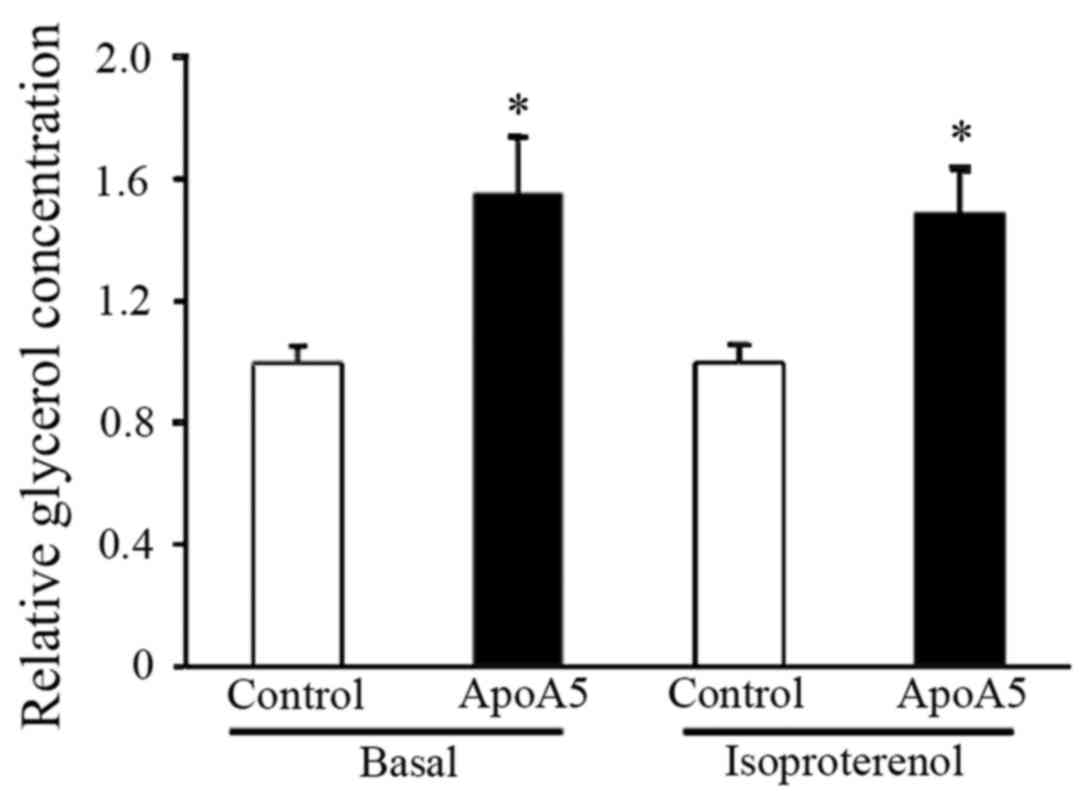
|
1
|
Wong K and Ryan RO: Characterization of
apolipoprotein A-V structure and mode of plasma triacylglycerol
regulation. Curr Opin Lipidol. 18:319–324. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Horvatovich K, Bokor S, Baráth A, Maász A,
Kisfali P, Járomi L, Polgár N, Tóth D, Répásy J, Endreffy E, et al:
Haplotype analysis of the apolipoprotein A5 gene in obese pediatric
patients. Int J Pediatr Obes. 6:e318–e325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Niculescu LS, Fruchart-Najib J, Fruchart
JC and Sima A: Apolipoprotein A-V gene polymorphisms in subjects
with metabolic syndrome. Clin Chem Lab Med. 45:1133–1139. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zheng XY, Zhao SP and Yan H: The role of
apolipoprotein A5 in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Biol Rev
Camb Philos Soc. 88:490–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang XS, Zhao SP, Hu M, Bai L, Zhang Q
and Zhao W: Decreased apolipoprotein A5 is implicated in insulin
resistance-related hypertriglyceridemia in obesity.
Atherosclerosis. 210:563–568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao SP, Hu S, Li J, Hu M, Liu Q, Wu LJ
and Zhang T: Association of human serum apolipoprotein A5 with
lipid profiles affected by gender. Clin Chim Acta. 376:68–71. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Corella D, Lai CQ, Demissie S, Cupples LA,
Manning AK, Tucker KL and Ordovas JM: APOA5 gene variation
modulates the effects of dietary fat intake on body mass index and
obesity risk in the Framingham Heart Study. J Mol Med (Berl).
85:119–128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Martin S, Nicaud V, Humphries SE and
Talmud PJ; EARS group, : Contribution of APOA5 gene variants to
plasma triglyceride determination and to the response to both fat
and glucose tolerance challenges. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1637:217–225. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shu X, Chan J, Ryan RO and Forte TM:
Apolipoprotein A-V association with intracellular lipid droplets. J
Lipid Res. 48:1445–1450. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shu X, Nelbach L, Ryan RO and Forte TM:
Apolipoprotein A-V associates with intrahepatic lipid droplets and
influences triglyceride accumulation. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1801:605–608. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ress C, Moschen AR, Sausgruber N, Tschoner
A, Graziadei I, Weiss H, Schgoer W, Ebenbichler CF, Konrad RJ,
Patsch JR, et al: The role of apolipoprotein A5 in non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Gut. 60:985–991. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng XY, Zhao SP, Yu BL, Wu CL and Liu L:
Apolipoprotein A5 internalized by human adipocytes modulates
cellular triglyceride content. Biol Chem. 393:161–167. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nilsson SK, Christensen S, Raarup MK, Ryan
RO, Nielsen MS and Olivecrona G: Endocytosis of apolipoprotein A-V
by members of the low density lipoprotein receptor and the VPS10p
domain receptor families. J Biol Chem. 283:25920–25927. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Farese RV Jr and Walther TC: Lipid
droplets finally get a little R-E-S-P-E-C-T. Cell. 139:855–860.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wolins NE, Brasaemle DL and Bickel PE: A
proposed model of fat packaging by exchangeable lipid droplet
proteins. FEBS Lett. 580:5484–5491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brasaemle DL: Thematic review series:
Adipocyte biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet
proteins: Stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis.
J Lipid Res. 48:2547–2559. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Souza SC, Muliro KV, Liscum L, Lien P,
Yamamoto MT, Schaffer JE, Dallal GE, Wang X, Kraemer FB, Obin M and
Greenberg AS: Modulation of hormone-sensitive lipase and protein
kinase A-mediated lipolysis by perilipin A in an adenoviral
reconstituted system. J Biol Chem. 277:8267–8272. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tansey JT, Sztalryd C, Gruia-Gray J, Roush
DL, Zee JV, Gavrilova O, Reitman ML, Deng CX, Li C, Kimmel AR and
Londos C: Perilipin ablation results in a lean mouse with aberrant
adipocyte lipolysis, enhanced leptin production, and resistance to
diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:6494–6499. 2001;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Martinez-Botas J, Anderson JB, Tessier D,
Lapillonne A, Chang BH, Quast MJ, Gorenstein D, Chen KH and Chan L:
Absence of perilipin results in leanness and reverses obesity in
Lepr(db/db) mice. Nat Genet. 26:474–479. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Keller P, Petrie JT, De Rose P, Gerin I,
Wright WS, Chiang SH, Nielsen AR, Fischer CP, Pedersen BK and
MacDougald OA: Fat-specific protein 27 regulates storage of
triacylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 283:14355–14365. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Puri V, Konda S, Ranjit S, Aouadi M,
Chawla A, Chouinard M, Chakladar A and Czech MP: Fat-specific
protein 27, a novel lipid droplet protein that enhances
triglyceride storage. J Biol Chem. 282:34213–34218. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nishino N, Tamori Y, Tateya S, Kawaguchi
T, Shibakusa T, Mizunoya W, Inoue K, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S,
Matsuki Y, et al: FSP27 contributes to efficient energy storage in
murine white adipocytes by promoting the formation of unilocular
lipid droplets. J Clin Invest. 118:2808–2821. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Toh SY, Gong J, Du G, Li JZ, Yang S, Ye J,
Yao H, Zhang Y, Xue B, Li Q, et al: Up-regulation of mitochondrial
activity and acquirement of brown adipose tissue-like property in
the white adipose tissue of fsp27 deficient mice. PLoS One.
3:e28902008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsusue K: A physiological role for fat
specific protein 27/cell death-inducing DFF45-like effector C in
adipose and liver. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:346–350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Inohara N, Koseki T, Chen S, Wu X and
Núñez G: CIDE, a novel family of cell death activators with
homology to the 45 kDa subunit of the DNA fragmentation factor.
EMBO J. 17:2526–2533. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Magnusson B, Gummesson A, Glad CA,
Goedecke JH, Jernås M, Lystig TC, Carlsson B, Fagerberg B, Carlsson
LM and Svensson PA: Cell death-inducing DFF45-like effector C is
reduced by caloric restriction and regulates adipocyte lipid
metabolism. Metabolism. 57:1307–1313. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Beckstead JA, Oda MN, Martin DD, Forte TM,
Bielicki JK, Berger T, Luty R, Kay CM and Ryan RO:
Structure-function studies of human apolipoprotein A-V: A regulator
of plasma lipid homeostasis. Biochemistry. 42:9416–9423. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gauthier B, Robb M and McPherson R:
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein gene expression during
differentiation of human preadipocytes to adipocytes in primary
culture. Atherosclerosis. 142:301–307. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Prawitt J, Niemeier A, Kassem M, Beisiegel
U and Heeren J: Characterization of lipid metabolism in
insulin-sensitive adipocytes differentiated from immortalized human
mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 314:814–824. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suganami T, Nishida J and Ogawa Y: A
paracrine loop between adipocytes and macrophages aggravates
inflammatory changes: Role of free fatty acids and tumor necrosis
factor alpha. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:2062–2068. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suganami T, Tanimoto-Koyama K, Nishida J,
Itoh M, Yuan X, Mizuarai S, Kotani H, Yamaoka S, Miyake K, Aoe S,
et al: Role of the Toll-like receptor 4/NF-kappaB pathway in
saturated fatty acid-induced inflammatory changes in the
interaction between adipocytes and macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 27:84–91. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Samad F, Pandey M, Bell PA and Loskutoff
DJ: Insulin continues to induce plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
gene expression in insulin-resistant mice and adipocytes. Mol Med.
6:680–692. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rousset S, Alves-Guerra MC, Mozo J, Miroux
B, Cassard-Doulcier AM, Bouillaud F and Ricquier D: The biology of
mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Diabetes. 53 Suppl 1:S130–S135.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cederberg A, Grønning LM, Ahrén B, Taskén
K, Carlsson P and Enerbäck S: FOXC2 is a winged helix gene that
counteracts obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, and diet-induced insulin
resistance. Cell. 106:563–573. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Masson O, Chavey C, Dray C, Meulle A,
Daviaud D, Quilliot D, Muller C, Valet P and Liaudet-Coopman E:
LRP1 receptor controls adipogenesis and is up-regulated in human
and mouse obese adipose tissue. PLoS One. 4:e74222009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
de Ferranti S and Mozaffarian D: The
perfect storm: Obesity, adipocyte dysfunction, and metabolic
consequences. Clin Chem. 54:945–955. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ko KW, Avramoglu RK, McLeod RS, Vukmirica
J and Yao Z: The insulin-stimulated cell surface presentation of
low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in 3T3-L1
adipocytes is sensitive to phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase
inhibition. Biochemistry. 40:752–759. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Corvera S, Graver DF and Smith RM: Insulin
increases the cell surface concentration of alpha 2-macroglobulin
receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Altered transit of the receptor
among intracellular endocytic compartments. J Biol Chem.
264:10133–10138. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sawada T, Miyoshi H, Shimada K, Suzuki A,
Okamatsu-Ogura Y, Perfield JW II, Kondo T, Nagai S, Shimizu C,
Yoshioka N, et al: Perilipin overexpression in white adipose tissue
induces a brown fat-like phenotype. PLoS One. 5:e140062010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Busiello RA, Savarese S and Lombardi A:
Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins and energy metabolism. Front
Physiol. 6:362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nicholls DG and Locke RM: Thermogenic
mechanisms in brown fat. Physiol Rev. 64:1–64. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kopecky J, Clarke G, Enerbäck S,
Spiegelman B and Kozak LP: Expression of the mitochondrial
uncoupling protein gene from the aP2 gene promoter prevents genetic
obesity. J Clin Invest. 96:2914–2923. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tiraby C, Tavernier G, Lefort C, Larrouy
D, Bouillaud F, Ricquier D and Langin D: Acquirement of brown fat
cell features by human white adipocytes. J Biol Chem.
278:33370–33376. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Si Y, Palani S, Jayaraman A and Lee K:
Effects of forced uncoupling protein 1 expression in 3T3-L1 cells
on mitochondrial function and lipid metabolism. J Lipid Res.
48:826–836. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Oberkofler H, Dallinger G, Liu YM, Hell E,
Krempler F and Patsch W: Uncoupling protein gene: Quantification of
expression levels in adipose tissues of obese and non-obese humans.
J Lipid Res. 38:2125–2133. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang X, Enerbäck S and Smith U: Reduced
expression of FOXC2 and brown adipogenic genes in human subjects
with insulin resistance. Obes Res. 11:1182–1191. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|