|
1
|
Garkavtsev I, Kazarov A, Gudkov A and
Riabowol K: Suppression of the novel growth inhibitor p33ING1
promotes neoplastic transformation. Nat Genet. 14:415–420. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shimada Y, Saito A, Suzuki M, Takahashi E
and Horie M: Cloning of a novel gene (ING1L) homologous to ING1, a
candidate tumor suppressor. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 83:232–235. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nagashima M, Shiseki M, Miura K, Hagiwara
K, Linke SP, Pedeux R, Wang XW, Yokota J, Riabowol K and Harris CC:
DNA damage-inducible gene p33ING2 negatively regulates cell
proliferation through acetylation of p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:9671–9676. 2001; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nagashima M, Shiseki M, Pedeux RM, Okamura
S, Kitahama-Shiseki M, Miura K, Yokota J and Harris CC: A novel
PHD-finger motif protein, p47ING3, modulates p53-mediated
transcription, cell cycle control, and apoptosis. Oncogene.
22:343–350. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shiseki M, Nagashima M, Pedeux RM,
Kitahama-Shiseki M, Miura K, Okamura S, Onogi H, Higashimoto Y,
Appella E, Yokota J and Harris CC: p29ING4 and p28ING5 bind to p53
and p300, and enhance p53 activity. Cancer Res. 63:2373–2378.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He GH, Helbing CC, Wagner MJ, Sensen CW
and Riabowol K: Phylogenetic analysis of the ING family of PHD
finger proteins. Mol Biol Evol. 22:104–116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Unoki M, Shen JC, Zheng ZM and Harris CC:
Novel splice variants of ING4 and their possible roles in the
regulation of cell growth and motility. J Biol Chem.
281:34677–34686. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Scott M, Bonnefin P, Vieyra D, Boisvert
FM, Young D, Bazett-Jones DP and Riabowol K: UV-induced binding of
ING1 to PCNA regulates the induction of apoptosis. J Cell Sci.
114:3455–3462. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Skowyra D, Zeremski M, Neznanov N, Li M,
Choi Y, Uesugi M, Hauser CA, Gu W, Gudkov AV and Qin J:
Differential association of products of alternative transcripts of
the candidate tumor suppressor ING1 with the mSin3/HDAC1
transcriptional corepressor complex. J Biol Chem. 276:8734–8739.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kuzmichev A, Zhang Y, Erdjument-Bromage H,
Tempst P and Reinberg D: Role of the Sin3-histone deacetylase
complex in growth regulation by the candidate tumor suppressor
p33(ING1). Mol Cell Biol. 22:835–848. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feng X, Hara Y and Riabowol K: Different
HATS of the ING1 gene family. Trends Cell Biol. 12:532–538. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Doyon Y, Cayrou C, Ullah M, Landry AJ,
Côté V, Selleck W, Lane WS, Tan S, Yang XJ and Côté J: ING tumor
suppressor proteins are critical regulators of chromatin
acetylation required for genome expression and perpetuation. Mol
Cell. 21:51–64. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
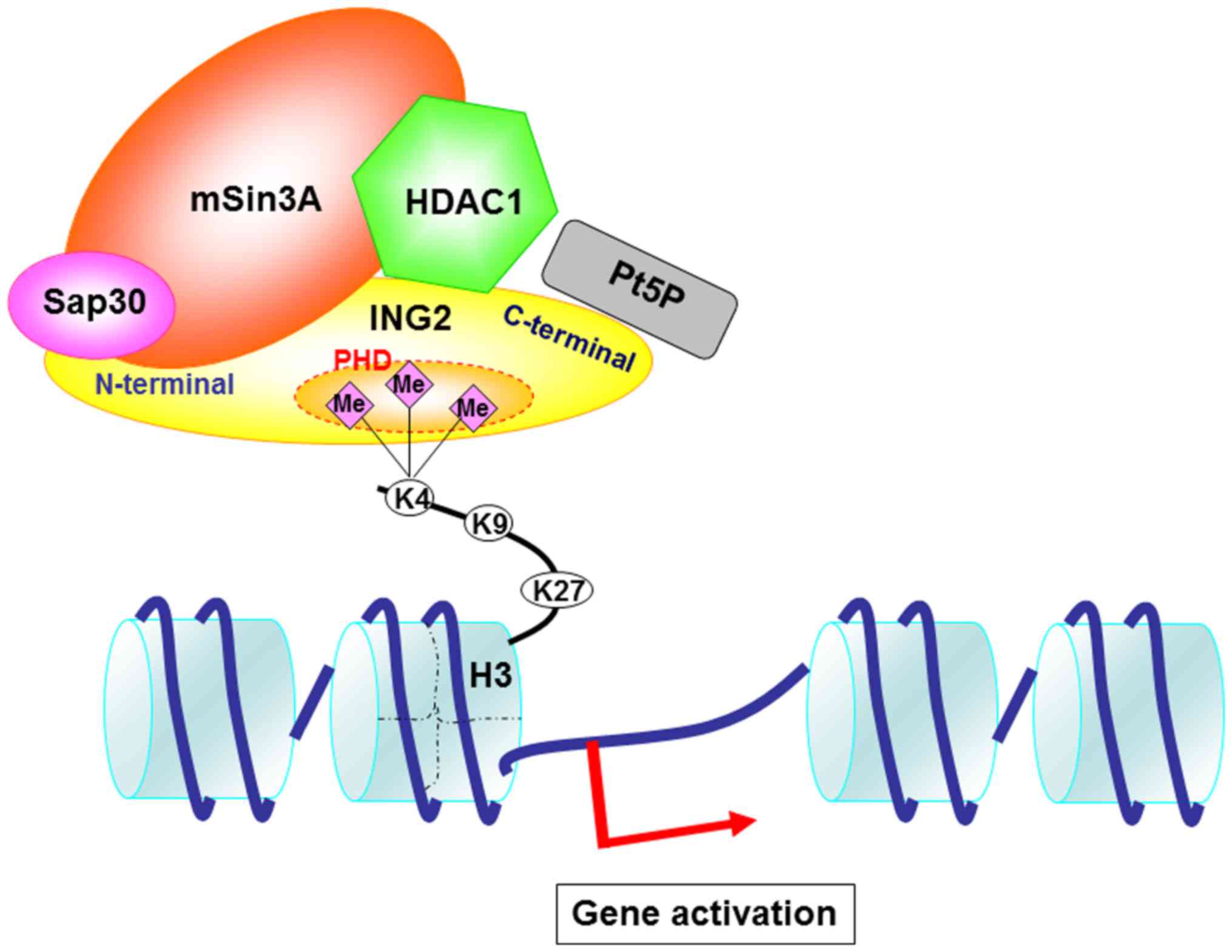
Peña PV, Davrazou F, Shi X, Walter KL,
Verkhusha VV, Gozani O, Zhao R and Kutateladze TG: Molecular
mechanism of histone H3K4me3 recognition by plant homeodomain of
ING2. Nature. 442:100–103. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi X, Hong T, Walter KL, Ewalt M,
Michishita E, Hung T, Carney D, Peña P, Lan F, Kaadige MR, et al:
ING2 PHD domain links histone H3 lysine 4 methylation to active
gene repression. Nature. 442:96–99. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Santos-Rosa H, Schneider R, Bannister AJ,
Sherriff J, Bernstein BE, Emre NC, Schreiber SL, Mellor J and
Kouzarides T: Active genes are tri-methylated at K4 of histone H3.
Nature. 419:407–411. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bernstein BE, Kamal M, Lindblad-Toh K,
Bekiranov S, Bailey DK, Huebert DJ, McMahon S, Karlsson EK,
Kulbokas EJ III, Gingeras TR, et al: Genomic maps and comparative
analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell.
120:169–181. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Berger SL: The complex language of
chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 447:407–412.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kumamoto K, Fujita K, Kurotani R, Saito M,
Unoki M, Hagiwara N, Shiga H, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, Okamura S, et
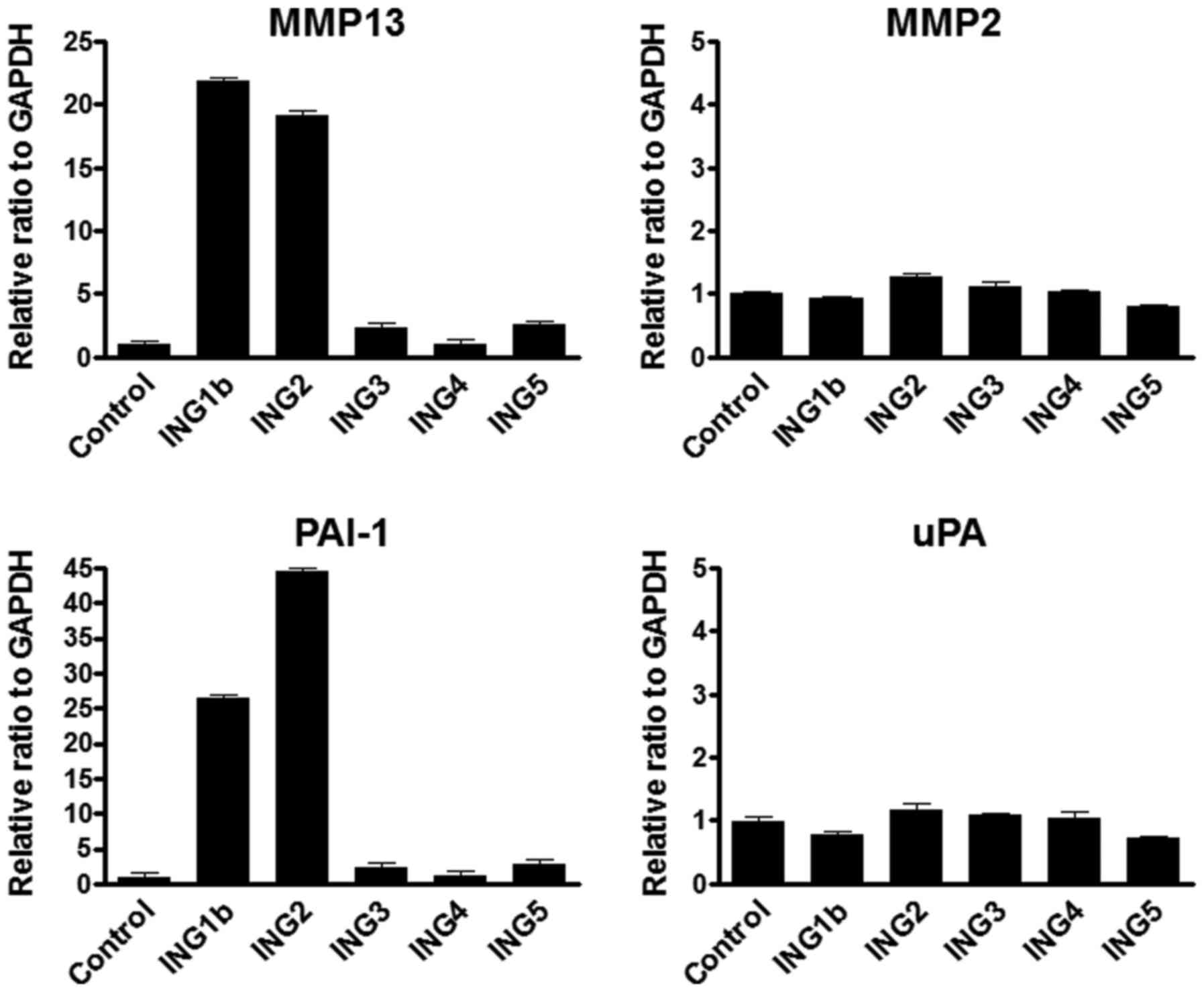
al: ING2 is upregulated in colon cancer and increases invasion by
enhanced MMP13 expression. Int J Cancer. 125:1306–1315. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gozani O, Karuman P, Jones DR, Ivanov D,
Cha J, Lugovskoy AA, Baird CL, Zhu H, Field SJ, Lessnick SL, et al:
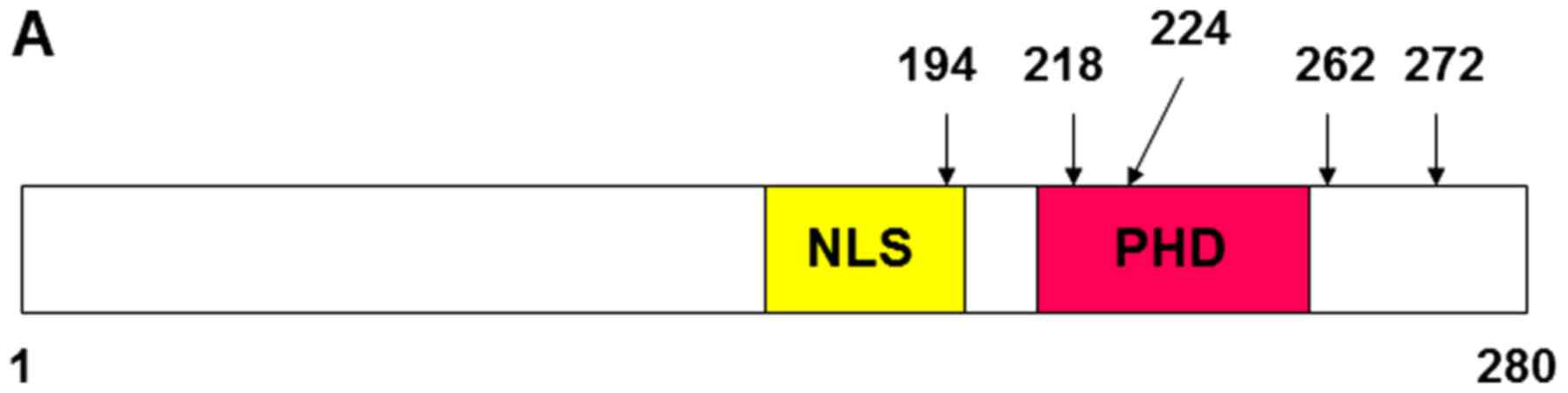
The PHD finger of the chromatin-associated protein ING2 functions
as a nuclear phosphoinositide receptor. Cell. 114:99–111. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Clarke JH, Letcher AJ, D'santos CS,
Halstead JR, Irvine RF and Divecha N: Inositol lipids are regulated
during cell cycle progression in the nuclei of murine
erythroleukaemia cells. Biochem J. 357:905–910. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roberts HF, Clarke JH, Letcher AJ, Irvine
RF and Hinchliffe KA: Effects of lipid kinase expression and
cellular stimuli on phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate levels in
mammalian cell lines. FEBS Lett. 579:2868–2872. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bunce MW, Gonzales ML and Anderson RA:
Stress-ING out: Phosphoinositides mediate the cellular stress
response. Sci STKE. 2006:pe462006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jones DR, Bultsma Y, Keune WJ, Halstead
JR, Elouarrat D, Mohammed S, Heck AJ, D'Santos CS and Divecha N:
Nuclear PtdIns5P as a transducer of stress signaling: An in vivo
role for PIP4Kbeta. Mol Cell. 23:685–695. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang W, Zhang H, Davrazou F, Kutateladze
TG, Shi X, Gozani O and Prestwich GD: Stabilized
phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate analogues as ligands for the
nuclear protein ING2: Chemistry, biology, and molecular modeling. J
Am Chem Soc. 129:6498–6506. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Unoki M, Kumamoto K and Harris CC: ING
proteins as potential anticancer drug targets. Curr Drug Targets.
10:442–454. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhong J, Yang L, Liu N, Zheng J and Lin
CY: Knockdown of inhibitor of growth protein 2 inhibits cell
invasion and enhances chemosensitivity to 5-FU in human gastric
cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci. 58:3189–3197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Staib F, Robles AI, Varticovski L, Wang
XW, Zeeberg BR, Sirotin M, Zhurkin VB, Hofseth LJ, Hussain SP,
Weinstein JN, et al: The p53 tumor suppressor network is a key
responder to microenvironmental components of chronic inflammatory
stress. Cancer Res. 65:10255–10264. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Koong AC, Denko NC, Hudson KM, Schindler
C, Swiersz L, Koch C, Evans S, Ibrahim H, Le QT, Terris DJ and
Giaccia AJ: Candidate genes for the hypoxic tumor phenotype. Cancer
Res. 60:883–887. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Higuchi C, Tanihata Y, Nishimura H, Naito
T and Sanaka T: Effects of glucose and plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1 on collagen metabolism in the peritoneum. Ther Apher
Dial. 9:173–181. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Diehl P, Hantke B, Hennig M, Tschesche H,
Mittelmeier W, Schmitt M and Muehlenweg B: Protein expression of
MMP-13, uPA, and PAI-1 in pseudocapsular and interface tissue
around implants of loose artificial hip joints and in
osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 13:711–715. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nouman GS, Anderson JJ, Lunec J and Angus
B: The role of the tumour suppressor p33 ING1b in human neoplasia.
J Clin Pathol. 56:491–496. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qiu Y, Zhao Y, Becker M, John S, Parekh
BS, Huang S, Hendarwanto A, Martinez ED, Chen Y, Lu H, et al: HDAC1
acetylation is linked to progressive modulation of steroid
receptor-induced gene transcription. Mol Cell. 22:669–679. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang XQ, Alfaro ML, Evans GF and Zuckerman
SH: Histone deacetylase inhibition results in decreased macrophage
CD9 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 294:660–666. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ferguson M, Henry PA and Currie RA:
Histone deacetylase inhibition is associated with transcriptional
repression of the Hmga2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:3123–3133.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Feng X, Bonni S and Riabowol K: HSP70
induction by ING proteins sensitizes cells to tumor necrosis factor
alpha receptor-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 26:9244–9255.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fujii T, Obara T, Tanno S, Ura H and Kohgo
Y: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1 as a prognostic factor in human colorectal carcinomas.
Hepatogastroenterology. 46:2299–2308. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang L, Xiao X, Li D, Chi Y, Wei P, Wang
Y, Ni S, Tan C, Zhou X and Du X: Abnormal expression of GADD45B in
human colorectal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 10:2152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hittelet A, Legendre H, Nagy N, Bronckart
Y, Pector JC, Salmon I, Yeaton P, Gabius HJ, Kiss R and Camby I:
Upregulation of galectins-1 and −3 in human colon cancer and their
role in regulating cell migration. Int J Cancer. 103:370–379. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim JH, Qu A, Reddy JK, Gao B and Gonzalez
FJ: Hepatic oxidative stress activates the Gadd45b gene by way of
degradation of the transcriptional repressor STAT3. Hepatology.
59:695–704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao XY, Chen TT, Xia L, Guo M, Xu Y, Yue
F, Jiang Y, Chen GQ and Zhao KW: Hypoxia inducible factor-1
mediates expression of galectin-1: The potential role in
migration/invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
31:1367–1375. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|