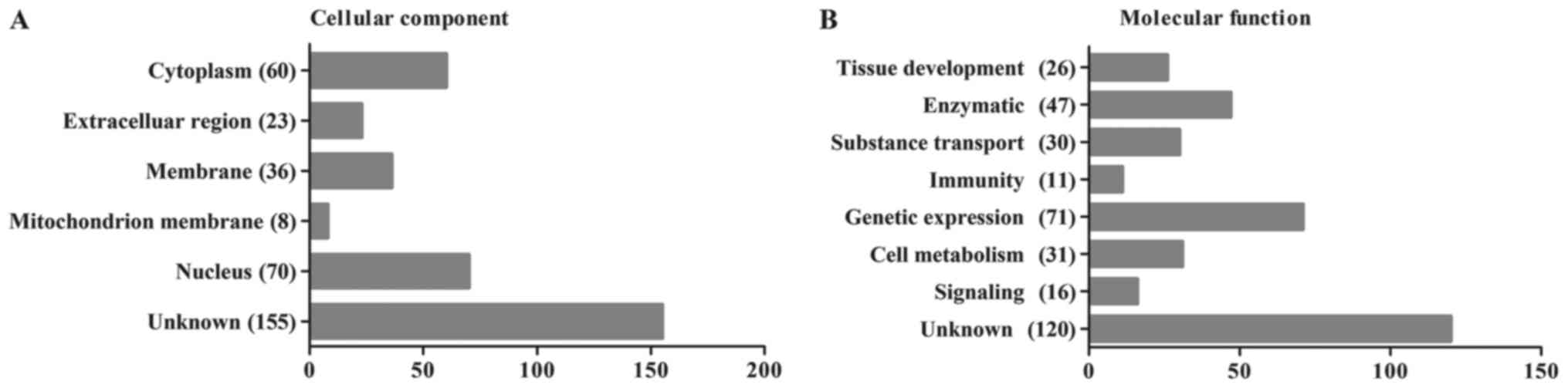
|
1
|
Phipps E, Prasanna D, Brima W and Jim B:
Preeclampsia: Updates in pathogenesis, definitions and guidelines.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 11:1102–1113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vikse BE, Irgens LM, Leivestad T,
Skjaerven R and Iversen BM: Preeclampsia and the risk of end-stage
renal disease. N Engl J Med. 359:800–809. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Drost JT, Maas AH, van Eyck J and van der
Schouw YT: Preeclampsia as a female-specific risk factor for
chronic hypertension. Maturitas. 67:321–326. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu L, Zhang X, Rong C, Rui C, Ji H, Qian
YJ, Jia R and Sun L: Distinct DNA methylomes of human placentas
between pre-eclampsia and gestational diabetes mellitus. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 34:1877–1889. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ghossein-Doha C, van Neer J, Wissink B,
Breetveld NM, de Windt LJ, van Dijk AP, Van Der Vlugt MJ, Janssen
MC, Heidema WM, Scholten RR and Spaanderman ME: Preeclampsia, an
important female specific risk factor for asymptomatic heart
failure. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 49:143–149. 2016.
|
|
6
|
Wang A, Rana S and Karumanchi SA:
Preeclampsia: The role of angiogenic factors in its pathogenesis.
Physiology (Bethesda). 24:147–158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Baumwell S and Karumanchi SA:
Pre-eclampsia: Clinical manifestations and molecular mechanisms.
Nephron Clin Pract. 106:C72–C81. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sankaralingam S, Arenas IA, Lalu MM and
Davidge ST: Preeclampsia: Current understanding of the molecular
basis of vascular dysfunction. Expert Rev Mol Med. 8:1–20. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Steegers EA, von Dadelszen P, Duvekot JJ
and Pijnenborg R: Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 376:631–644. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jia R, Li J, Rui C, Ji H, Ding H, Lu Y, De
W and Sun L: Comparative Proteomic profile of the human umbilical
cord blood exosomes between normal and preeclampsia pregnancies
with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:2299–2306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pillar N, Yoffe L, Hod M and Shomron N:
The possible involvement of microRNAs in preeclampsia and
gestational diabetes mellitus. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol.
29:176–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang YG, Yang HL, Long Y and Li WL:
Circular RNA in blood corpuscles combined with plasma protein
factor for early prediction of pre-eclampsia. BJOG. 123:2113–2118.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qian Y, Lu Y, Rui C, Qian Y, Cai M and Jia
R: Potential Significance of circular RNA in human placental tissue
for patients with preeclampsia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 39:1380–1390.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu L, Ye M and Zou H: Recent advances in
mass spectrometry-based peptidome analysis. Expert Rev Proteomics.
6:433–447. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schrader M and Schulz-Knappe P:
Peptidomics technologies for human body fluids. Trends Biotechnol.
19:55–60. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xiang Y, Kurokawa MS, Kanke M, Takakuwa Y
and Kato T: Peptidomics: Identification of pathogenic and marker
peptides. Methods Mol Biol. 615:259–271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Casalegno-Garduño R, Schmitt A and Schmitt
M: Clinical peptide vaccination trials for leukemia patients.
Expert Rev Vaccines. 10:785–799. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsangaris GT, Karamessinis P, Kolialexi A,
Garbis SD, Antsaklis A, Mavrou A and Fountoulakis M: Proteomic
analysis of amniotic fluid in pregnancies with Down syndrome.
Proteomics. 6:4410–4419. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li X, Wu LJ, Gu M, Chen YM, Zhang QJ, Li
H, Cheng ZJ, Hu P, Han SP, Yu ZB and Qian LM: Peptidomic analysis
of amniotic fluid for identification of putative bioactive peptides
in ventricular septal defect. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:1999–2014.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hsu JL, Huang SY, Chow NH and Chen SH:
Stable-isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. Anal
Chem. 75:6843–6852. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu F, Zhao C, Liu L, Ding H, Huo R and
Shi Z: Peptidome profiling of umbilical cord plasma associated with
gestational diabetes-induced fetal macrosomia. J Proteomics.
139:38–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wan J, Cui XW, Zhang J, Fu ZY, Guo XR, Sun
LZ and Ji CB: Peptidome analysis of human skim milk in term and
preterm milk. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 438:236–241. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cui X, Li Y, Yang L, You L, Wang X, Shi C,
Ji C and Guo X: Peptidome analysis of human milk from women
delivering macrosomic fetuses reveals multiple means of protection
for infants. Oncotarget. 7:63514–63525. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghulmiyyah L and Sibai B: Maternal
mortality from preeclampsia/eclampsia. Semin Perinatol. 36:56–59.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shah DM: Preeclampsia: New insights. Curr
Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 16:213–220. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ivanov VT and Yatskin ON: Peptidomics: A
logical sequel to proteomics. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2:463–473.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dallas DC, Guerrero A, Parker EA, Robinson
RC, Gan J, German JB, Barile D and Lebrilla CB: Current
peptidomics: Applications, purification, identification,
quantification, and functional analysis. Proteomics. 15:1026–1038.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu RN, Fan L, Rieser MJ and El-Shourbagy
TA: Recent advances in high-throughput quantitative bioanalysis by
LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 44:342–355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang F, Zhu J, Hu L, Qin H, Ye M and Zou
H: Comprehensive analysis of the N and C terminus of endogenous
serum peptides reveals a highly conserved cleavage site pattern
derived from proteolytic enzymes. Protein Cell. 3:669–674. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gigli M, Begay RL, Morea G, Graw SL,
Sinagra G, Taylor MRG, Granzier H and Mestroni L: A review of the
giant protein titin in clinical molecular diagnostics of
cardiomyopathies. Front Cardiovasc Med. 3:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lindstedt S and Nishikawa K: Huxleys'
missing filament: Form and function of titin in vertebrate striated
muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 79:145–166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Walker JS and de Tombe PP: Titin and the
developing heart. Circ Res. 94:860–862. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liang Y, Lin Q, Luo F, Wu W, Yang T and
Wan S: Requirement of miR-144 in CsA induced proliferation and
invasion of human trophoblast cells by targeting titin. J Cell
Biochem. 115:690–696. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Farina A, Morano D, Arcelli D, De Sanctis
P, Sekizawa A, Purwosunu Y, Zucchini C, Simonazzi G, Okai T and
Rizzo N: Gene expression in chorionic villous samples at 11 weeks
of gestation in women who develop preeclampsia later in pregnancy:
Implications for screening. Prenat Diagn. 29:1038–1044. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Araki Y, Nonaka D, Tajima A, Maruyama M,
Nitto T, Ishikawa H, Yoshitake H, Yoshida E, Kuronaka N, Asada K,
et al: Quantitative peptidomic analysis by a newly developed
one-step direct transfer technology without depletion of major
blood proteins: Its potential utility for monitoring of
pathophysiological status in pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Proteomics. 11:2727–2737. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|