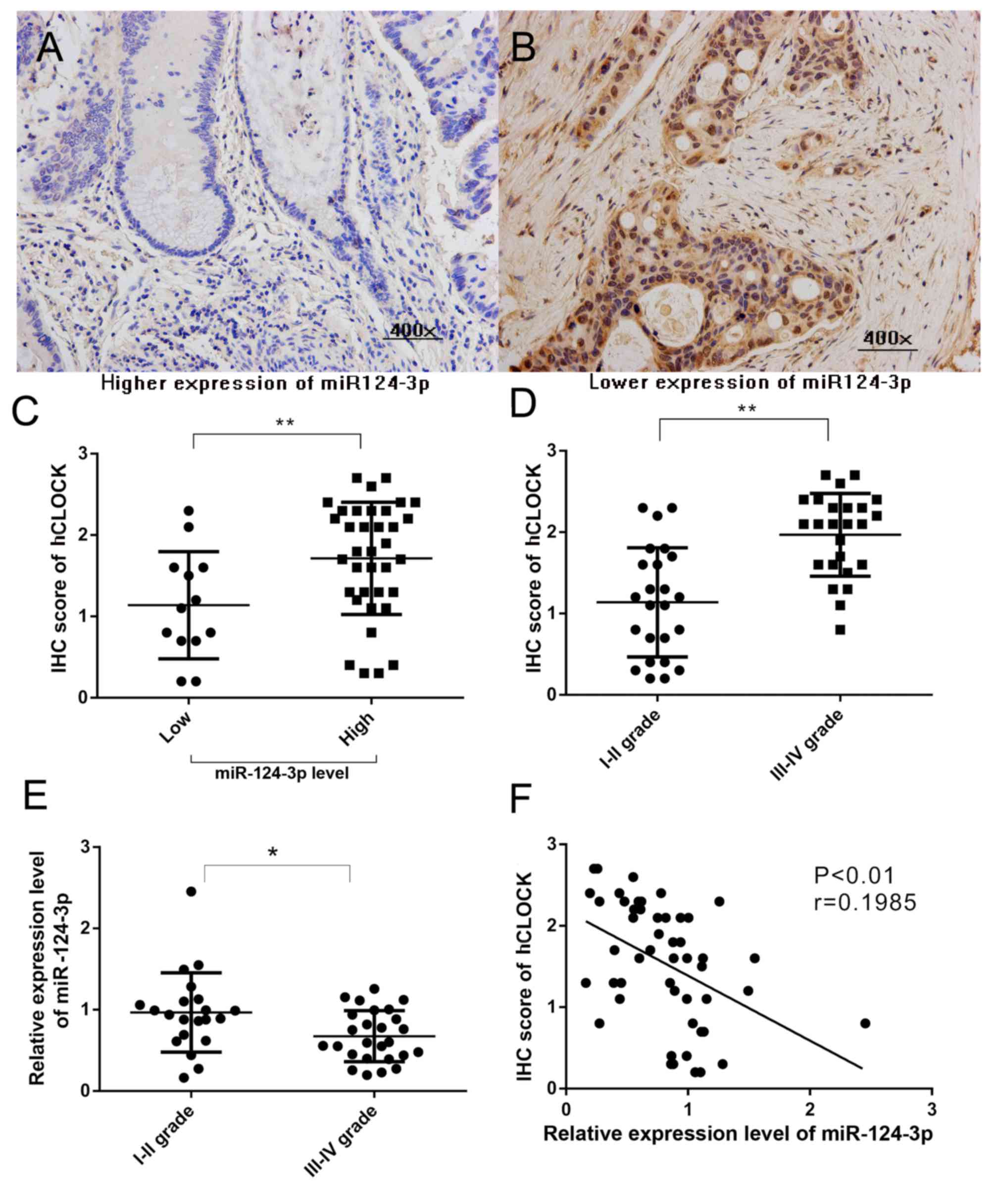
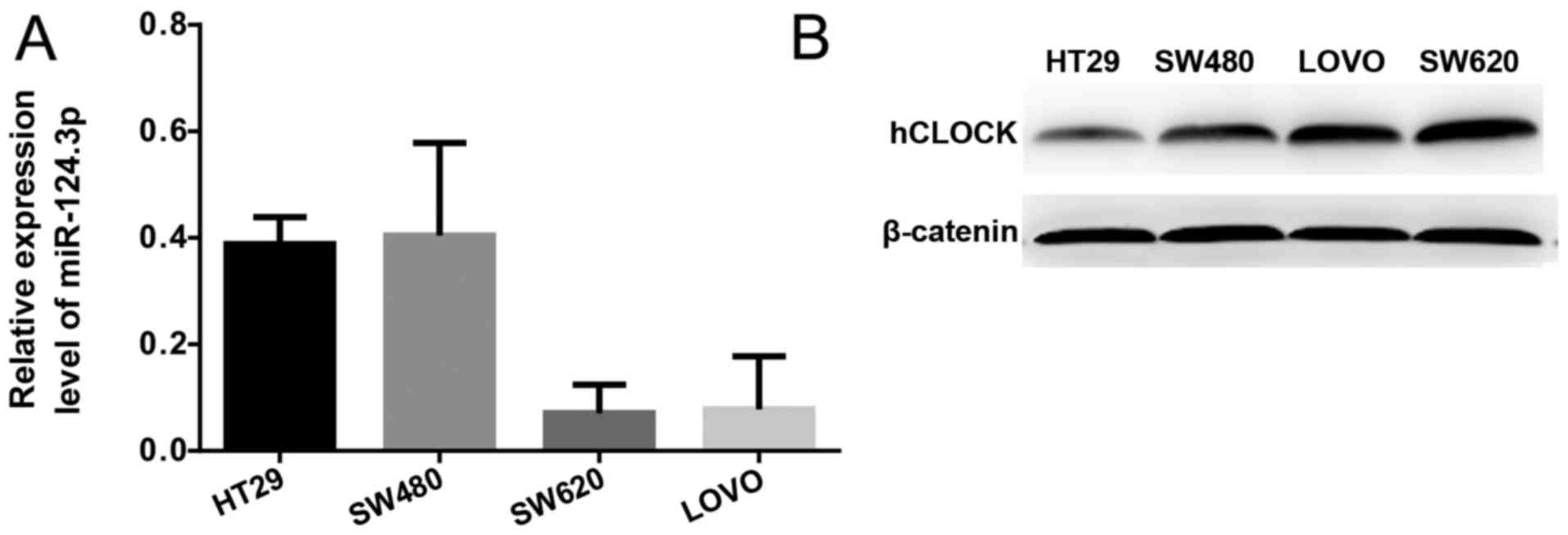
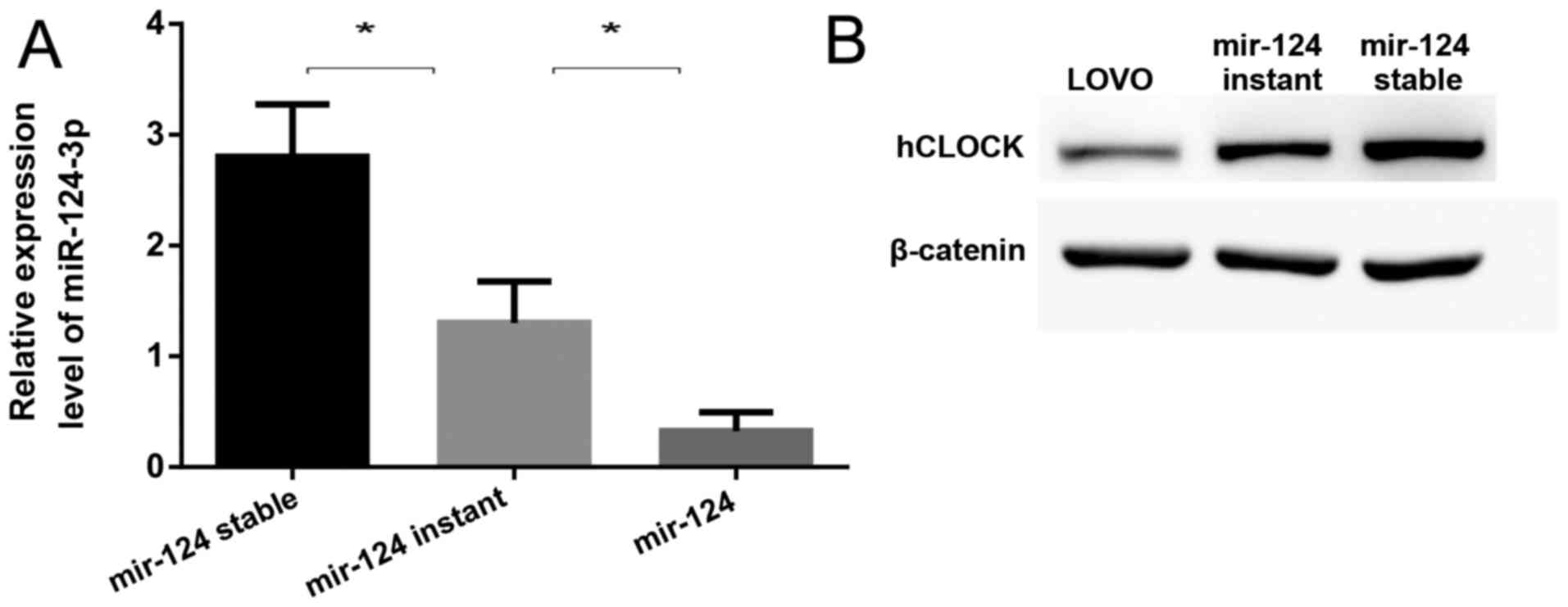
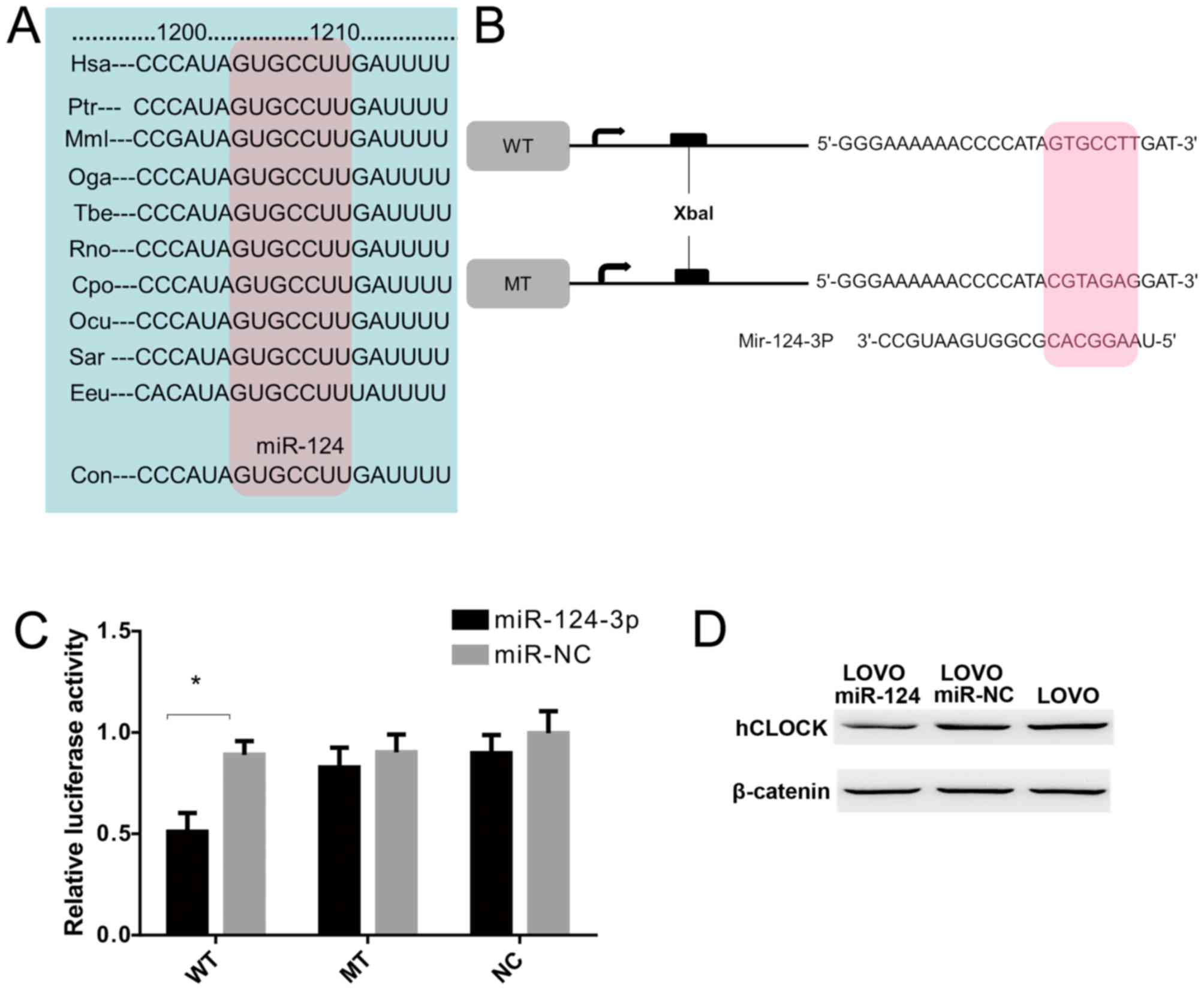
|
1
|
Hoffman AE, Yi CH, Zheng T, Stevens RG,
Leaderer D, Zhang Y, Holford TR, Hansen J, Paulson J and Zhu Y:
CLOCK in breast tumorigenesis: Genetic, epigenetic, and
transcriptional profiling analyses. Cancer Res. 70:1459–1468. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ko CH and Takahashi JS: Molecular
components of the mammalian circadian Clock. Hum Mol Genet.
15:R271–R277. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Storch KF, Lipan O, Leykin I, Viswanathan
N, Davis FC, Wong WH and Weitz CJ: Extensive and divergent
circadian gene expression in liver and heart. Nature. 417:78–83.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Benca R, Duncan MJ, Frank E, McClung C,
Nelson RJ and Vicentic A: Biological rhythms, higher brain
function, and behavior: Gaps, opportunities, and challenges. Brain
Res Rev. 62:57–70. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen ST, Choo KB, Hou MF, Yeh KT, Kuo SJ
and Chang JG: Deregulated expression of the PER1, PER2 and PER3
genes in breast cancers. Carcinogenesis. 26:1241–1246. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu L, Pelicano H, Liu J, Huang P and Lee
C: The circadian gene period2 plays an important role in tumor
suppression and DNA damage response in vivo. Cell. 111:41–50. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Hua L, Lu C and Chen Z: Expression
of circadian Clock gene human period2 (hPer2) in human colorectal
carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 9:1662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang L, Chen B, Wang Y, Sun N, Lu C, Qian
R and Hua L: hClock gene expression in human colorectal carcinoma.
Mol Med Rep. 8:1017–1022. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dibner C, Schibler U and Albrecht U: The
mammalian circadian timing system: Organization and coordination of
central and peripheral clocks. Ann Rev Physiol. 72:517–549. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Harms E, Kivimäe S, Young MW and Saez L:
Posttranscriptional and posttranslational regulation of clock
genes. J Biol Rhythms. 19:361–373. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Asher G, Gatfield D, Stratmann M, Reinke
H, Dibner C, Kreppel F, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW and Schibler U:
SIRT1 regulates circadian clock gene expression through PER2
deacetylation. Cell. 134:317–328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Long JM and Lahiri DK: Advances in
microRNA experimental approaches to study physiological regulation
of gene products implicated in CNS disorders. Exp Neurol.
235:402–418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang MJ, Li Y, Wang R, Wang C, Yu YY, Yang
L, Zhang Y, Zhou B, Zhou ZG and Sun XF: Downregulation of
microRNA-124 is an independent prognostic factor in patients with
colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 28:183–189. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Lu Y, Yue X, Li H, Luo X, Wang Y,
Wang K and Wan J: MiR-124 suppresses growth of human colorectal
cancer by inhibiting STAT3. PLoS One. 8:e703002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jinushi T, Shibayama Y, Kinoshita I,
Oizumi S, Jinushi M, Aota T, Takahashi T, Horita S, Dosaka-Akita H
and Iseki K: Low expression levels of microRNA-124-5p correlated
with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer via targeting of SMC4.
Cancer Med. 3:1544–1552. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu K, Zhao H, Yao H, Lei S, Lei Z, Li T
and Qi H: MicroRNA-124 regulates the proliferation of colorectal
cancer cells by targeting iASPP. Biomed Res Int.
2013:8675372013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition.
New York: Springer; 2010
|
|
19
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36(Database Issue): D149–D153. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz HJ, et al:
CALGB/SWOG 80405: Phase III trial of irinotecan/5-FU/leucovorin
(FOLFIRI) or oxaliplatin/5-FU/leucovorin (mFOLFOX6) with
bevacizumab (BV) or cetuximab (CET) for patients with KRAS
wild-type untreated metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon or
rectum [abstract]; 2014 American Society of Clinical Oncology
Annual Meeting; 2014 May 30-June 3; Chicago, USA. Alexandria (VA).
American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2014;
|
|
25
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, .
Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal
cancer. Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Fearon ER: Molecular genetics of
colorectal cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:479–507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Harada T, Yamamoto E, Yamano HO, Nojima M,
Maruyama R, Kumegawa K, Ashida M, Yoshikawa K, Kimura T, Harada E,
et al: Analysis of DNA methylation in bowel lavage fluid for
detection of colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
7:1002–1010. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|