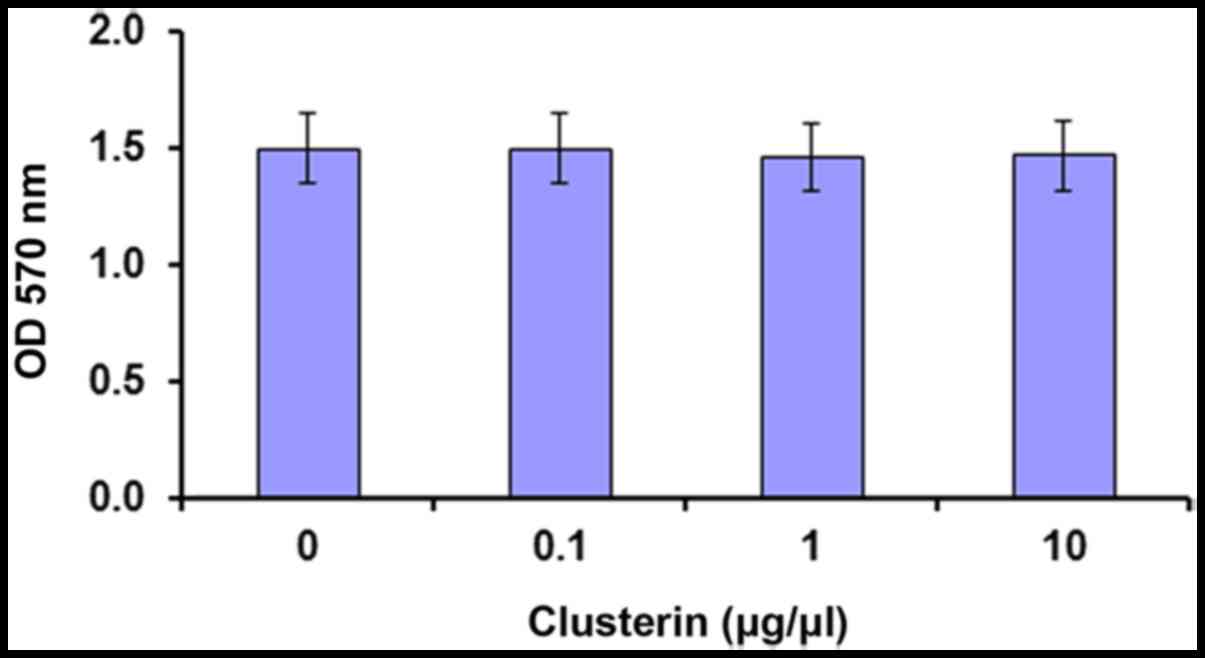
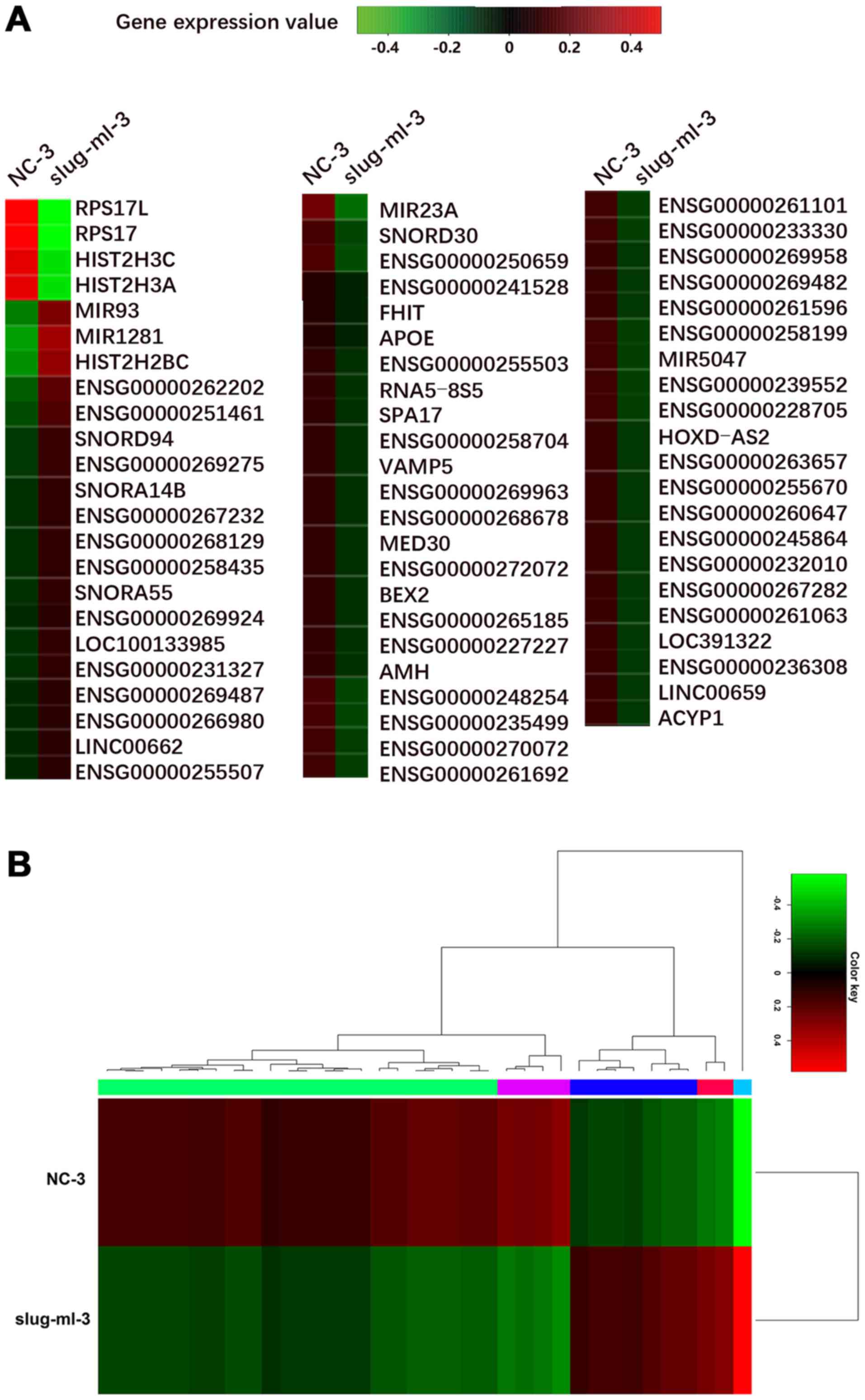
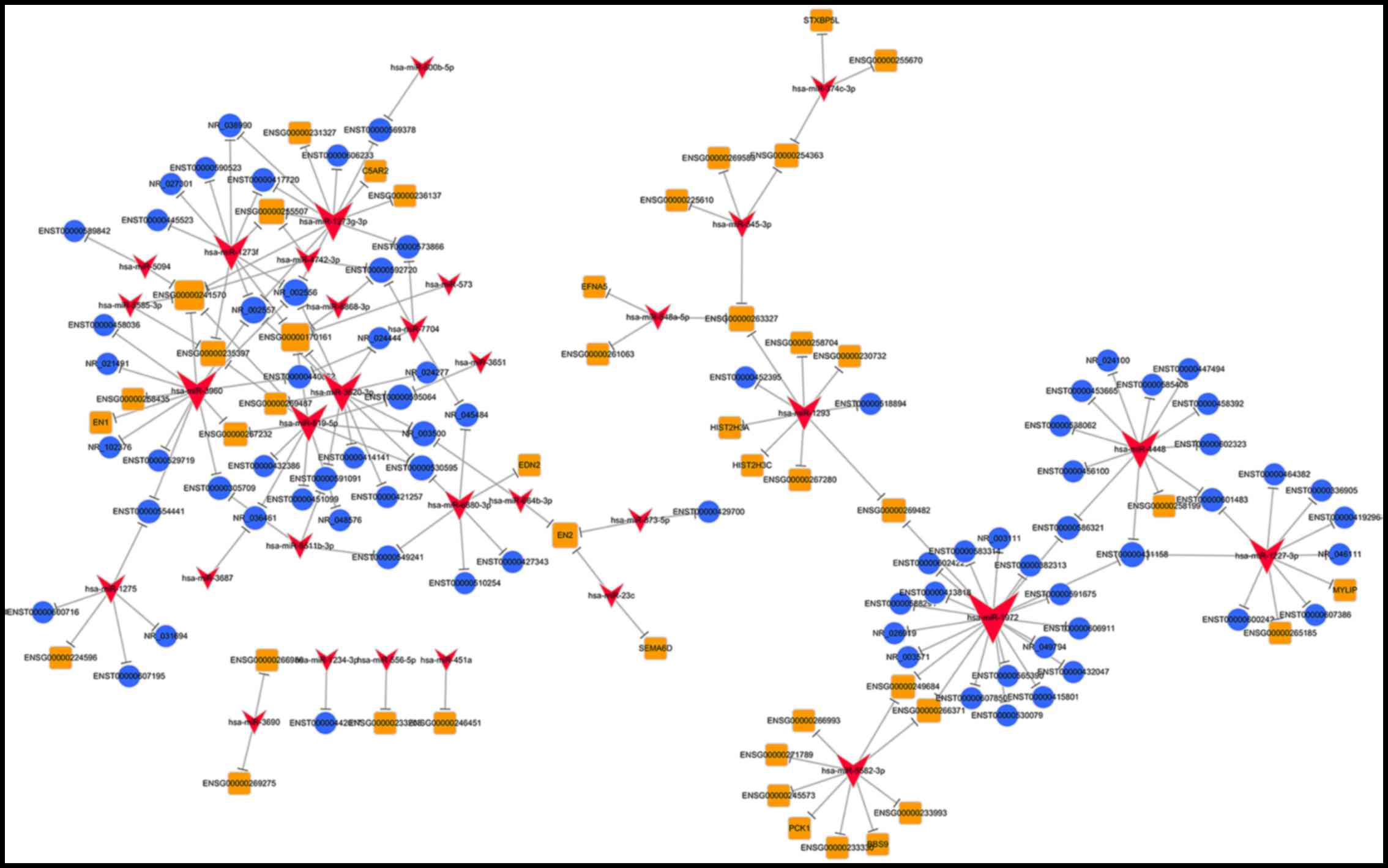
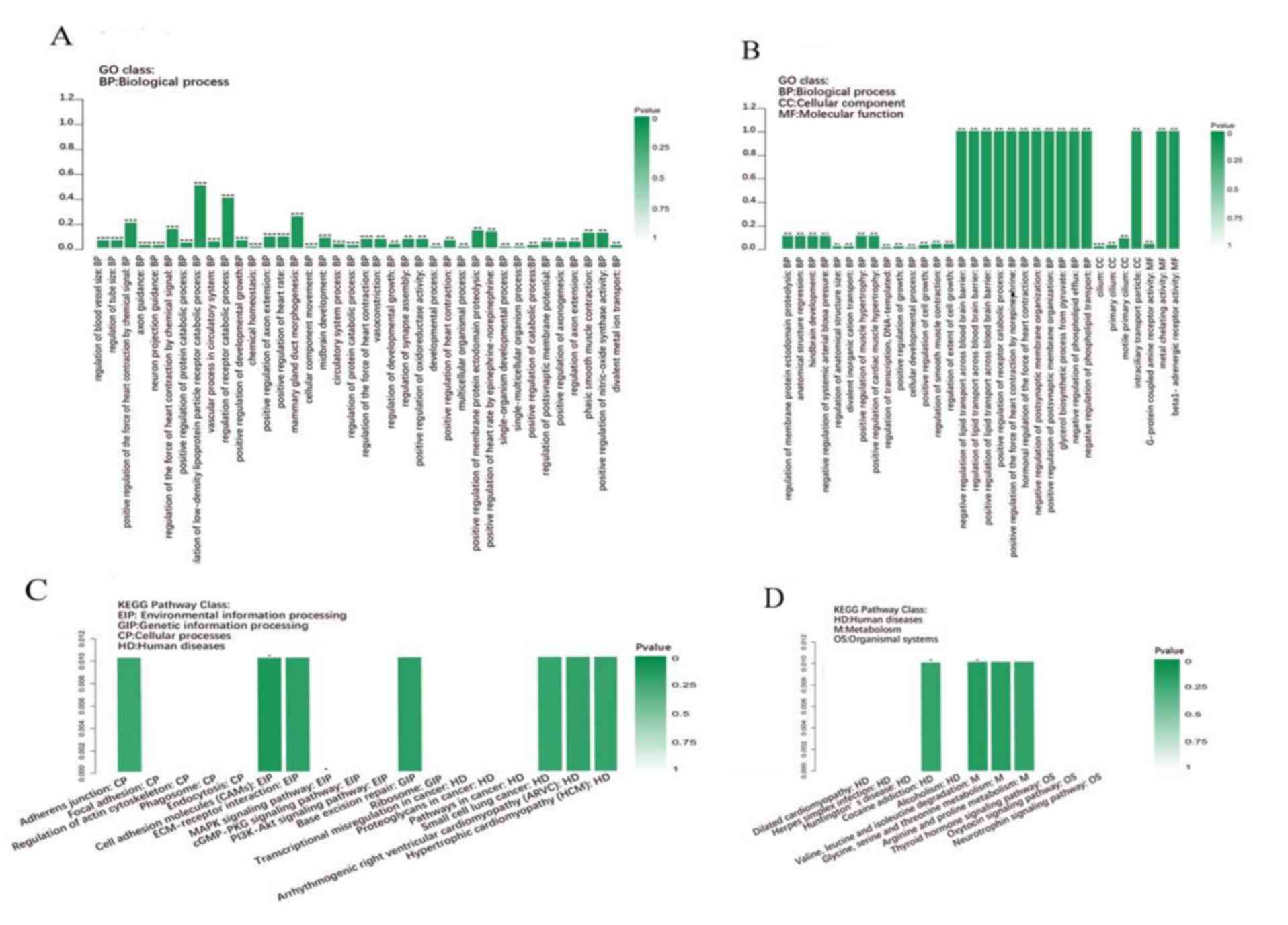
|
1
|
Klein R, Chou CF, Klein BE, Zhang X, Meuer
SM and Saaddine JB: Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration
in the US population. Arch Ophthalmol. 129:75–80. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gehrs KM, Anderson DH, Johnson LV and
Hageman GS: Age-related macular degeneration-emerging pathogenetic
and therapeutic concepts. Ann Med. 38:450–471. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gehrs KM, Jackson JR, Brown EN, Allikmets
R and Hageman GS: Complement, age-related macular degeneration and
a vision of the future. Arch Ophthalmol. 128:349–358. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anderson DH, Radeke MJ, Gallo NB, Chapin
EA, Johnson PT, Curletti CR, Hancox LS, Hu J, Ebright JN, Malek G,
et al: The pivotal role of the complement system in aging and
age-related macular degeneration: Hypothesis re-visited. Prog Retin
Eye Res. 29:95–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chakravarthy U, Wong TY, Fletcher A,
Piault E, Evans C, Zlateva G, Buggage R, Pleil A and Mitchell P:
Clinical risk factors for age-related macular degeneration: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Ophthalmol. 10:312010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chong EW, Robman LD, Simpson JA, Hodge AM,
Aung KZ, Dolphin TK, English DR, Giles GG and Guymer RH: Fat
consumption and its association with age-related macular
degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 127:674–680. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seddon JM, George S and Rosner B:
Cigarette smoking, fish consumption, omega-3 fatty acid intake, and
associations with age-related macular degeneration: The US twin
study of age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol.
124:995–1001. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research
Group, ; SanGiovanni JP, Chew EY, Clemons TE, Ferris FL III,
Gensler G, Lindblad AS, Milton RC, Seddon JM and Sperduto RD: The
relationship of dietary carotenoid and vitamin AE, and C intake
with age-related macular degeneration in a case-control study:
AREDS Report No. 22. Arch Ophthalmol. 125:1225–1232. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Donoso LA, Kim D, Frost A, Callahan A and
Hageman G: The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of
age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 51:137–152.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beatty S, Koh H, Phil M, Henson D and
Boulton M: The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of
age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 45:115–134.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reynolds R, Hartnett ME, Atkinson JP,
Giclas PC, Rosner B and Seddon JM: Plasma complement components and
activation fragments: Associations with age-related macular
degeneration genotypes and phenotypes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
50:5818–5827. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Suuronen T, Nuutinen T, Ryhänen T,
Kaarniranta K and Salminen A: Epigenetic regulation of
clusterin/apolipoprotein J expression in retinal pigment epithelial
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 357:397–401. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anderson DH, Mullins RF, Hageman GS and
Johnson LV: A role for local inflammation in the formation of
drusen in the aging eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 134:411–431. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jenne DE, Lowin B, Peitsch M, Böttcher A,
Schmitz G and Tschopp J: Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor)
forms a high density lipoprotein complex with apolipoprotein AI in
human plasma. J Biol Chem. 266:11030–11036. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gemenetzi M and Lotery AJ: The role of
epigenetics in age-related macular degeneration. Eye (Lond).
28:1407–1417. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bell JT and Spector TD: A twin approach to
unraveling epigenetics. Trends Genet. 27:116–125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li YY, Cui JG, Hill JM, Bhattacharjee S,
Zhao Y and Lukiw WJ: Increased expression of miRNA-146a in
Alzheimer's disease transgenic mouse models. Neurosci Lett.
487:94–98. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li YY, Cui JG, Dua P, Pogue AI,
Bhattacharjee S and Lukiw WJ: Differential expression of
miRNA-146a-regulated inflammatory genes in human primary neural,
astroglial and microglial cells. Neurosci Lett. 499:109–113. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pogue AI, Percy ME, Cui JG, Li YY,
Bhattacharjee S, Hill JM, Kruck TP, Zhao Y and Lukiw WJ:
Up-regulation of NF-kB-sensitive miRNA-125b and miRNA-146a in metal
sulfate-stressed human astroglial (HAG) primary cell cultures. J
Inorg Biochem. 105:1434–1437. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kociok N and Joussen AM: Enhanced
expression of the complement factor H mRNA in proliferating human
RPE cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 248:1145–1153. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The rosetta stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ebert MS, Neilson JR and Sharp PA:
MicroRNA sponges: Competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian
cells. Nat Methods. 4:721–726. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Zhang J, Carver B,
Haveman WJ and Pandolfi PP: A coding-independent function of gene
and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature.
465:1033–1038. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu H: CREB up-regulates long non-coding
RNA, HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver
cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:5366–5383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Langmead B: Aligning short sequencing
reads with Bowtie. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics Chapter. 11:Unit
11.72010.
|
|
26
|
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G,
Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL and Pachter L:
Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 7:562–578. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen X, Li Q, Wang J, Guo X, Jiang X, Ren
Z, Weng C, Sun G, Wang X, Liu Y, et al: Identification and
characterization of novel amphioxus microRNAs by Solexa sequencing.
Genome Biol. 10:R782009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hofacker IL, Fontana W, Stadler PF,
Bonhoeffer LS, Tacker M and Schuster P: Fast folding and comparison
of RNA secondary structures. Monatshefte für Chemie/Chemical
Monthly. 125:167–188. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M and
Giegerich R: Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target
duplexes. RNA. 10:1507–1517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vlachos IS, Paraskevopoulou MD, Karagkouni
D, Georgakilas G, Vergoulis T, Kanellos I, Anastasopoulos IL,
Maniou S, Karathanou K, Kalfakakou D, et al: DIANA-TarBase v7.0:
Indexing more than half a million experimentally supported
miRNA:mRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(Database issue):
D153–D159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
An E, Lu X, Flippin J, Devaney JM,
Halligan B, Hoffman EP, Strunnikova N, Csaky K and Hathout Y:
Secreted proteome profiling in human RPE cell cultures derived from
donors with age related macular degeneration and age matched
healthy donors. J Proteome Res. 5:2599–2610. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wapinski O and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs and human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 21:354–361. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Guduric-Fuchs J, O'Connor A, Cullen A,
Harwood L, Medina RJ, O'Neill CL, Stitt AW, Curtis TM and Simpson
DA: Deep sequencing reveals predominant expression of miR-21
amongst the small non-coding RNAs in retinal microvascular
endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 113:2098–2111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yuan JH, Yang F, Wang F, Ma JZ, Guo YJ,
Tao QF, Liu F, Pan W, Wang TT, Zhou CC, et al: A long noncoding RNA
activated by TGF-β promotes the invasion-metastasis cascade in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 25:666–681. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Augoff K, McCue B, Plow EF and
Sossey-Alaoui K: miR-31 and its host gene lncRNA LOC554202 are
regulated by promoter hypermethylation in triple-negative breast
cancer. Mol Cancer. 11:52012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tsang FH, Au SL, Wei L, Fan DN, Lee JM,
Wong CC, Ng IO and Wong CM: Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP is
frequently up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and is targeted
by tumour suppressive miR-125b. Liver Int. 35:1597–1606. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu YR, Jiang YZ, Xu XE, Hu X, Yu KD and
Shao ZM: Comprehensive transcriptome profiling reveals multigene
signatures in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
22:1653–1662. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Su X, Malouf GG, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yao H,
Valero V, Weinstein JN, Spano JP, Meric-Bernstam F, Khayat D and
Esteva FJ: Comprehensive analysis of long non-coding RNAs in human
breast cancer clinical subtypes. Oncotarget. 5:9864–9876. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pundir P, MacDonald CA and Kulka M: The
novel receptor C5aR2 is required for C5a-mediated human mast cell
adhesion, migration, and proinflammatory mediator production. J
Immunol. 195:2774–2787. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Donoso LA, Kim D, Frost A, Callahan A and
Hageman G: The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of
age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 51:137–152.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|