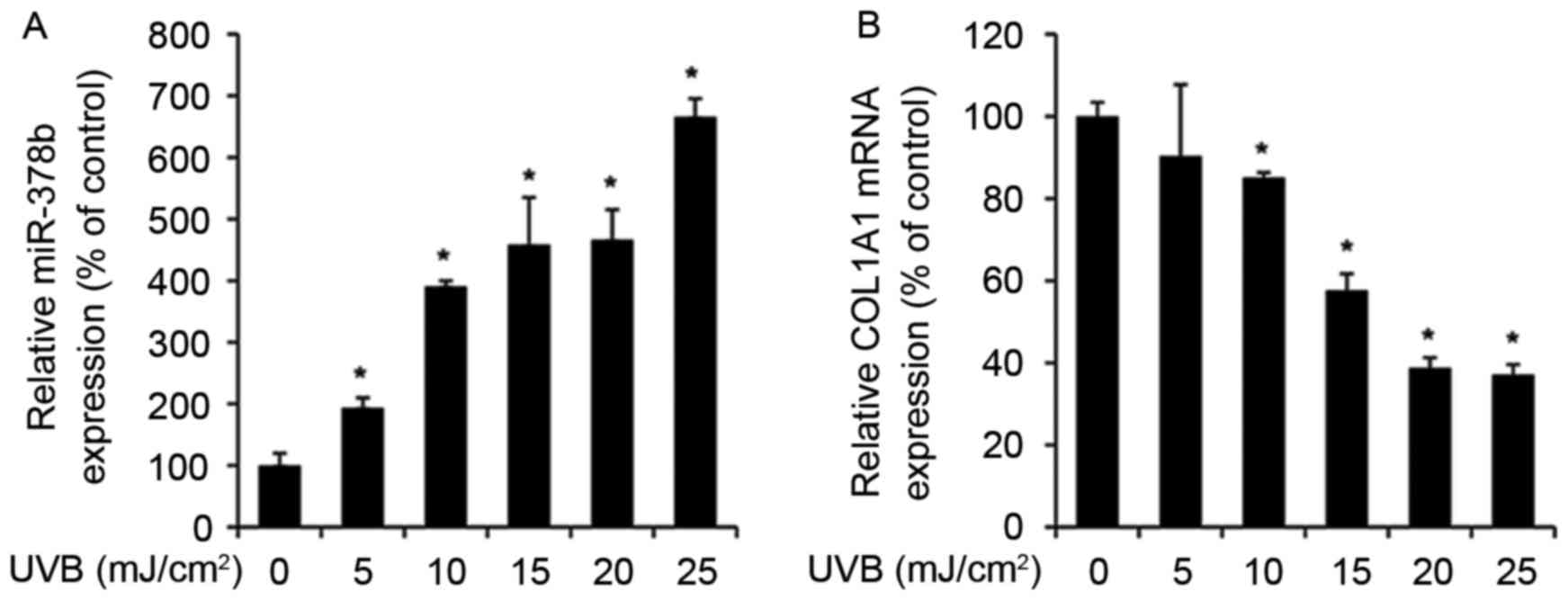
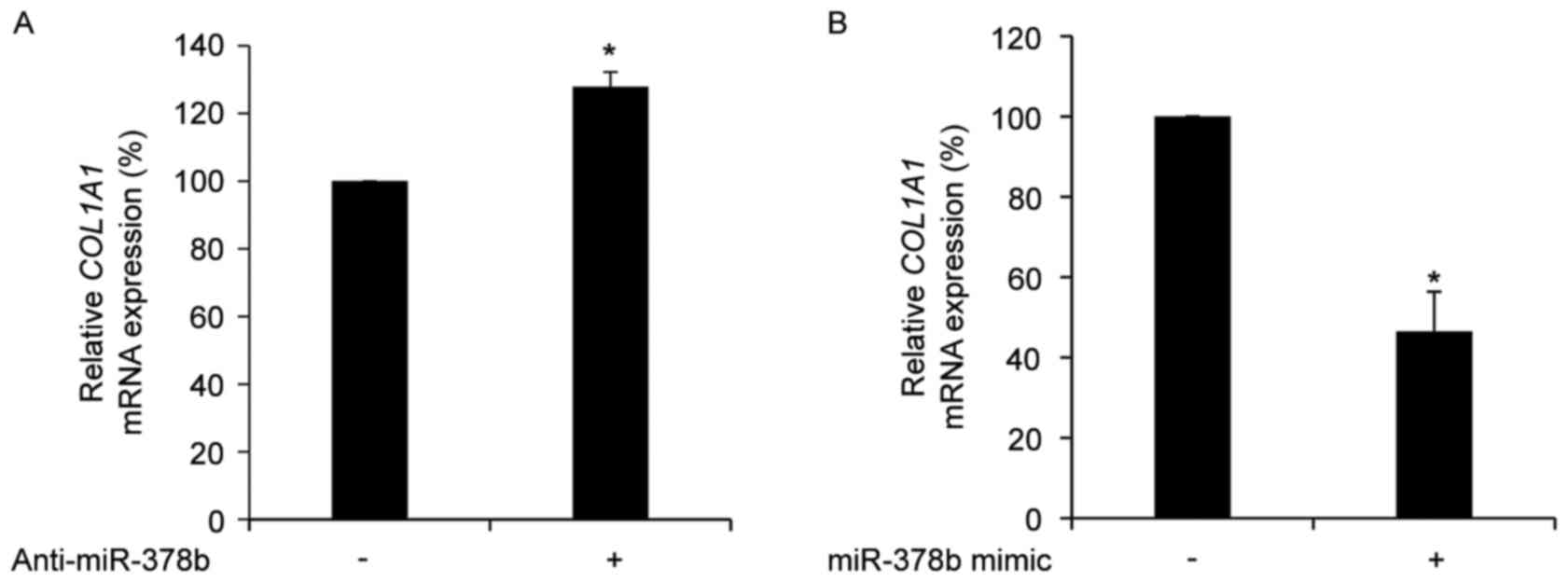
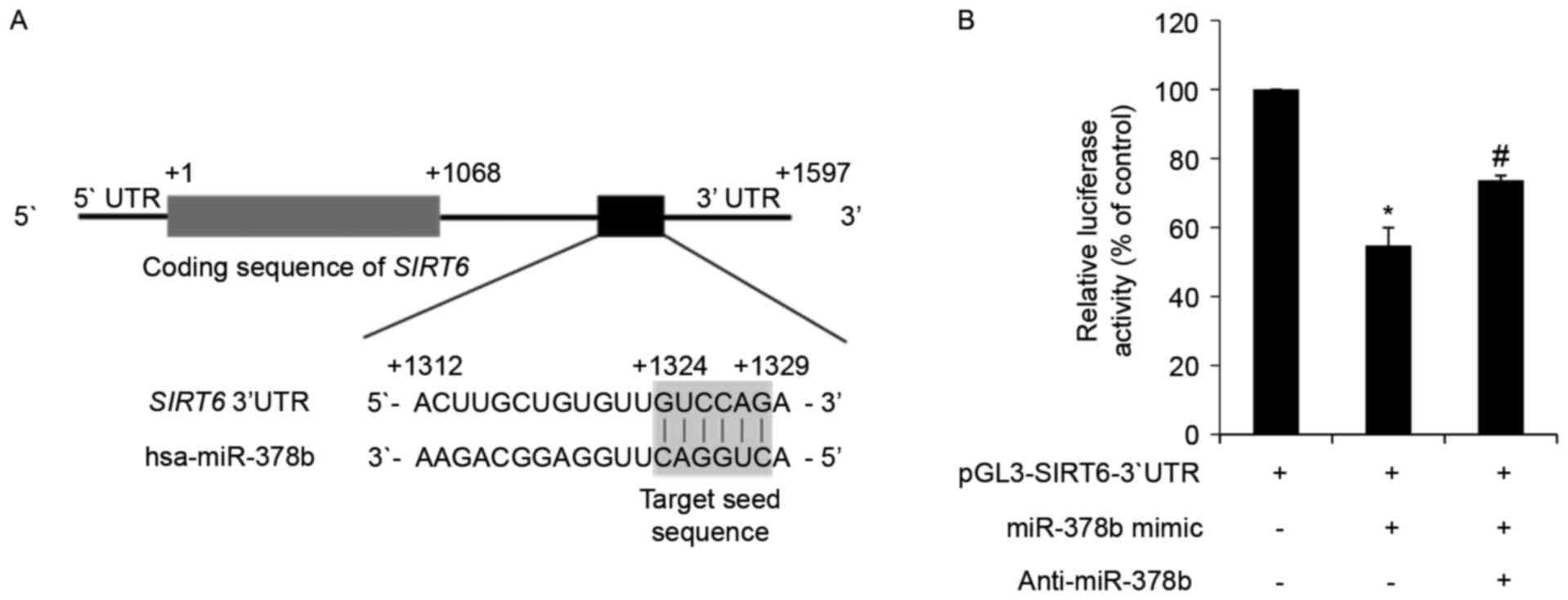
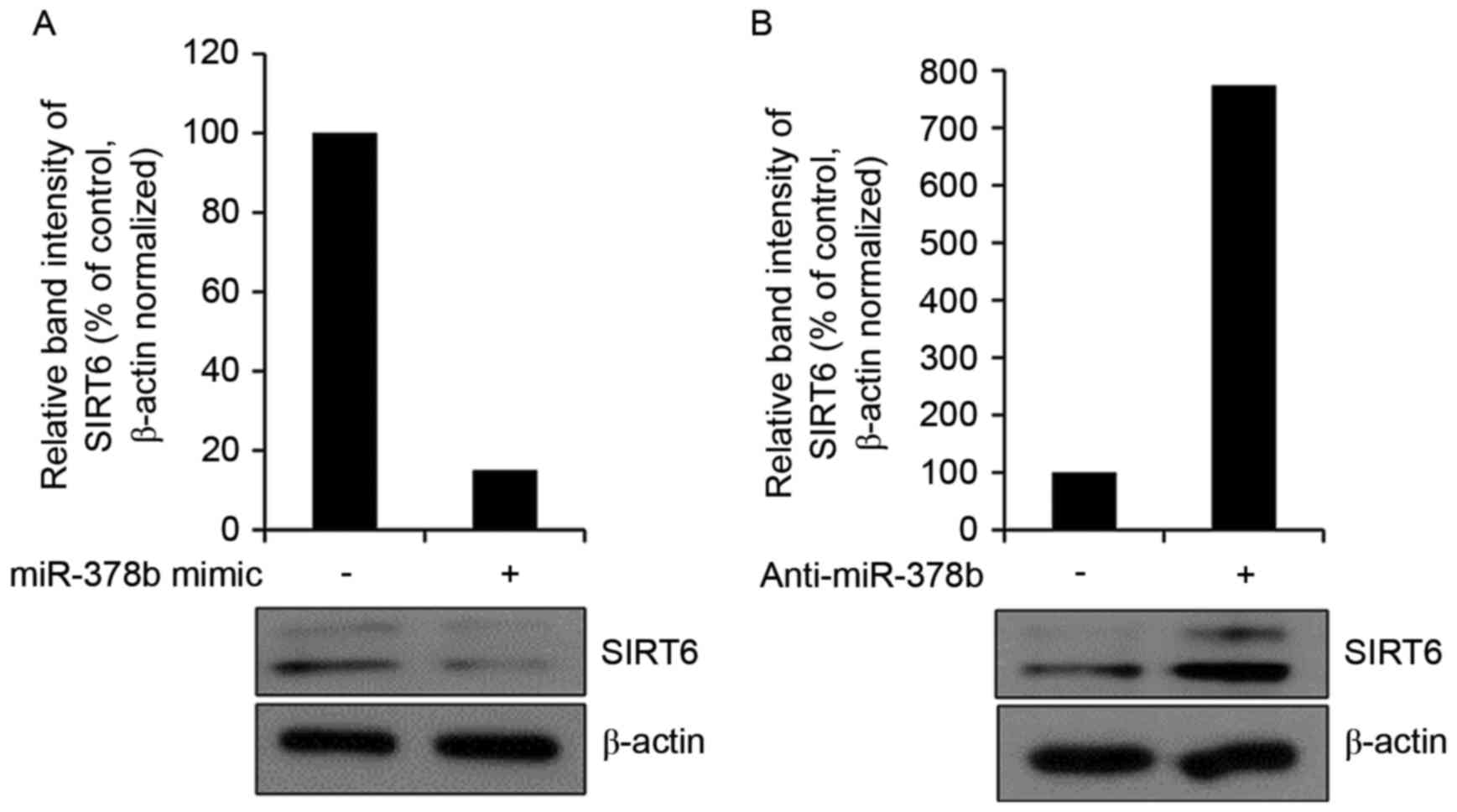
|
1
|
Lee YK, Cha HJ, Hong M, Yoon Y, Lee H and
An S: Role of NF-κB-p53 crosstalk in ultraviolet A-induced cell
death and G1 arrest in human dermal fibroblasts. Arch Dermatol Res.
304:73–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Varani J, Dame MK, Rittie L, Fligiel SE,
Kang S, Fisher GJ and Voorhees JJ: Decreased collagen production in
chronologically aged skin: Roles of age-dependent alteration in
fibroblast function and defective mechanical stimulation. Am J
Pathol. 168:1861–1868. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wulf HC, Sandby-Møller J, Kobayasi T and
Gniadecki R: Skin aging and natural photoprotection. Micron.
35:185–191. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Quan T and Fisher GJ: Role of
age-associated alterations of the dermal extracellular matrix
microenvironment in human skin aging: A mini-review. Gerontology.
61:427–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Darlenski R, Kazandjieva J and Tsankov N:
Skin barrier function: Morphological basis and regulatory
mechanisms. J Clin Med. 4:36–45. 2011.
|
|
6
|
Egbert M, Ruetze M, Sattler M, Wenck H,
Gallinat S, Lucius R and Weise JM: The matricellular protein
periostin contributes to proper collagen function and is
downregulated during skin aging. J Dermatol Sci. 73:40–48. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Newton VL, Mcconnell JC, Hibbert SA,
Graham HK and Watson RE: Skin aging: Molecular pathology, dermal
remodelling and the imaging revolution. G Ital Dermatol Venereol.
150:665–674. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Borradaile NM and Pickering JG: NAD (+),
sirtuins, and cardiovascular disease. Curr Pharm Des. 15:110–117.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Law IK, Liu L, Xu A, Lam KS, Vanhoutte PM,
Che CM, Leung PT and Wang Y: Identification and characterization of
proteins interacting with SIRT1 and SIRT3: Implications in the
anti-aging and metabolic effects of sirtuins. Proteomics.
9:2444–2456. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Han SH: Potential role of sirtuin as a
therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases. J Clin Neurol.
5:120–125. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roth M and Chen WY: Sorting out functions
of sirtuins in cancer. Oncogene. 33:1609–1620. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Balcerczyk A and Pirola L: Therapeutic
potential of activators and inhibitors of sirtuins. Biofactors.
36:383–393. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chou WW, Chen KC, Wang YS, Wang JY, Liang
CL and Juo SH: The role of SIRT1/AKT/ERK pathway in ultraviolet B
induced damage on human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Toxicol
In Vitro. 27:1728–1736. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan W and Luo J: SIRT1 regulates
UV-induced DNA repair through deacetylating XPA. Mol Cell.
39:247–258. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xia J, Wu X, Yang Y, Zhao Y, Fang M, Xie
W, Wang H and Xu Y: SIRT1 deacetylates RFX5 and antagonizes
repression of collagen type I (COL1A2) transcription in smooth
muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 428:264–270. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baohua Y and Li L: Effects of SIRT6
silencing on collagen metabolism in human dermal fibroblasts. Cell
Biol Int. 36:105–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
An IS, An S, Park S, Lee SN and Bae S:
Involvement of microRNAs in epigallocatechin gallate-mediated UVB
protection in human dermal fibroblasts. Oncol Rep. 29:253–259.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee MJ, Cha HJ, Lim KM, Lee OK, Bae S, Kim
CH, Lee KH, Lee YN, Ahn KJ and An S: Analysis of the microRNA
expression profile of normal human dermal papilla cells treated
with 5α-dihydrotestosterone. Mol Med Rep. 12:1205–1212. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fahs F, Bi X, Yu FS, Zhou L and Mi QS: New
insights into microRNAs in skin wound healing. IUBMB Life.
67:889–896. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Virant-Klun I, Ståhlberg A, Kubista M and
Skutella T: MicroRNAs: From female fertility, germ cells, and stem
cells to cancer in humans. Stem Cells Int. 2016:39849372016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nothnick WB: Non-coding RNAs in uterine
development, function and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 886:171–189.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garg M: MicroRNAs, stem cells and cancer
stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 4:62–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dumortier O and Van Obberghen E: MicroRNAs
in pancreas development. Diabetes Obes Metab. 14 Suppl 3:S22–S28.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou BR, Xu Y and Luo D: Effect of UVB
irradiation on microRNA expression in mouse epidermis. Oncol Lett.
3:560–564. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang YM, Juan HF, Lee TY, Chang YY, Yeh
YM, Li WH and Shih AC: Prediction of human miRNAs using
tissue-selective motifs in 3′ UTRs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp.
17061–17066. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kawahara TL, Rapicavoli NA, Wu AR, Qu K,
Quake SR and Chang HY: Dynamic chromatin localization of Sirt6
shapes stress- and aging-related transcriptional networks. PLoS
Genet. 7:e10021532011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sharma A, Diecke S, Zhang WY, Lan F, He C,
Mordwinkin NM, Chua KF and Wu JC: The role of SIRT6 protein in
aging and reprogramming of human induced pluripotent stem cells. J
Biol Chem. 288:18439–18447. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|