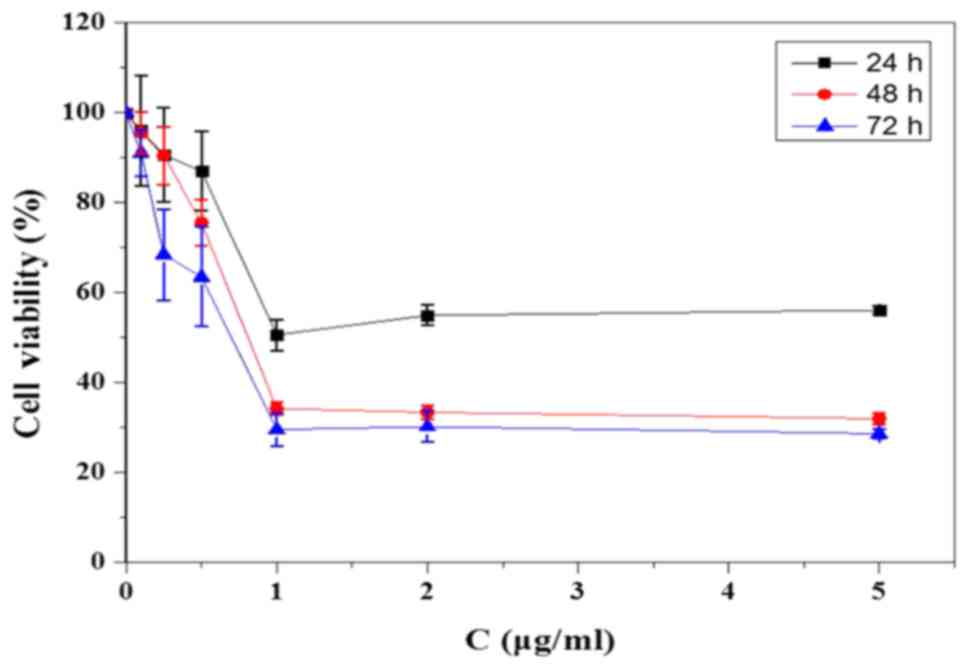
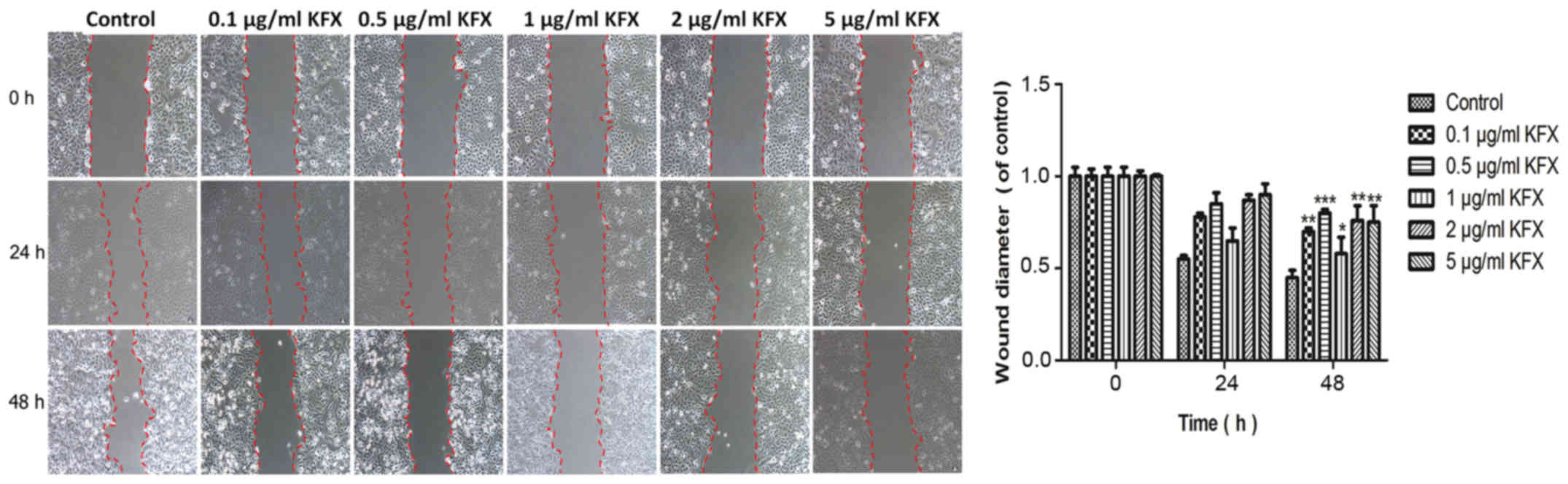
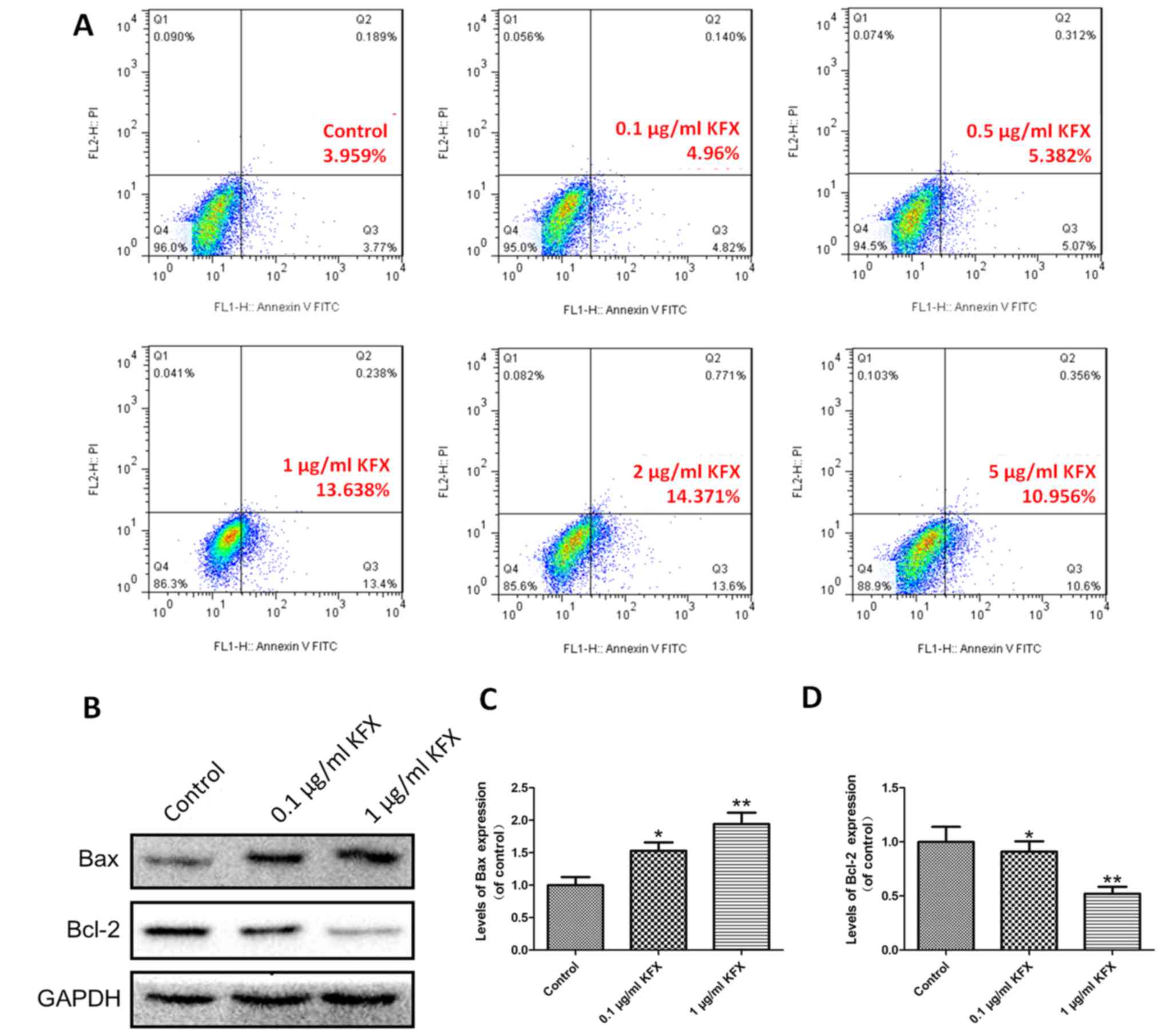
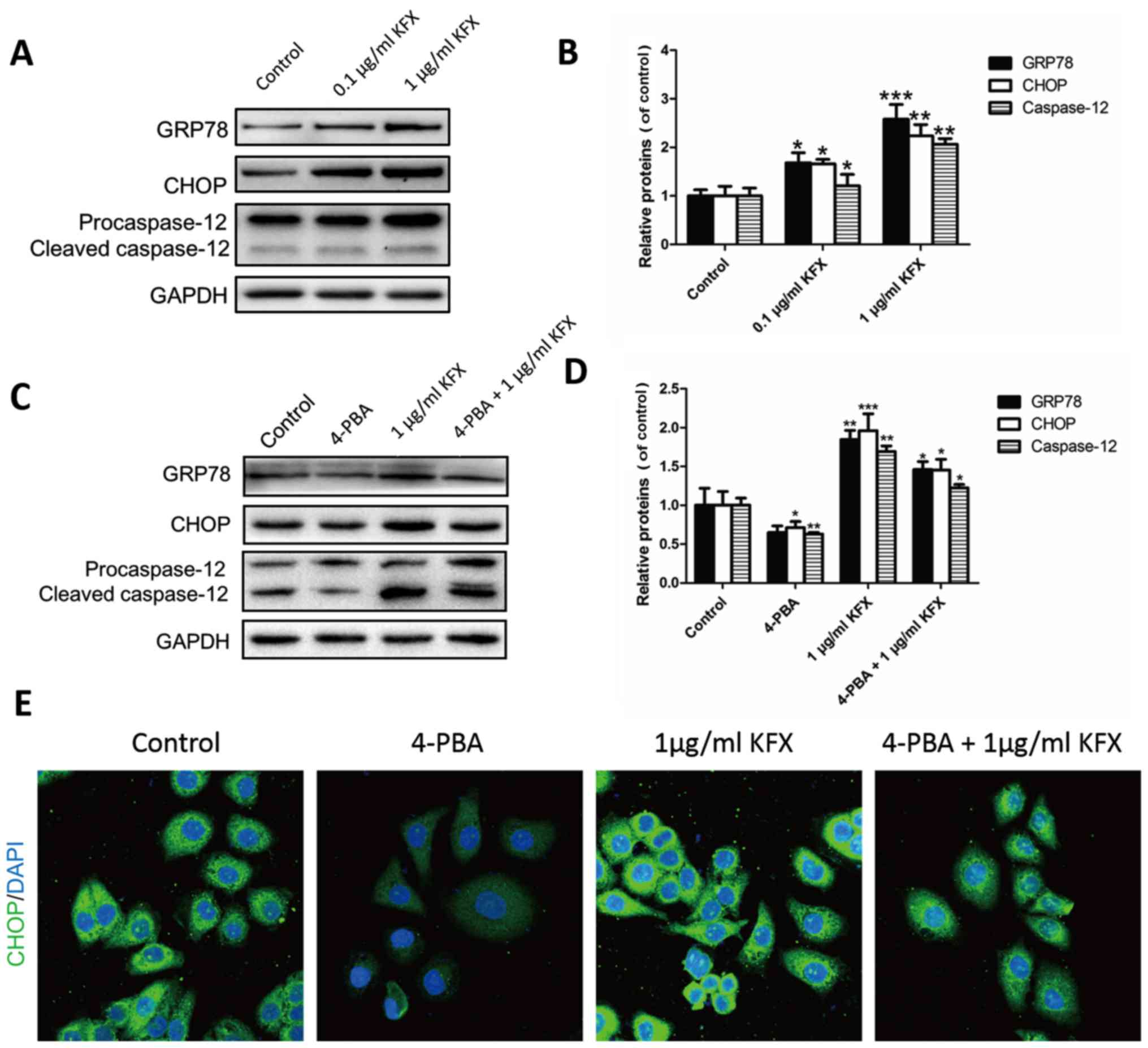
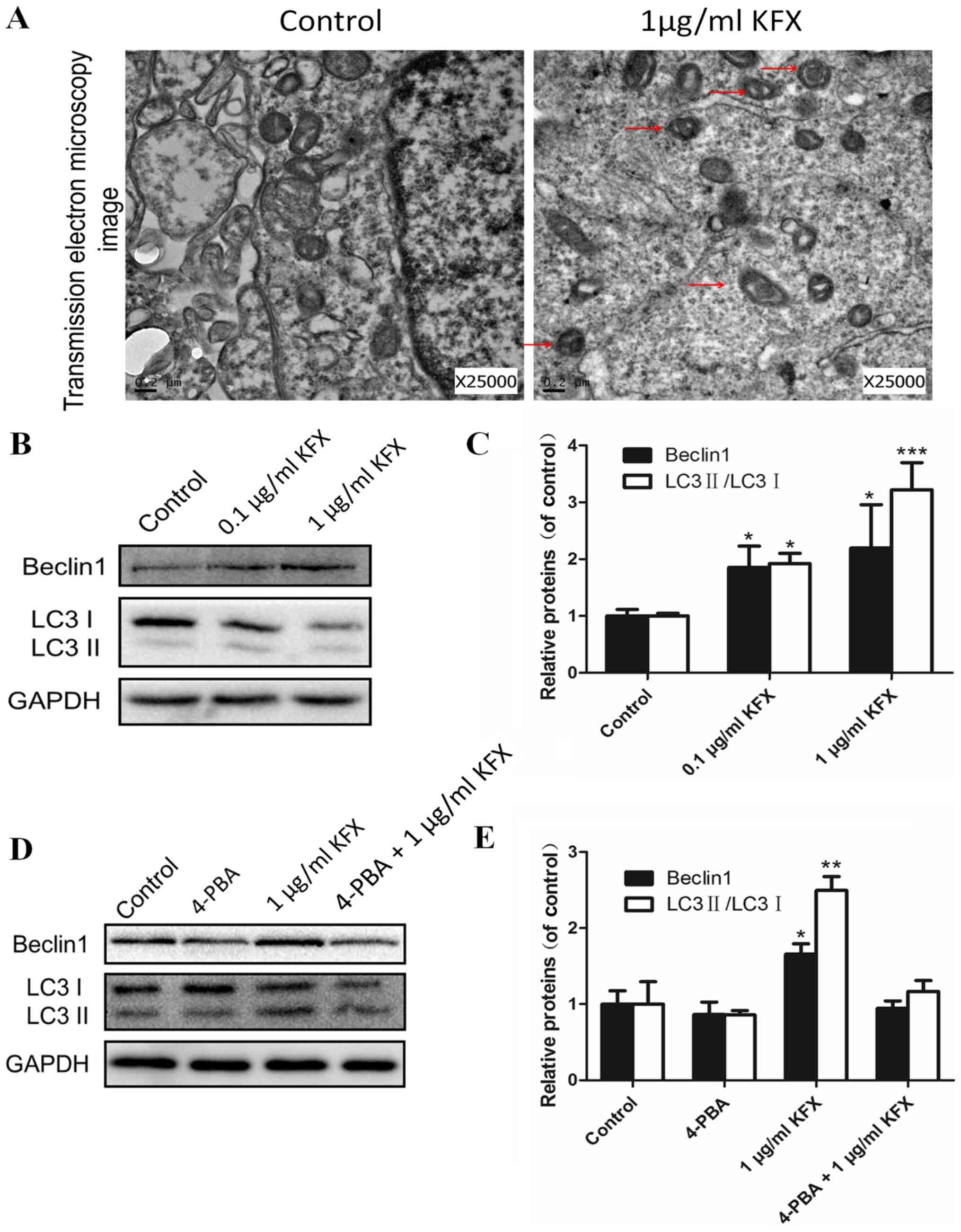
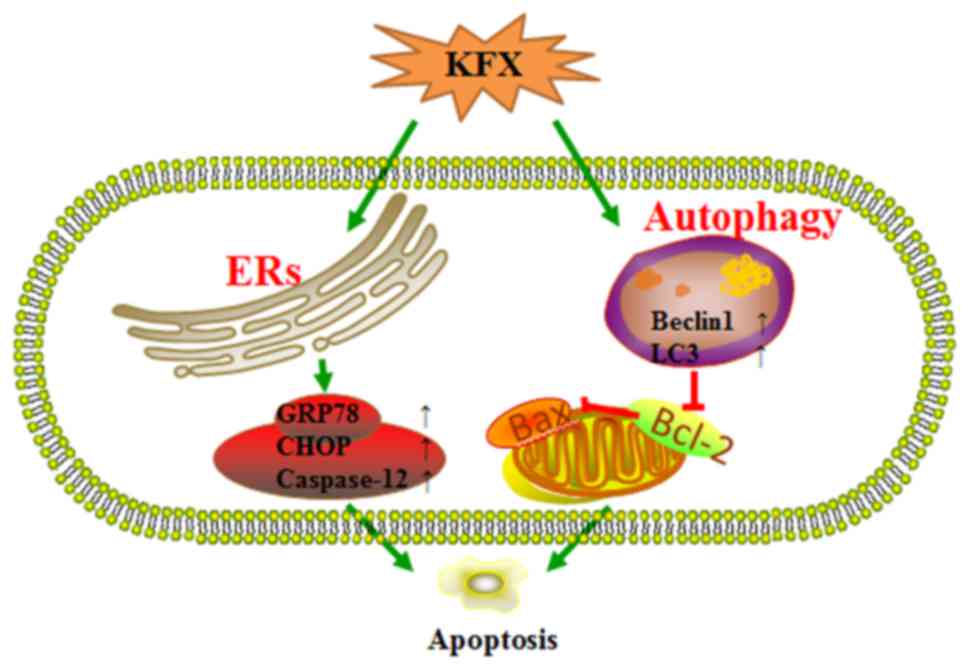
|
1
|
Li Y, Li B, Xiang CP, Zhang Y, Li YY and
Wu XL: Characterization of gastric cancer models from different
cell lines orthotopically constructed using improved implantation
techniques. World J Gastroenterol. 18:136–143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zou P, Xia Y, Chen T, Zhang J, Wang Z,
Chen W, Chen M, Kanchana K, Yang S and Liang G: Selective killing
of gastric cancer cells by a small molecule targeting ROS-mediated
ER stress activation. Mol Carcinog. 55:1073–1086. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Honda K and Jacobson JS: Use of
complementary and alternative medicine among United States adults:
The influences of personality, coping strategies, and social
support. Prev Med. 40:46–53. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang XY, He ZC, Song LY, Spencer S, Yang
LX, Peng F, Liu GM, Hu MH, Li HB, Wu XM, et al: Chemotherapeutic
effects of bioassay-guided extracts of the American cockroach,
Periplaneta americana. Integr Cancer Ther. 10:NP12–NP23. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Efferth T, Li PC, Konkimalla VS and Kaina
B: From traditional Chinese medicine to rational cancer therapy.
Trends Mol Med. 13:353–361. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alves RR, Lima HN, Tavares MC, Souto WM,
Barboza RR and Vasconcellos A: Animal-based remedies as
complementary medicines in Santa Cruz do Capibaribe, Brazil. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 8:442008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bonnemain B: Helix and Drugs: Snails for
Western Health Care From Antiquity to the Present. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2:25–28. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Castro ML, Vilela WR, Zauli RC, Ikegaki M,
Rehder VL, Foglio MA, de Alencar SM and Rosalen PL: Bioassay guided
purification of the antimicrobial fraction of a Brazilian propolis
from Bahia state. BMC Complement Altern Med. 9:252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang Z, Liu Y, Liao J, Gong C, Sun C, Zhou
X, Wei X, Zhang T, Gao Q, Ma D and Chen G: Quercetin induces
endoplasmic reticulum stress to enhance cDDP cytotoxicity in
ovarian cancer: Involvement of STAT3 signaling. FEBS J.
282:1111–1125. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM and Samali
A: Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 7:880–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaufman RJ: Orchestrating the unfolded
protein response in health and disease. J Clin Invest.
110:1389–1398. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu SP, Wang ZG, Zhao YZ, Wu J, Shi HX, Ye
LB, Wu FZ, Cheng Y, Zhang HY, He S, et al: Gelatin nanostructured
lipid carriers incorporating nerve growth factor inhibit
endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and improve recovery
in spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 53:4375–4386. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ogata M, Hino S, Saito A, Morikawa K,
Kondo S, Kanemoto S, Murakami T, Taniguchi M, Tanii I, Yoshinaga K,
et al: Autophagy is activated for cell survival after endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol. 26:9220–9231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang XY, Zhang TT, Song DD, Zhou J, Han
R, Qin ZH and Sheng R: Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone GRP78 is
involved in autophagy activation induced by ischemic
preconditioning in neural cells. Mol Brain. 8:202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi S, Tan P, Yan B, Gao RI, Zhao J, Wang
J, Guo J, Li N and Ma Z: ER stress and autophagy are involved in
the apoptosis induced by cisplatin in human lung cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 35:2606–2614. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshida T, Shiraishi T, Nakata S, Horinaka
M, Wakada M, Mizutani Y, Miki T and Sakai T: Proteasome inhibitor
MG132 induces death receptor 5 through CCAAT/enhancer-binding
protein homologous protein. Cancer Res. 65:5662–5667. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang CC, Chen LH, Gillespie S, Kiejda KA,
Mhaidat N, Wang YF, Thorne R, Zhang XD and Hersey P: Tunicamycin
sensitizes human melanoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of
TRAIL-R2 via the unfolded protein response. Cancer Res.
67:5880–5888. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He Q, Lee DI, Rong R, Yu M, Luo X, Klein
M, El-Deiry WS, Huang Y, Hussain A and Sheikh MS: Endoplasmic
reticulum calcium pool depletion-induced apoptosis is coupled with
activation of the death receptor 5 pathway. Oncogene. 21:2623–2633.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bouman L, Schlierf A, Lutz AK, Shan J,
Deinlein A, Kast J, Galehdar Z, Palmisano V, Patenge N, Berg D, et
al: Parkin is transcriptionally regulated by ATF4: Evidence for an
interconnection between mitochondrial stress and ER stress. Cell
Death Differ. 18:769–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu J, Chen M, Chen N, Ma A, Zhu C, Zhao
R, Jiang M, Zhou J, Ye L, Fu H and Zhang X: Glycyrrhetinic acid
induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest in human non-small cell lung
cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Int J
Oncol. 46:981–988. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang YS, Shen Q and Li J: Traditional
Chinese medicine targeting apoptotic mechanisms for esophageal
cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:295–302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim B, Kim HS, Jung EJ, Lee JY, K Tsang B,
Lim JM and Song YS: Curcumin induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis
through selective generation of reactive oxygen species in cervical
cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 55:918–928. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim HS, Lim JM, Kim JY, Kim Y, Park S and
Sohn J: Panaxydol, a component of Panax ginseng, induces apoptosis
in cancer cells through EGFR activation and ER stress and inhibits
tumor growth in mouse models. Int J Cancer. 138:1432–1441. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang W, Chen L, Shen Y and Xu J:
Rifampicin-induced injury in L02 cells is alleviated by 4-PBA via
inhibition of the PERK-ATF4-CHOP pathway. Toxicol In Vitro.
36:186–196. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tork OM, Khaleel EF and Abdelmaqsoud OM:
Altered cell to cell communication, autophagy and mitochondrial
dysfunction in a model of hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential
protective effects of curcumin and stem cell therapy. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:8271–8279. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma K, Huang MY, Guo YX and Hu GQ:
Matrine-induced autophagy counteracts cell apoptosis via the ERK
signaling pathway in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Lett. 12:1854–1860.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu L, Maimaitirexiati X, Jiang Y and Liu
L: Parkin regulates mitochondrial autophagy after myocardial
infarction in rats. Med Sci Monit. 22:1553–1559. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang C, Li H, Zhou H, Zhang S, Liu Z,
Zhou Q and Sun F: Recombinant Lz-8 from Ganoderma lucidum induces
endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagic cell death in
SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:1079–1089. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiong HY, Guo XL, Bu XX, Zhang SS, Ma NN,
Song JR, Hu F, Tao SF, Sun K, Li R, et al: Autophagic cell death
induced by 5-FU in Bax or PUMA deficient human colon cancer cell.
Cancer Lett. 288:68–74. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li X, Zhu F, Jiang J, Sun C, Zhong Q, Shen
M, Wang X, Tian R, Shi C, Xu M, et al: Simultaneous inhibition of
the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy enhances apoptosis
induced by ER stress aggravators in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Autophagy. 12:1521–1537. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xie WY, Zhou XD, Yang J, Chen LX and Ran
DH: Inhibition of autophagy enhances heat-induced apoptosis in
human non-small cell lung cancer cells through ER stress pathways.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 607:55–66. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xie WY, Zhou XD, Li Q, Chen LX and Ran DH:
Acid-induced autophagy protects human lung cancer cells from
apoptosis by activating ER stress. Exp Cell Res. 339:270–279. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sharma K, Ishaq M, Sharma G, Khan MA,
Dutta RK and Majumdar S: Pentoxifylline triggers autophagy via ER
stress response that interferes with Pentoxifylline induced
apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 103:17–28.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Periyasamy P, Guo ML and Buch S: Cocaine
induces astrocytosis through ER stress-mediated activation of
autophagy. Autophagy. 12:1310–1329. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang K, Liu R, Li J, Mao J, Lei Y, Wu J,
Zeng J, Zhang T, Wu H, Chen L, et al: Quercetin induces protective
autophagy in gastric cancer cells: Involvement of Akt-mTOR- and
hypoxia-induced factor 1α-mediated signaling. Autophagy. 7:966–978.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|