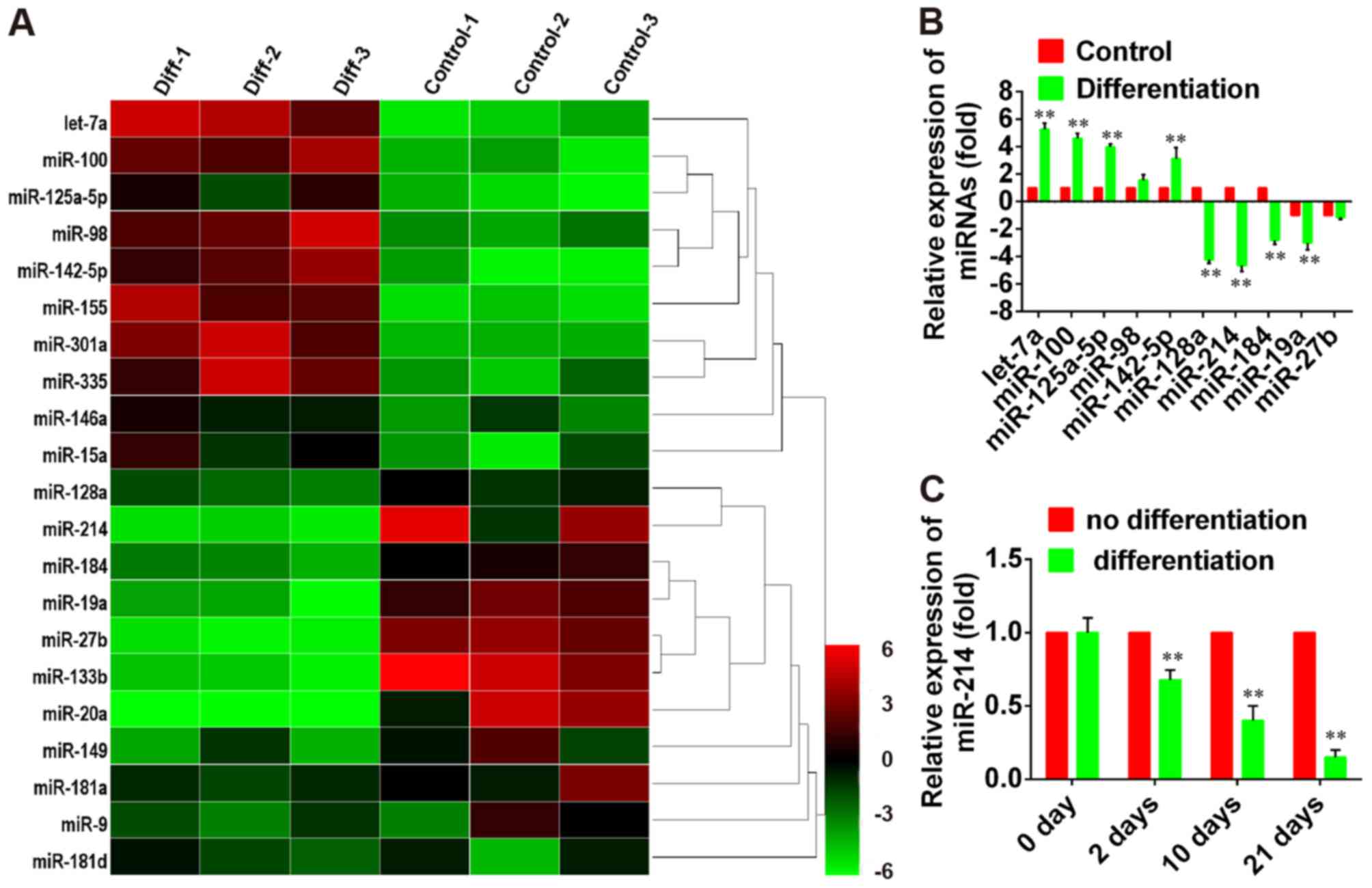
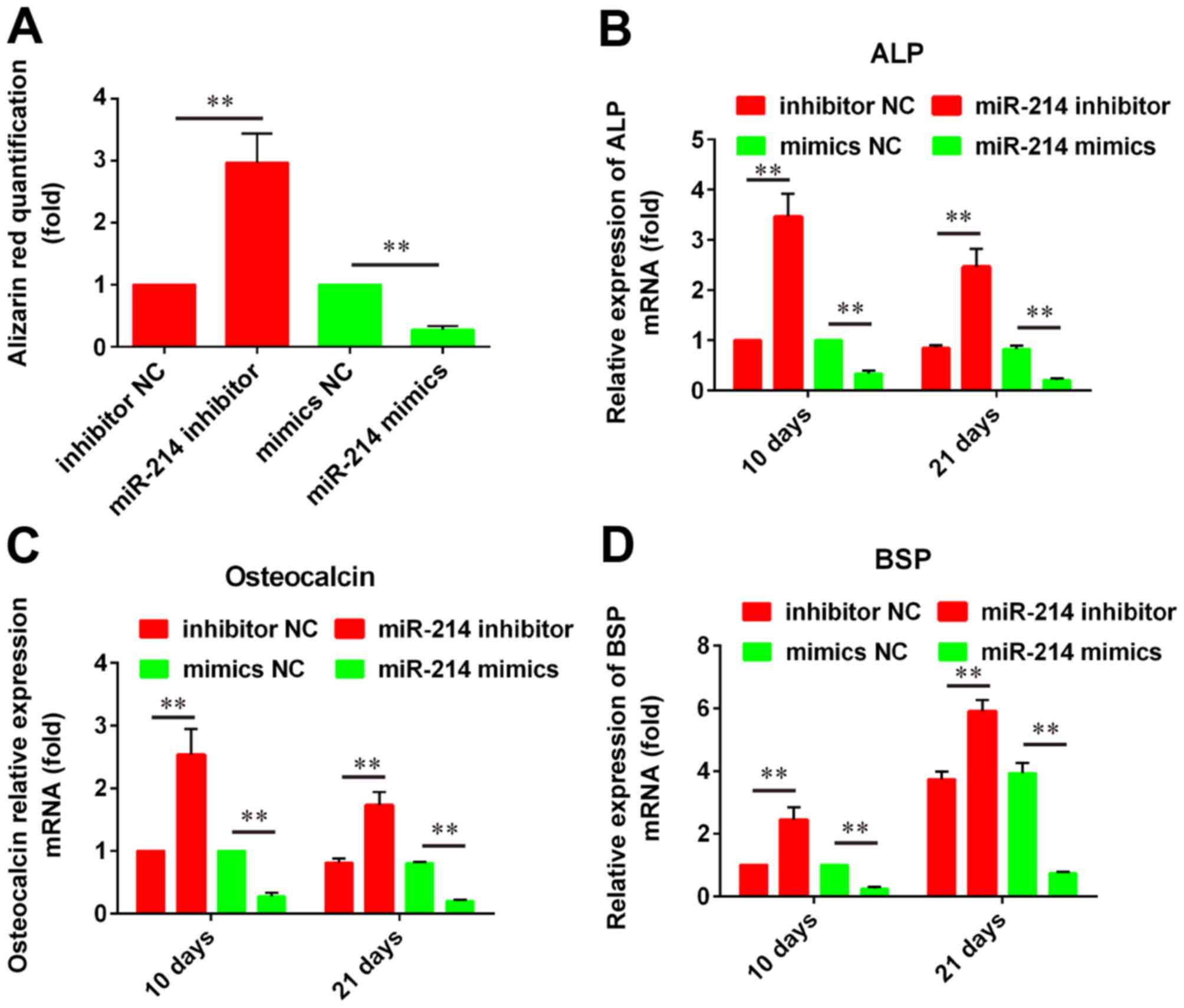
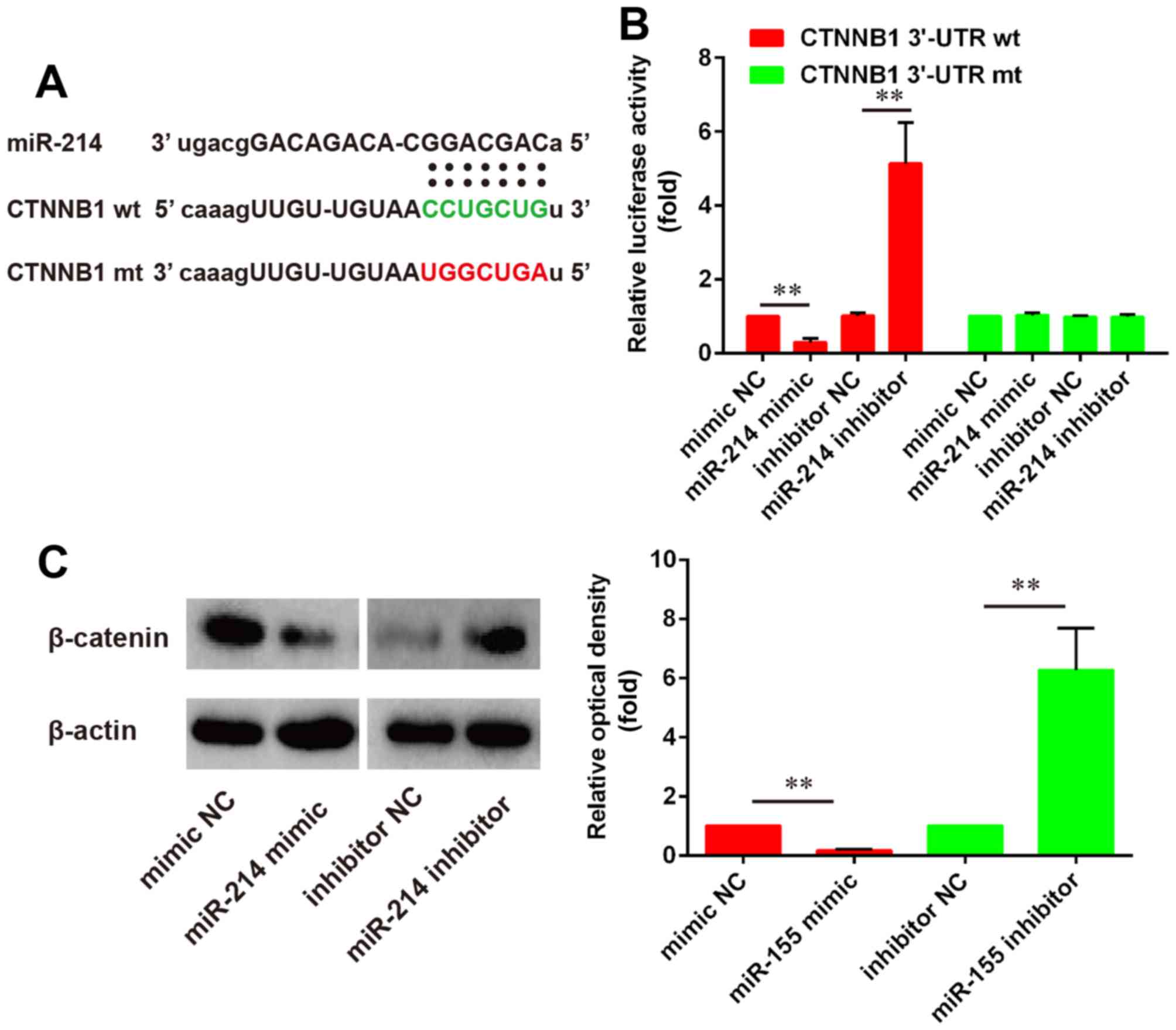
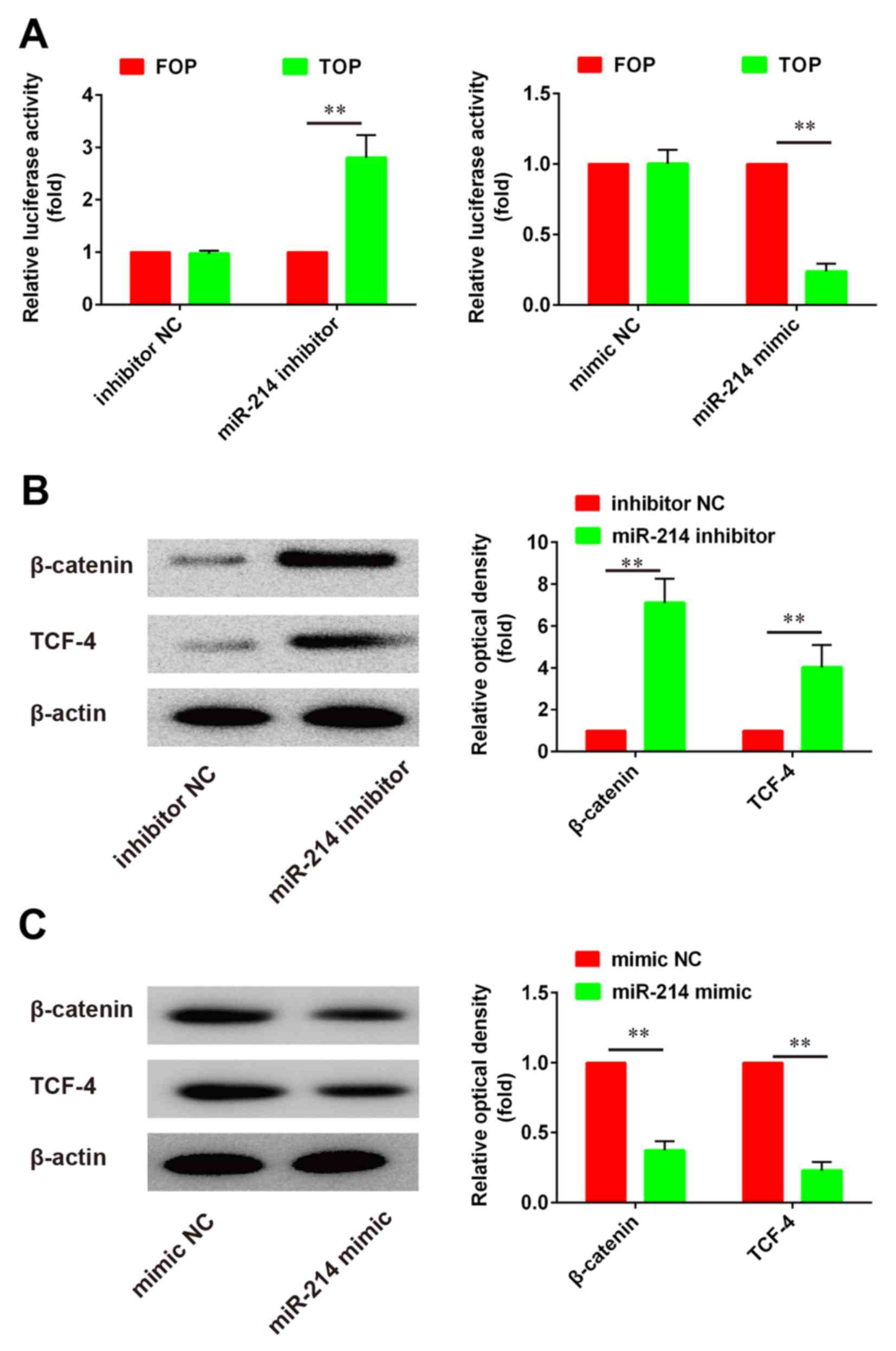
|
1
|
Armitage GC: Periodontal diagnoses and
classification of periodontal diseases. Periodontol. 34:9–21. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hiraga T, Ninomiya T, Hosoya A, Takahashi
M and Nakamura H: Formation of bone-like mineralized matrix by
periodontal ligament cells in vivo: A morphological study in rats.
J Bone Miner Metab. 27:149–157. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang GT, Gronthos S and Shi S:
Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from
other sources: Their biology and role in regenerative medicine. J
Dent Res. 88:792–806. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kato T, Hattori K, Deguchi T, Katsube Y,
Matsumoto T, Ohgushi H and Numabe Y: Osteogenic potential of rat
stromal cells derived from periodontal ligament. J Tissue Eng Regen
Med. 5:798–805. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lamplot JD, Qin J, Nan G, Wang J, Liu X,
Yin L, Tomal J, Li R, Shui W, Zhang H, et al: BMP9 signaling in
stem cell differentiation and osteogenesis. Am J Stem Cells.
2:1–21. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Coleman DT, Gray AL, Stephens CA, Scott ML
and Cardelli JA: Repurposed drug screen identifies cardiac
glycosides as inhibitors of TGF-β-induced cancer-associated
fibroblast differentiation. Oncotarget. 7:32200–32209. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ishitani T, Kishida S, Hyodo-Miura J, Ueno
N, Yasuda J, Waterman M, Shibuya H, Moon RT, Ninomiya-Tsuji J and
Matsumoto K: The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade
functions in the Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway to antagonize
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 23:131–139. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boland GM, Perkins G, Hall DJ and Tuan RS:
Wnt 3a promotes proliferation and suppresses osteogenic
differentiation of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell
Biochem. 93:1210–1230. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hartmann C and Tabin CJ: Dual roles of Wnt
signaling during chondrogenesis in the chicken limb. Development.
127:3141–3159. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN,
Lucas PC, Erickson RL and MacDougald OA: Inhibition of adipogenesis
by Wnt signaling. Science. 289:950–953. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shang Y, Zhang C, Wang S, Xiong F, Zhao C,
Peng F, Feng S, Yu M, Li M and Zhang Y: Activated beta-catenin
induces myogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis in BM-derived
mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 9:667–681. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mizuno Y, Yagi K, Tokuzawa Y,
Kanesaki-Yatsuka Y, Suda T, Katagiri T, Fukuda T, Maruyama M, Okuda
A, Amemiya T, et al: miR-125b inhibits osteoblastic differentiation
by down-regulation of cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 368:267–272. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang H, Li X, Wang L, Yu S, Xu Z, Gu Y,
Pan Z, Li T, Hu M, Cui H, et al: MicroRNAs contribute to
promyelocyte apoptosis in As2O3-treated APL cells. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 32:1818–1829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng J, Iwama A, Satake M and Kohu K:
MicroRNA-27 enhances differentiation of myeloblasts into
granulocytes by post-transcriptionally downregulating Runx1. Br J
Haematol. 145:412–423. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McDaneld TG, Smith TP, Doumit ME, Miles
JR, Coutinho LL, Sonstegard TS, Matukumalli LK, Nonneman DJ and
Wiedmann RT: MicroRNA transcriptome profiles during swine skeletal
muscle development. BMC Genomics. 10:772009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou Q, Zhao ZN, Cheng JT, Zhang B, Xu J,
Huang F, Zhao RN and Chen YJ: Ibandronate promotes osteogenic
differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells by regulating
the expression of microRNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
404:127–132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, Bartold PM,
Batouli S, Brahim J, Young M, Robey PG, Wang CY and Shi S:
Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human
periodontal ligament. Lancet. 364:149–155. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li B, Qu C, Chen C, Liu Y, Akiyama K, Yang
R, Chen F, Zhao Y and Shi S: Basic fibroblast growth factor
inhibits osteogenic differentiation of stem cells from human
exfoliated deciduous teeth through ERK signaling. Oral Dis.
18:285–292. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Han L, Yang Y, Yue X, Huang K, Liu X, Pu
P, Jiang H, Yan W, Jiang T and Kang C: Inactivation of PI3K/AKT
signaling inhibits glioma cell growth through modulation of
β-catenin-mediated transcription. Brain Res. 1366:9–17. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jones-Rhoades MW and Bartel DP:
Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets,
including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol Cell. 14:787–799. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi K, Lu J, Zhao Y, Wang L, Li J, Qi B,
Li H and Ma C: MicroRNA-214 suppresses osteogenic differentiation
of C2C12 myoblast cells by targeting Osterix. Bone. 55:487–494.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang L, Ge D, Cao X, Ge Y, Chen H, Wang W
and Zhang H: MiR-214 Attenuates osteogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells via targeting FGFR1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:809–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Su J, Zhang A, Shi Z, Ma F, Pu P, Wang T,
Zhang J, Kang C and Zhang Q: MicroRNA-200a suppresses the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by interacting with β-catenin. Int
J Oncol. 40:1162–1170. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen H, Mo D, Li M, Zhang Y, Chen L, Zhang
X, Li M, Zhou X and Chen Y: miR-709 inhibits 3T3-L1 cell
differentiation by targeting GSK3β of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell
Signal. 26:2583–2589. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang T and Xu Z: miR-27 promotes
osteoblast differentiation by modulating Wnt signaling. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 402:186–189. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|