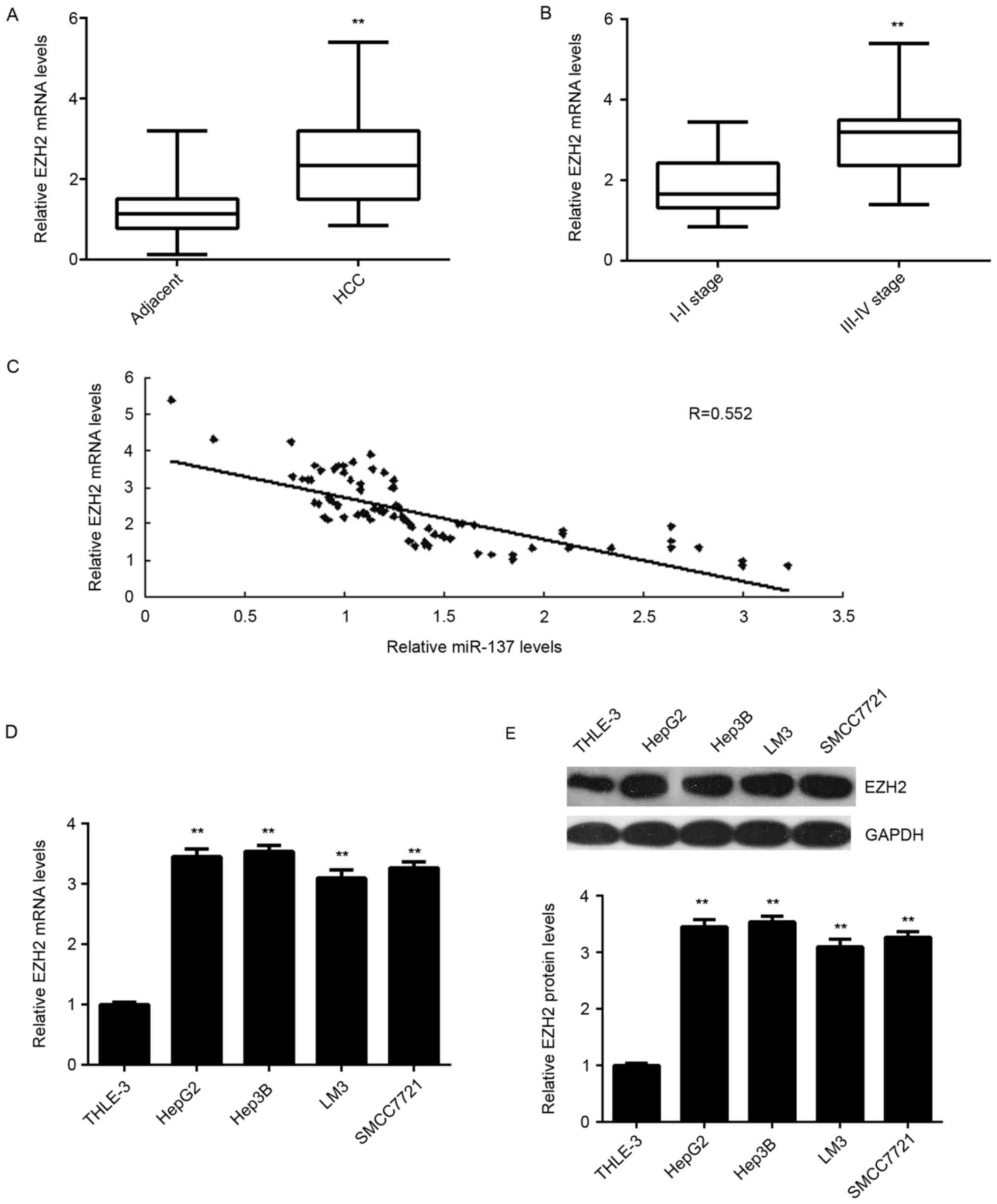
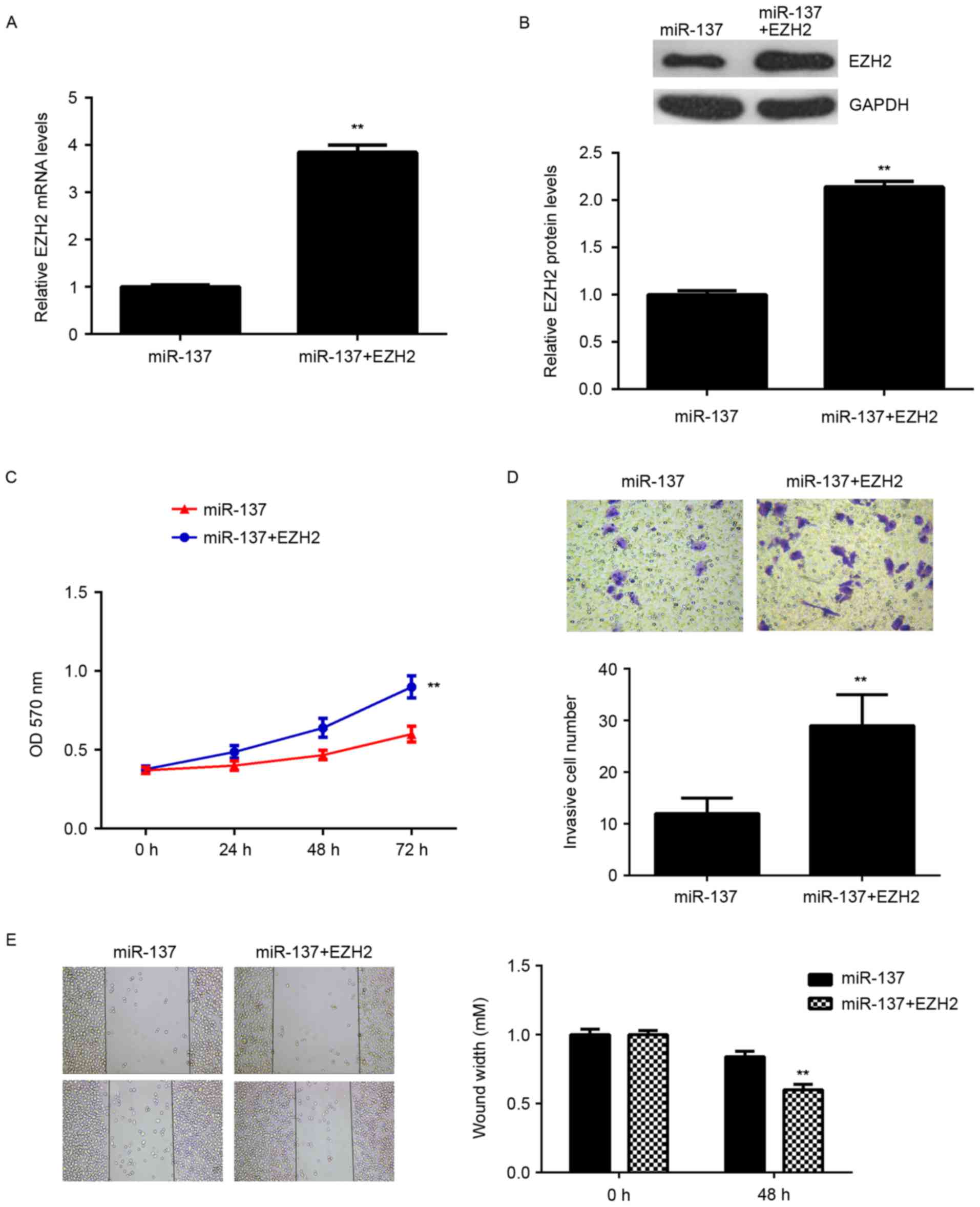
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moss EG: MicroRNAs: Hidden in the genome.
Curr Biol. 12:R138–R140. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li N, Fu H, Tie Y, Hu Z, Kong W, Wu Y and
Zheng X: miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulation
of c-Met expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer
Lett. 275:44–53. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang R, Deng L, Zhao L, Li X, Zhang F,
Xia Y, Gao Y, Wang X and Sun B: miR-22 promotes HBV-related
hepatocellular carcinoma development in males. Clin Cancer Res.
17:5593–5603. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dou C, Wang Y, Li C, Liu Z, Jia Y, Li Q,
Yang W, Yao Y, Liu Q and Tu K: MicroRNA-212 suppresses tumor growth
of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting FOXA1. Oncotarget.
6:13216–13228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang CY, Zhang JJ, Hua L, Yao KH, Chen JT
and Ren XQ: MicroRNA-98 suppresses cell proliferation, migration
and invasion by targeting collagen triple helix repeat containing 1
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:2639–2644. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen H, Wang L, Ge X, Jiang CF, Shi ZM, Li
DM, Liu WT, Yu X and Shu YQ: MicroRNA-137 inhibits tumor growth and
sensitizes chemosensitivity to paclitaxel and cisplatin in lung
cancer. Oncotarget. 7:20728–20742. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang ML, Hsieh TH, Ng KH, Tsai YN, Tsai
CF, Chao ME, Liu DJ, Chu SS, Chen W, Liu YR, et al: Downregulation
of miR-137 and miR-6500-3p promotes cell proliferation in pediatric
high-grade gliomas. Oncotarget. 7:19723–19737. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu DC, Zhang MF, Su SG, Fang HY, Wang XH,
He D, Xie YY and Liu XH: HEY2, a target of miR-137, indicates poor
outcomes and promotes cell proliferation and migration in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:38052–38063. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu LL, Lu SX, Li M, Li LZ, Fu J, Hu W,
Yang YZ, Luo RZ, Zhang CZ and Yun JP: FoxD3-regulated microRNA-137
suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting AKT2. Oncotarget. 5:5113–5124. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao M, Liu L, Li S, Zhang X, Chang Z and
Zhang M: Inhibition of cell proliferation and metastasis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma by miR-137 is regulated by CDC42. Oncol
Rep. 34:2523–2532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen DL, Wang DS, Wu WJ, Zeng ZL, Luo HY,
Qiu MZ, Ren C, Zhang DS, Wang ZQ, Wang FH, et al: Overexpression of
paxillin induced by miR-137 suppression promotes tumor progression
and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:803–811.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bier A, Giladi N, Kronfeld N, Lee HK,
Cazacu S, Finniss S, Xiang C, Poisson L, deCarvalho AC, Slavin S,
et al: MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits
the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting RTVP-1. Oncotarget.
4:665–676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng J, Lei W, Xiang X, Zhang L, Lei J,
Gong Y, Song M, Wang Y, Fang Z, Yu F, et al: Cullin 4A (CUL4A), a
direct target of miR-9 and miR-137, promotes gastric cancer
proliferation and invasion by regulating the Hippo signaling
pathway. Oncotarget. 7:10037–10050. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang B, Ma L, Wei J, Hu J, Zhao Z, Wang
Y, Chen Y and Zhao F: miR-137 suppresses the phosphorylation of AKT
and improves the dexamethasone sensitivity in multiple myeloma
cells via targeting MITF. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 16:807–817.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong S, Jin M, Li Y, Ren P and Liu J:
miR-137 acts as a tumor suppressor in papillary thyroid carcinoma
by targeting CXCL12. Oncol Rep. 35:2151–2158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Italiano A: Role of the EZH2 histone
methyltransferase as a therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol
Ther. 165:26–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhong J, Min L, Huang H, Li L, Li D, Li J,
Ma Z and Dai L: EZH2 regulates the expression of p16 in the
nasopharyngeal cancer cells. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 12:269–274.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Ren K, Zhao G, Yan K and
Ma B: MicroRNA-101 inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by
downregulation of EZH2 expression. Oncol Rep. 32:2143–2149. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sudo T, Utsunomiya T, Mimori K, Nagahara
H, Ogawa K, Inoue H, Wakiyama S, Fujita H, Shirouzu K and Mori M:
Clinicopathological significance of EZH2 mRNA expression in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 92:1754–1758.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Au SL, Wong CC, Lee JM, Fan DN, Tsang FH,
Ng IO and Wong CM: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 epigenetically
silences multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs to promote liver
cancer metastasis. Hepatology. 56:622–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun J, Zheng G, Gu Z and Guo Z: MiR-137
inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of human glioblastoma cells
by targeting EZH2. J Neurooncol. 122:481–489. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ren X, Bai X, Zhang X, Li Z, Tang L, Zhao
X, Li Z, Ren Y, Wei S, Wang Q, et al: Quantitative nuclear
proteomics identifies that miR-137-mediated EZH2 reduction
regulates resveratrol-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 14:316–328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Luo C, Tetteh PW, Merz PR, Dickes E,
Abukiwan A, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Holland-Cunz S, Sinnberg T, Schittek
B, Schadendorf D, et al: miR-137 inhibits the invasion of melanoma
cells through downregulation of multiple oncogenic target genes. J
Invest Dermatol. 133:768–775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|