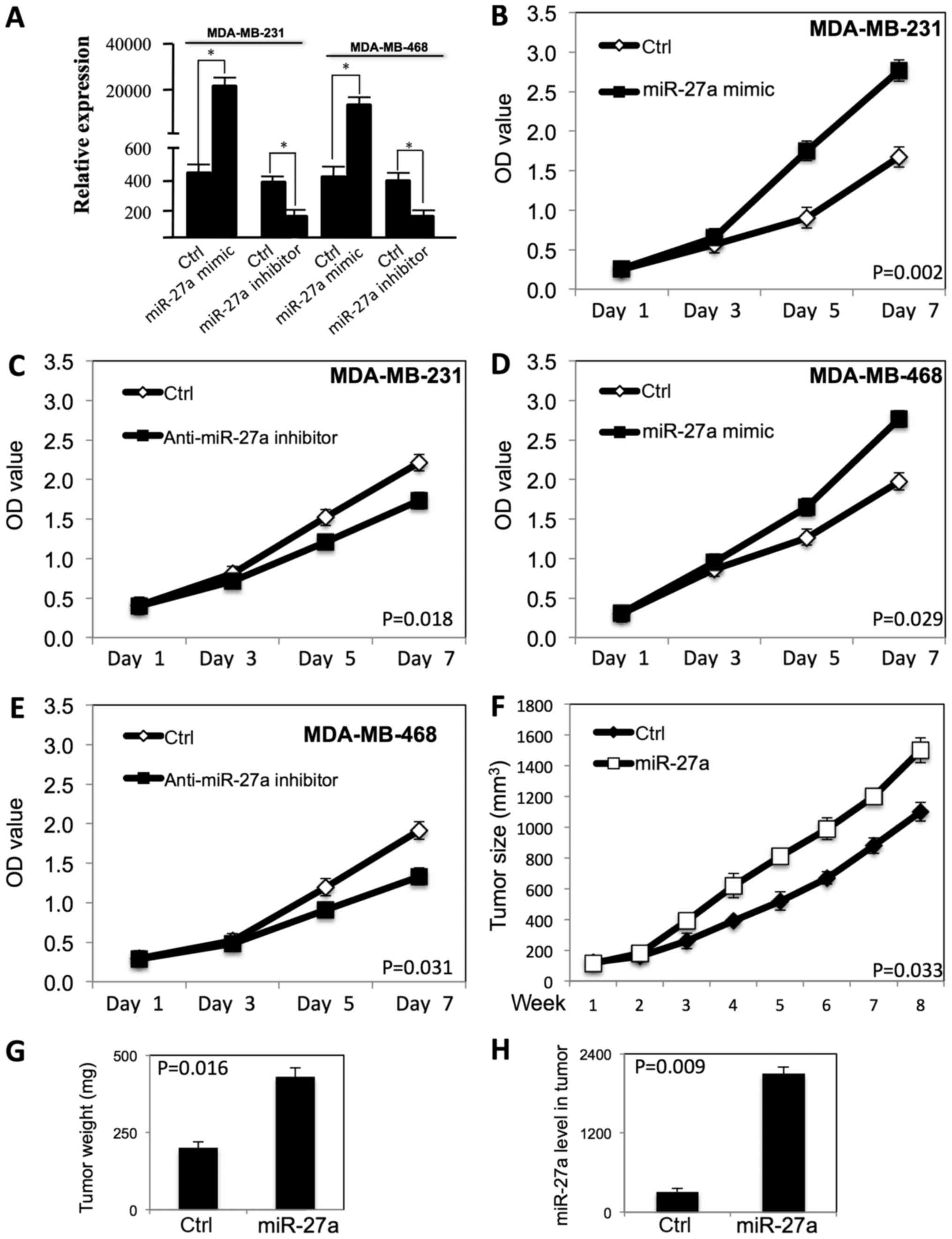
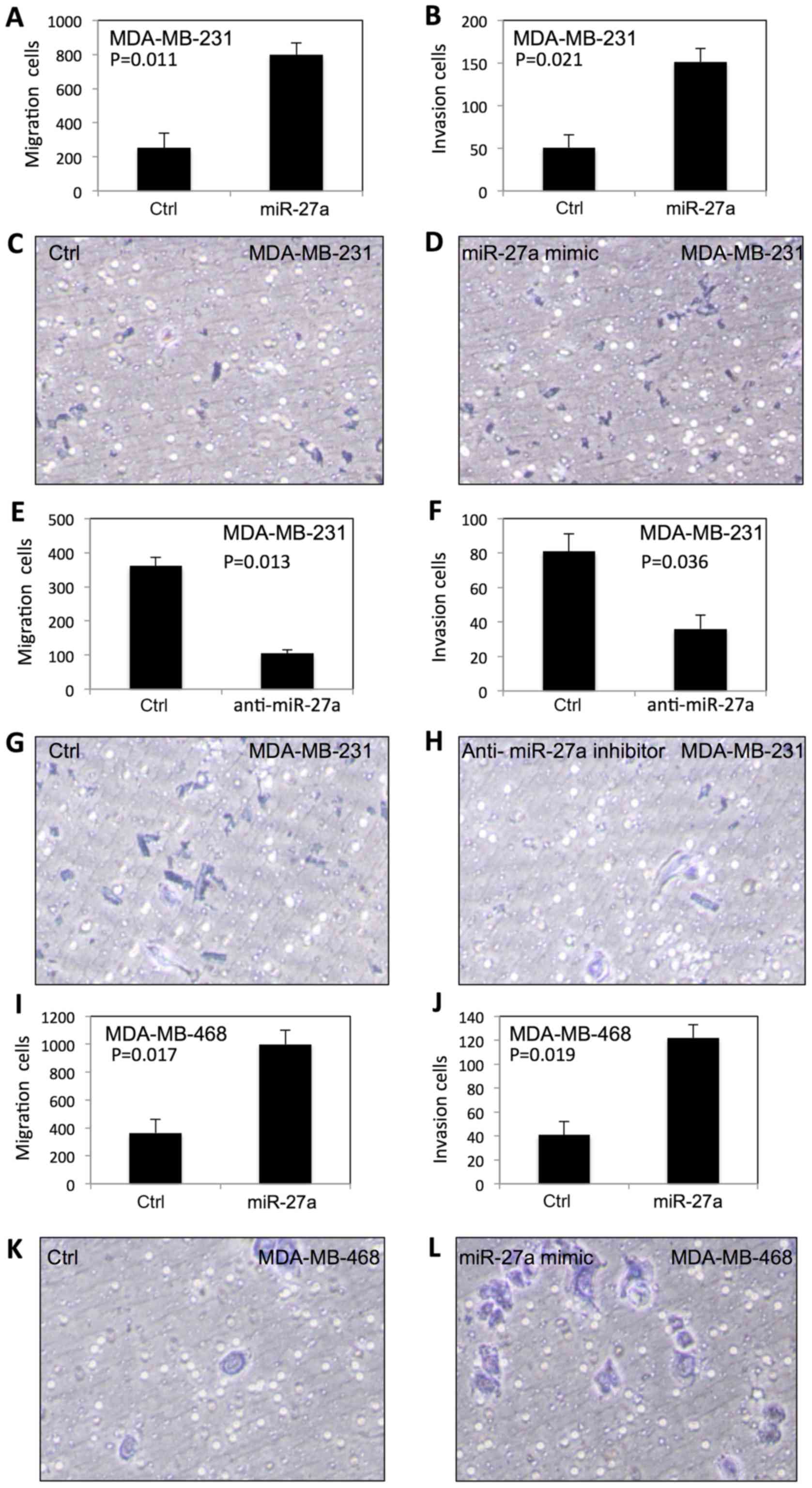
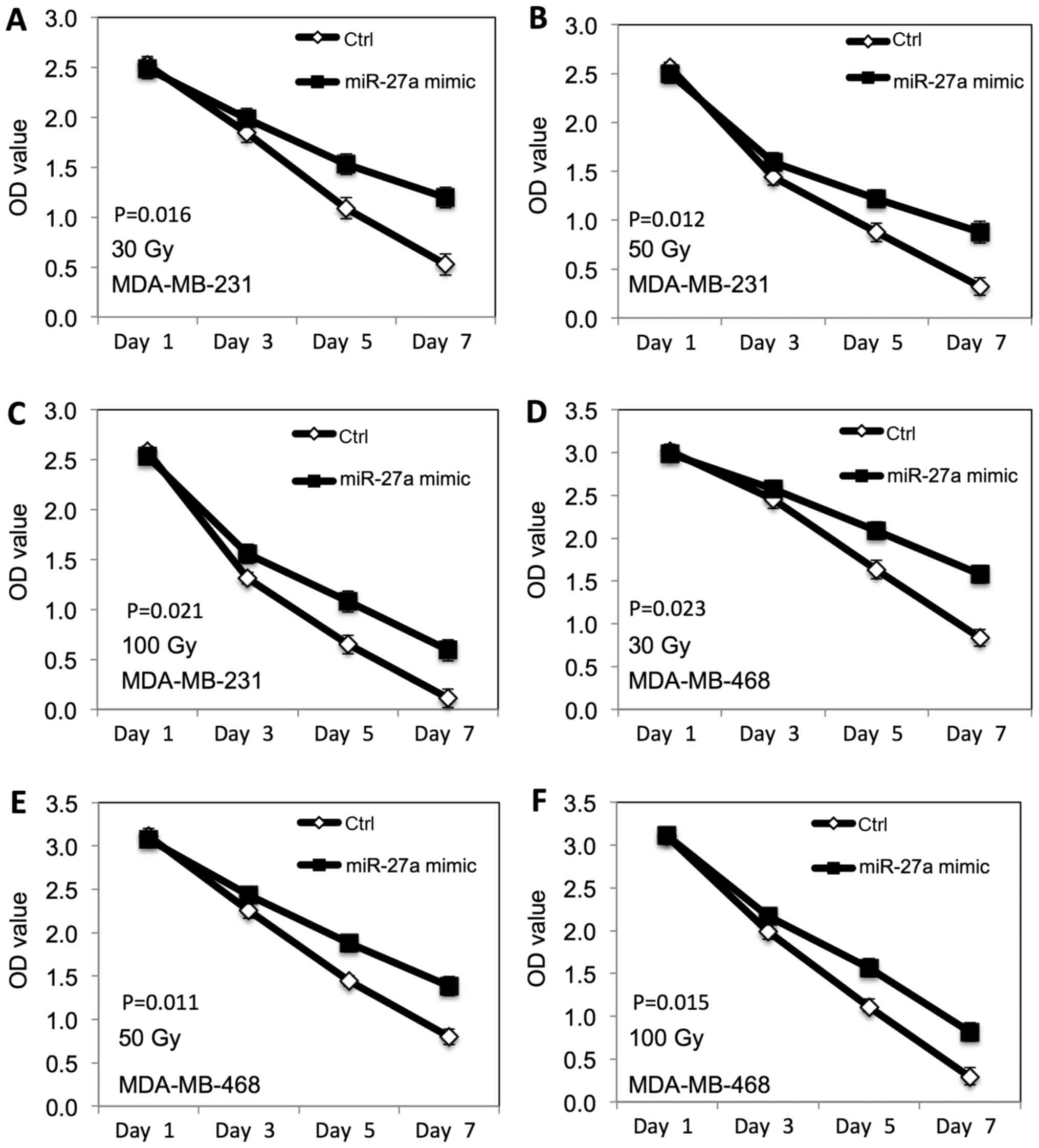
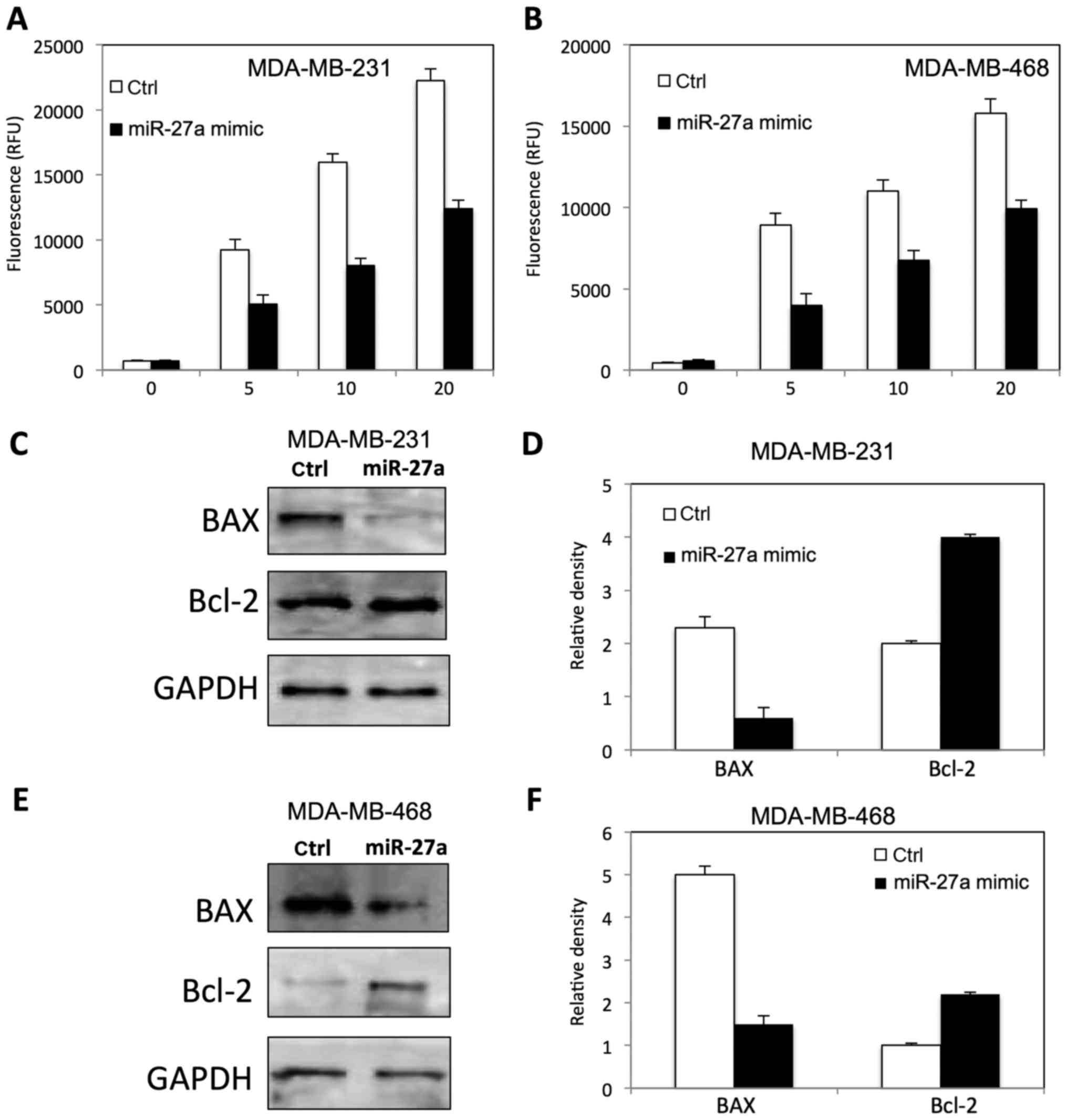
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Webb PM, Cummings MC, Bain CJ and Furnival
CM: Changes in survival after breast cancer: Improvements in
diagnosis or treatment? Breast. 13:7–14. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Di Leo A, Curigliano G, Diéras V, Malorni
L, Sotiriou C, Swanton C, Thompson A, Tutt A and Piccart M: New
approaches for improving outcomes in breast cancer in Europe.
Breast. 24:321–330. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
American Cancer Society: Breast Cancer.
http://www.cancer.org/cancer/breastcancer/detailedguide/breast-cancer-key-statistics
|
|
5
|
Boyle P: Triple-negative breast cancer:
Epidemiological considerations and recommendations. Ann Oncol. 23
Suppl 6:vi7–vi12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Negi P, Kingsley PA, Jain K, Sachdeva J,
Srivastava H, Marcus S and Pannu A: Survival of triple negative
versus triple positive breast cancers: Comparison and contrast.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:3911–3916. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Braicu C, Chiorean R, Irimie A, Chira S,
Tomuleasa C, Neagoe E, Paradiso A, Achimas-Cadariu P, Lazar V and
Berindan-Neagoe I: Novel insight into triple-negative breast
cancers, the emerging role of angiogenesis, and antiangiogenic
therapy. Expert Rev Mol Med. 18:e182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Linklater ES, Tovar EA, Essenburg CJ,
Turner L, Madaj Z, Winn ME, Melnik MK, Korkaya H, Maroun CR,
Christensen JG, et al: Targeting MET and EGFR crosstalk signaling
in triple-negative breast cancers. Oncotarget. 7:69903–69915.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gray MJ, Gong J, Hatch MM, Nguyen V,
Hughes CC, Hutchins JT and Freimark BD:
Phosphatidylserine-targeting antibodies augment the
anti-tumorigenic activity of anti-PD-1 therapy by enhancing immune
activation and downregulating pro-oncogenic factors induced by
T-cell checkpoint inhibition in murine triple-negative breast
cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 18:502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xue J, Yang J, Luo M, Cho WC and Liu X:
MicroRNA-targeted therapeutics for lung cancer treatment. Expert
Opin Drug Discov. 12:141–157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Canlorbe G, Wang Z, Laas E, Bendifallah S,
Castela M, Lefevre M, Chabbert-Buffet N, Daraï E, Aractingi S,
Méhats C and Ballester M: Identification of microRNA expression
profile related to lymph node status in women with early-stage
grade 1–2 endometrial cancer. Mod Pathol. 29:391–401. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mullany LE, Herrick JS, Wolff RK, Buas MF
and Slattery ML: Impact of polymorphisms in microRNA biogenesis
genes on colon cancer risk and microRNA expression levels: A
population-based, case-control study. BMC Med Genomics. 9:212016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang TH, Wu F, Loeb GB, Hsu R,
Heidersbach A, Brincat A, Horiuchi D, Lebbink RJ, Mo YY, Goga A and
McManus MT: Up-regulation of miR-21 by HER2/neu signaling promotes
cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 284:18515–18524. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu J, Mao Q, Liu Y, Hao X, Zhang S and
Zhang J: Analysis of miR-205 and miR-155 expression in the blood of
breast cancer patients. Chin J Cancer Res. 25:46–54.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Cai Q, Bao PP, Su Y, Cai H, Wu J,
Ye F, Guo X, Zheng W, Zheng Y and Shu XO: Tumor tissue microRNA
expression in association with triple-negative breast cancer
outcomes. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 152:183–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng Y, Chen F, Melamed J, Chiriboga L,
Wei J, Kong X, McLeod M, Li Y, Li CX, Feng A, et al: Distinct
nuclear and cytoplasmic functions of androgen receptor cofactor p44
and association with androgen-independent prostate cancer. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:5236–5241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu
W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL and Massagué J: Genes
that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature. 436:518–524.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gottardo F, Liu CG, Ferracin M, Calin GA,
Fassan M, Bassi P, Sevignani C, Byrne D, Negrini M, Pagano F, et
al: Micro-RNA profiling in kidney and bladder cancers. Urol Oncol.
25:387–392. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mertens-Talcott SU, Chintharlapalli S, Li
X and Safe S: The oncogenic microRNA-27a targets genes that
regulate specificity protein transcription factors and the G2-M
checkpoint in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
67:11001–11011. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu T, Tang H, Lang Y, Liu M and Li X:
MicroRNA-27a functions as an oncogene in gastric adenocarcinoma by
targeting prohibitin. Cancer Lett. 273:233–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS,
Meyers C and Zheng ZM: Aberrant expression of oncogenic and
tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for
cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 3:e25572008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pan W, Wang H, Jianwei R and Ye Z:
MicroRNA-27a promotes proliferation, migration and invasion by
targeting MAP2K4 in human osteosarcoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem.
33:402–412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi R and Zhao G: miR-27
promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Genet. 204:486–491.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kong LY, Xue M, Zhang QC and Su CF: In
vivo and in vitro effects of microRNA-27a on proliferation,
migration and invasion of breast cancer cells through targeting of
SFRP1 gene via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget.
8:15507–15519. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Drayton RM, Dudziec E, Peter S, Bertz S,
Hartmann A, Bryant HE and Catto JW: Reduced expression of miRNA-27a
modulates cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer by targeting the
cystine/glutamate exchanger SLC7A11. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1990–2000.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang W, Zhu J, Su S, Wu W, Liu Q, Su F and
Yu F: MiR-27 as a prognostic marker for breast cancer progression
and patient survival. PLoS One. 7:e517022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dent R, Hanna WM, Trudeau M, Rawlinson E,
Sun P and Narod SA: Pattern of metastatic spread in triple-negative
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 115:423–428. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board:
Childhood craniopharyngioma treatment (PDQ®): Health
professional versionIn: PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. National
Cancer Institute (US); Bethesda, MD: 2002
|
|
31
|
Abdulkarim BS, Cuartero J, Hanson J,
Deschênes J, Lesniak D and Sabri S: Increased risk of locoregional
recurrence for women with T1-2N0 triple-negative breast cancer
treated with modified radical mastectomy without adjuvant radiation
therapy compared with breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol.
29:2852–2858. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cully M, You H, Levine AJ and Mak TW:
Beyond PTEN mutations: The PI3K pathway as an integrator of
multiple inputs during tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:184–192.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
López-Knowles E, O'Toole SA, McNeil CM,
Millar EK, Qiu MR, Crea P, Daly RJ, Musgrove EA and Sutherland RL:
PI3K pathway activation in breast cancer is associated with the
basal-like phenotype and cancer-specific mortality. Int J Cancer.
126:1121–1131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|