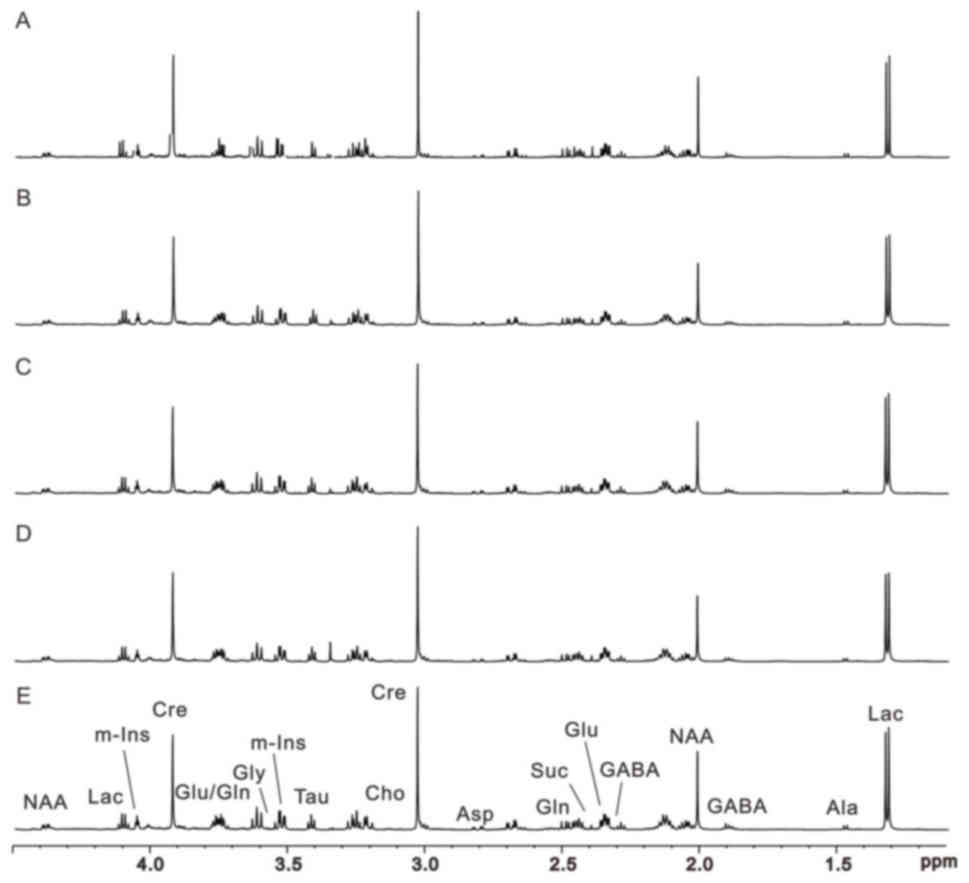
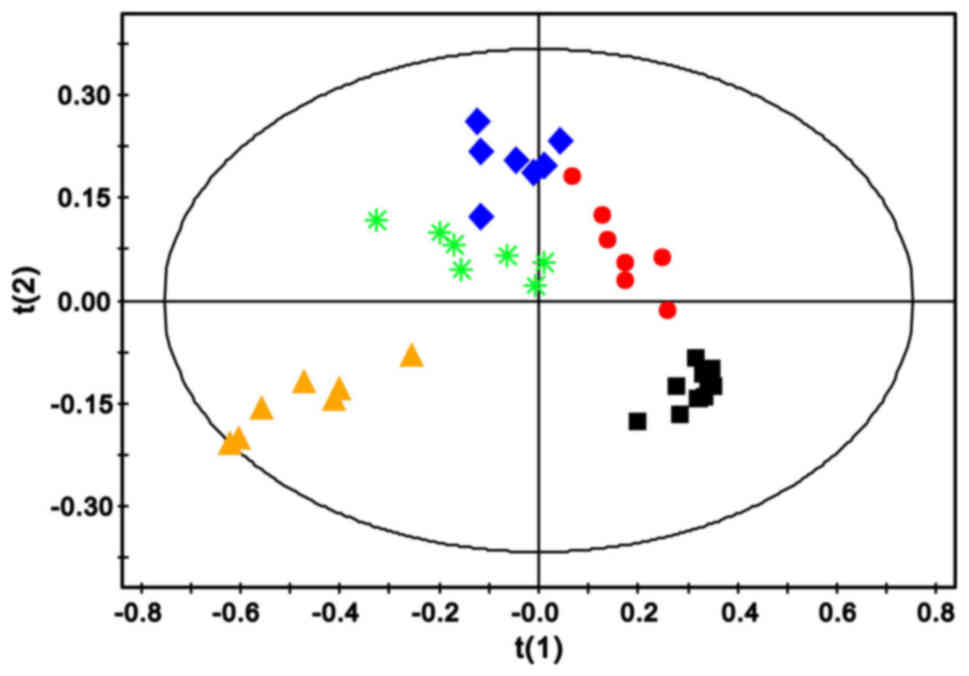
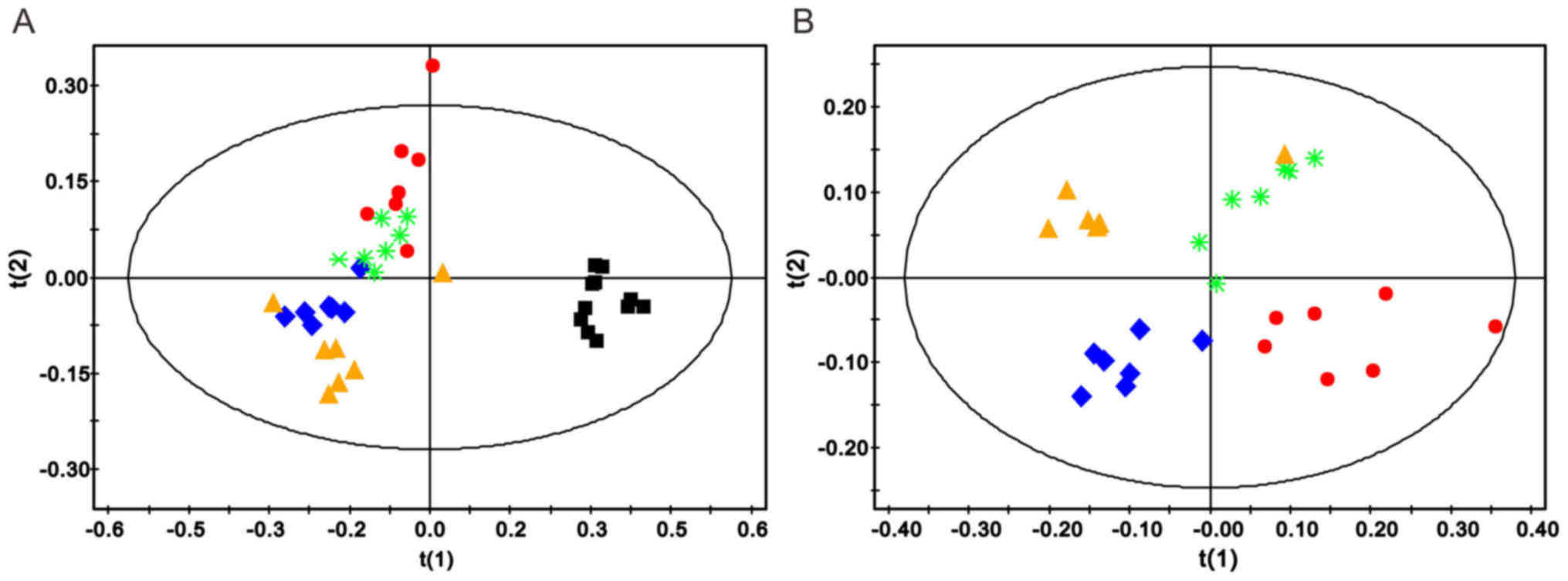
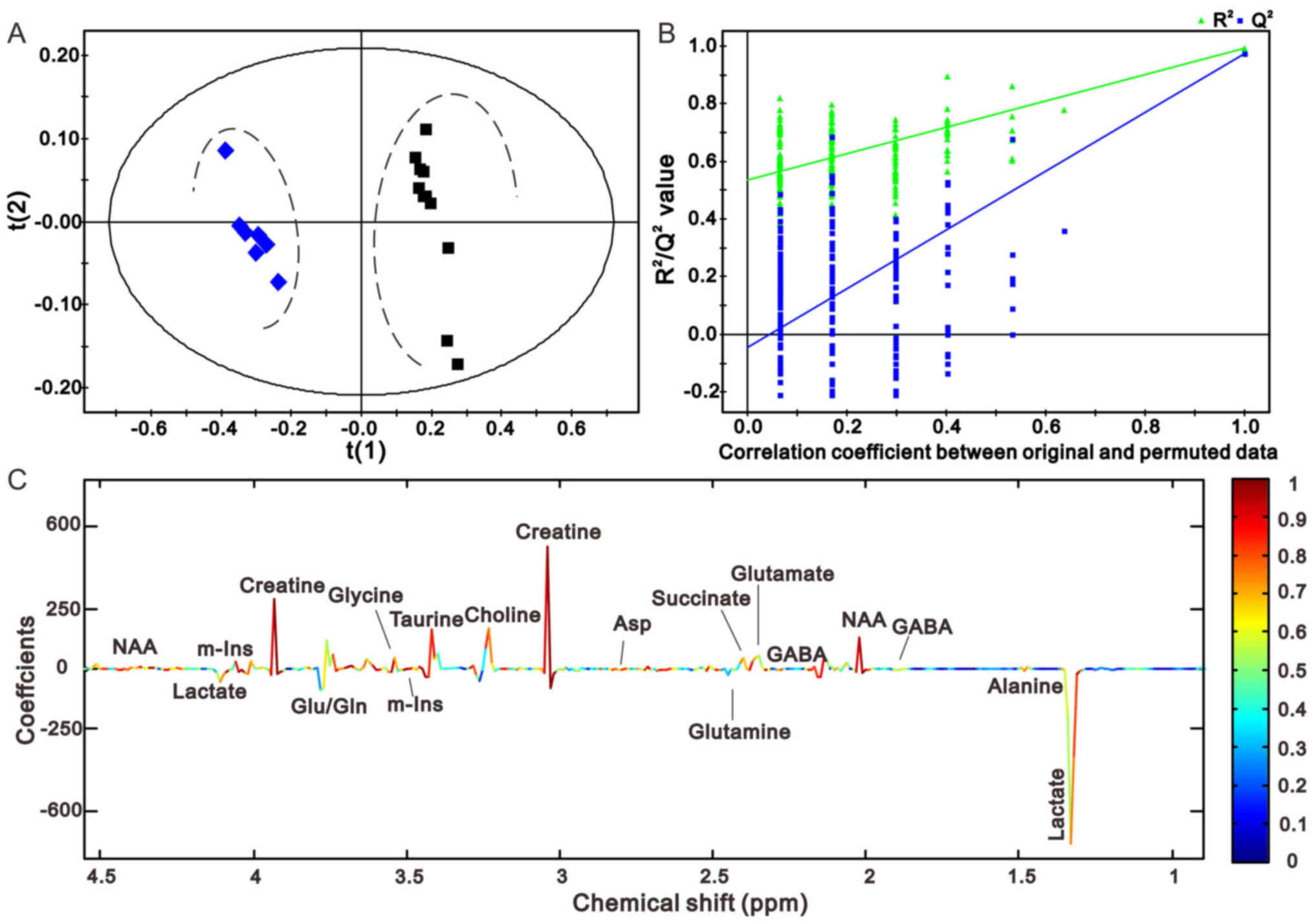
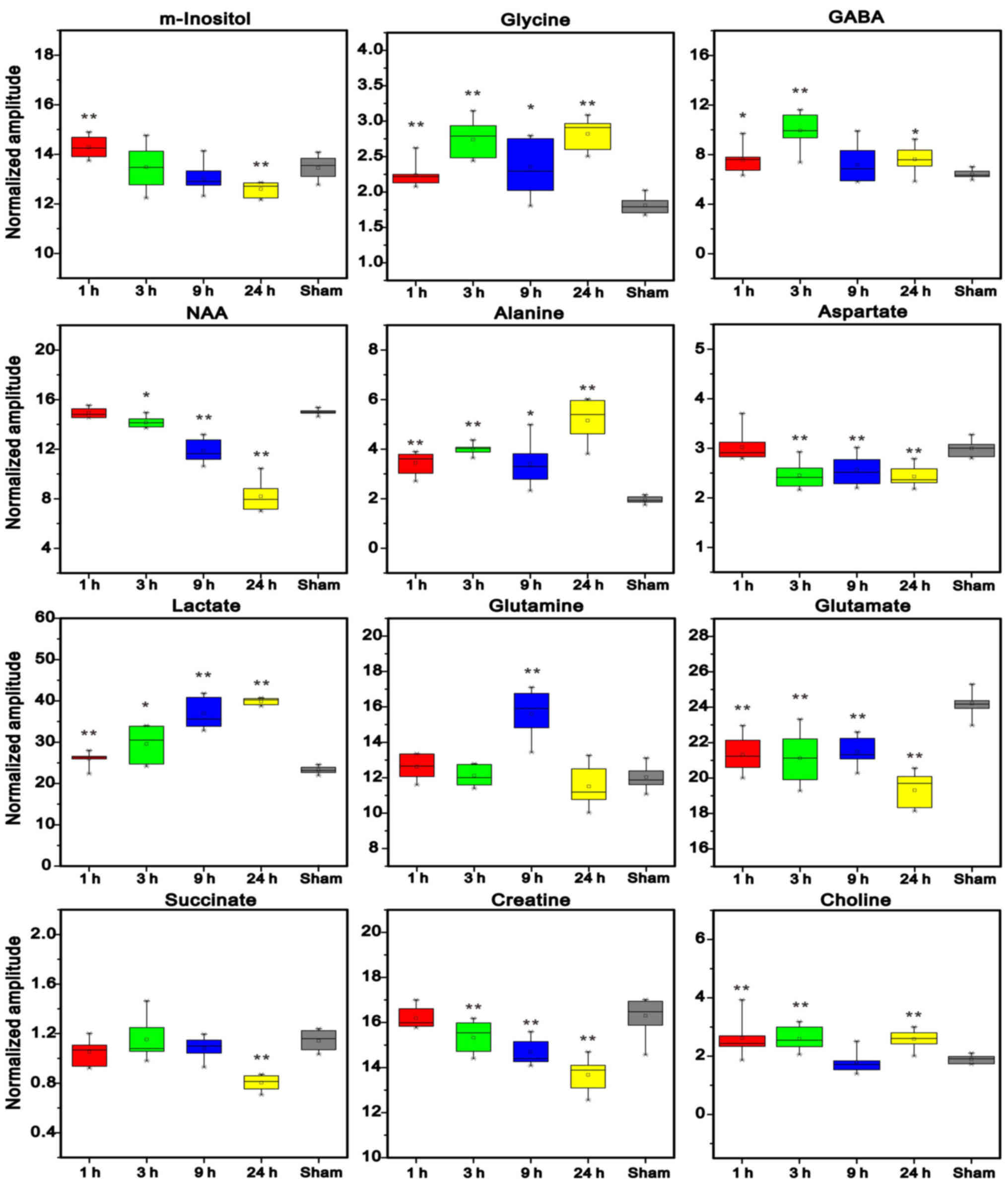
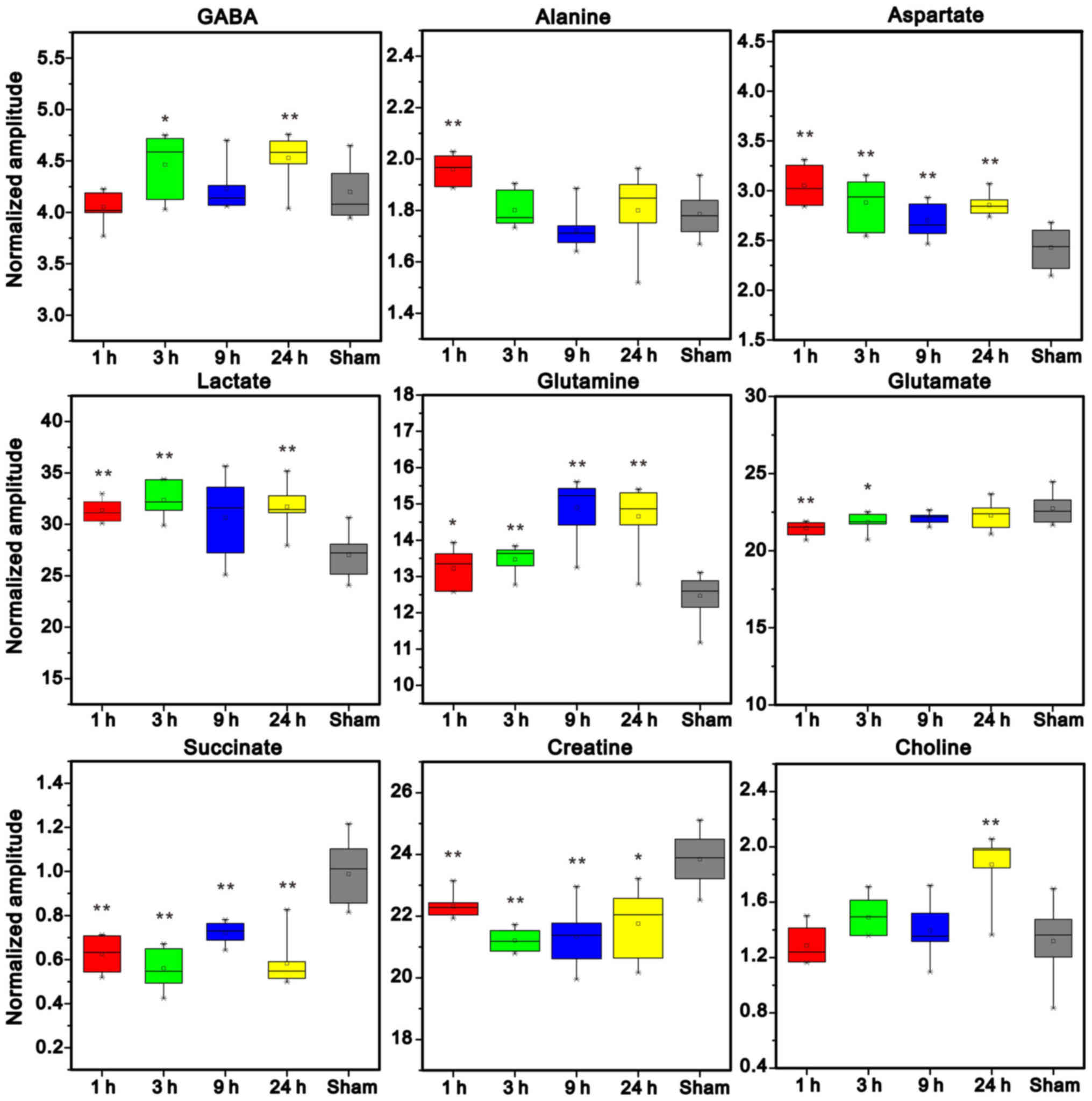
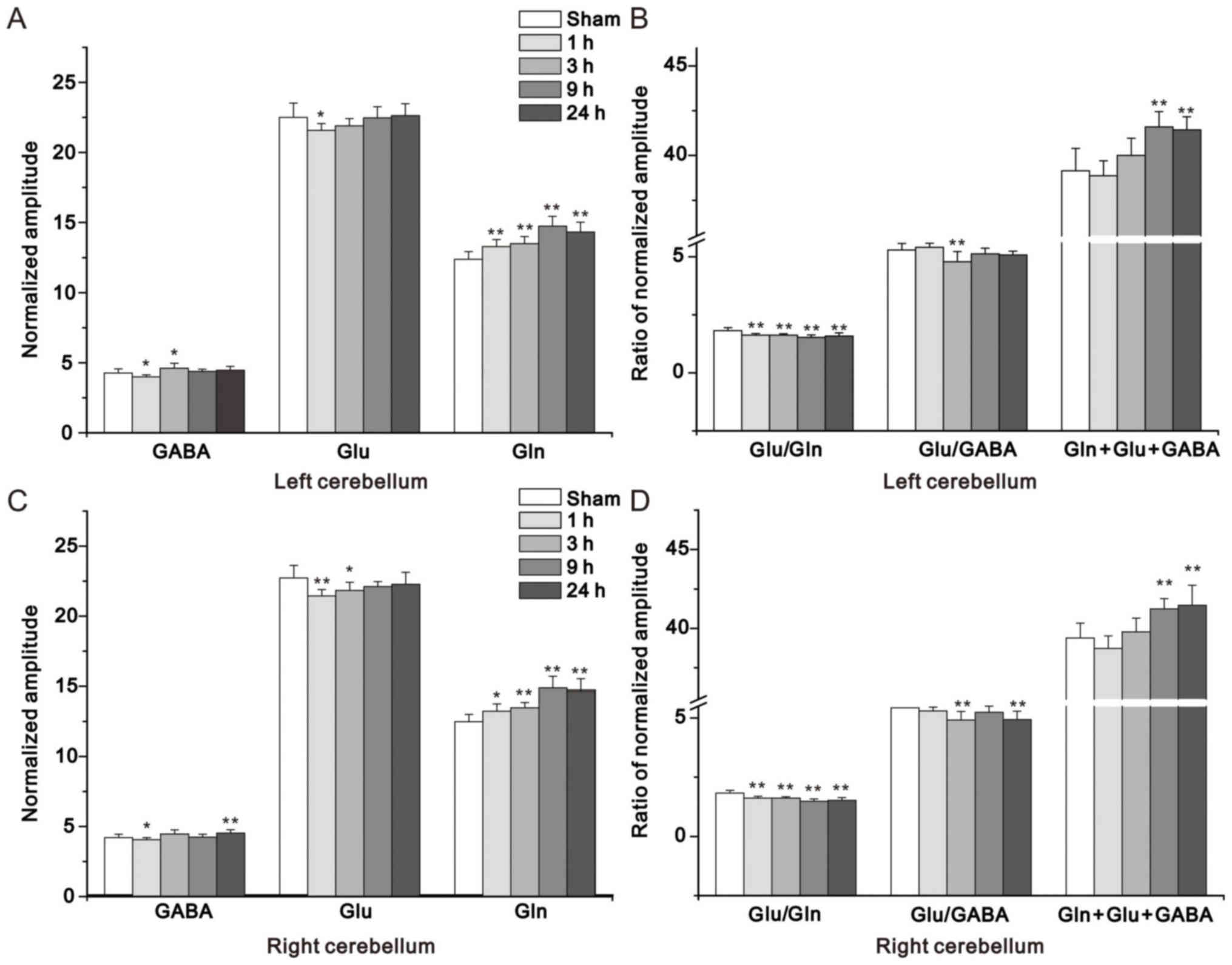
|
1
|
Håberg AK, Qu H and Sonnewald U: Acute
changes in intermediary metabolism in cerebellum and contralateral
hemisphere following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat. J
Neurochem. 109 Suppl 1:S174–S181. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Baron JC, Bousser MG, Comar D and
Castaigne P: ‘Crossed cerebellar diaschisis’ in human
supratentorial brain infarction. Trans Am Neurol Assoc.
105:459–461. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pantano P, Baron JC, Samson Y, Bousser MG,
Derouesne C and Comar D: Crossed cerebellar diaschisis. Further
studies. Brain. 109:677–694. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Meyer JS, Obara K and Muramatsu K:
Diaschisis. Neurol Res. 15:362–366. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gold L and Lauritzen M: Neuronal
deactivation explains decreased cerebellar blood flow in response
to focal cerebral ischemia or suppressed neocortical function. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:7699–7704. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rubin G, Levy EI, Scarrow AM, Firlik AD,
Karakus A, Wechsler L, Jungreis CA and Yonas H: Remote effects of
acute ischemic stroke: A xenon CT cerebral blood flow study.
Cerebrovasc Dis. 10:221–228. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meneghetti G, Vorstrup S, Mickey B,
Lindewald H and Lassen NA: Crossed cerebellar diaschisis in
ischemic stroke: A study of regional cerebral blood flow by 133Xe
inhalation and single photon emission computerized tomography. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 4:235–240. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ito H, Kanno I, Shimosegawa E, Tamura H,
Okane K and Hatazawa J: Hemodynamic changes during neural
deactivation in human brain: A positron emission tomography study
of crossed cerebellar diaschisis. Ann Nucl Med. 16:249–254. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Y, Karonen JO, Nuutinen J, Vanninen E,
Kuikka JT and Vanninen RL: Crossed cerebellar diaschisis in acute
ischemic stroke: A study with serial SPECT and MRI. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 27:1724–1732. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin DD, Kleinman JT, Wityk RJ, Gottesman
RF, Hillis AE, Lee AW and Barker PB: Crossed cerebellar diaschisis
in acute stroke detected by dynamic susceptibility contrast MR
perfusion imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 30:710–715. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Madai VI, Altaner A, Stengl KL, Zaro-Weber
O, Heiss WD, von Samson-Himmelstjerna FC and Sobesky J: Crossed
cerebellar diaschisis after stroke: Can perfusion-weighted MRI show
functional inactivation? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 31:1493–1500.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jeon YW, Kim SH, Lee JY, Whang K, Kim MS,
Kim YJ and Lee MS: Brain Research Group: Dynamic CT perfusion
imaging for the detection of crossed cerebellar diaschisis in acute
ischemic stroke. Korean J Radiol. 13:12–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen S, Guan M, Lian HJ, Ma LJ, Shang JK,
He S, Ma MM, Zhang ML, Li ZY, Wang MY, et al: Crossed cerebellar
diaschisis detected by arterial spin-labeled perfusion magnetic
resonance imaging in subacute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc
Dis. 23:2378–2383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kang KM, Sohn CH, Kim BS, Kim YI, Choi SH,
Yun TJ, Kim JH, Park SW, Cheon GJ and Han MH: Correlation of
asymmetry indices measured by arterial spin-labeling MR imaging and
SPECT in patients with crossed cerebellar diaschisis. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 36:1662–1668. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Swanson RA, Sagar SM and Sharp FR:
Regional brain glycogen stores and metabolism during complete
global ischaemia. Neurol Res. 11:24–28. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pouwels PJ and Frahm J: Regional
metabolite concentrations in human brain as determined by
quantitative localized proton MRS. Magn Reson Med. 39:53–60. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Duarte JM, Lei H, Mlynárik V and Gruetter
R: The neurochemical profile quantified by in vivo 1H NMR
spectroscopy. Neuroimage. 61:342–362. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Emir UE, Auerbach EJ, Van De Moortele PF,
Marjańska M, Uğurbil K, Terpstra M, Tkáč I and Oz G: Regional
neurochemical profiles in the human brain measured by (1)H MRS at 7
T using local B(1) shimming. NMR Biomed. 25:152–160. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Szilágyi G, Vas A, Kerényi L, Nagy Z,
Csiba L and Gulyás B: Correlation between crossed cerebellar
diaschisis and clinical neurological scales. Acta Neurol Scand.
125:373–381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao H, Dong B, Liu X, Xuan H, Huang Y and
Lin D: Metabonomic profiling of renal cell carcinoma:
High-resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of
human serum with multivariate data analysis. Anal Chim Acta.
624:269–277. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Westerhuis JA, van Velzen EJ, Hoefsloot HC
and Smilde AK: Multivariate paired data analysis: Multilevel PLSDA
versus OPLSDA. Metabolomics. 6:119–128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cloarec O, Dumas ME, Trygg J, Craig A,
Barton RH, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK and Holmes E: Evaluation of the
orthogonal projection on latent structure model limitations caused
by chemical shift variability and improved visualization of
biomarker changes in 1H NMR spectroscopic metabonomic studies. Anal
Chem. 77:517–526. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao H, Xiang Y, Sun N, Zhu H, Wang Y, Liu
M, Ma Y and Lei H: Metabolic changes in rat prefrontal cortex and
hippocampus induced by chronic morphine treatment studied ex vivo
by high resolution 1H NMR spectroscopy. Neurochem Int. 50:386–394.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Katsura K, de Turco Rodriguez EB,
Folbergrová J, Bazan NG and Siesjö BK: Coupling among energy
failure, loss of ion homeostasis, and phospholipase A2 and C
activation during ischemia. J Neurochem. 61:1677–1684. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Igarashi H, Kwee IL, Nakada T, Katayama Y
and Terashi A: 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of
permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rat: Longitudinal metabolic
changes in ischemic core and rim. Brain Res. 907:208–221. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Frykholm P, Hillered L, Långström B,
Persson L, Valtysson J and Enblad P: Relationship between cerebral
blood flow and oxygen metabolism, and extracellular glucose and
lactate concentrations during middle cerebral artery occlusion and
reperfusion: A microdialysis and positron emission tomography study
in nonhuman primates. J Neurosurg. 102:1076–1084. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brouns R, Sheorajpanday R, Wauters A, De
Surgeloose D, Mariën P and De Deyn PP: Evaluation of lactate as a
marker of metabolic stress and cause of secondary damage in acute
ischemic stroke or TIA. Clin Chim Acta. 397:27–31. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cvoro V, Wardlaw JM, Marshall I, Armitage
PA, Rivers CS, Bastin ME, Carpenter TK, Wartolowska K, Farrall AJ
and Dennis MS: Associations between diffusion and perfusion
parameters, N-acetyl aspartate, and lactate in acute ischemic
stroke. Stroke. 40:767–772. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bruhn H, Frahm J, Gyngell ML, Merboldt KD,
Hänicke W and Sauter R: Cerebral metabolism in man after acute
stroke: New observations using localized proton NMR spectroscopy.
Magn Reson Med. 9:126–131. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wardlaw JM, Marshall I, Wild J, Dennis MS,
Cannon J and Lewis SC: Studies of acute ischemic stroke with proton
magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Relation between time from onset,
neurological deficit, metabolite abnormalities in the infarct,
blood flow, and clinical outcome. Stroke. 29:1618–1624. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Federico F, Simone IL, Lucivero V,
Giannini P, Laddomada G, Mezzapesa DM and Tortorella C: Prognostic
value of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in ischemic stroke.
Arch Neurol. 55:489–494. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pereira AC, Saunders DE, Doyle VL, Bland
JM, Howe FA, Griffiths JR and Brown MM: Measurement of initial
N-acetyl aspartate concentration by magnetic resonance spectroscopy
and initial infarct volume by MRI predicts outcome in patients with
middle cerebral artery territory infarction. Stroke. 30:1577–1582.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Graham SH, Chen J, Sharp FR and Simon RP:
Limiting ischemic injury by inhibition of excitatory amino acid
release. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 13:88–97. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Melani A, Pantoni L, Corsi C, Bianchi L,
Monopoli A, Bertorelli R, Pepeu G and Pedata F: Striatal outflow of
adenosine, excitatory amino acids, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and
taurine in awake freely moving rats after middle cerebral artery
occlusion: Correlations with neurological deficit and
histopathological damage. Stroke. 30:2448–2455. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Iltis I, Koski DM, Eberly LE, Nelson CD,
Deelchand DK, Valette J, Ugurbil K, Lim KO and Henry PG:
Neurochemical changes in the rat prefrontal cortex following acute
phencyclidine treatment: An in vivo localized (1)H MRS study. NMR
Biomed. 22:737–744. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Håberg A, Qu H, Haraldseth O, Unsgård G
and Sonnewald U: In vivo injection of [1-13C]glucose and
[1,2-13C]acetate combined with ex vivo 13C nuclear magnetic
resonance spectroscopy: A novel approach to the study of middle
cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
18:1223–1232. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Barbaresi P, Fabri M, Conti F and Manzoni
T: D-[3H]aspartate retrograde labelling of callosal and association
neurones of somatosensory areas I and II of cats. J Comp Neurol.
263:159–178. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gyngell ML, Busch E, Schmitz B, Kohno K,
Back T, Hoehn-Berlage M and Hossmann KA: Evolution of acute focal
cerebral ischaemia in rats observed by localized 1H MRS,
diffusion-weighted MRI, and electrophysiological monitoring. NMR
Biomed. 8:206–214. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Berthet C, Xin L, Buscemi L, Benakis C,
Gruetter R, Hirt L and Lei H: Non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers
for estimating the onset time of permanent cerebral ischemia. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 34:1848–1855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Demougeot C, Marie C, Giroud M and Beley
A: N-acetylaspartate: A literature review of animal research on
brain ischaemia. J Neurochem. 90:776–783. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Miller BL: A review of chemical issues in
1H NMR spectroscopy: N-acetyl-L-aspartate, creatine and choline.
NMR Biomed. 4:47–52. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li S, Huang M, Wang X, Wang X, Chen F, Lei
H and Jiang F: Retinal metabolic changes in an experimental model
of optic nerve transection by ex vivo 1H magnetic resonance
spectroscopy. Neurochem Res. 36:2427–2433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cecil KM and Jones BV: Magnetic resonance
spectroscopy of the pediatric brain. Top Magn Reson Imaging.
12:435–452. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang M, Wang S, Hao F, Li Y, Tang H and
Shi X: NMR analysis of the rat neurochemical changes induced by
middle cerebral artery occlusion. Talanta. 88:136–144. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Alf MF, Lei H, Berthet C, Hirt L, Gruetter
R and Mlynarik V: High-resolution spatial mapping of changes in the
neurochemical profile after focal ischemia in mice. NMR Biomed.
25:247–254. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nonaka M, Yoshimine T, Kohmura E, Wakayama
A and Yamashita TTH: Changes in brain organic osmolytes in
experimental cerebral ischemia. J Neurol Sci. 157:25–30. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lowry OH, Passonneau JV, Hasselberger FX
and Schulz DW: Effect of ischemia on known substrates and cofactors
of the glycolytic pathway in brain. J Biol Chem. 239:18–30.
1964.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Petroff OA, Ogino T and Alger JR:
High-resolution proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of rabbit
brain: Regional metabolite levels and postmortem changes. J
Neurochem. 51:163–171. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kong J, Shepel PN, Holden CP, Mackiewicz
M, Pack AI and Geiger JD: Brain glycogen decreases with increased
periods of wakefulness: Implications for homeostatic drive to
sleep. J Neurosci. 22:5581–5587. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cruz NF and Dienel GA: High glycogen
levels in brains of rats with minimal environmental stimuli:
Implications for metabolic contributions of working astrocytes. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 22:1476–1489. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|