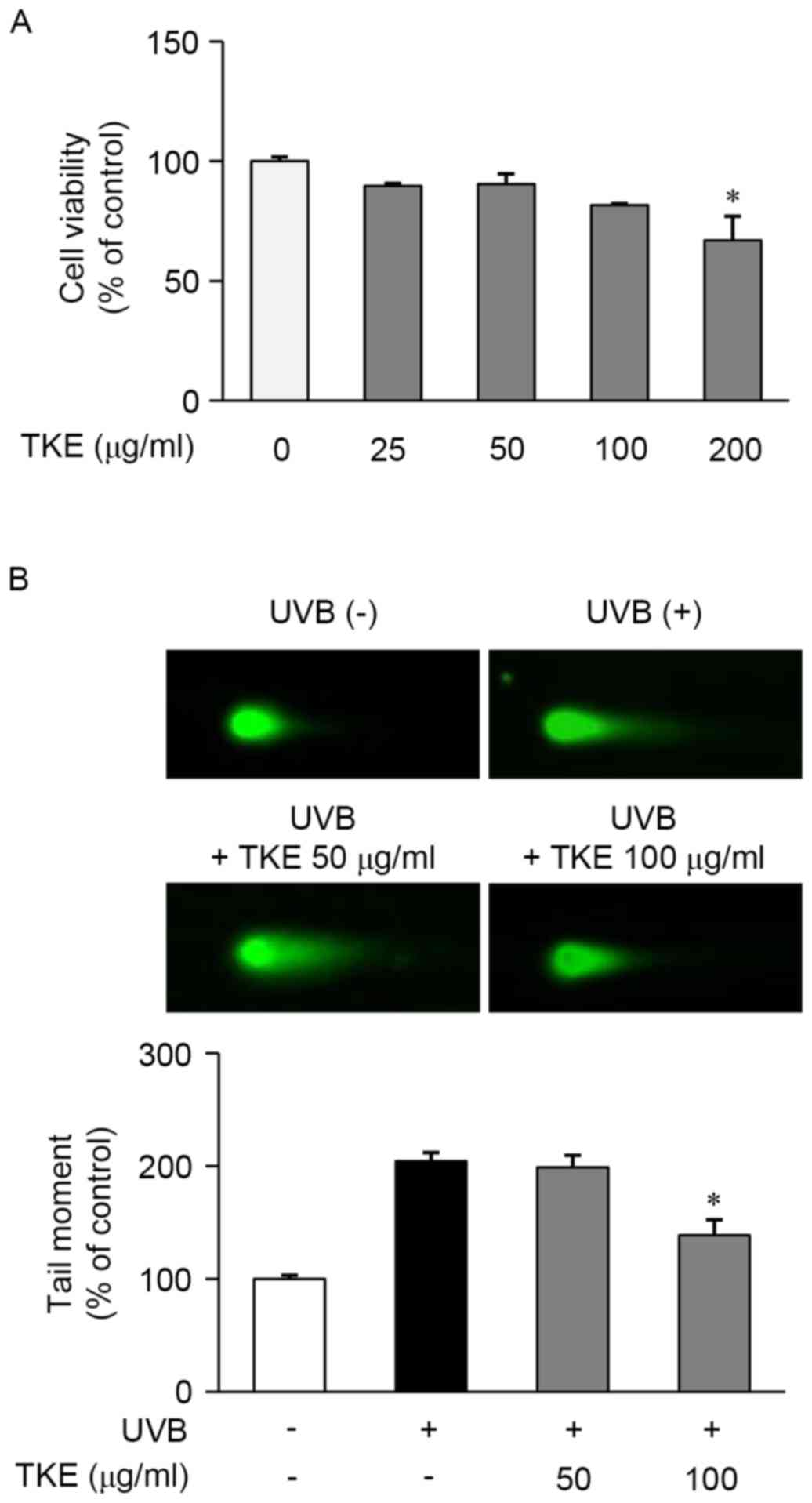
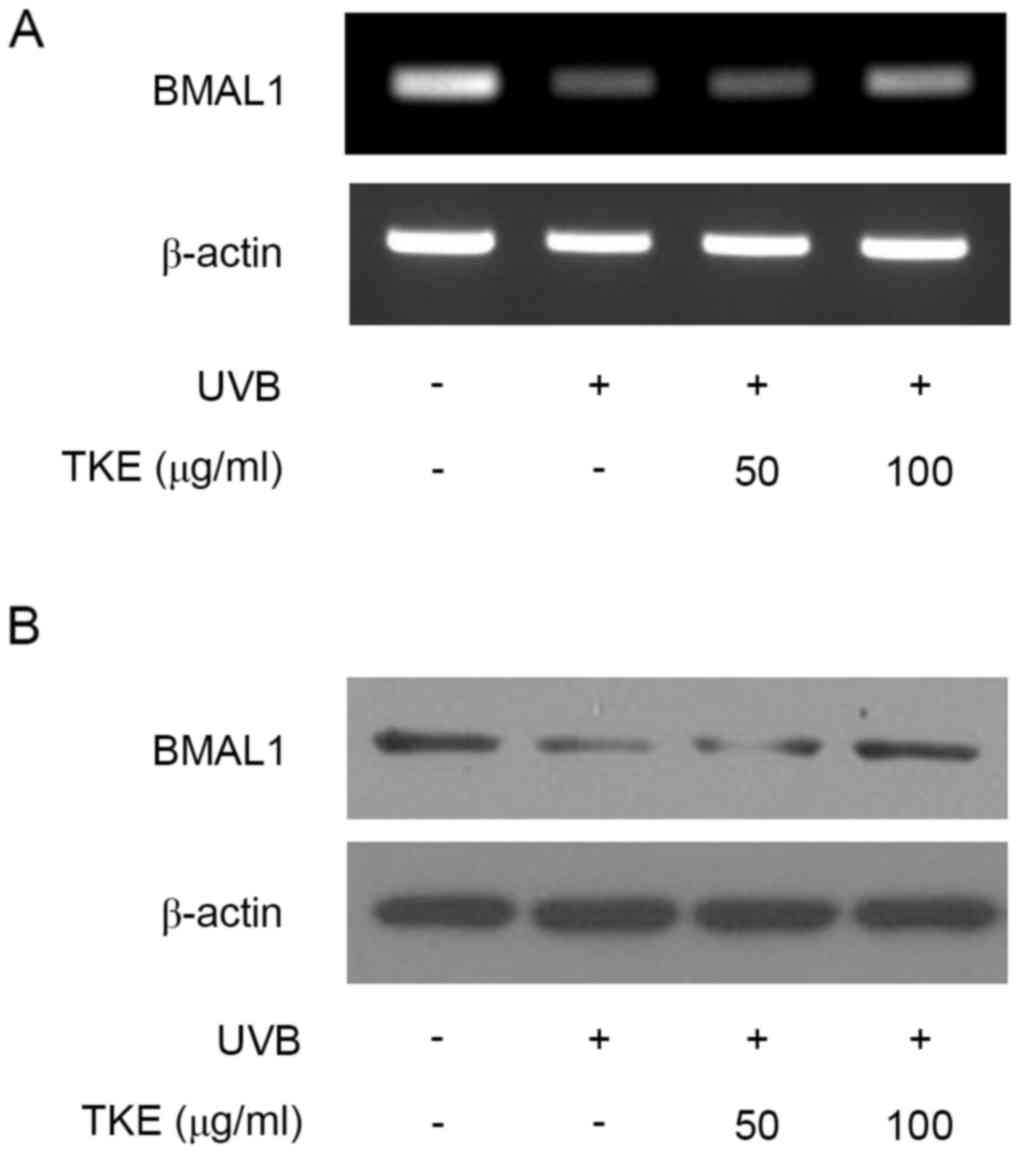
|
1
|
Sinha RP and Häder DP: UV-induced DNA
damage and repair: A review. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 1:225–236.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Kang TH,
Reardon JT, Lee JH and Ozturk N: Circadian clock control of the
cellular response to DNA damage. FEBS Lett. 584:2618–2625. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sancar A: DNA excision repair. Annu Rev
Biochem. 65:43–81. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Matsunaga N, Itcho K, Hamamura K, Ikeda E,
Ikeyama H, Furuichi Y, Watanabe M, Koyanagi S and Ohdo S: 24-Hour
rhythm of aquaporin-3 function in the epidermis is regulated by
molecular clocks. J Invest Dermatol. 134:1636–1644. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Watanabe M, Hida A, Kitamura S, Enomoto M,
Ohsawa Y, Katayose Y, Nozaki K, Moriguchi Y, Aritake S, Higuchi S,
et al: Rhythmic expression of circadian clock genes in human
leukocytes and beard hair follicle cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 425:902–907. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ando N, Nakamura Y, Aoki R, Ishimaru K,
Ogawa H, Okumura K, Shibata S, Shimada S and Nakao A: Circadian
gene clock regulates psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. J
Invest Dermatol. 135:3001–3008. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Desotelle JA, Wilking MJ and Ahmad N: The
circadian control of skin and cutaneous photodamage. Photochem
Photobiol. 88:1037–1047. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kang T and Sancar A: Circadian regulation
of DNA excision repair: Implications for chrono-chemotherapy. Cell
Cycle. 8:1665–1667. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gery S, Komatsu N, Baldjyan L, Yu A, Koo D
and Koeffler HP: The circadian gene per1 plays an important role in
cell growth and DNA damage control in human cancer cells. Mol Cell.
22:375–382. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kawara S, Mydlarski R, Mamelak AJ, Freed
I, Wang B, Watanabe H, Shivji G, Tavadia SK, Suzuki H, Bjarnason
GA, et al: Low-dose ultraviolet B rays alter the mRNA expression of
the circadian clock genes in cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest
Dermatol. 119:1220–1223. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ambros V and Lee RC: Identification of
microRNAs and other tiny noncoding RNAs by cDNA cloning. Methods
Mol Biol. 265:131–158. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hildebrand J, Rütze M, Walz N, Gallinat S,
Wenck H, Deppert W, Grundhoff A and Knott A: A comprehensive
analysis of microRNA expression during human keratinocyte
differentiation in vitro and in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 131:20–29.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J and Ford LP:
Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an
involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:1290–1297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang X, Wang J, Guo SL, Fan KJ, Li J, Wang
YL, Teng Y and Yang X: miR-21 promotes keratinocyte migration and
re-epithelialization during wound healing. Int J Boil Sci.
7:685–690. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xu N, Brodin P, Wei T, Meisgen F, Eidsmo
L, Nagy N, Kemeny L, Ståhle M, Sonkoly E and Pivarcsi A: MiR-125b,
a microRNA downregulated in psoriasis, modulates keratinocyte
proliferation by targeting FGFR2. J Invest Dermatol. 131:1521–1529.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu K and Wang R: MicroRNA-mediated
regulation in the mammalian circadian rhythm. J Theor Biol.
304:103–110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheng HY, Papp JW, Varlamova O, Dziema H,
Russell B, Curfman JP, Nakazawa T, Shimizu K, Okamura H, Impey S
and Obrietan K: microRNA modulation of circadian-clock period and
entrainment. Neuron. 54:813–829. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shende VR, Neuendorff N and Earnest DJ:
Role of miR-142-3p in the post-transcriptional regulation of the
clock gene Bmal1 in the mouse SCN. PLoS One. 8:e653002013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tan X, Zhang P, Zhou L, Yin B, Pan H and
Peng X: Clock-controlled mir-142-3p can target its activator,
Bmal1. BMC Mol Biol. 13:272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou BR, Xu Y, Permatasari F, Liu WL, Li
W, Guo XF, Huang QH, Guo Z and Luo D: Characterization of the miRNA
profile in UVB-irradiated normal human keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol.
21:317–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cha HJ, Kim OY, Lee GT, Lee KS, Lee JH,
Park I, Lee SJ, Kim YR, Ahn KJ, An IS, et al: Identification of
ultraviolet B radiation-induced microRNAs in normal human dermal
papilla cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:1663–1670. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pothof J, Verkaik NS, van IJcken W, Wiemer
EA, Ta VT, van der Horst GT, Jaspers NG, van Gent DC, Hoeijmakers
JH and Persengiev SP: MicroRNA-mediated gene silencing modulates
the UV-induced DNA-damage response. EMBO J. 28:2090–2099. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim SR, Seo HS, Choi HS, Cho SG, Kim YK,
Hong EH, Shin YC and Ko SG: Trichosanthes kirilowii ethanol extract
and cucurbitacin D inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis through
inhibition of STAT3 activity in breast cancer cells. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:9753502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shin JW, Son JY, Kang JK, Han SH, Cho CK
and Son CG: Trichosanthes kirilowii tuber extract induces G2/M
phase arrest via inhibition of tubulin polymerization in HepG2
cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 115:209–216. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Anlysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kang TH, Reardon JT, Kemp M and Sancar A:
Circadian oscillation of nucleotide excision repair in mammalian
brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:2864–2867. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kang TH, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Reardon JT and
Sancar A: Circadian control of XPA and excision repair of
cisplatin-DNA damage by cryptochrome and HERC2 ubiquitin ligase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:4890–4895. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Geyfman M, Kumar V, Liu Q, Ruiz R, Gordon
W, Espitia F, Cam E, Millar SE, Smyth P, Ihler A, et al: Brain and
muscle Arnt-like protein-1 (BMAL1) controls circadian cell
proliferation and susceptibility to UVB-induced DNA damage in the
epidermis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:11758–11763. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xie QH, He XX, Chang Y, Sun SZ, Jiang X,
Li PY and Lin JS: MiR-192 inhibits nucleotide excision repair by
targeting ERCC3 and ERCC4 in HepG2.2.15 cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 410:440–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ni L, Zhu X, Gong C, Luo Y, Wang L, Zhou
W, Zhu S and Li Y: Trichosanthes kirilowii fruits inhibit non-small
cell lung cancer cell growth through mitotic cell-cycle arrest. Am
J Chin Med. 43:349–364. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bee L, Marini S, Pontarin G, Ferraro P,
Costa R, Albrecht U and Celotti L: Nucleotide excision repair
efficiency in quiescent human fibroblasts is modulated by circadian
clock. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:2126–2137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ramkissoon SH, Mainwaring LA, Ogasawara Y,
Keyvanfar K, McCoy JP Jr, Sloand EM, Kajigaya S and Young NS:
Hematopoietic-specific microRNA expression in human cells. Leuk
Res. 30:643–647. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang XS, Gong JN, Yu J, Wang F, Zhang XH,
Yin XL, Tan ZQ, Luo ZM, Yang GH, Shen C and Zhang JW: MicroRNA-29a
and microRNA-142-3p are regulators of myeloid differentiation and
acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 119:4992–5004. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lv M, Zhang X, Jia H, Li D, Zhang B, Zhang
H, Hong M, Jiang T, Jiang Q, Lu J, et al: An oncogenic role of
miR-142-3p in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) by
targeting glucocorticoid receptor-α and cAMP/PKA pathways.
Leukemia. 26:769–777. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lei Z, Xu G, Wang L, Yang H, Liu X, Zhao J
and Zhang HT: MiR-142-3p represses TGF-β-induced growth inhibition
through repression of TGFβR1 in non-small cell lung cancer. FASEB
J. 28:2696–2704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Joyce CE, Zhou X, Xia J, Ryan C, Thrash B,
Menter A, Zhang W and Bowcock AM: Deep sequencing of small RNAs
from human skin reveals major alterations in the psoriasis
miRNAome. Hum Mol Genet. 20:4025–4040. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vennegaard MT, Bonefeld CM, Hagedorn PH,
Bangsgaard N, Løvendorf MB, Odum N, Woetmann A, Geisler C and Skov
L: Allergic contact dermatitis induces upregulation of identical
microRNAs in humans and mice. Contact Dermatitis. 67:298–305. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Makino K, Jinnin M, Kajihara I, Honda N,
Sakai K, Masuguchi S, Fukushima S, Inoue Y and Ihn H: Circulating
miR-142-3p levels in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 37:34–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|