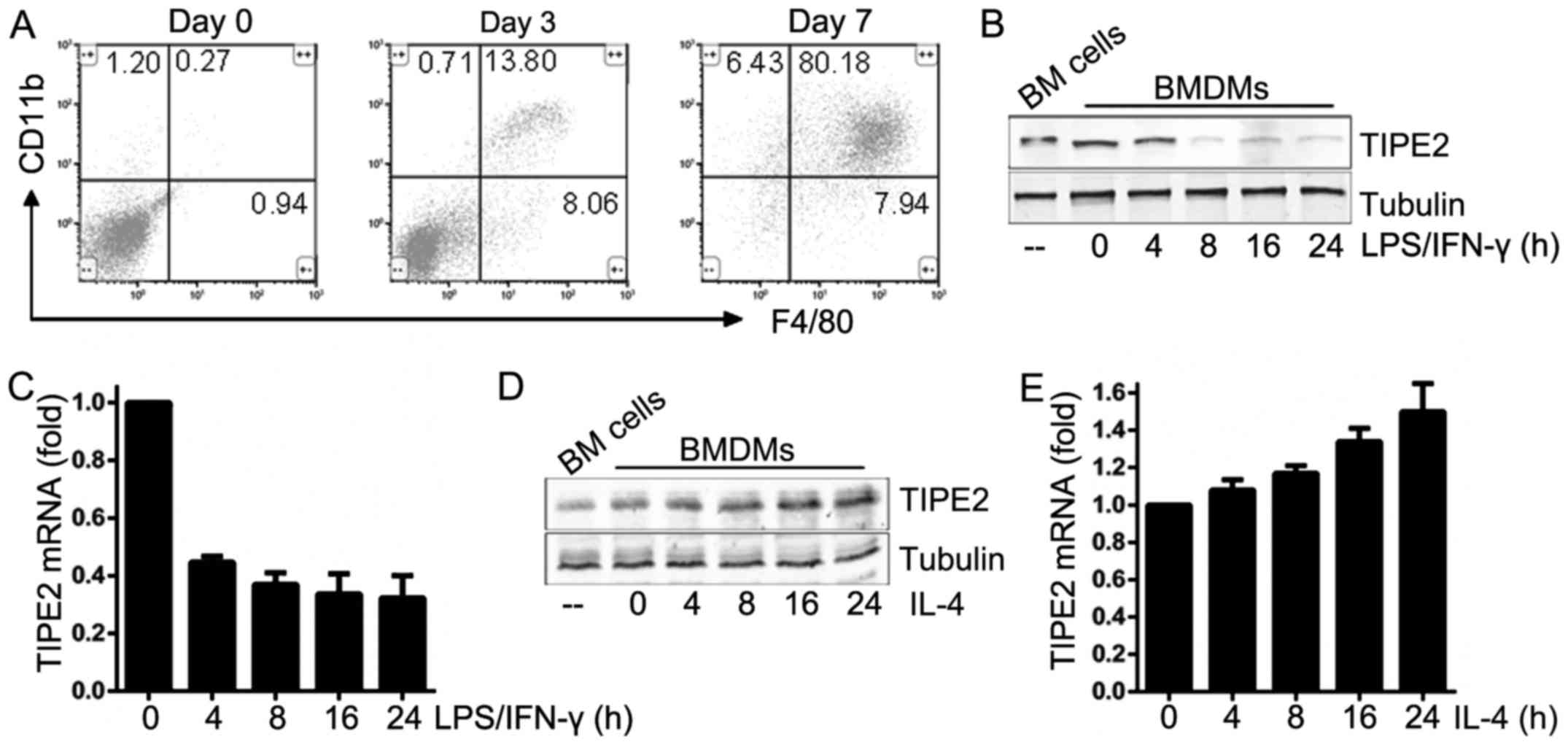
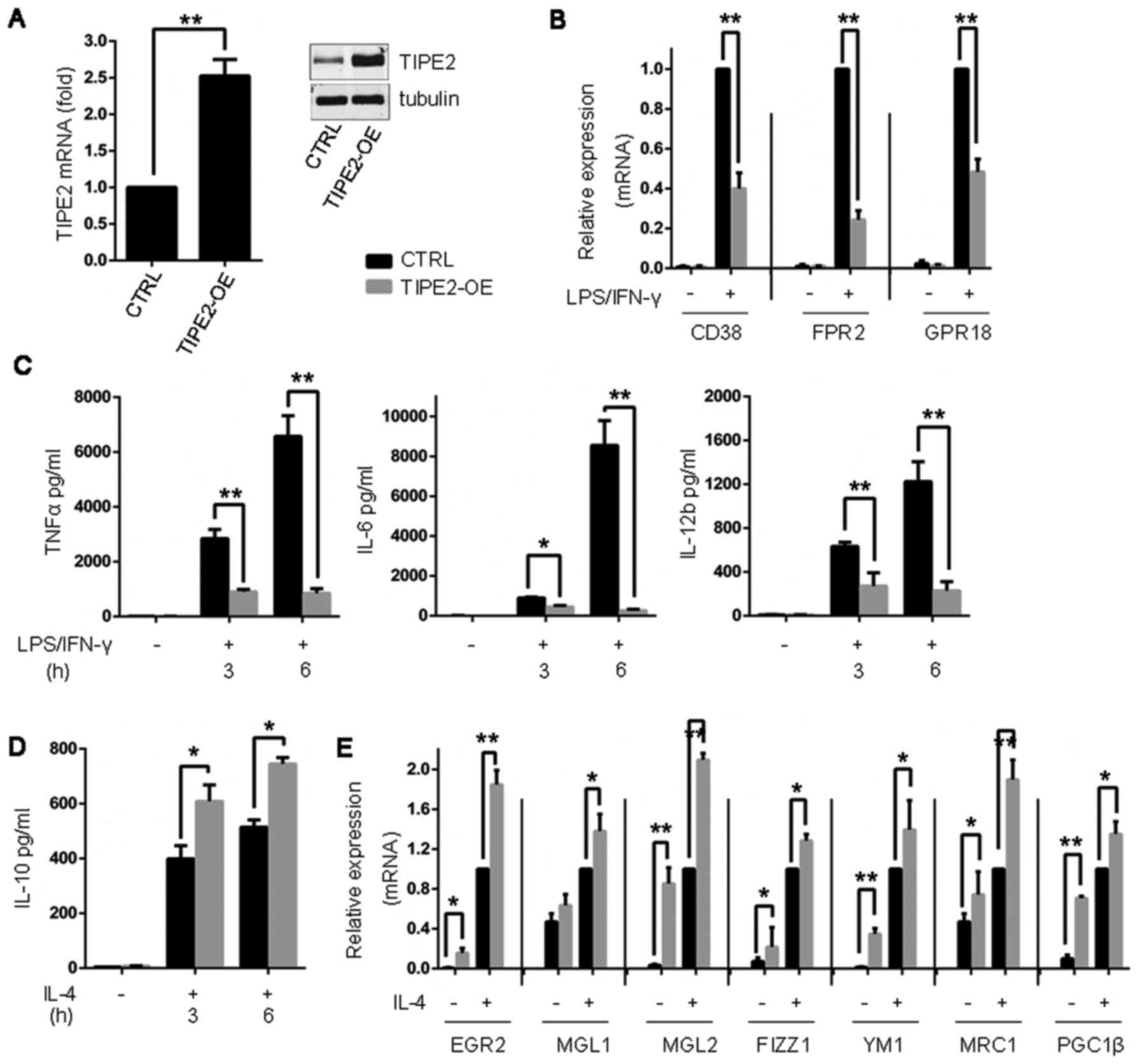
|
1
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ginhoux F and Jung S: Monocytes and
macrophages: Developmental pathways and tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev
Immunol. 14:392–404. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Varol C, Mildner A and Jung S:
Macrophages: Development and tissue specialization. Annu Rev
Immunol. 33:643–675. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Italiani P and Boraschi D: From Monocytes
to M1/M2 Macrophages: Phenotypical vs. functional differentiation.
Front Immunol. 5:5142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saeed S, Quintin J, Kerstens HH, Rao NA,
Aghajanirefah A, Matarese F, Cheng SC, Ratter J, Berentsen K, van
der Ent MA, et al: Epigenetic programming of monocyte-to-macrophage
differentiation and trained innate immunity. Science.
345:12510862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Byles V, Covarrubias AJ, Ben-Sahra I,
Lamming DW, Sabatini DM, Manning BD and Horng T: The TSC-mTOR
pathway regulates macrophage polarization. Nat Commun. 4:28342013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Covarrubias AJ, Aksoylar HI and Horng T:
Control of macrophage metabolism and activation by mTOR and Akt
signaling. Semin Immunol. 27:286–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weichhart T, Hengstschläger M and Linke M:
Regulation of innate immune cell function by mTOR. Nat Rev Immunol.
15:599–614. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang SC, Smith AM, Everts B, Colonna M,
Pearce EL, Schilling JD and Pearce EJ: Metabolic reprogramming
mediated by the mTORC2-IRF4 signaling axis is essential for
macrophage alternative activation. Immunity. 45:817–830. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brown J, Wang H, Suttles J, Graves DT and
Martin M: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2)
negatively regulates Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory
response via FoxO1. J Biol Chem. 286:44295–44305. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Covarrubias AJ, Aksoylar HI, Yu J, Snyder
NW, Worth AJ, Iyer SS, Wang J, Ben-Sahra I, Byles V,
Polynne-Stapornkul T, et al: Akt-mTORC1 signaling regulates Acly to
integrate metabolic input to control of macrophage activation.
Elife. 5:pii: e11612. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun H, Gong S, Carmody RJ, Hilliard A, Li
L, Sun J, Kong L, Xu L, Hilliard B, Hu S, et al: TIPE2, a negative
regulator of innate and adaptive immunity that maintains immune
homeostasis. Cell. 133:415–426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu Y, Tao M, Wu J, Meng Y, Xu C, Tian Y,
Zhou X, Xiang J, Zhang H and Xie Y: Adenovirus-directed expression
of TIPE2 suppresses gastric cancer growth via induction of
apoptosis and inhibition of AKT and ERK1/2 signaling. Cancer Gene
Ther. 23:98–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lou Y, Zhang G, Geng M, Zhang W, Cui J and
Liu S: TIPE2 negatively regulates inflammation by switching
arginine metabolism from nitric oxide synthase to arginase. PLoS
One. 9:e965082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li F, Zhu X, Yang Y, Huang L and Xu J:
TIPE2 alleviates systemic lupus erythematosus through regulating
macrophage polarization. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:330–339. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oho M, Nakano R, Nakayama R, Sakurai W,
Miyamoto A, Masuhiro Y and Hanazawa S: TIPE2 (tumor necrosis factor
alpha-induced protein 8-like 2) is a novel negative regulator of
TAK1 signal. J Biol Chem. 291:22650–22660. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ren J, Chen X and Chen ZJ: IKKβ is an IRF5
kinase that instigates inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:17438–17443. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lopez-Pelaez M, Lamont DJ, Peggie M,
Shpiro N, Gray NS and Cohen P: Protein kinase IKKβ-catalyzed
phosphorylation of IRF5 at Ser462 induces its dimerization and
nuclear translocation in myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:17432–17437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mihaly SR, Morioka S, Ninomiya-Tsuji J and
Takaesu G: Activated macrophage survival is coordinated by TAK1
binding proteins. PLoS One. 9:e949822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chantranupong L, Scaria SM, Saxton RA,
Gygi MP, Shen K, Wyant GA, Wang T, Harper JW, Gygi SP and Sabatini
DM: The CASTOR proteins are arginine sensors for the mTORC1
pathway. Cell. 165:153–164. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun H, Zhuang G, Chai L, Wang Z, Johnson
D, Ma Y and Chen YH: TIPE2 controls innate immunity to RNA by
targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Rac pathway. J Immunol.
189:2768–2773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Z, Fayngerts S, Wang P, Sun H,
Johnson DS, Ruan Q, Guo W and Chen YH: TIPE2 protein serves as a
negative regulator of phagocytosis and oxidative burst during
infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:15413–15418. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Munder M: Arginase: An emerging key player
in the mammalian immune system. Br J Pharmacol. 158:638–651. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nissim I, Luhovyy B, Horyn O, Daikhin Y,
Nissim I and Yudkoff M: The role of mitochondrially bound arginase
in the regulation of urea synthesis: Studies with [U-15N4]arginine,
isolated mitochondria, and perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem.
280:17715–17724. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Comalada M, Yeramian A, Modolell M,
Lloberas J and Celada A: Arginine and macrophage activation.
Methods Mol Biol. 844:223–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rath M, Müller I, Kropf P, Closs EI and
Munder M: Metabolism via arginase or nitric oxide synthase: Two
competing arginine pathways in macrophages. Front Immunol.
5:5322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McNeill E, Crabtree MJ, Sahgal N, Patel J,
Chuaiphichai S, Iqbal AJ, Hale AB, Greaves DR and Channon KM:
Regulation of iNOS function and cellular redox state by macrophage
Gch1 reveals specific requirements for tetrahydrobiopterin in NRF2
activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 79:206–216. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thomas AC and Mattila JT: ‘Of mice and
men’: Arginine metabolism in macrophages. Front Immunol. 5:4792014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|