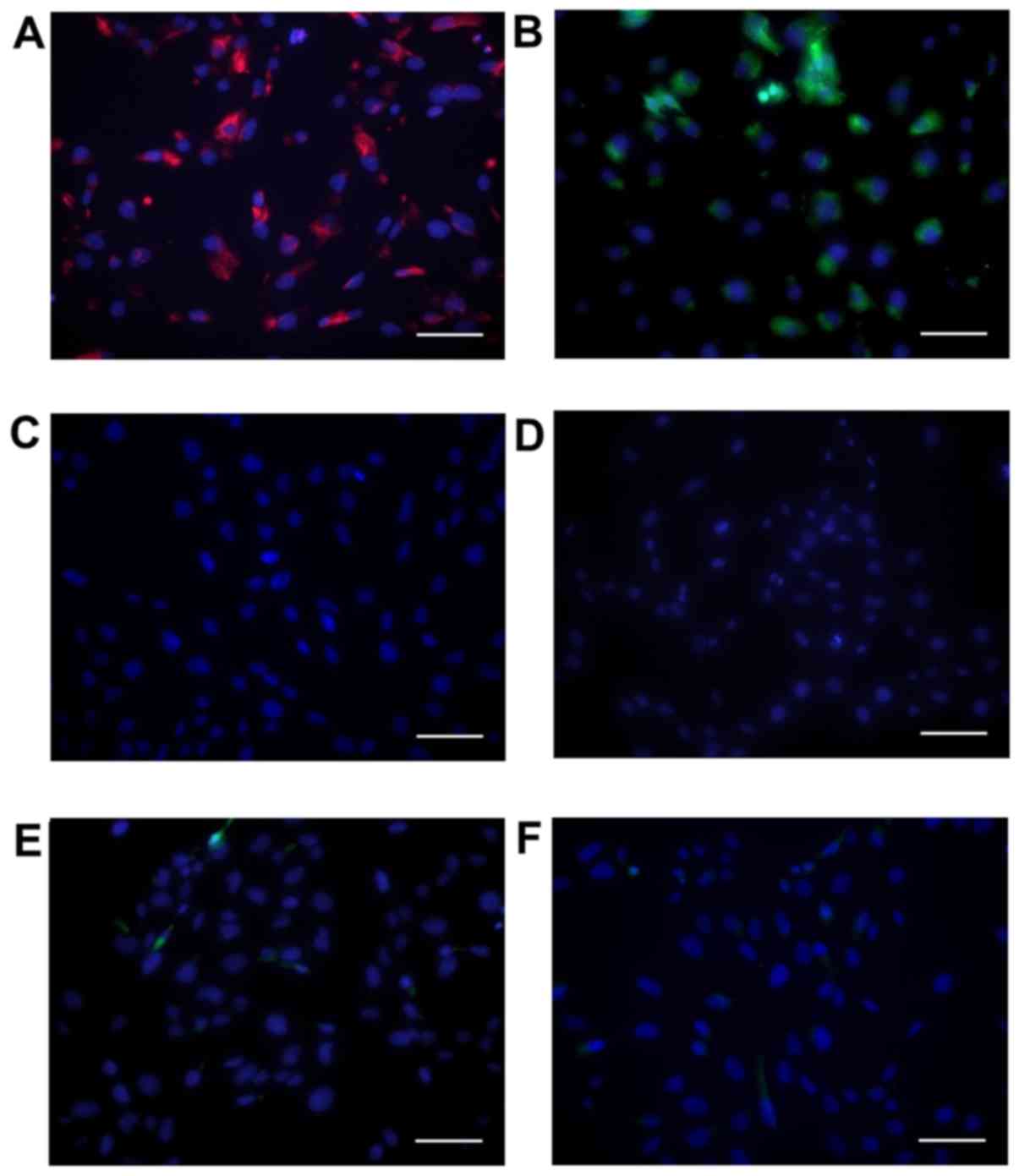
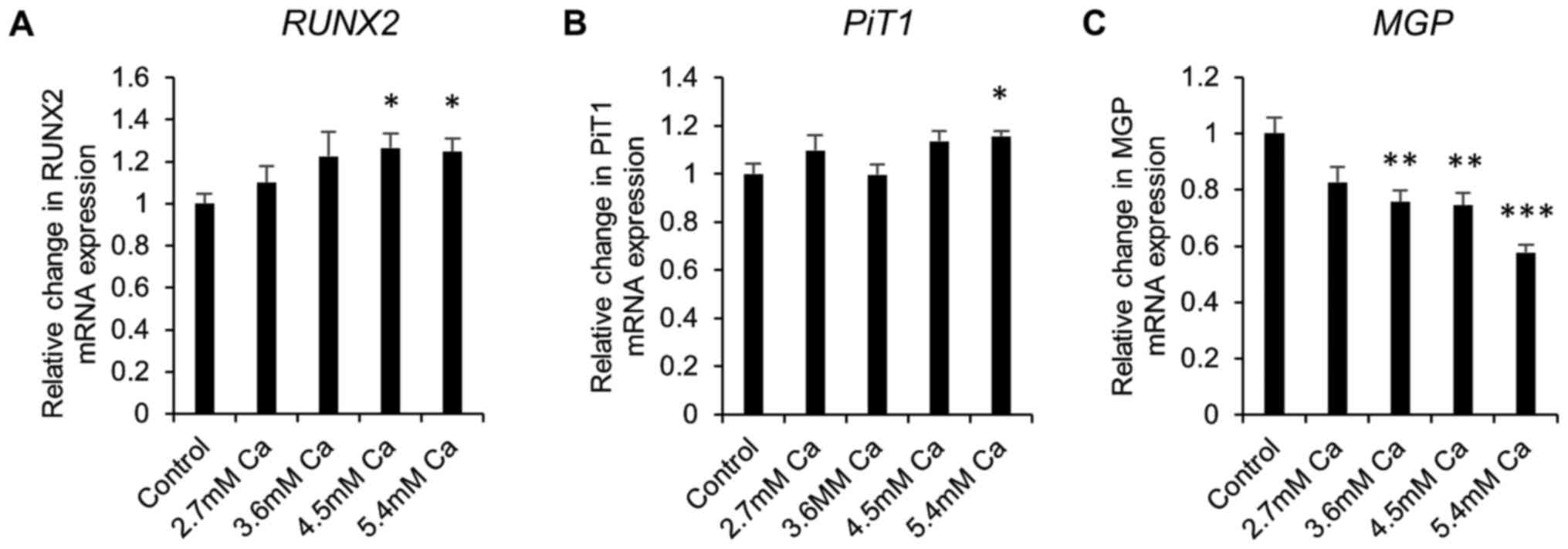
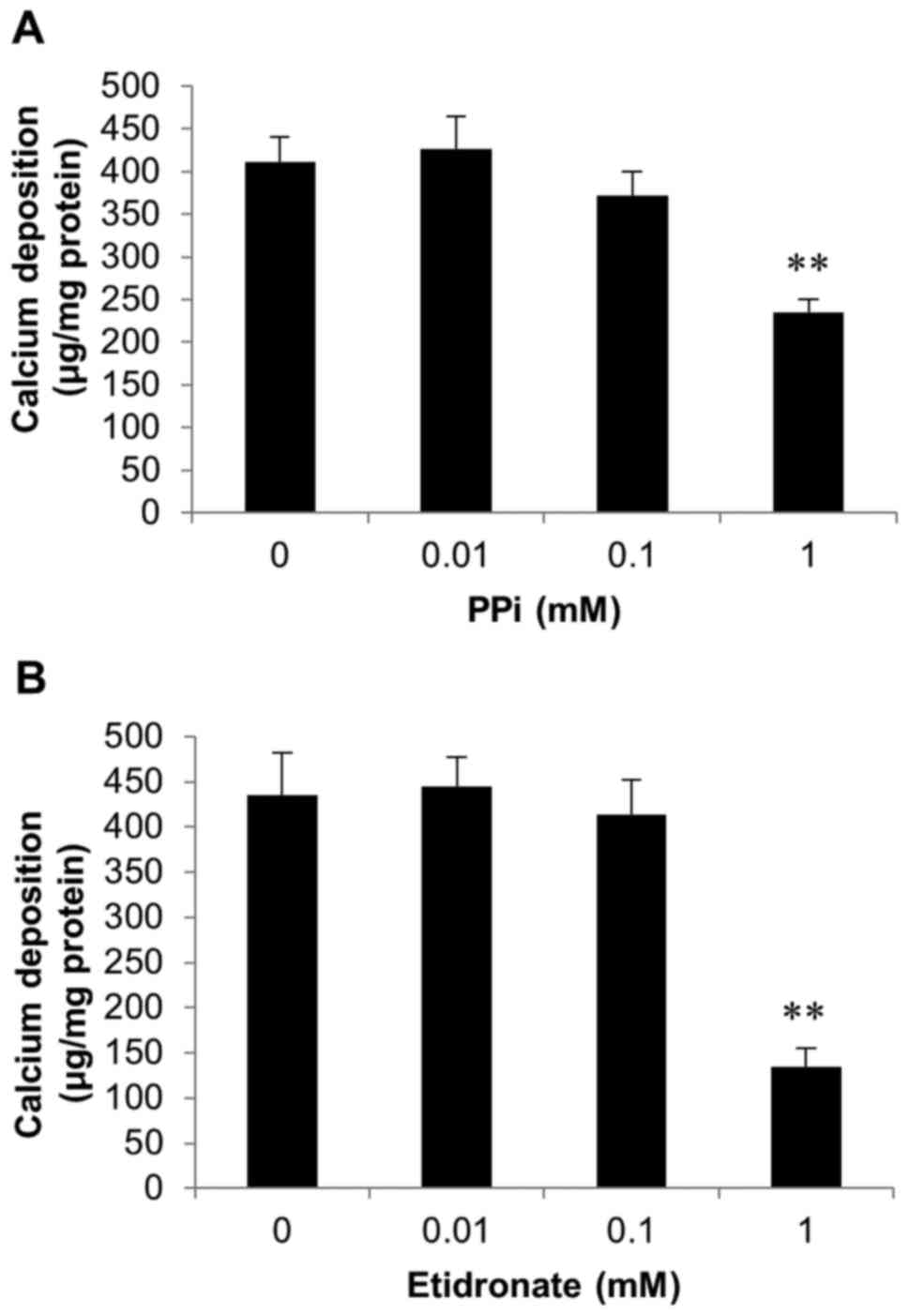
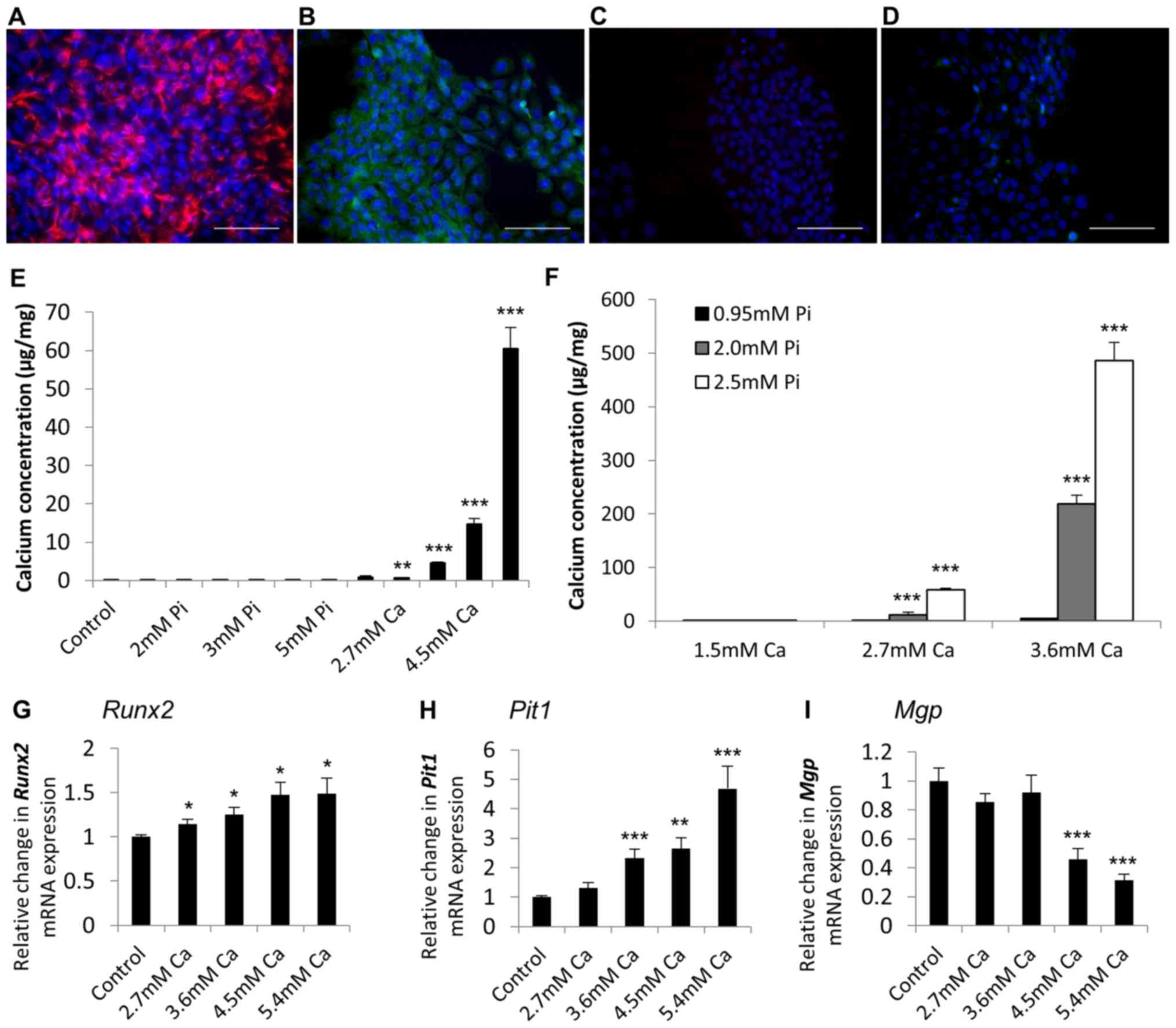
|
1
|
Freeman RV and Otto CM: Spectrum of
calcific aortic valve disease: Pathogenesis, disease progression
and treatment strategies. Circulation. 111:3316–3326. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stewart BF, Siscovick D, Lind BK, Gardin
JM, Gottdiener JS, Smith VE, Kitzman DW and Otto CM: Clinical
factors associated with calcific aortic valve disease.
Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 29:630–634. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coffey S, Cox B and Williams MJ: The
prevalence, incidence, progression and risks of aortic valve
sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 63:2852–2861. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lindman BR, Clavel MA, Mathieu P, Gardin
JM, Gottdiener JS, Smith VE, Kitzman DW and Otto CM: Calcific
aortic stenosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2:160062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Balaoing LR, Post AD, Liu H, Minn KT and
Grande-Allen KJ: Age-related changes in aortic valve hemostatic
protein regulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:72–80. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yutzey KE, Demer LL, Body SC, Huggins GS,
Towler DA, Giachelli CM, Hofmann-Bowman MA, Mortlock DP, Rogers MB,
Sadeghi MM and Aikawa E: Calcific aortic valve disease: A consensus
summary from the alliance of investigators on calcific aortic valve
disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:2387–2393. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pawade TA, Newby DE and Dweck MR:
Calcification in aortic stenosis: The skeleton key. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 66:561–577. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
New SE and Aikawa E: Molecular imaging
insights into early inflammatory stages of arterial and aortic
valve calcification. Circ Res. 108:1381–1391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dweck MR, Pawade TA and Newby DE: Aortic
stenosis begets aortic stenosis: Between a rock and a hard place?
Heart. 101:919–920. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Leopold JA: Cellular mechanisms of aortic
valve calcification. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 5:605–614. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mohler ER III, Gannon F, Reynolds C,
Zimmerman R, Keane MG and Kaplan FS: Bone formation and
inflammation in cardiac valves. Circulation. 103:1522–1528. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Poggio P, Sainger R, Branchetti E, Grau
JB, Lai EK, Gorman RC, Sacks MS, Parolari A, Bavaria JE and Ferrari
G: Noggin attenuates the osteogenic activation of human valve
interstitial cells in aortic valve sclerosis. Cardiovasc Res.
98:402–410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Monzack EL and Masters KS: Can valvular
interstitial cells become true osteoblasts? A side-by-side
comparison. J Heart Valve Dis. 20:449–463. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Osman L, Yacoub MH, Latif N, Amrani M and
Chester AH: Role of human valve interstitial cells in valve
calcification and their response to atorvastatin. Circulation.
114:I547–I552. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yip CY, Chen JH, Zhao R and Simmons CA:
Calcification by valve interstitial cells is regulated by the
stiffness of the extracellular matrix. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 29:936–942. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cloyd KL, El-Hamamsy I, Boonrungsiman S,
Grau JB, Lai EK, Gorman RC, Sacks MS, Parolari A, Bavaria JE and
Ferrari G: Characterization of porcine aortic valvular interstitial
cell ‘calcified’ nodules. PLoS One. 7:e481542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gomez-Stallons MV, Wirrig-Schwendeman EE,
Hassel KR, Conway SJ and Yutzey KE: Bone morphogenetic protein
signaling is required for aortic valve calcification. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 36:1398–1405. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Côté N, El Husseini D, Pépin A,
Guauque-Olarte S, Ducharme V, Bouchard-Cannon P, Audet A, Fournier
D, Gaudreault N, Derbali H, et al: ATP acts as a survival signal
and prevents the mineralization of aortic valve. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 52:1191–1202. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
El Husseini D, Boulanger MC, Fournier D,
Mahmut A, Bossé Y, Pibarot P and Mathieu P: High expression of the
Pi-transporter SLC20A1/Pit1 in calcific aortic valve disease
promotes mineralization through regulation of Akt-1. PLoS One.
8:e533932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seya K, Yu Z, Kanemaru K, Daitoku K,
Akemoto Y, Shibuya H, Fukuda I, Okumura K, Motomura S and Furukawa
K: Contribution of bone morphogenetic protein-2 to aortic valve
calcification in aged rat. J Pharmacol Sci. 115:8–14. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Acharya A, Hans CP, Koenig SN, Nichols HA,
Galindo CL, Garner HR, Merrill WH, Hinton RB and Garg V: Inhibitory
role of Notch1 in calcific aortic valve disease. PLoS One.
6:e277432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cui L, Rashdan NA, Zhu D, Milne EM, Ajuh
P, Milne G, Helfrich MH, Lim K, Prasad S, Lerman DA, et al: End
stage renal disease-induced hypercalcemia may promotes aortic valve
calcification via Annexin VI enrichment of valve interstitial
cell-derived matrix vesicles. J Cell Physiol. 232:2985–2995. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rattazzi M, Bertacco E, Iop L, D'Andrea S,
Puato M, Buso G, Causin V, Gerosa G, Faggin E and Pauletto P:
Extracellular pyrophosphate is reduced in aortic interstitial valve
cells acquiring a calcifying profile: Implications for aortic valve
calcification. Atherosclerosis. 237:568–576. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rattazzi M, Iop L, Faggin E, Bertacco E,
Zoppellaro G, Baesso I, Puato M, Torregrossa G, Fadini GP, Agostini
C, et al: Clones of interstitial cells from bovine aortic valve
exhibit different calcifying potential when exposed to endotoxin
and phosphate. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:2165–2172. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reynolds JL, Joannides AJ, Skepper JN,
McNair R, Schurgers LJ, Proudfoot D, Jahnen-Dechent W, Weissberg PL
and Shanahan CM: Human vascular smooth muscle cells undergo
vesicle-mediated calcification in response to changes in
extracellular calcium and phosphate concentrations: A potential
mechanism for accelerated vascular calcification in ESRD. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 15:2857–2867. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu D, Mackenzie NC, Millan JL,
Farquharson C and Macrae VE: Upregulation of IGF2 expression during
vascular calcification. J Mol Endocrinol. 52:77–85. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu D, Mackenzie NC, Shanahan CM, Shroff
RC, Farquharson C and MacRae VE: BMP-9 regulates the osteoblastic
differentiation and calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells
through an ALK1 mediated pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 19:165–174. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mackenzie NC, Zhu D, Longley L, Patterson
CS, Kommareddy S and MacRae VE: MOVAS-1 cell line: A new in vitro
model of vascular calcification. Int J Mol Med. 27:663–668.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Staines KA, Zhu D, Farquharson C and
MacRae VE: Identification of novel regulators of osteoblast matrix
mineralization by time series transcriptional profiling. J Bone
Miner Metab. 32:240–251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu AC, Joag VR and Gotlieb AI: The
emerging role of valve interstitial cell phenotypes in regulating
heart valve pathobiology. Am J Pathol. 171:1407–1418. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Latif N, Quillon A, Sarathchandra P,
McCormack A, Lozanoski A, Yacoub MH and Chester AH: Modulation of
human valve interstitial cell phenotype and function using a
fibroblast growth factor 2 formulation. PLoS One. 10:e01278442015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Register TC and Wuthier RE: Effect of
pyrophosphate and two diphosphonates on 45Ca and 32Pi uptake and
mineralization by matrix vesicle-enriched fractions and by
hydroxyapatite. Bone. 6:307–312. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lomashvili KA, Garg P, Narisawa S, Millan
JL and O'Neill WC: Upregulation of alkaline phosphatase and
pyrophosphate hydrolysis: Potential mechanism for uremic vascular
calcification. Kidney Int. 73:1024–1030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lomashvili KA, Monier-Faugere MC, Wang X,
Malluche HH and O'Neill WC: Effect of bisphosphonates on vascular
calcification and bone metabolism in experimental renal failure.
Kidney Int. 75:617–625. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Afroze T, Yang LL, Wang C, Gros R, Kalair
W, Hoque AN, Mungrue IN, Zhu Z and Husain M:
Calcineurin-independent regulation of plasma membrane
Ca2+ ATPase-4 in the vascular smooth muscle cell cycle.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 285:C88–C95. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Idelevich A, Rais Y and Monsonego-Ornan E:
Bone Gla protein increases HIF-1alpha-dependent glucose metabolism
and induces cartilage and vascular calcification. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:e55–e71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kelynack KJ and Holt SG: An in vitro
murine model of vascular smooth muscle cell mineralization. Methods
Mol Biol. 1397:209–220. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhu D, Rashdan NA, Chapman KE, Hadoke PW
and MacRae VE: A novel role for the mineralocorticoid receptor in
glucocorticoid driven vascular calcification. Vascul Pharmacol.
86:87–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu D, Hadoke PW, Wu J, Vesey AT, Lerman
DA, Dweck MR, Newby DE, Smith LB and MacRae VE: Ablation of the
androgen receptor from vascular smooth muscle cells demonstrates a
role for testosterone in vascular calcification. Sci Rep.
6:248072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Johnson RC, Leopold JA and Loscalzo J:
Vascular calcification: Pathobiological mechanisms and clinical
implications. Circ Res. 99:1044–1059. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li X, Yang HY and Giachelli CM: Role of
the sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter, Pit-1, in vascular
smooth muscle cell calcification. Circ Res. 98:905–912. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yao Y, Bennett BJ, Wang X, Rosenfeld ME,
Giachelli C, Lusis AJ and Boström KI: Inhibition of bone
morphogenetic proteins protects against atherosclerosis and
vascular calcification. Circ Res. 107:485–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Luo G, Ducy P, McKee MD, Pinero GJ, Loyer
E, Behringer RR and Karsenty G: Spontaneous calcification of
arteries and cartilage in mice lacking matrix GLA protein. Nature.
386:78–81. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Koos R, Krueger T, Westenfeld R, Kühl HP,
Brandenburg V, Mahnken AH, Stanzel S, Vermeer C, Cranenburg EC,
Floege J, et al: Relation of circulating Matrix Gla-Protein and
anticoagulation status in patients with aortic valve calcification.
Thromb Haemost. 101:706–713. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Villa-Bellosta R, Wang X, Millan JL,
Dubyak GR and O'Neill WC: Extracellular pyrophosphate metabolism
and calcification in vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 301:H61–H68. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li Q, Kingman J, Sundberg JP, Levine MA
and Uitto J: Dual effects of bisphosphonates on ectopic skin and
vascular soft tissue mineralization versus bone microarchitecture
in a mouse model of generalized arterial calcification of infancy.
J Invest Dermatol. 136:275–283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|