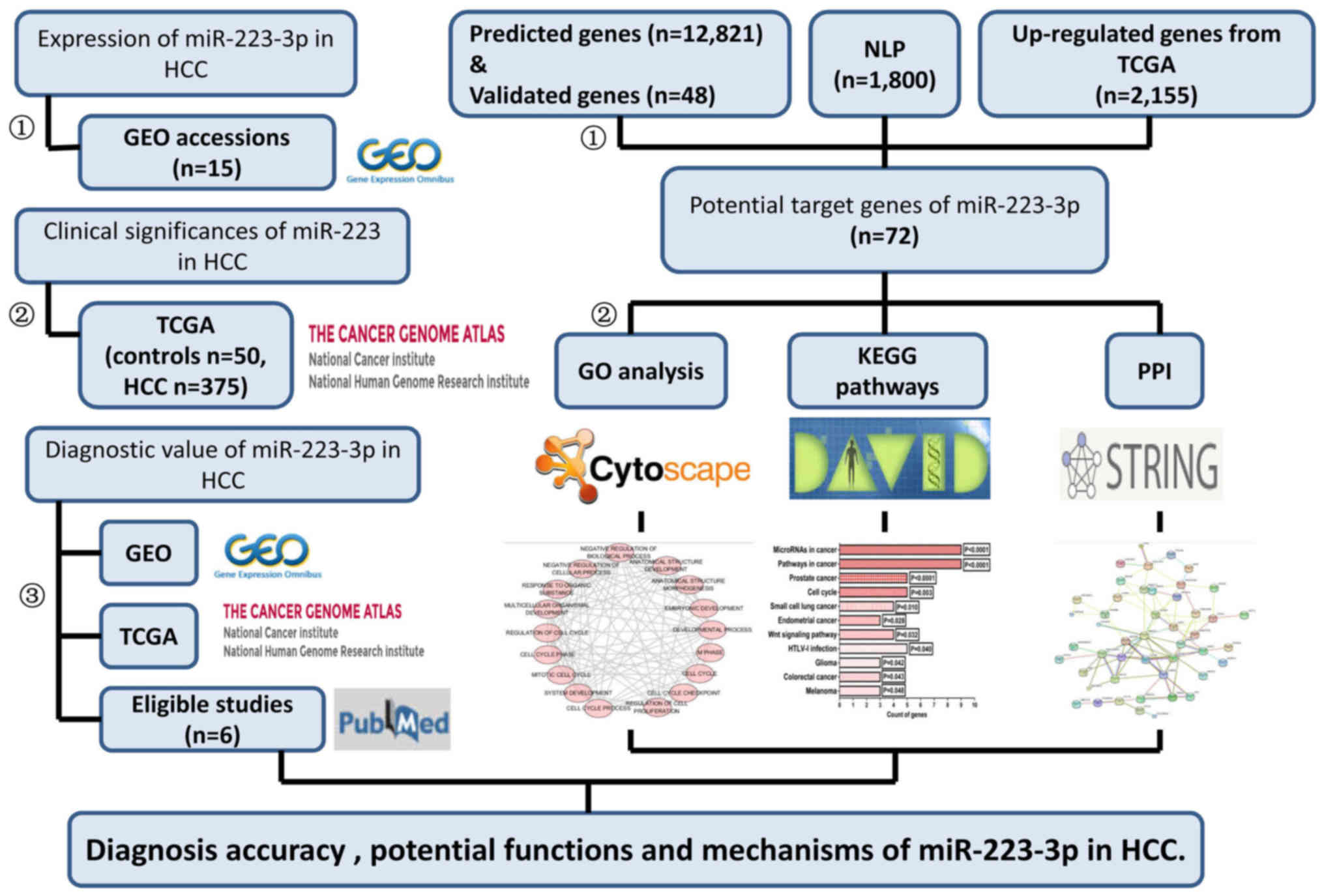
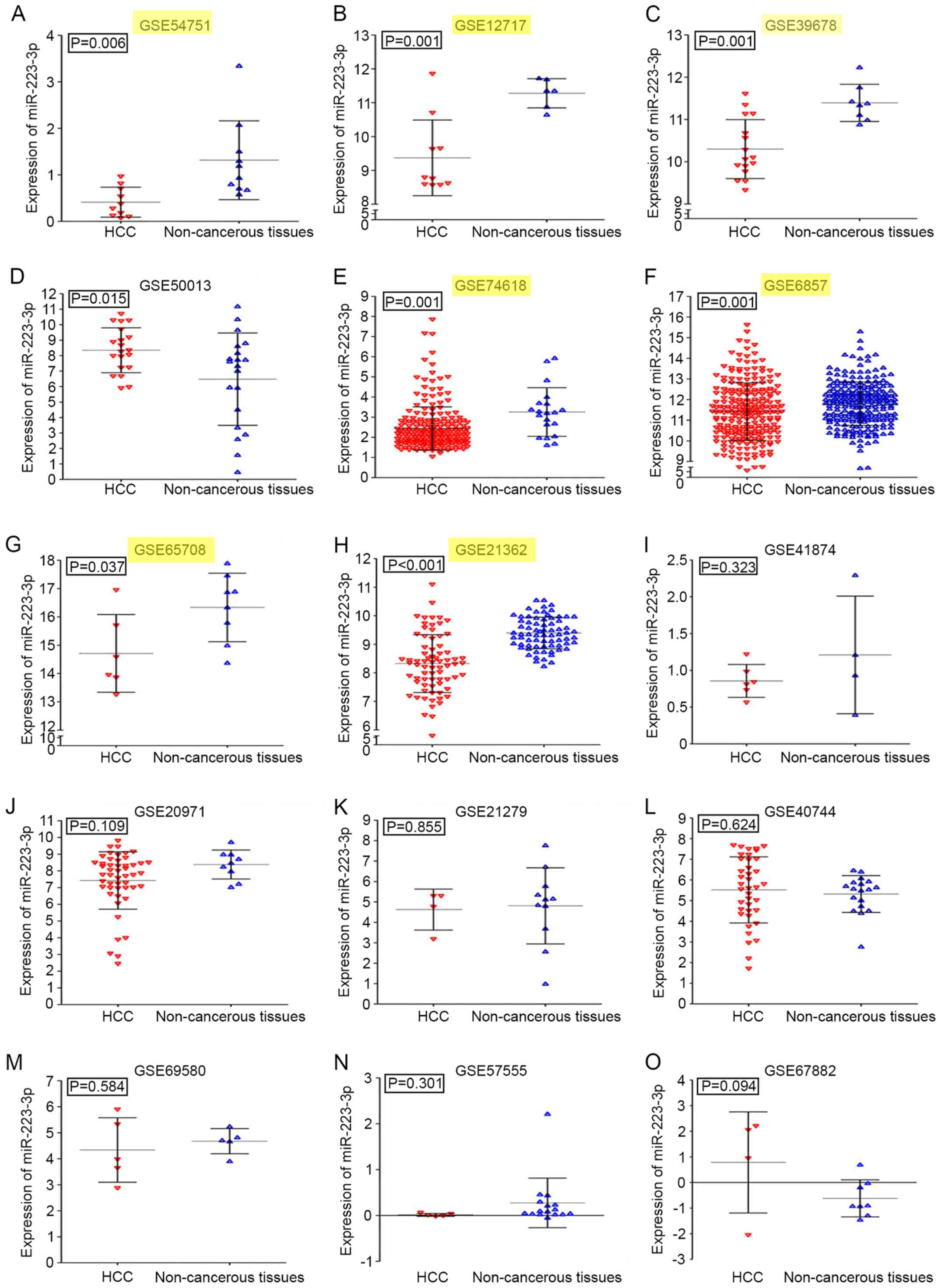
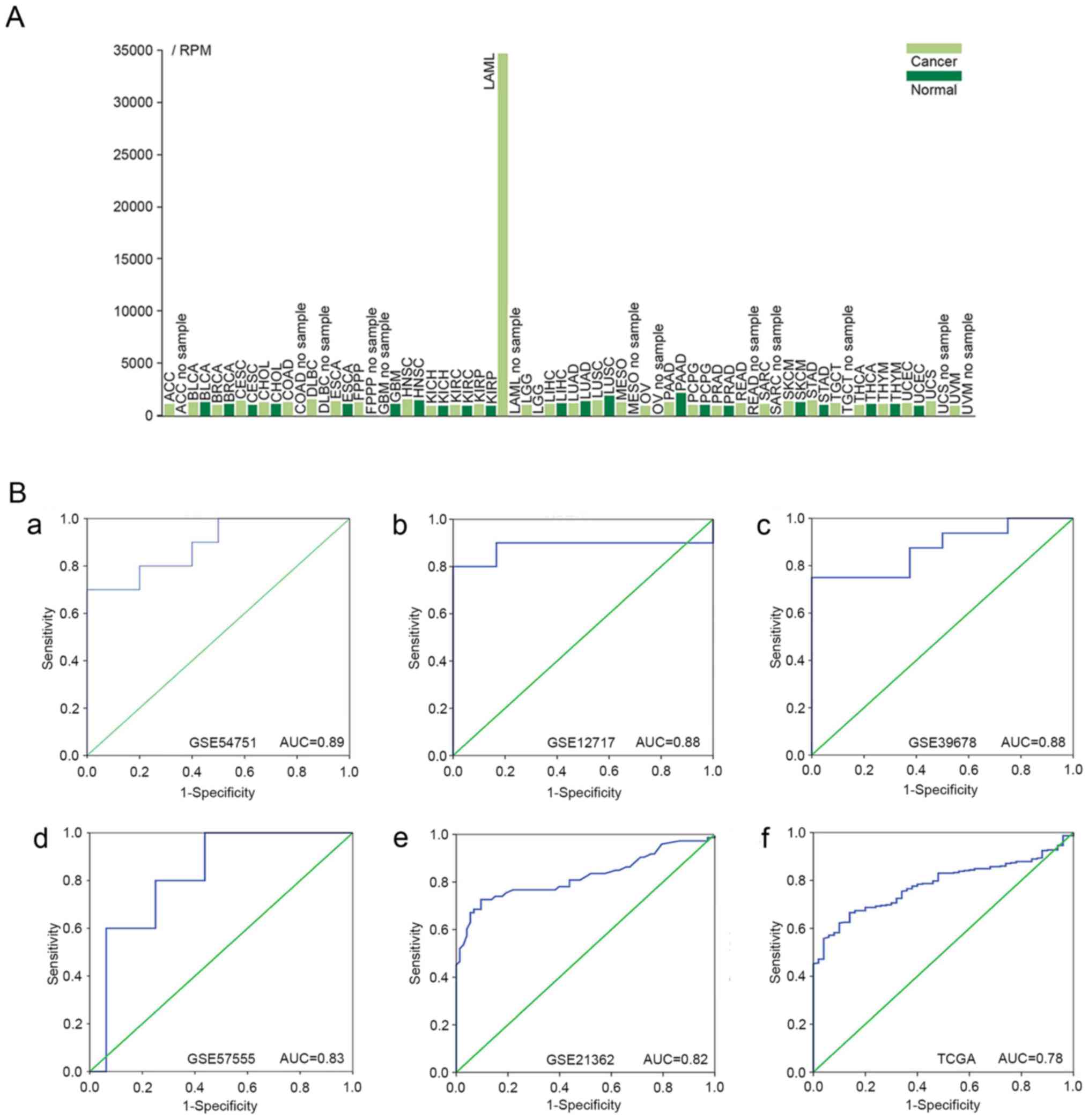
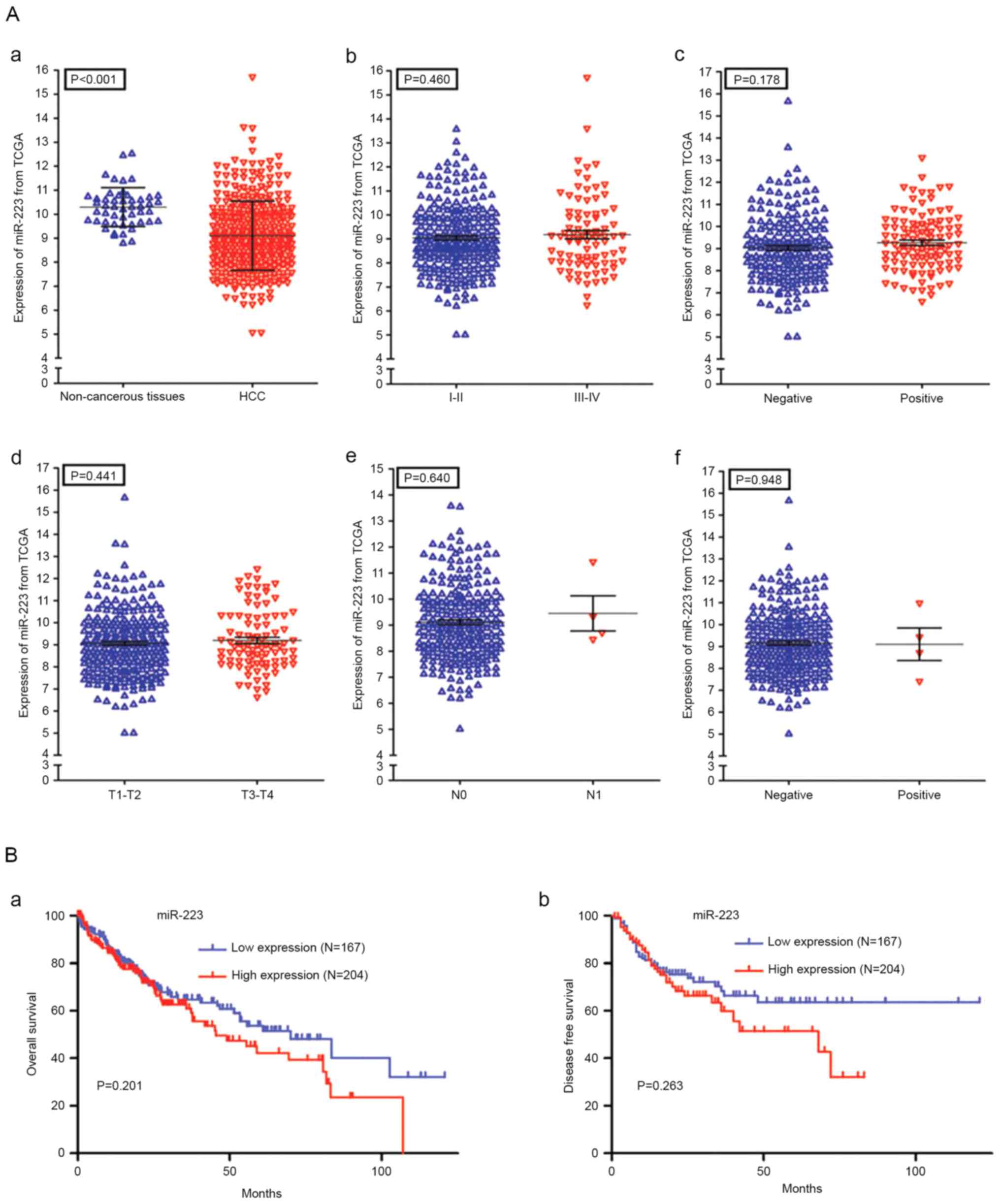
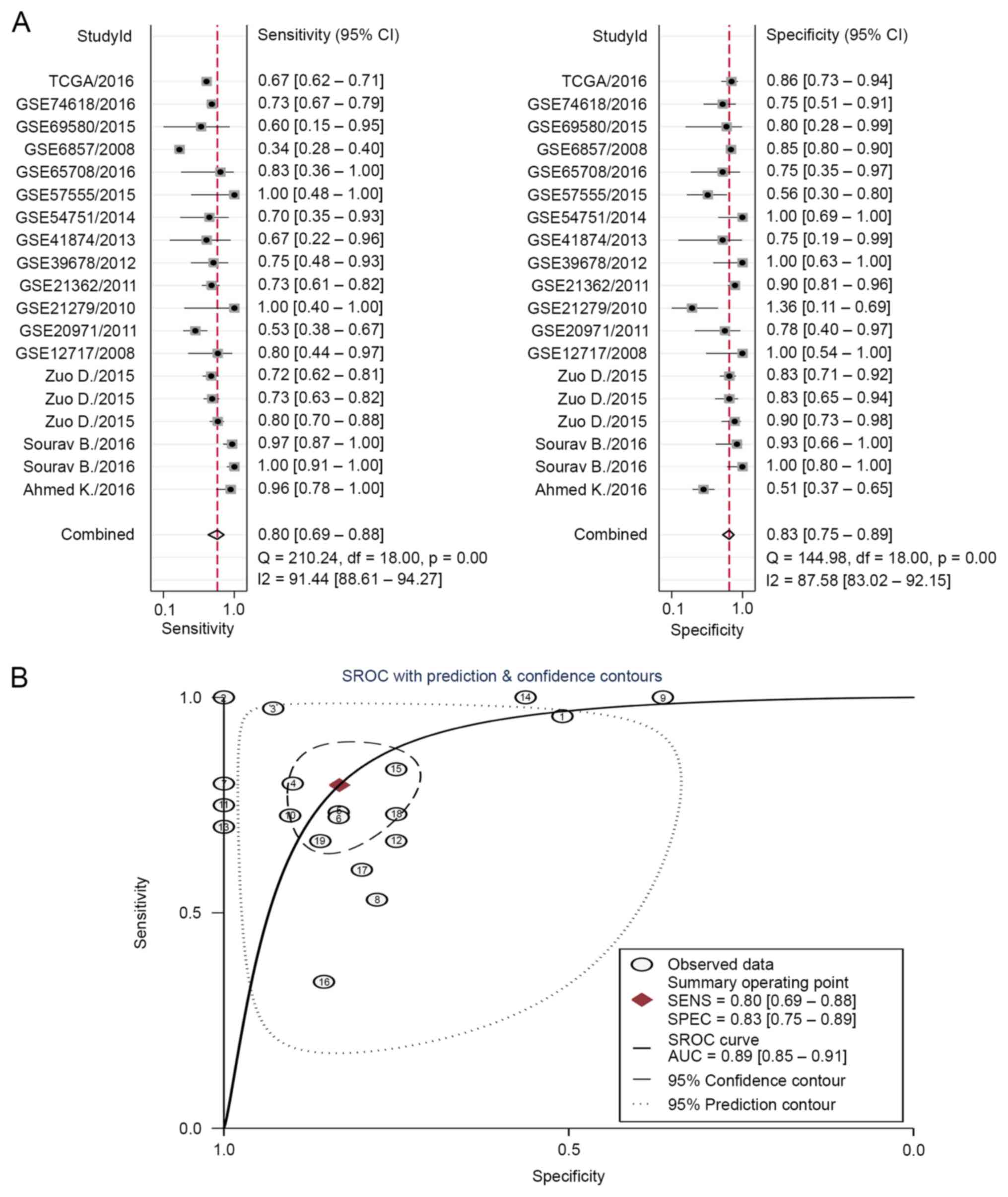
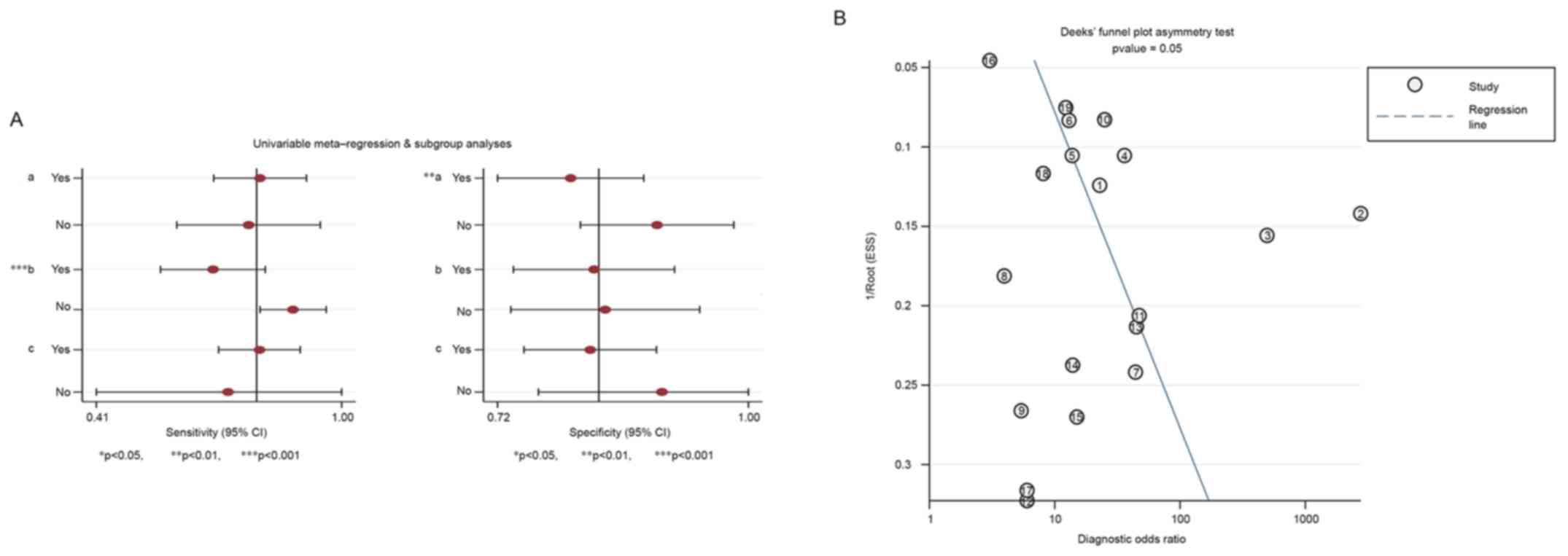
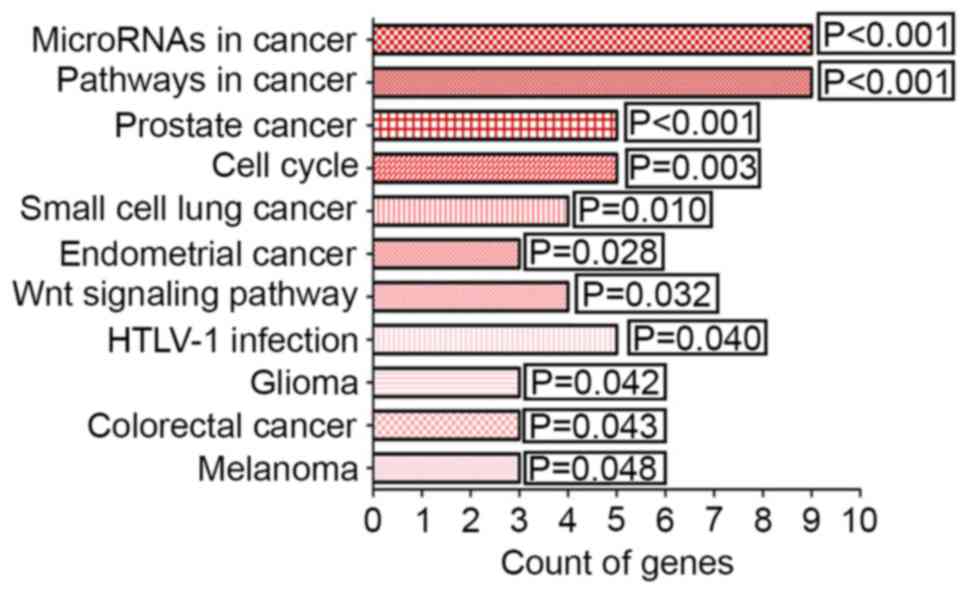
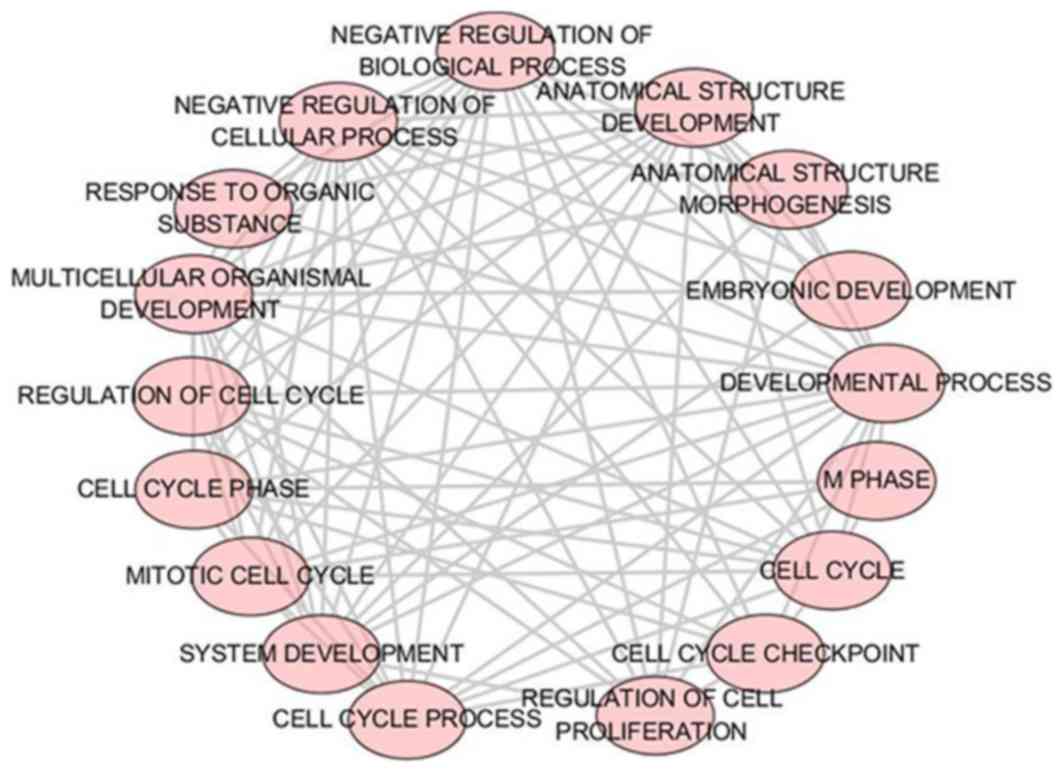
|
1
|
Mo Z, Zheng S, Lv Z, Zhuang Y, Lan X, Wang
F, Lu X, Zhao Y and Zhou S: Senescence marker protein 30 (SMP30)
serves as a potential prognostic indicator in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Sci Rep. 6:393762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lafaro KJ, Demirjian AN and Pawlik TM:
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am.
24:1–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zheng W, Yao M, Qian Q, Sai W, Qiu L, Yang
J, Wu W, Dong Z and Yao D: Oncogenic secretory clusterin in
hepatocellular carcinoma: Expression at early staging and emerging
molecular target. Oncotarget. 8:52321–52332. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang W, Cui X, Chen Y, Shao M, Shao X,
Shen Y, Liu Q, Wu M, Liu J, Ni W, et al: High VRK1 expression
contributes to cell proliferation and survival in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 212:171–178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu C, Cao Q, Chen P, Yang S, Gong X, Deng
M, Ruan B and Li L: Tissue transglutaminase 2 exerts a
tumor-promoting role in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mazzola A, Costantino A, Petta S,
Bartolotta TV, Raineri M, Sacco R, Brancatelli G, Cammà C and
Cabibbo G: Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver
transplantation: An update. Future Oncol. 11:2923–2936. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang H, Zhang X, Tao Y, Shan L, Jiang Q,
Yu Y, Cai F and Ma L: Prognostic and clinicopathologic significance
of SIRT1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:52357–52365. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang T, Zhang X, Shi W, Xu J, Fan H,
Zhang S and Ni R: The DNA damage repair protein Ku70 regulates
tumor cell and hepatic carcinogenesis by interacting with FOXO4.
Pathol Res Pract. 212:153–161. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ke M, Xu T, Li N, Ren Y, Shi A, Lv Y and
He H: Prognostic nutritional index predicts short-term outcomes
after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan
criteria. Oncotarget. 7:81611–81620. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu Y, Rong J, Duan S, Chen C, Li Y, Peng
B, Yi B, Zheng Z, Gao Y, Wang K, et al: High expression of GNA13 is
associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci
Rep. 6:359482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li J, Gao JZ, Du JL and Wei LX: Prognostic
and clinicopathological significance of glypican-3 overexpression
in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:6336–6344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang N, Gu J, Yin L, Wu J, Du MY, Ding K,
Huang T and He X: Incorporation of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) into
subclassification of BCLC C stage hepatocellular carcinoma
according to a 5-year survival analysis based on the SEER database.
Oncotarget. 7:81389–81401. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen J, Wu FX, Luo HL, Liu JJ, Luo T, Bai
T, Li LQ and Fan XH: Berberine upregulates miR-22-3p to suppress
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting Sp1. Am J
Transl Res. 8:4932–4941. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yates LA, Norbury CJ and Gilbert RJ: The
long and short of microRNA. Cell. 153:516–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Z, Wang C, Jiao X, Zhao S, Liu X, Wang
Y and Zhang J: miR-221 promotes growth and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by constitutive activation of NFκB.
Am J Transl Res. 8:4764–4777. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Blanco-Calvo M, Calvo L, Figueroa A,
Haz-Conde M, Antón-Aparicio L and Valladares-Ayerbes M: Circulating
microRNAs: Molecular microsensors in gastrointestinal cancer.
Sensors. 12:9349–9362. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao L, Xie B, Yang X, Liang H, Jiang X,
Zhang D, Xue P, Chen D and Shao Z: miR-324-5p suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion by counteracting ECM
degradation through post-transcriptionally downregulating ETS1 and
SP1. PLoS One. 10:e01330742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zekri AN, Youssef AS, El-Desouky ED, Ahmed
OS, Lotfy MM, Nassar AA and Bahnassey AA: Serum microRNA panels as
potential biomarkers for early detection of hepatocellular
carcinoma on top of HCV infection. Tumour Biol. 37:12273–12286.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xue HY, Liu Y, Liao JZ, Lin JS, Li B, Yuan
WG, Lee RJ, Li L, Xu CR and He XX: Gold nanoparticles delivered
miR-375 for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
7:86675–86686. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shen S, Lin Y, Yuan X, Shen L, Chen J,
Chen L, Qin L and Shen B: Biomarker microRNAs for diagnosis,
prognosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A functional
survey and comparison. Sci Rep. 6:383112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao L and Wang W: miR-125b suppresses the
proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting
Sirtuin7. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:18469–18475. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu B, Sun T, Wu G, Shang-Guan H, Jiang
ZJ, Zhang JR and Zheng YF: miR-15a suppresses hepatocarcinoma cell
migration and invasion by directly targeting cMyb. Am J Transl Res.
9:520–532. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He R, Yang L, Lin X, Chen X, Lin X, Wei F,
Liang X, Luo Y, Wu Y, Gan T, et al: miR-30a-5p suppresses cell
growth and enhances apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via
targeting AEG-1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:15632–15641.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu S, Liu K, Zhang W, Wang Y, Jin Z, Jia
B and Liu Y: miR-449a inhibits proliferation and invasion by
regulating ADAM10 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res.
8:2609–2619. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu Y, Zhang W, Liu K, Liu S, Ji B and
Wang Y: miR-138 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by
inhibiting SOX9 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res.
8:2159–2168. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yao H, Liu X, Chen S, Xia W and Chen X:
Decreased expression of serum miR-424 correlates with poor
prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:14830–14835. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun J, Fang K, Shen H and Qian Y:
MicroRNA-9 is a ponderable index for the prognosis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:17748–17756.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang CS, Yu W, Cui H, Wang YJ, Zhang L,
Han F and Huang T: Increased expression of miR-21 predicts poor
prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:7234–7238. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gan TQ, Tang RX, He RQ, Dang YW, Xie Y and
Chen G: Upregulated miR-1269 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its
clinical significance. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:714–721.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun XF, Sun JP, Hou HT, Li K, Liu X and Ge
QX: MicroRNA-27b exerts an oncogenic function by targeting Fbxw7 in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:15325–15332. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuasne H, Barros-Filho MC, Busso-Lopes A,
Marchi FA, Pinheiro M, Muñoz JJ, Scapulatempo-Neto C, Faria EF,
Guimarães GC, Lopes A, et al: Integrative miRNA and mRNA analysis
in penile carcinomas reveals markers and pathways with potential
clinical impact. Oncotarget. 8:15294–15306. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou X, Wen W, Zhu J, Huang Z, Zhang L,
Zhang H, Qi LW, Shan X, Wang T, Cheng W, et al: A six-microRNA
signature in plasma was identified as a potential biomarker in
diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:34468–34480. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guo J, Cao R, Yu X, Xiao Z and Chen Z:
MicroRNA-223-3p inhibits human bladder cancer cell migration and
invasion. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176916782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu G, Chen X, Chen S, Ye W, Hou K and
Liang M: miR-19a, miR-122 and miR-223 are differentially regulated
by hepatitis B virus X protein and involve in cell proliferation in
hepatoma cells. J Transl Med. 14:1222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Giray BG, Emekdas G, Tezcan S, Ulger M,
Serin MS, Sezgin O, Altintas E and Tiftik EN: Profiles of serum
microRNAs; miR-125b-5p and miR223-3p serve as novel biomarkers for
HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 41:4513–4519.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bhattacharya S, Steele R, Shrivastava S,
Chakraborty S, Di Bisceglie AM and Ray RB: Serum miR-30e and
miR-223 as novel noninvasive biomarkers for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 186:242–247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou J, Yu L, Gao X, Hu J, Wang J, Dai Z,
Wang JF, Zhang Z, Lu S, Huang X, et al: Plasma microRNA panel to
diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 29:4781–4788. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu J, Wu C, Che X, Wang L, Yu D, Zhang T,
Huang L, Li H, Tan W, Wang C and Lin D: Circulating microRNAs,
miR-21, miR-122, and miR-223, in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma or chronic hepatitis. Mol Carcinog. 50:136–142. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ji J, Zheng X, Forgues M, Yamashita T,
Wauthier EL, Reid LM, Wen X, Song Y, Wei JS, Khan J, et al:
Identification of microRNAs specific for epithelial cell adhesion
molecule-positive tumor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 62:829–840. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li G, Shen Q, Li C, Li D, Chen J and He M:
Identification of circulating microRNAs as novel potential
biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma detection: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Clin Transl Oncol. 17:684–693. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fiorino S, Bacchi-Reggiani ML, Visani M,
Acquaviva G, Fornelli A, Masetti M, Tura A, Grizzi F, Zanello M,
Mastrangelo L, et al: MicroRNAs as possible biomarkers for
diagnosis and prognosis of hepatitis B- and
C-related-hepatocellular-carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
22:3907–3936. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao FY, Han J, Chen XW, Wang J, Wang XD,
Sun JG and Chen ZT: miR-223 enhances the sensitivity of non-small
cell lung cancer cells to erlotinib by targeting the insulin-like
growth factor-1 receptor. Int J Mol Med. 38:183–191. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Juzėnas S, Saltenienė V, Kupcinskas J,
Link A, Kiudelis G, Jonaitis L, Jarmalaite S, Kupcinskas L,
Malfertheiner P and Skieceviciene J: Analysis of deregulated
microRNAs and their target genes in gastric cancer. PLoS One.
10:e01323272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wong QW, Lung RW, Law PT, Lai PB, Chan KY,
To KF and Wong N: MicroRNA-223 is commonly repressed in
hepatocellular carcinoma and potentiates expression of stathmin1.
Gastroenterology. 135:257–269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao WY, Wang DD, Song MQ, Yang L, Ye J
and Chen LB: Role of microRNA-223 and its target gene oncogene
c-myc in hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. Zhonghua Gan Zang
Bing Za Zhi. 19:114–117. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME,
Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA and Bossuyt
PM; QUADAS-2 Group, : QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality
assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med.
155:529–536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zintzaras E and Ioannidis JP:
Heterogeneity testing in meta-analysis of genome searches. Genet
Epidemiol. 28:123–137. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P and Irwig L: The
performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size
effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was
assessed. J Clin Epidemiol. 58:882–893. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang WT, Wang HL, Yang H, Ren FH, Luo YH,
Huang CQ, Liang YY, Liang HW, Chen G and Dang YW: Lower expressed
miR-198 and its potential targets in hepatocellular carcinoma: A
clinicopathological and in silico study. Onco Targets Ther.
9:5163–5180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Settles B: ABNER: An open source tool for
automatically tagging genes, proteins and other entity names in
text. Bioinformatics. 21:3191–3192. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
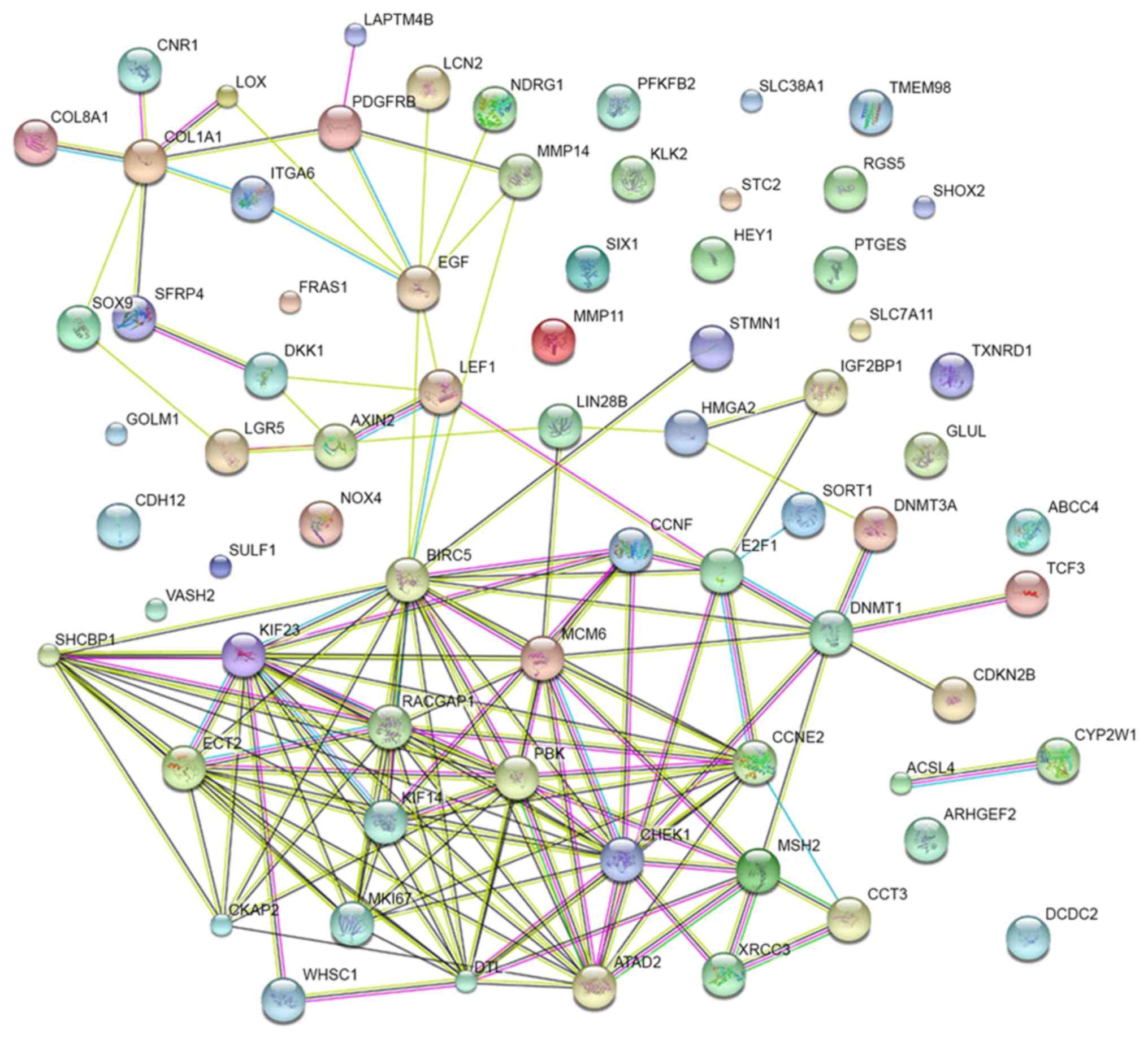
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(Database issue): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Khairy A, Hamza I, Shaker O and Yosry A:
Serum miRNA panel in egyptian patients with chronic hepatitis C
related hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
17:2699–2703. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zuo D, Chen L, Liu X, et al: Combination
of miR-125b and miR-27a enhances sensitivity and specificity of
AFP-based diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
37:6539–6549. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Oksuz Z, Serin MS, Kaplan E, Dogen A,
Tezcan S, Aslan G, Emekdas G, Sezgin O, Altintas E and Tiftik EN:
Serum microRNAs; miR-30c-5p, miR-223-3p, miR-302c-3p and miR-17-5p
could be used as novel non-invasive biomarkers for HCV-positive
cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 42:713–720.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li LM, Hu ZB, Zhou ZX, Chen X, Liu FY,
Zhang JF, Shen HB, Zhang CY and Zen K: Serum microRNA profiles
serve as novel biomarkers for HBV infection and diagnosis of
HBV-positive hepatocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 70:9798–9807. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Laios A, O'Toole S, Flavin R, Martin C,
Kelly L, Ring M, Finn SP, Barrett C, Loda M, Gleeson N, et al:
Potential role of miR-9 and miR-223 in recurrent ovarian cancer.
Mol Cancer. 7:352008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tachibana H, Sho R, Takeda Y, Zhang X,
Yoshida Y, Narimatsu H, Otani K, Ishikawa S, Fukao A, Asao H and
Iino M: Circulating miR-223 in oral cancer: Its potential as a
novel diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target. PLoS One.
11:e01596932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Swets JA: Measuring the accuracy of
diagnostic systems. Science. 240:1285–1293. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Han ZB, Zhong L, Teng MJ, Fan JW, Tang HM,
Wu JY, Chen HY, Wang ZW, Qiu GQ and Peng ZH: Identification of
recurrence-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma following
liver transplantation. Mol Oncol. 6:445–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wei Y, Yang J, Yi L, Wang Y, Dong Z, Liu
Z, Ou-yang S, Wu H, Zhong Z, Yin Z, et al: miR-223-3p targeting
SEPT6 promotes the biological behavior of prostate cancer. Sci Rep.
4:75462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhi Y, Pan J, Shen W, He P, Zheng J, Zhou
X, Lu G, Chen Z and Zhou Z: Ginkgolide B inhibits human bladder
cancer cell migration and invasion through microRNA-223-3p. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 39:1787–1794. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ulbing M, Kirsch AH, Leber B, Lemesch S,
Münzker J, Schweighofer N, Hofer D, Trummer O, Rosenkranz AR,
Müller H, et al: MicroRNAs 223–3p and 93-5p in patients with
chronic kidney disease before and after renal transplantation.
Bone. 95:115–123. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dong Z, Qi R, Guo X, Zhao X, Li Y, Zeng Z,
Bai W, Chang X, Hao L, Chen Y, et al: miR-223 modulates
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation through promoting
apoptosis via the Rab1-mediated mTOR activation. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 483:630–637. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Dong YW, Wang R, Cai QQ, Qi B, Wu W, Zhang
YH and Wu XZ: Sulfatide epigenetically regulates miR-223 and
promotes the migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J
Hepatol. 60:792–801. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yang T, Zheng ZM, Li XN, Li ZF, Wang Y,
Geng YF, Bai L and Zhang XB: miR-223 modulates multidrug resistance
via downregulation of ABCB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exp
Biol Med (Maywood). 238:1024–1032. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang XM, Li J, Feng XC, Wang Q, Guan DY
and Shen ZH: Involvement of the role of Chk1 in lithium-induced
G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J
Cell Biochem. 104:1181–1191. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Xie Y, Wei RR, Huang GL, Zhang MY, Yuan YF
and Wang HY: Checkpoint kinase 1 is negatively regulated by miR-497
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31:8442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hong J, Hu K, Yuan Y, Sang Y, Bu Q, Chen
G, Yang L, Li B, Huang P, Chen D, et al: CHK1 targets spleen
tyrosine kinase (L) for proteolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Clin Invest. 122:2165–2175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yan L, Yang X and Davidson NE: Role of DNA
methylation and histone acetylation in steroid receptor expression
in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 6:183–192. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Fang QL, Yin YR, Xie CR, Zhang S, Zhao WX,
Pan C, Wang XM and Yin ZY: Mechanistic and biological significance
of DNA methyltransferase 1 upregulated by growth factors in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 46:782–790. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li H, Yang F, Gao B, Yu Z, Liu X, Xie F
and Zhang J: Hepatitis B virus infection in hepatocellular
carcinoma tissues upregulates expression of DNA methyltransferases.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:4175–4185. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Saito Y, Kanai Y, Nakagawa T, Sakamoto M,
Saito H, Ishii H and Hirohashi S: Increased protein expression of
DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) 1 is significantly correlated with the
malignant potential and poor prognosis of human hepatocellular
carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 105:527–532. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Neef R, Klein UR, Kopajtich R and Barr FA:
Cooperation between mitotic kinesins controls the late stages of
cytokinesis. Curr Biol. 16:301–307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wang SM, Ooi LL and Hui KM: Upregulation
of Rac GTPase-activating protein 1 is significantly associated with
the early recurrence of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 17:6040–6051. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cao L, Li C, Shen S, Yan Y, Ji W, Wang J,
Qian H, Jiang X, Li Z and Wu M: OCT4 increases BIRC5 and CCND1
expression and promotes cancer progression in hepatocellular
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 13:822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Jin B, Wang W, Du G, Huang GZ, Han LT,
Tang ZY, Fan DG, Li J and Zhang SZ: Identifying hub genes and
dysregulated pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 19:592–601. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Koilan S, Hamilton D, Baburyan N, Padala
MK, Weber KT and Guntaka RV: Prevention of liver fibrosis by triple
helix-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotides targeted to the promoter
region of type I collagen gene. Oligonucleotides. 20:231–237. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yang MR, Zhang Y, Wu XX and Chen W:
Critical genes of hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by network and
module analysis of RNA-seq data. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:4248–4256. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hayashi M, Nomoto S, Hishida M, Inokawa Y,
Kanda M, Okamura Y, Nishikawa Y, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, Yamada S,
et al: Identification of the collagen type 1 α 1 gene (COL1A1) as a
candidate survival-related factor associated with hepatocellular
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 14:1082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|