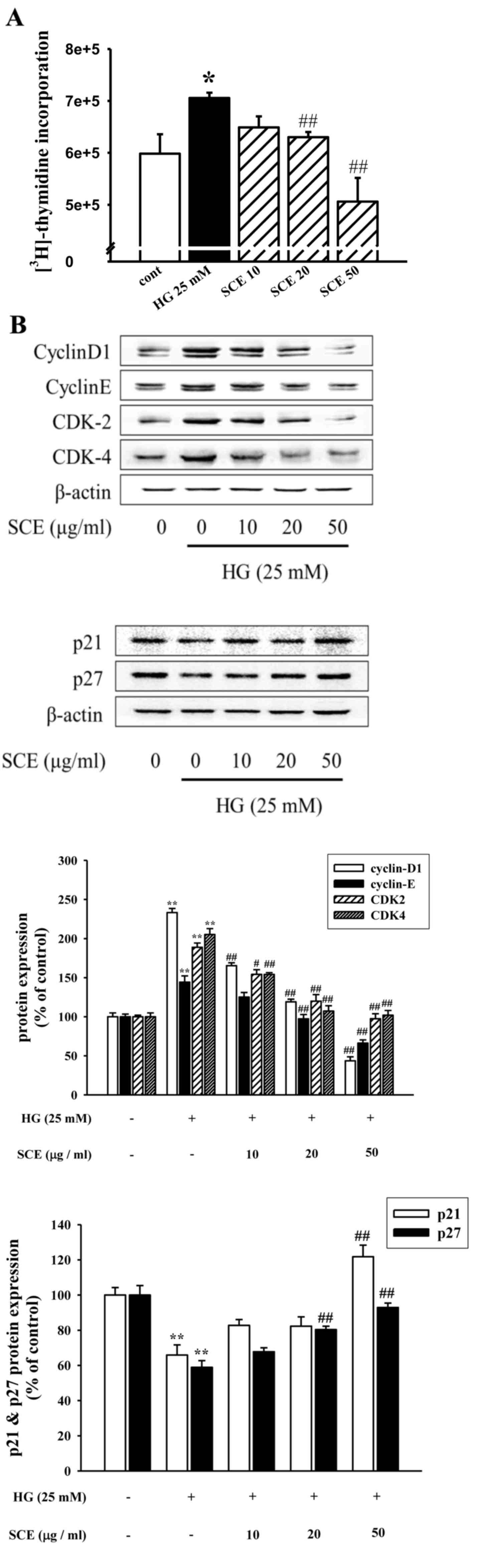
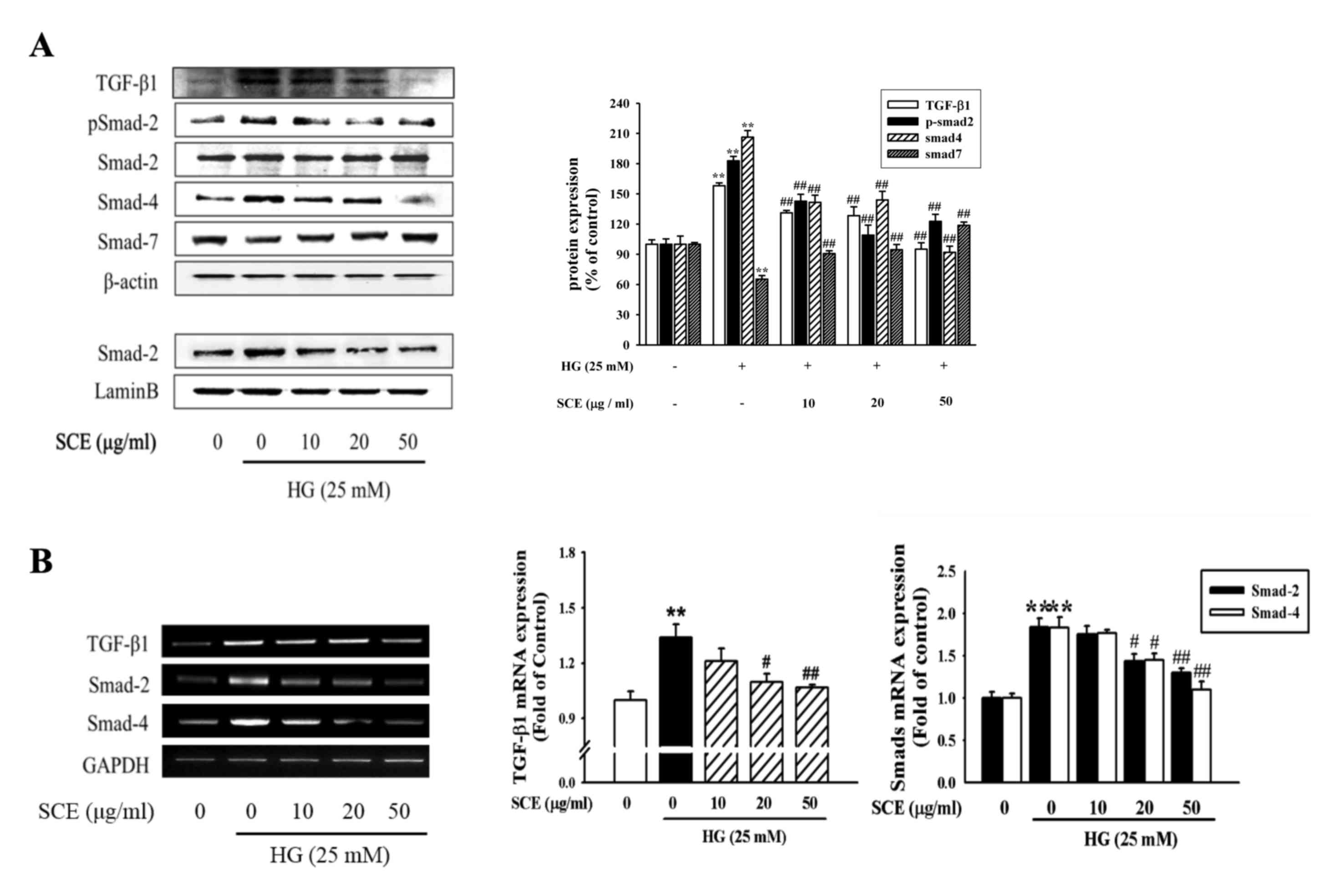
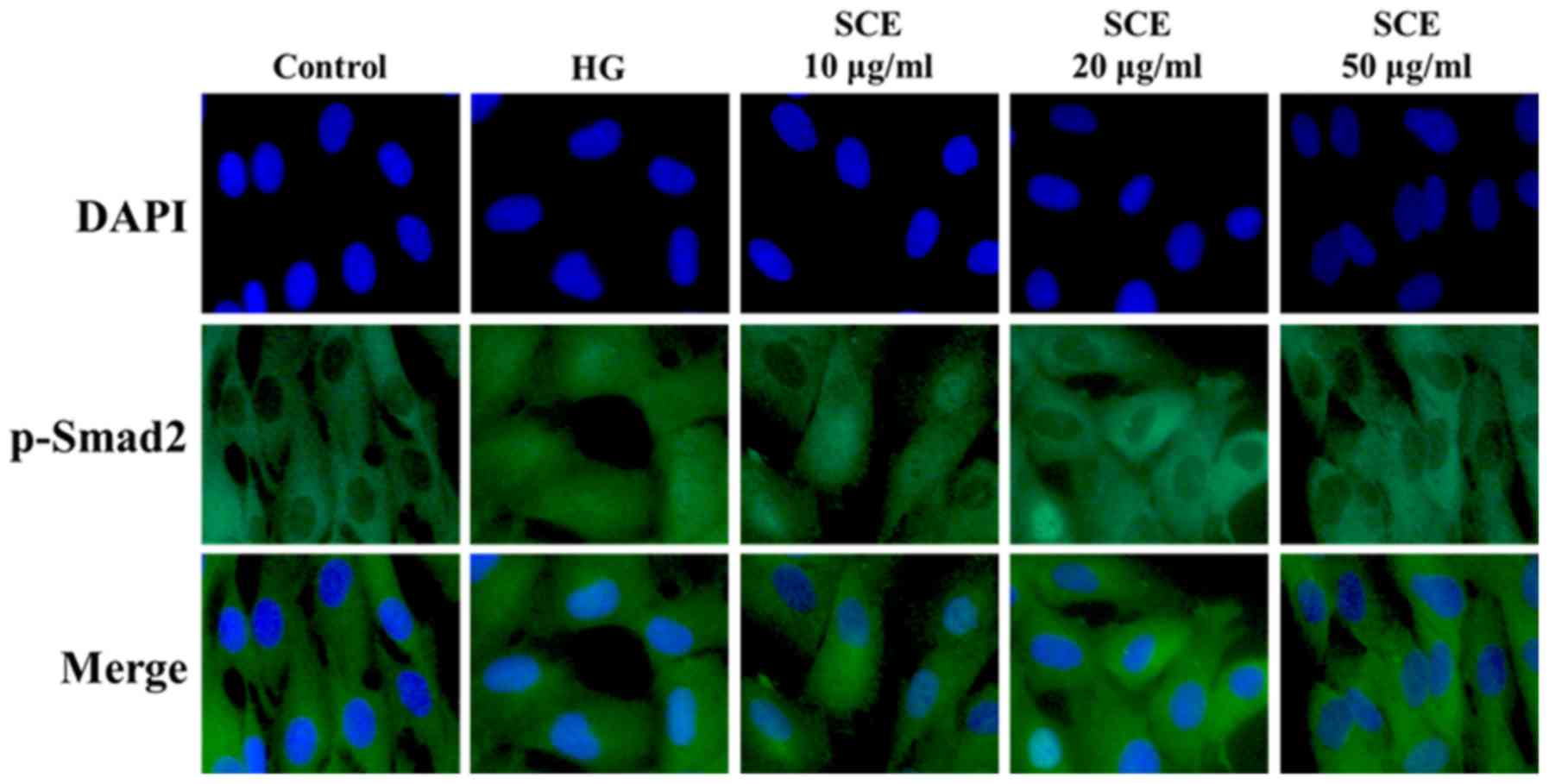
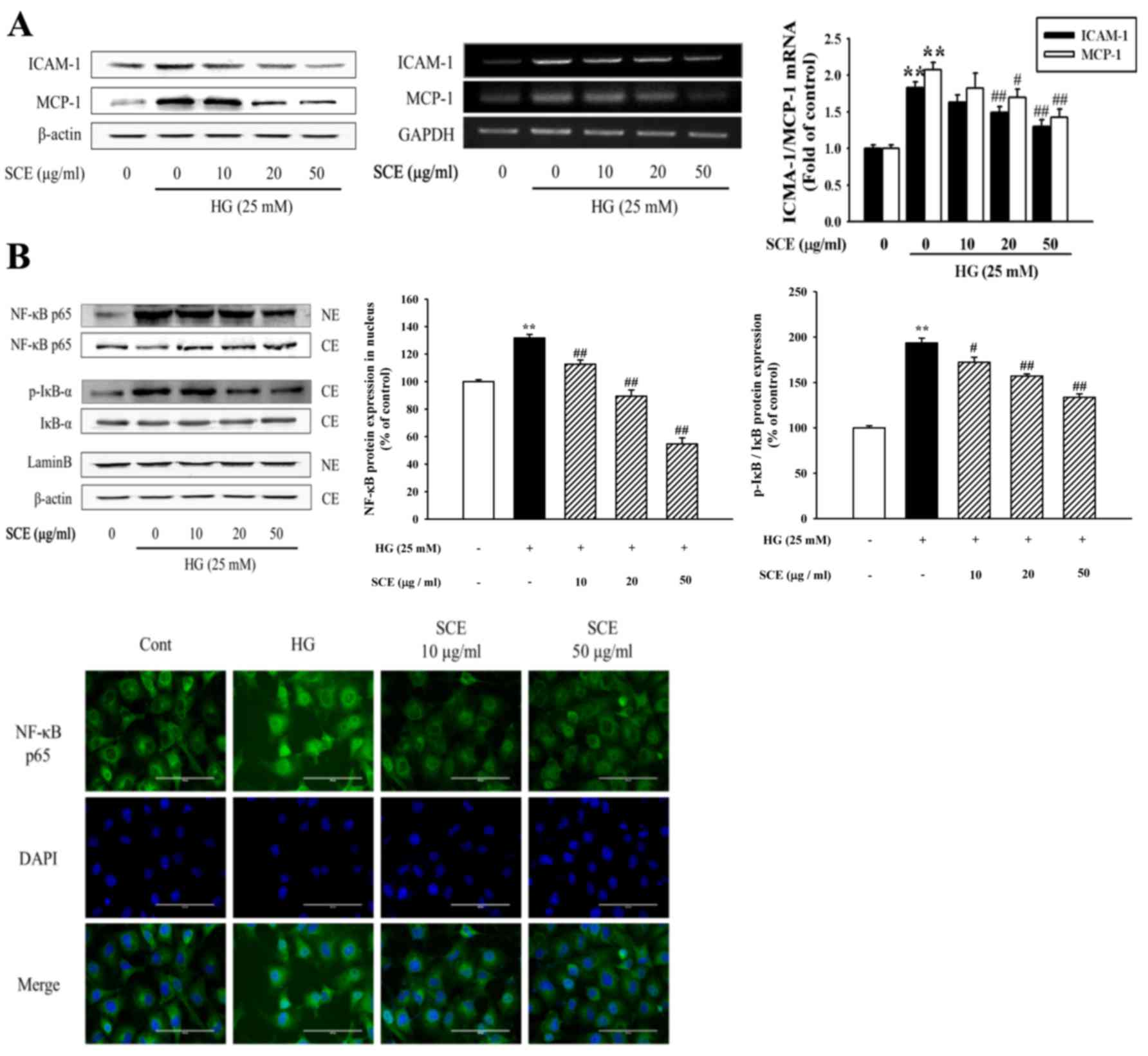
|
1
|
Kolset SO, Reinholt FP and Jenssen T:
Diabetic nephropathy and extracellular matrix. J Histochem
Cytochem. 60:976–986. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mason RM and Wahab NA: Extra-cellular
matrix metabolism in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14:1358–1373. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abrass CK, Peterson CV and Raugi GJ:
Phenotypic expression of collagen types in mesangial matrix of
diabetic and non-diabetic rats. Diabetes. 37:1695–1702. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mauer SM, Steffes MW, Ellis EN, Sutherland
DE, Brown DM and Goetz FC: Structural-functional relationships in
diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 74:1143–1155. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ziyadeh FN, Sharma K, Ericksen M and Wolf
G: Stimulation of collagen gene expression and protein synthesis in
murine mesangial cells by high glucose is mediated by autocrine
activation of transforming growth factor-beta. J Clin Invest.
93:536–542. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Young BA, Johnson RJ, Alpers CE, Eng E,
Gordon K, Floege J, Couser WG and Seidel K: Cellular events in the
evolution of experimental diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int.
47:935–944. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuan CJ, Al-Douahji M and Shankland SJ:
The cyclin kinase inhibitor p21WAF1, CIP1 is increased in
experimental diabetic nephropathy: Potential role in glomerular
hypertrophy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 9:986–993. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adler S: Structure-function relationships
associated with extracellular matrix alterations in diabetic
glomerulopathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 5:1165–1172. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang K, Liu W, Lan T, Xie X, Peng J,
Huang J, Wang S, Shen X, Liu P and Huang H: Berberine reduces
fibronectin expression by suppressing the S1P-S1P2 receptor pathway
in experimental diabetic nephropathy models. PLoS One.
7:e438742012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Köppel H, Riedl E, Braunagel M,
Sauerhoefer S, Ehnert S, Godoy P, Sternik P, Dooley S and Yard BA:
L-carnosine inhibits high-glucose-mediated matrix accumulation in
human mesangial cells by interfering with TGF-β production and
signalling. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 26:3852–3858. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pozzi A, Voziyan PA, Hudson BG and Zent R:
Regulation of matrix synthesis, remodeling and accumulation in
glomerulosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des. 15:1318–1333. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abboud HE: Mesangial cell biology. Exp
Cell Res. 318:979–985. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McLennan SV, Fisher EJ, Yue DK and Turtle
JR: High glucose concentration causes a decrease in mesangium
degradation. A factor in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetes. 43:1041–1045. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bernardo MM and Fridman R: TIMP-2 (tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2) regulates MMP-2 (matrix
metalloproteinase-2) activity in the extracellular environment
after pro-MMP-2 activation by MT1 (membrane type 1)-MMP. Biochem J.
374:739–745. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McLennan SV, Wang XY, Moreno V, Yue DK and
Twigg SM: Connective tissue growth factor mediates high glucose
effects on matrix degradation through tissue inhibitor of matrix
metalloproteinase type 1: Implications for diabetic nephropathy.
Endocrinology. 145:5646–5655. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sharma K and Ziyadeh FN: Hyperglycemia and
diabetic kidney disease: The case for transforming growth
factor-beta as a key mediator. Diabetes. 44:1139–1146. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ask K, Bonniaud P, Maass K, Eickelberg O,
Margetts PJ, Warburton D, Groffen J, Gauldie J and Kolb M:
Progressive pulmonary fibrosis is mediated by TGF-beta isoform 1
but not TGF-beta3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:484–495. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Massagué J, Seoane J and Wotton D: Smad
transcription factors. Genes Dev. 19:2783–2810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signaling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fornoni A, Ijaz A, Tejada T and Lenz O:
Role of inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diabetes Rev.
4:10–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Clavreul N, Sansilvestri-Morel P, Magard
D, Verbeuren TJ and Rupin A: (Pro)renin promotes fibrosis gene
expression in HEK cells through a Nox4-dependent mechanism. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 300:F1310–F1318. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bondar IA, Klimontov VV and Nadeev AP:
Urinary excretion of proinflammatory cytokines and transforming
growth factor beta at early stages of diabetic nephropathy. Ter
Arkh. 80:52–56. 2008.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and
the 22DDCT Method. METHODS. 25:402–8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Michelini E, Cevenini L, Mezzanotte L,
Ablamsky D, Southworth T, Branchini B and Roda A: Spectral-resolved
gene technology for multiplexed bioluminescence and high-content
screening. Anal Chem. 80:260–7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kang SW, Choi JS, Choi YJ, Bae JY and Li
J: Licorice isoliquiritigenin dampens angiogenic activity via
inhibition of MAPK-responsive signaling pathways leading to
induction of matrix metalloproteinases. J Nutr Nutr Nutr Biochem.
21:55–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Okada S, Shikata K, Matsuda M, Ogawa D,
Usui H, Kido Y, et al: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1-deficient
mice are resistant against renal injury after induction of
diabetes. Diabetes. 52:2586–93. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Poljakovic M, Nygren JM and Persson K:
Signalling pathways regulating inducible nitricoxide synthase
expression in human kidney epithelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
469:21–8. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ha H and Lee HB: Oxidative stress in
diabetic nephropathy: Basic and clinical information. Curr Diab
Rep. 1:282–7. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mahadevan P, Larkins RG, Fraser JR and
Dunlop ME: Effect of prostaglandin E2 and hyalurunan on mesangial
cell proliferation: A potential contribution to glomerular
hypercellularity in diabetes. Diabetes. 45:44–50. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pozzi A, Voziyan PA, Hudson BG and Zent R:
Regulation of matrix synthesis, remodeling and accumulation in
glomerulosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des. 15:1318–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Park IS, Kiyomoto H, Abboud SL and Abboud
HE: Expression of transforming growth factor-β and type IV collagen
in early streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetes. 46:473–80.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huse M, Muir TW, Xu L, Chen YG, Kuriyan J
and Massague J: The TGFβ receptor activation process: Aan
inhibitor- to substrate-binding switch. Mol Cell. 8:671–82. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ohga S, Shikata K, Yozai K, Okada S, Ogawa
D and Usui H: Thiazolidinedione ameliorates renal injury in
experimental diabetic rats through anti-inflammatory effects
mediated by inhibition of NF-κB activation. Am J J Physiol.
292:F1141–50. 2007.
|
|
34
|
Yin D, Yao W, Chen S, Hu R and Gao X:
Salidroside, the main active compound of Rhodiola plants, inhibits
high glucose-induced mesangial cell proliferation. Planta Med.
75:1191–5. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|