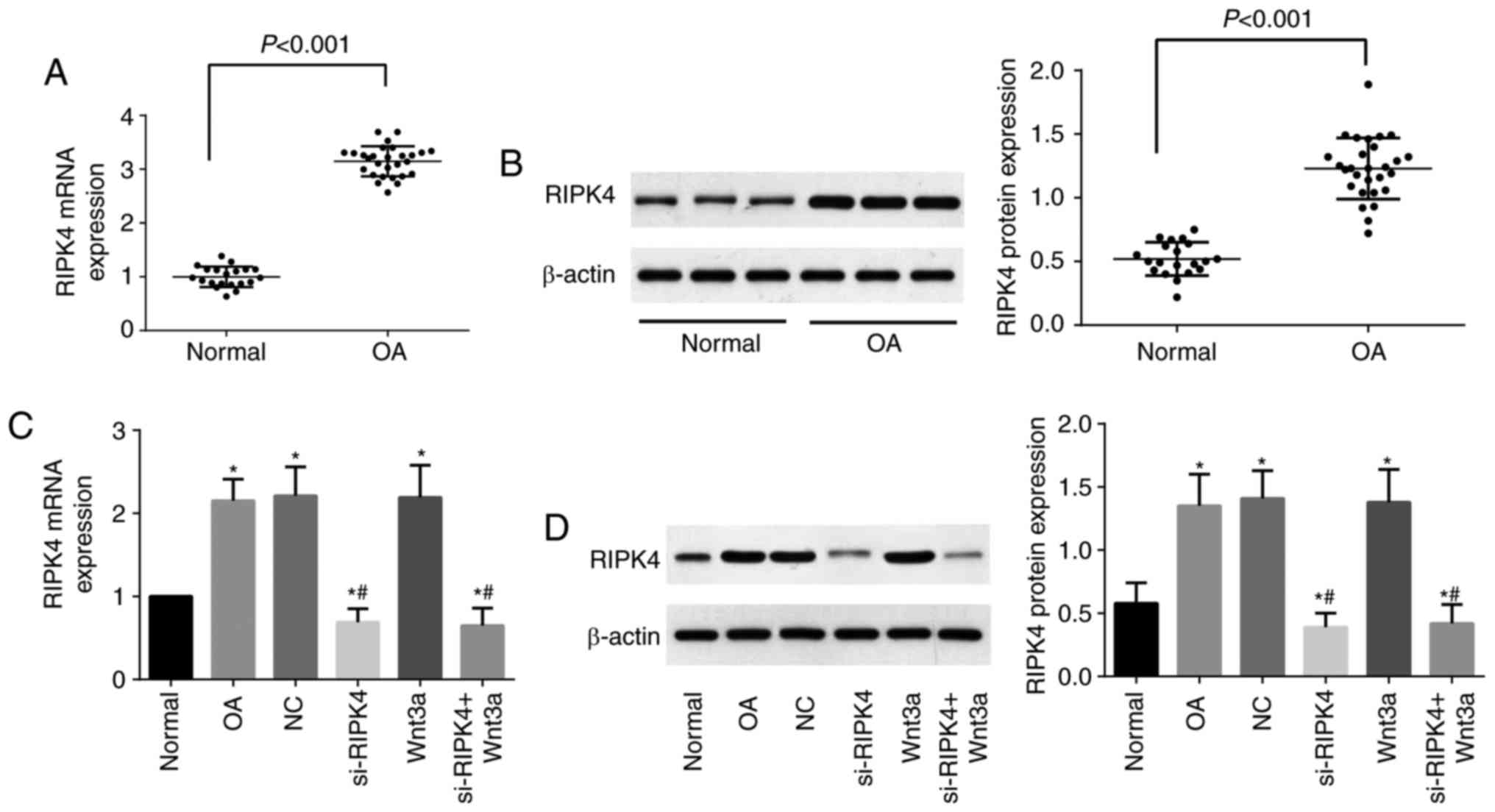
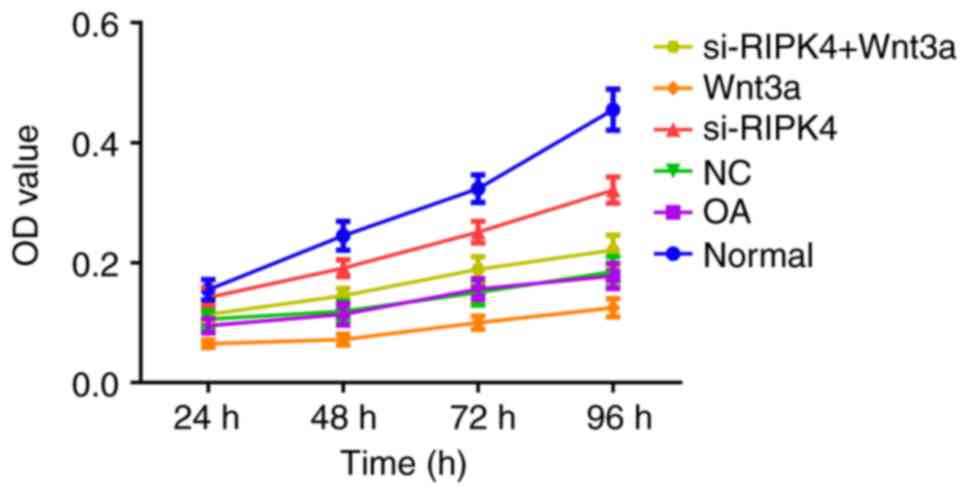
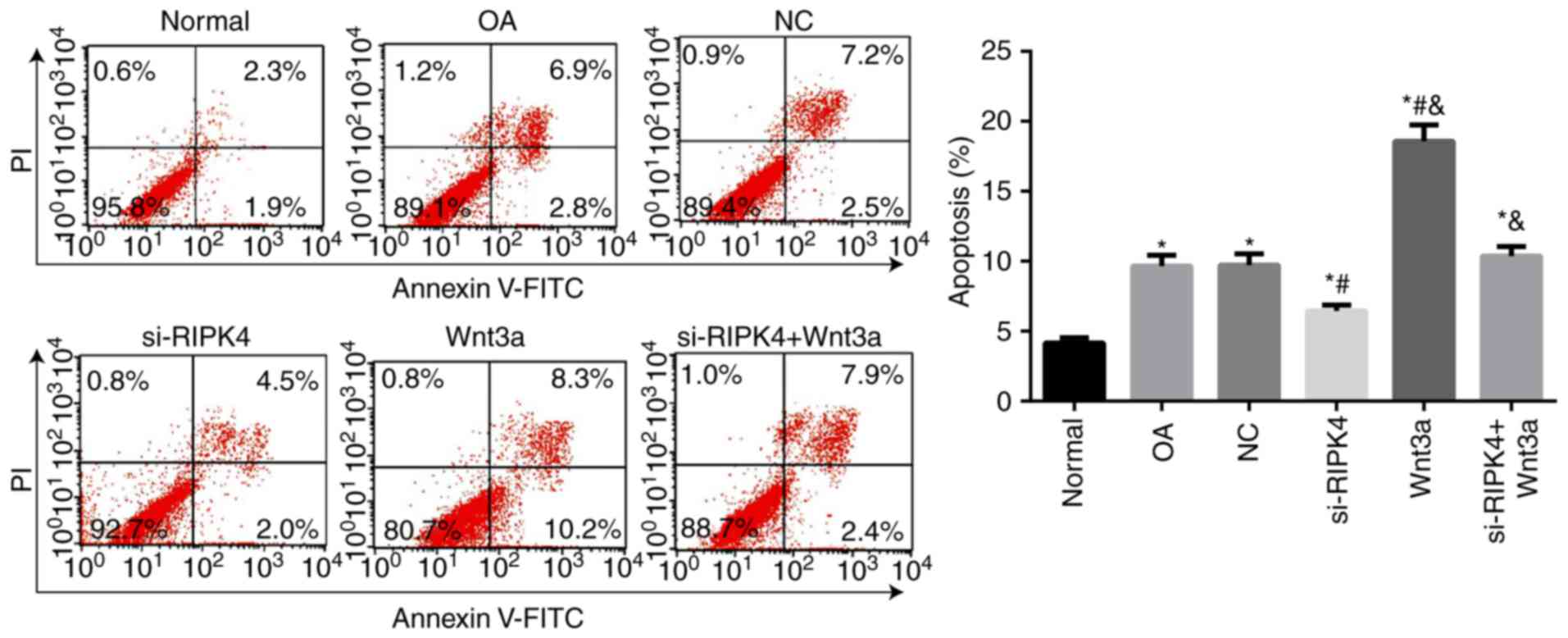
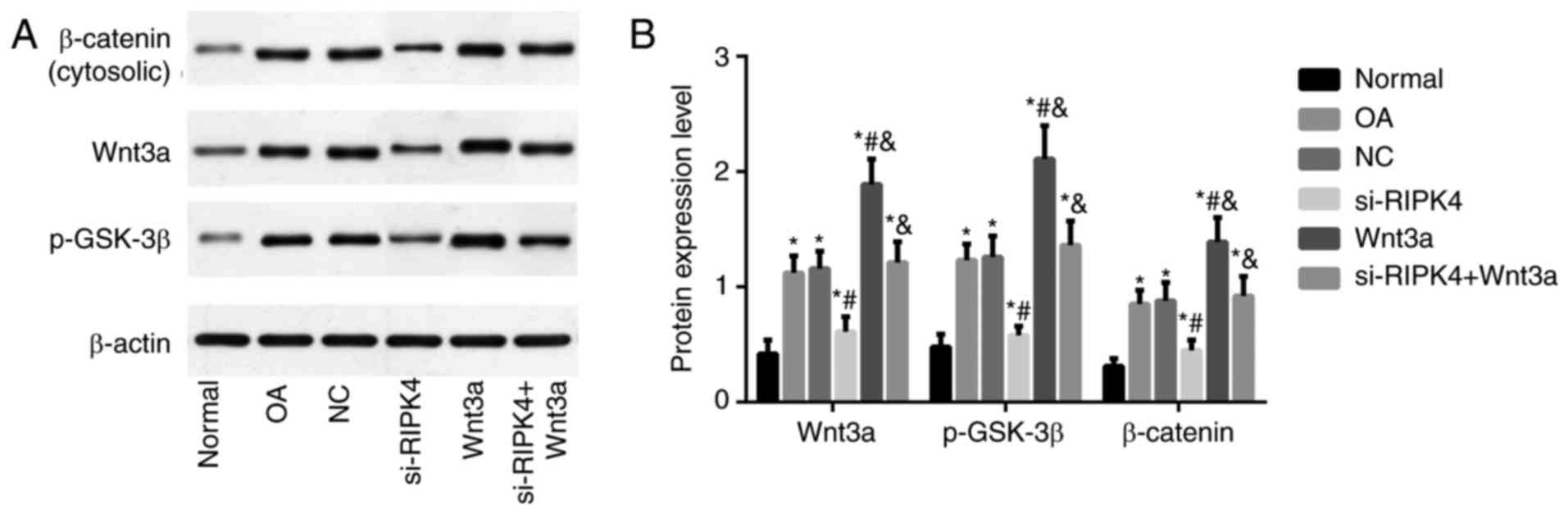
|
1
|
Collison J: Osteoarthritis: Removing old
chondrocytes to combat disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 73:3882017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Johnson VL and Hunter DJ: The epidemiology
of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 28:5–15. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, Arnold
LM, Choi H, Deyo RA, Gabriel S, Hirsch R, Hochberg MC, Hunder GG,
et al: Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic
conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum.
58:26–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gomes-Neto M, Araujo AD, Junqueira ID,
Oliveira D, Brasileiro A and Arcanjo FL: Comparative study of
functional capacity and quality of life among obese and non-obese
elderly people with knee osteoarthritis. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed.
56:126–130. 2016.(In English, Portuguese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iannone F and Lapadula G: The
pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 15:364–372.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Neogi T and Zhang Y: Epidemiology of
osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 39:1–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Michael JW, Schluter-Brust KU and Eysel P:
The epidemiology, etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of
osteoarthritis of the knee. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 107:152–162.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Alcaraz MJ, Megias J, Garcia-Arnandis I,
Clérigues V and Guillén MI: New molecular targets for the treatment
of osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:13–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang D, Lin J and Han J:
Receptor-interacting protein (RIP) kinase family. Cell Mol Immunol.
7:243–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bhr C, Rohwer A, Stempka L, Rincke G,
Marks F and Gschwendt M: DIK, a novel protein kinase that interacts
with protein kinase Cdelta. Cloning, characterization, and gene
analysis. J Biol Chem. 275:36350–36357. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen L, Haider K, Ponda M, Cariappa A,
Rowitch D and Pillai S: Protein kinase C-associated kinase (PKK), a
novel membrane-associated, ankyrin repeat-containing protein
kinase. J Biol Chem. 276:21737–21744. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meylan E, Martinon F, Thome M, Gschwendt M
and Tschopp J: RIP4 (DIK/PKK), a novel member of the RIP kinase
family, activates NF-kappa B and is processed during apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 3:1201–1208. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meylan E and Tschopp J: The RIP kinases:
Crucial integrators of cellular stress. Trends Biochem Sci.
30:151–159. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Adams S and Munz B: RIP4 is a target of
multiple signal transduction pathways in keratinocytes:
Implications for epidermal differentiation and cutaneous wound
repair. Exp Cell Res. 316:126–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang X, McGann JC, Liu BY, Hannoush RN,
Lill JR, Pham V, Newton K, Kakunda M, Liu J, Yu C, et al:
Phosphorylation of Dishevelled by protein kinase RIPK4 regulates
Wnt signaling. Science. 339:1441–1445. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu DQ, Li FF, Zhang JB, Zhou TJ, Xue WQ,
Zheng XH, Chen YB, Liao XY, Zhang L, Zhang SD, et al: Increased
RIPK4 expression is associated with progression and poor prognosis
in cervical squamous cell carcinoma patients. Sci Rep. 5:119552015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rountree RB, Willis CR, Dinh H, Blumberg
H, Bailey K, Dean C Jr, Peschon JJ and Holland PM: RIP4 regulates
epidermal differentiation and cutaneous inflammation. J Invest
Dermatol. 130:102–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Adams S, Pankow S, Werner S and Munz B:
Regulation of NF-kappaB activity and keratinocyte differentiation
by the RIP4 protein: Implications for cutaneous wound repair. J
Invest Dermatol. 127:538–544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rose J, Söder S, Skhirtladze C, Schmitz N,
Gebhard PM, Sesselmann S and Aigner T: DNA damage, discoordinated
gene expression and cellular senescence in osteoarthritic
chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:1020–1028. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
The helsinki declaration of the world
medical association (WMA), . Ethical principles of medical research
involving human subjects. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 36:298–301. 2014.(In
Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dias RC, Dias JM and Ramos LR: Impact of
an exercise and walking protocol on quality of life for elderly
people with OA of the knee. Physiother Res Int. 8:121–130. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tuo YL, Li XM and Luo J: Long noncoding
RNA UCA1 modulates breast cancer cell growth and apoptosis through
decreasing tumor suppressive miR-143. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
19:3403–3411. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ebrahimzadeh MH, Makhmalbaf H,
Birjandinejad A and Soltani-Moghaddas SH: Cross-cultural adaptation
and validation of the persian version of the oxford knee score in
patients with knee osteoarthritis. Iran J Med Sci. 39:529–535.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Holland P, Willis C, Kanaly S, Glaccum M,
Warren A, Charrier K, Murison J, Derry J, Virca G, Bird T and
Peschon J: RIP4 is an ankyrin repeat-containing kinase essential
for keratinocyte differentiation. Curr Biol. 12:1424–1428. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kwa MQ, Scholz GM and Reynolds EC: RIPK4
activates an IRF6-mediated proinflammatory cytokine response in
keratinocytes. Cytokine. 83:19–26. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Azizmohammadi S, Azizmohammadi S, Safari
A, Kaghazian M, Sadrkhanlo M, Behnod V and Seifoleslami M:
High-level expression of RIPK4 and EZH2 contributes to lymph node
metastasis and predicts favorable prognosis in patients with
cervical cancer. Oncol Res. 25:495–501. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang Z, Li J, Du S, Chen G, Qi Y, Huang
L, Xiao L and Tong P: Effects of UCP4 on the proliferation and
apoptosis of chondrocytes: Its possible involvement and regulation
in osteoarthritis. PLoS One. 11:e01506842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schroeppel JP, Crist JD, Anderson HC and
Wang J: Molecular regulation of articular chondrocyte function and
its significance in osteoarthritis. Histol Histopathol. 26:377–394.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhong JH, Li J, Liu CF, Liu N, Bian RX,
Zhao SM, Yan SY and Zhang YB: Effects of microRNA-146a on the
proliferation and apoptosis of human osteoarthritis chondrocytes by
targeting TRAF6 through the NF-κB signalling pathway. Biosci Rep.
37:pii: BSR201605782017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Li YP, Paulson C, Shao JZ, Zhang
X, Wu M and Chen W: Wnt and the Wnt signaling pathway in bone
development and disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 19:379–407.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lad EM, Cheshier SH and Kalani MY:
Wnt-signaling in retinal development and disease. Stem Cells Dev.
18:7–16. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Corr M: Wnt-beta-catenin signaling in the
pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol.
4:550–556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnson ML and Kamel MA: The Wnt signaling
pathway and bone metabolism. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 19:376–382. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Reinhold MI, Kapadia RM, Liao Z and Naski
MC: The Wnt-inducible transcription factor Twist1 inhibits
chondrogenesis. J Biol Chem. 281:1381–1388. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nalesso G, Sherwood J, Bertrand J, Pap T,
Ramachandran M, De Bari C, Pitzalis C and Dell'accio F: WNT-3A
modulates articular chondrocyte phenotype by activating both
canonical and noncanonical pathways. J Cell Biol. 193:551–564.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Funck-Brentano T, Bouaziz W, Marty C,
Geoffroy V, Hay E and Cohen-Solal M: Dkk-1-mediated inhibition of
Wnt signaling in bone ameliorates osteoarthritis in mice. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 66:3028–3039. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rockel JS, Yu C, Whetstone H, Craft AM,
Reilly K, Ma H, Tsushima H, Puviindran V, Al-Jazrawe M, Keller GM
and Alman BA: Hedgehog inhibits β-catenin activity in synovial
joint development and osteoarthritis. J Clin Invest. 126:1649–1663.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Delgado E, Bahal R, Yang J, Lee JM, Ly DH
and Monga SP: β-Catenin knockdown in liver tumor cells by a cell
permeable gamma guanidine-based peptide nucleic acid. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 13:867–878. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gosens R, Meurs H and Schmidt M: The
GSK-3/beta-catenin-signalling axis in smooth muscle and its
relationship with remodelling. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
378:185–191. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cui XP, Xing Y, Chen JM, Dong SW, Ying DJ
and Yew DT: Wnt/beta-catenin is involved in the proliferation of
hippocampal neural stem cells induced by hypoxia. Ir J Med Sci.
180:387–393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhou X, Li W, Jiang L, Bao J, Tao L, Li J
and Wu L: Tetrandrine Inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway
and alleviates osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:8095792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen L, Wu Y, Wu Y, Wang Y, Sun L and Li
F: The inhibition of EZH2 ameliorates osteoarthritis development
through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Sci Rep. 6:291762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhu M, Tang D, Wu Q, Hao S, Chen M, Xie C,
Rosier RN, O'Keefe RJ, Zuscik M and Chen D: Activation of
beta-catenin signaling in articular chondrocytes leads to
osteoarthritis-like phenotype in adult beta-catenin conditional
activation mice. J Bone Miner Res. 24:12–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|