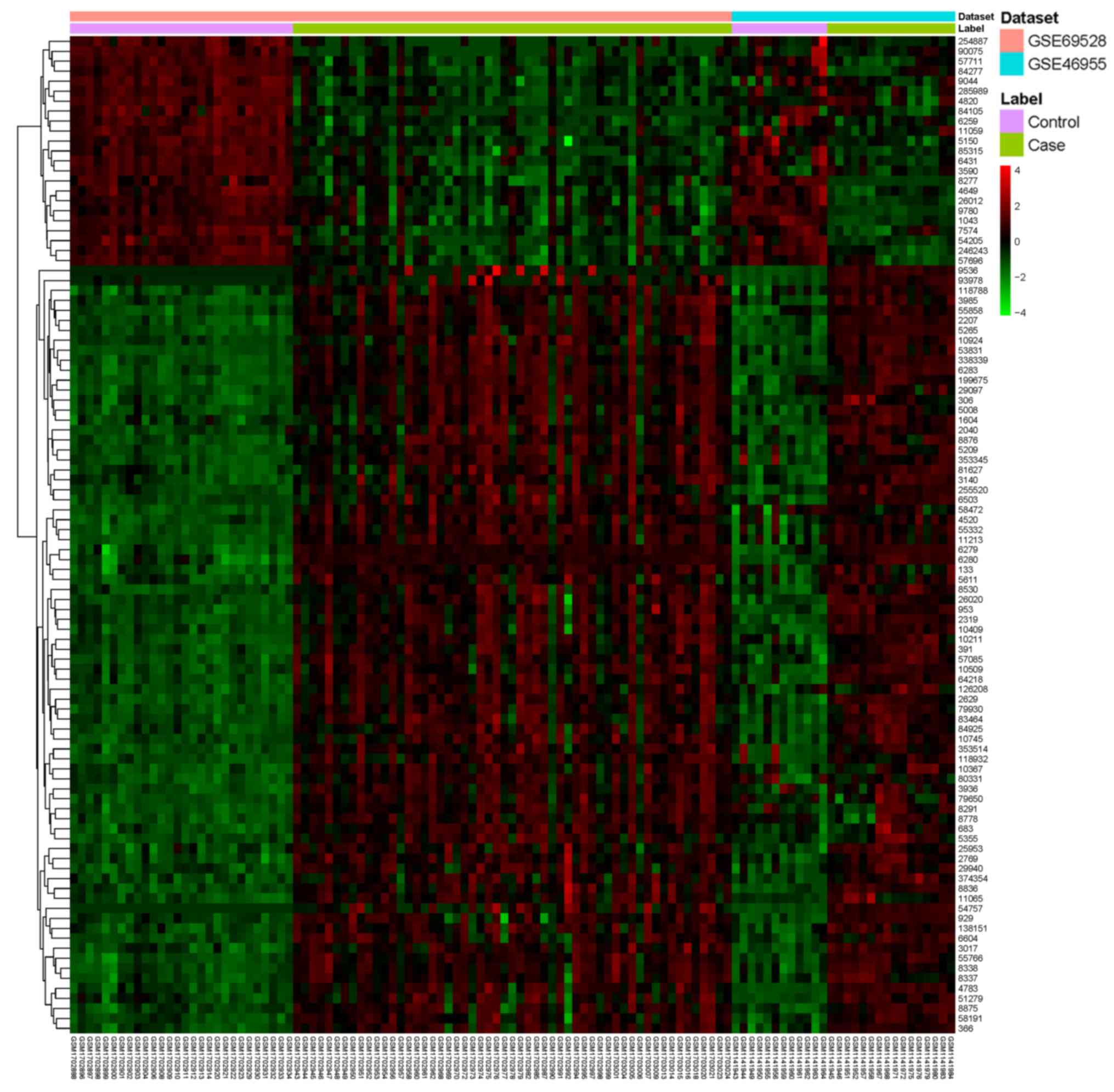
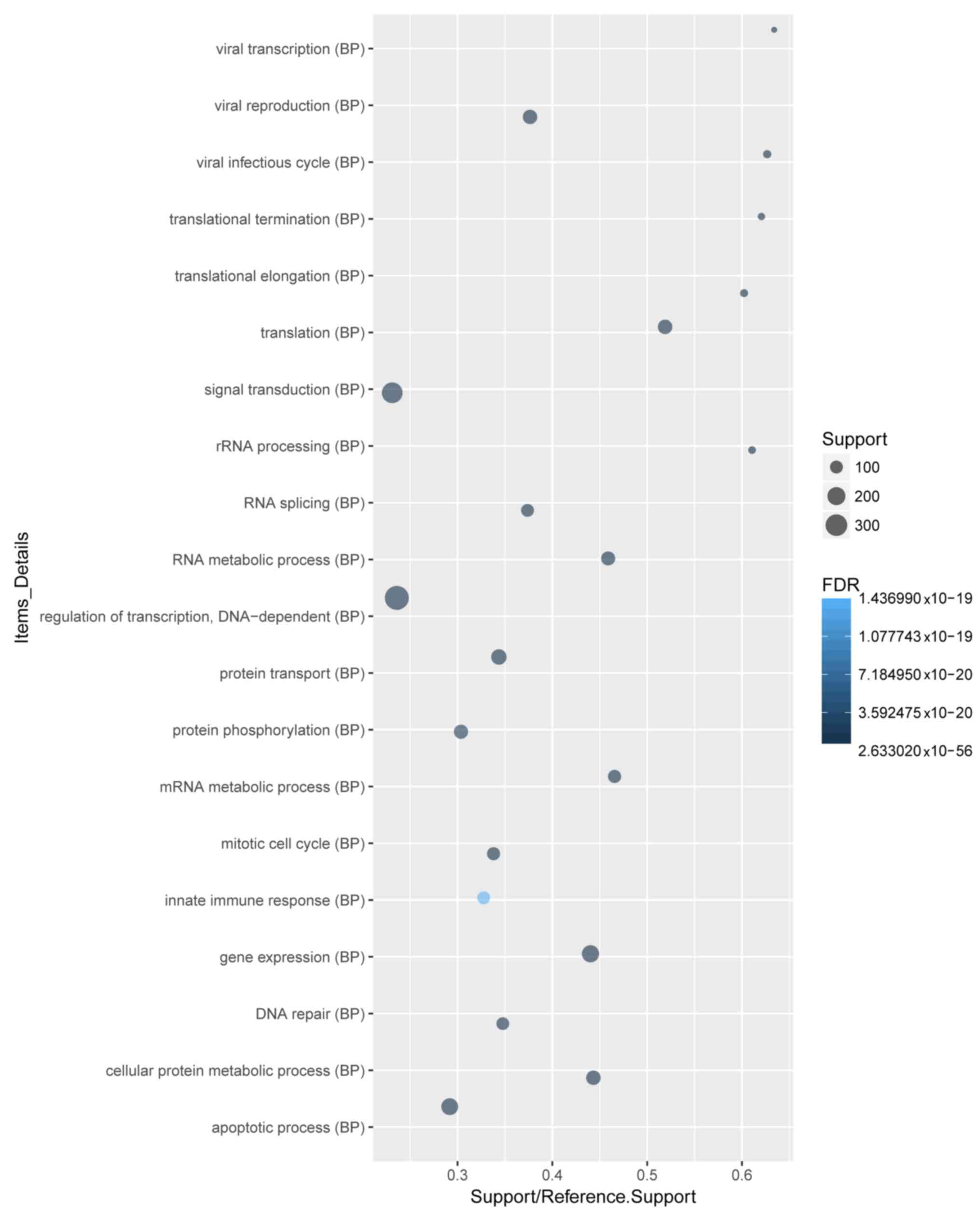
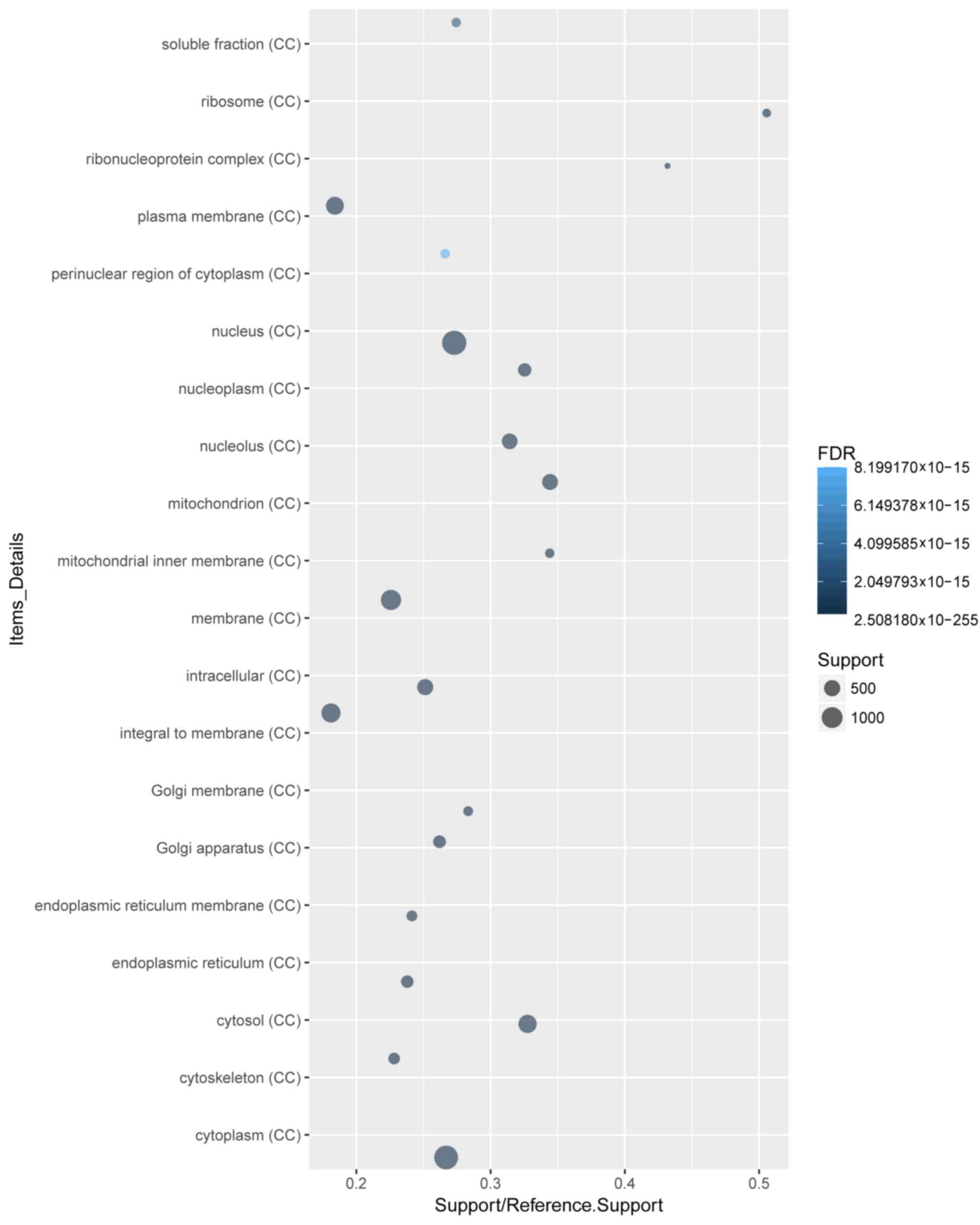
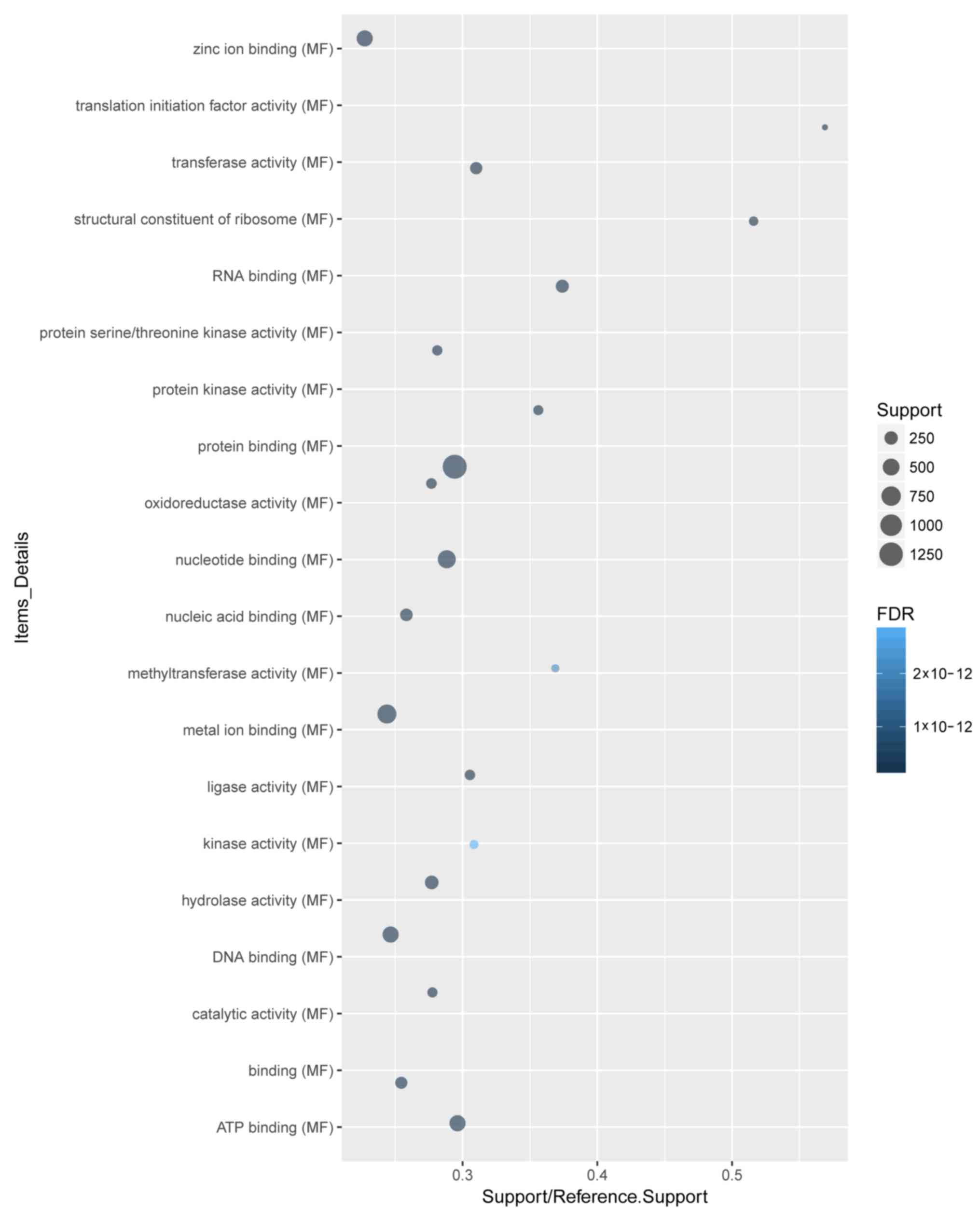
|
1
|
Bao R, Shui X, Hou J, Li J, Deng X, Zhu X
and Yang T: Adenosine and the adenosine A2A receptor agonist,
CGS21680, upregulate CD39 and CD73 expression through E2F-1 and
CREB in regulatory T cells isolated from septic mice. Int J Mol
Med. 38:969–975. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jawad I, Lukšić I and Rafnsson SB:
Assessing available information on the burden of sepsis: Global
estimates of incidence, prevalence and mortality. J Glob Health.
2:0104042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martin GS, Mannino DM and Moss M: The
effect of age on the development and outcome of adult sepsis. Criti
Care Med. 34:15–21. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Strehlow MC, Emond SD, Shapiro NI,
Pelletier AJ and Camargo CA Jr: National study of emergency
department visits for sepsis, 1992 to 2001. Ann Emerg Med.
48:326–331, 331.e1-e3. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S and Moss M:
The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through
2000. N Engl J Med. 348:1546–1554. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Murphy SL: Deaths: Final data for 1998.
Natl Vital Stat Rep. 48:1–105. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hotchkiss RS and Karl IE: The
pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 348:138–150.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calvano SE, Xiao W, Richards DR, Felciano
RM, Baker HV, Cho RJ, Chen RO, Brownstein BH, Cobb JP, Tschoeke SK,
et al: A network-based analysis of systemic inflammation in humans.
Nature. 437:1032–1037. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wurfel MM, Gordon AC, Holden TD, Radella
F, Strout J, Kajikawa O, Ruzinski JT, Rona G, Black RA, Stratton S,
et al: Toll-like receptor 1 polymorphisms affect innate immune
responses and outcomes in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
178:710–720. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J,
Clermont G, Carcillo J and Pinsky MR: Epidemiology of severe sepsis
in the United States: Analysis of incidence, outcome, and
associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 29:1303–1310. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pankla R, Buddhisa S, Berry M, Blankenship
DM, Bancroft GJ, Banchereau J, Lertmemongkolchai G and Chaussabel
D: Genomic transcriptional profiling identifies a candidate blood
biomarker signature for the diagnosis of septicemic melioidosis.
Genome Biol. 10:R1272009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu JQ, Sassé TR, Wolkenstein G, Conceicao
V, Saksena MM, Soedjono M, Perera SS, Wang B, Dwyer DE and Saksena
NK: Transcriptome analysis of primary monocytes shows global
down-regulation of genetic networks in HIV viremic patients versus
long-term non-progressors. Virology. 435:308–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marot G, Foulley JL, Mayer CD and
Jaffrézic F: Moderated effect size and P-value combinations for
microarray meta-analyses. Bioinformatics. 25:2692–2699. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reiner-Benaim A: FDR control by the BH
procedure for two-sided correlated tests with implications to gene
expression data analysis. Biom J. 49:107–126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate-a practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Royal Stat Soc. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
16
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pino-Yanes M, Ma SF, Sun X, Tejera P,
Corrales A, Blanco J, Pérez-Méndez L, Espinosa E, Muriel A, Blanch
L, et al: Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 3 gene
associates with susceptibility to acute lung injury. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 45:740–745. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kesik V, Ataş E, Gülcan Kurt Y, Aydın FN,
Babacan O, Gülgün M and Korkmazer N: Adrenomedullin predicts high
risk and culture positivity in children with solid tumors suffering
from neutropenic fever. J Infect Chemother. 22:617–621. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pavanelli WR, Gutierrez FR, Mariano FS,
Prado CM, Ferreira BR, Teixeira MM, Canetti C, Rossi MA, Cunha FQ
and Silva JS: 5-lipoxygenase is a key determinant of acute
myocardial inflammation and mortality during Trypanosoma cruzi
infection. Microbes Infect. 12:587–597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shogan BD, Belogortseva N, Luong PM,
Zaborin A, Lax S, Bethel C, Ward M, Muldoon JP, Singer M, An G, et
al: Collagen degradation and MMP9 activation by Enterococcus
faecalis contribute to intestinal anastomotic leak. Sci Transl Med.
7:286ra2682015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang LN, Wang XH, Wu L, Huang L, Zhao CG,
Peng QY and Ai YH: Diagnostic and predictive levels of
calcium-binding protein A8 and tumor necrosis factor
receptor-associated factor 6 in sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A
prospective observational study. Chin Med J (Engl). 129:1674–1681.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hall MW, Gavrilin MA, Knatz NL, Duncan MD,
Fernandez SA and Wewers MD: Monocyte mRNA phenotype and adverse
outcomes from pediatric multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.
Pediatr Res. 62:597–603. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Escoll P, del Fresno C, García L, Vallés
G, Lendínez MJ, Arnalich F and López-Collazo E: Rapid up-regulation
of IRAK-M expression following a second endotoxin challenge in
human monocytes and in monocytes isolated from septic patients.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 311:465–472. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cazalis MA, Lepape A, Venet F, Frager F,
Mougin B, Vallin H, Paye M, Pachot A and Monneret G: Early and
dynamic changes in gene expression in septic shock patients: A
genome-wide approach. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2:202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng JC, Cheng G, Newstead MW, Zeng X,
Kobayashi K, Flavell RA and Standiford TJ: Sepsis-induced
suppression of lung innate immunity is mediated by IRAK-M. The J
Clin Invest. 116:2532–2542. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ueda S, Nishio K, Minamino N, Kubo A, Akai
Y, Kangawa K, Matsuo H, Fujimura Y, Yoshioka A, Masui K, et al:
Increased plasma levels of adrenomedullin in patients with systemic
inflammatory response syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
160:132–136. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hirata Y, Mitaka C, Sato K, Nagura T,
Tsunoda Y, Amaha K and Marumo F: Increased circulating
adrenomedullin, a novel vasodilatory peptide, in sepsis. J Clin
Endocrinol Metabol. 81:1449–1453. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sugo S, Minamino N, Shoji H, Kangawa K,
Kitamura K, Eto T and Matsuo H: Interleukin-1, tumor necrosis
factor and lipopolysaccharide additively stimulate production of
adrenomedullin in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 207:25–32. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Musson DS, McLachlan JL, Sloan AJ, Smith
AJ and Cooper PR: Adrenomedullin is expressed during rodent dental
tissue development and promotes cell growth and mineralization.
Biol Cell. 102:145–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
So S, Hattori Y, Kasai K, Shimoda S and
Gross SS: Up-regulation of rat adrenomedullin gene expression by
endotoxin: Relation to nitric oxide synthesis. Life sciences.
58:Pl309–P1315. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Simon TP, Martin L, Doemming S, Humbs A,
Bruells C, Kopp R, Hartmann O, Struck J, Bergmann A, Marx G and
Schuerholz T: Plasma adrenomedullin in critically ill patients with
sepsis after major surgery: A pilot study. J Crit Care. 38:68–72.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Talwar S, Munson PJ, Barb J, Fiuza C,
Cintron AP, Logun C, Tropea M, Khan S, Reda D, Shelhamer JH, et al:
Gene expression profiles of peripheral blood leukocytes after
endotoxin challenge in humans. Physiol Genomics. 25:203–215. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Prabhakar U, Conway TM, Murdock P, Mooney
JL, Clark S, Hedge P, Bond BC, Jazwinska EC, Barnes MR, Tobin F, et
al: Correlation of protein and gene expression profiles of
inflammatory proteins after endotoxin challenge in human subjects.
DNA Cell Biol. 24:410–431. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Peters-Golden M and Henderson WR Jr:
Leukotrienes. N Engl J Med. 357:1841–1854. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Monteiro AP, Soledade E, Pinheiro CS,
Dellatorre-Teixeira L, Oliveira GP, Oliveira MG, Peters-Golden M,
Rocco PR, Benjamim CF and Canetti C: Pivotal role of the
5-lipoxygenase pathway in lung injury after experimental sepsis. Am
J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:87–95. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Collin M, Rossi A, Cuzzocrea S, Patel NS,
Di Paola R, Hadley J, Collino M, Sautebin L and Thiemermann C:
Reduction of the multiple organ injury and dysfunction caused by
endotoxemia in 5-lipoxygenase knockout mice and by the
5-lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton. J Leukoc Biol. 76:961–970. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Das UN: Combination of aspirin with
essential fatty acids is superior to aspirin alone to prevent or
ameliorate sepsis or ARDS. Lipids Health Dis. 15:2062016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stamenkovic I: Extracellular matrix
remodelling: The role of matrix metalloproteinases. J Pathol.
200:448–464. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chakrabarti S and Patel KD: Regulation of
matrix metalloproteinase-9 release from IL-8-stimulated human
neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. 78:279–288. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sheu JR, Fong TH, Liu CM, Shen MY, Chen
TL, Chang Y, Lu MS and Hsiao G: Expression of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in human platelets: Regulation of platelet
activation in in vitro and in vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol.
143:193–201. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee YM, Lee JJ, Shen MY, Hsiao G and Sheu
JR: Inhibitory mechanisms of activated matrix metalloproteinase-9
on platelet activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 537:52–58. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jin LY, Li CF, Zhu GF, Wu CT, Wang J and
Yan SF: Effect of siRNA against NF-κB on sepsisinduced acute lung
injury in a mouse model. Mol Med Rep. 10:631–637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cizmeci MN, Kara S, Kanburoglu MK, Simavli
S, Duvan CI and Tatli MM: Detection of cord blood hepcidin levels
as a biomarker for early-onset neonatal sepsis. Med Hypotheses.
82:310–312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hoffmann U, Bertsch T, Dvortsak E,
Liebetrau C, Lang S, Liebe V, Huhle G, Borggrefe M and Brueckmann
M: Matrix-metalloproteinases and their inhibitors are elevated in
severe sepsis: Prognostic value of TIMP-1 in severe sepsis. Scand J
Infect Dis. 38:867–872. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Edgar JD, Gabriel V, Gallimore JR,
McMillan SA and Grant J: A prospective study of the sensitivity,
specificity and diagnostic performance of soluble intercellular
adhesion molecule 1, highly sensitive C-reactive protein, soluble
E-selectin and serum amyloid A in the diagnosis of neonatal
infection. BMC Pediatr. 10:222010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gebhardt C, Nemeth J, Angel P and Hess J:
S100A8 and S100A9 in inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1622–1631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Buhimschi IA and Buhimschi CS: The role of
proteomics in the diagnosis of chorioamnionitis and early-onset
neonatal sepsis. Clin Perinatol. 37:355–374. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Buhimschi CS, Buhimschi IA, Abdel-Razeq S,
Rosenberg VA, Thung SF, Zhao G, Wang E and Bhandari V: Proteomic
biomarkers of intra-amniotic inflammation: Relationship with
funisitis and early-onset sepsis in the premature neonate. Pediatr
Res. 61:318–324. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Buhimschi CS, Bhandari V, Dulay AT, Nayeri
UA, Abdel-Razeq SS, Pettker CM, Thung S, Zhao G, Han YW, Bizzarro M
and Buhimschi IA: Proteomics mapping of cord blood identifies
haptoglobin ‘switch-on’ pattern as biomarker of early-onset
neonatal sepsis in preterm newborns. PLoS One. 6:e261112011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Csóka B, Németh ZH, Törő G, Koscsó B,
Kókai E, Robson SC, Enjyoji K, Rolandelli RH, Erdélyi K, Pacher P
and Haskó G: CD39 improves survival in microbial sepsis by
attenuating systemic inflammation. FASEB J. 29:25–36. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Haskó G, Csóka B, Koscsó B, Chandra R,
Pacher P, Thompson LF, Deitch EA, Spolarics Z, Virág L, Gergely P,
et al: Ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) decreases mortality and organ
injury in sepsis. J Immunol. 187:4256–4267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Eltzschig HK, Thompson LF, Karhausen J,
Cotta RJ, Ibla JC, Robson SC and Colgan SP: Endogenous adenosine
produced during hypoxia attenuates neutrophil accumulation:
Coordination by extracellular nucleotide metabolism. Blood.
104:3986–3992. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Köhler D, Eckle T, Faigle M, Grenz A,
Mittelbronn M, Laucher S, Hart ML, Robson SC, Müller CE and
Eltzschig HK: CD39/ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1
provides myocardial protection during cardiac ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Circulation. 116:1784–1794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Grenz A, Zhang H, Hermes M, Eckle T,
Klingel K, Huang DY, Müller CE, Robson SC, Osswald H and Eltzschig
HK: Contribution of E-NTPDase1 (CD39) to renal protection from
ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J. 21:2863–2873. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hart ML, Gorzolla IC, Schittenhelm J,
Robson SC and Eltzschig HK: SP1-dependent induction of CD39
facilitates hepatic ischemic preconditioning. J Immunol.
184:4017–4024. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Riedemann NC, Guo RF and Ward PA: The
enigma of sepsis. J Clin Invest. 112:460–467. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nakada TA, Russell JA, Boyd JH, McLaughlin
L, Nakada E, Thair SA, Hirasawa H, Oda S and Walley KR: Association
of angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein gene
polymorphism with increased mortality in septic shock. Crit Care
Med. 39:1641–1648. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mares CA, Ojeda SS, Morris EG, Li Q and
Teale JM: Initial delay in the immune response to Francisella
tularensis is followed by hypercytokinemia characteristic of severe
sepsis and correlating with upregulation and release of
damage-associated molecular patterns. Infect Immun. 76:3001–3010.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fontaine M, Pachot A, Larue A, Mougin B,
Landelle C, Venet F, Allombert C, Cazalis MA, Monneret G and Lepape
A: Delayed increase of S100A9 messenger RNA predicts
hospital-acquired infection after septic shock. Crit Care Med.
39:2684–2690. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Feuerstein GZ: Cardiac RAGE in sepsis:
Call TOLL free for anti-RAGE. Circ Res. 102:1153–1154. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
van Zoelen MA, Vogl T, Foell D, Van Veen
SQ, van Till JW, Florquin S, Tanck MW, Wittebole X, Laterre PF,
Boermeester MA, et al: Expression and role of myeloid-related
protein-14 in clinical and experimental sepsis. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 180:1098–1106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
West AP, Koblansky AA and Ghosh S:
Recognition and signaling by toll-like receptors. Ann Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 22:409–437. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Buchholz BM and Bauer AJ: Membrane TLR
signaling mechanisms in the gastrointestinal tract during sepsis.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 22:232–245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Savva A and Roger T: Targeting toll-like
receptors: Promising therapeutic strategies for the management of
sepsis-associated pathology and infectious diseases. Front Immunol.
4:3872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Mansur A, von Gruben L, Popov AF, Steinau
M, Bergmann I, Ross D, Ghadimi M, Beissbarth T, Bauer M and Hinz J:
The regulatory toll-like receptor 4 genetic polymorphism rs11536889
is associated with renal, coagulation and hepatic organ failure in
sepsis patients. J Transl Med. 12:1772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|