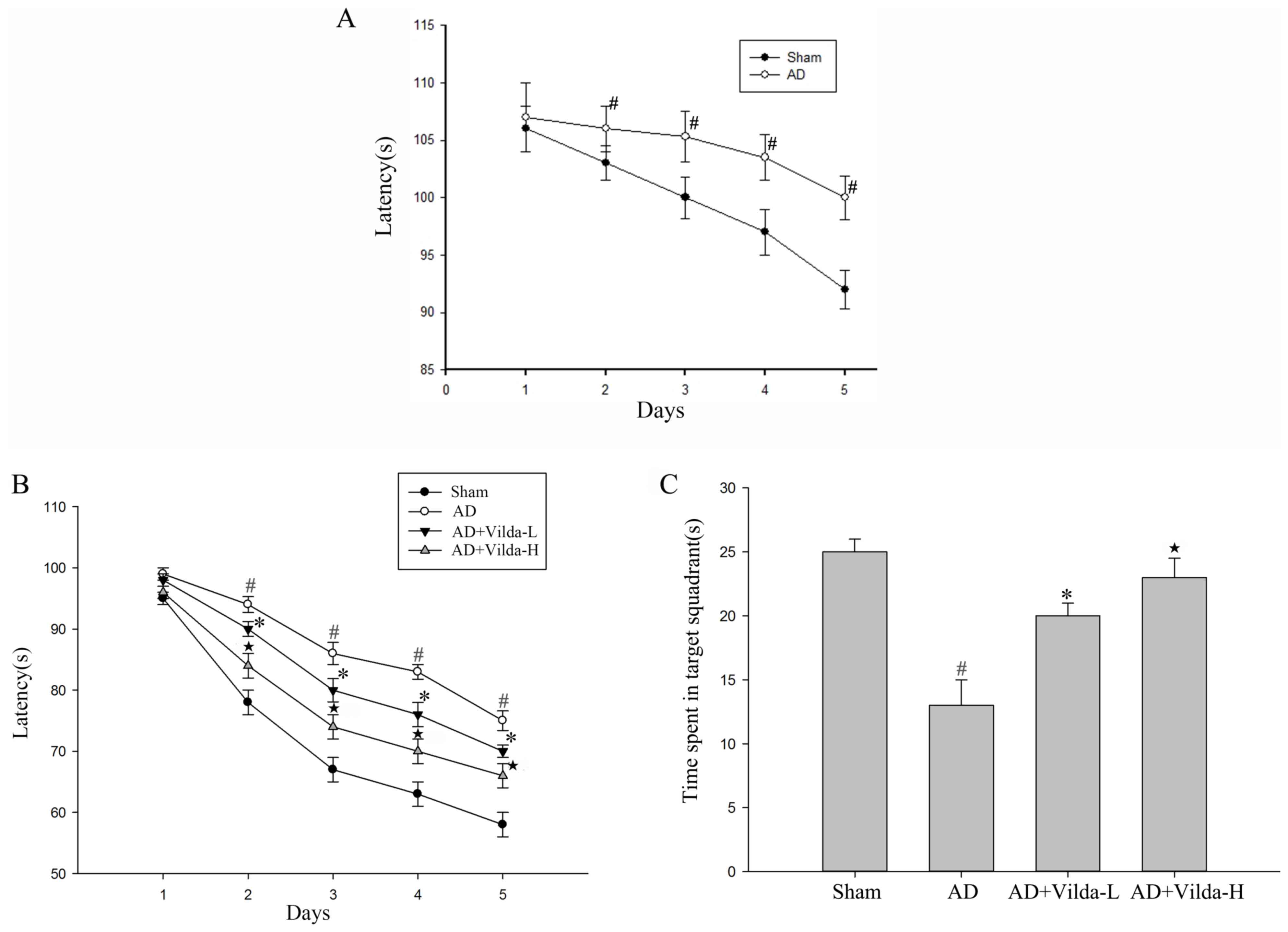
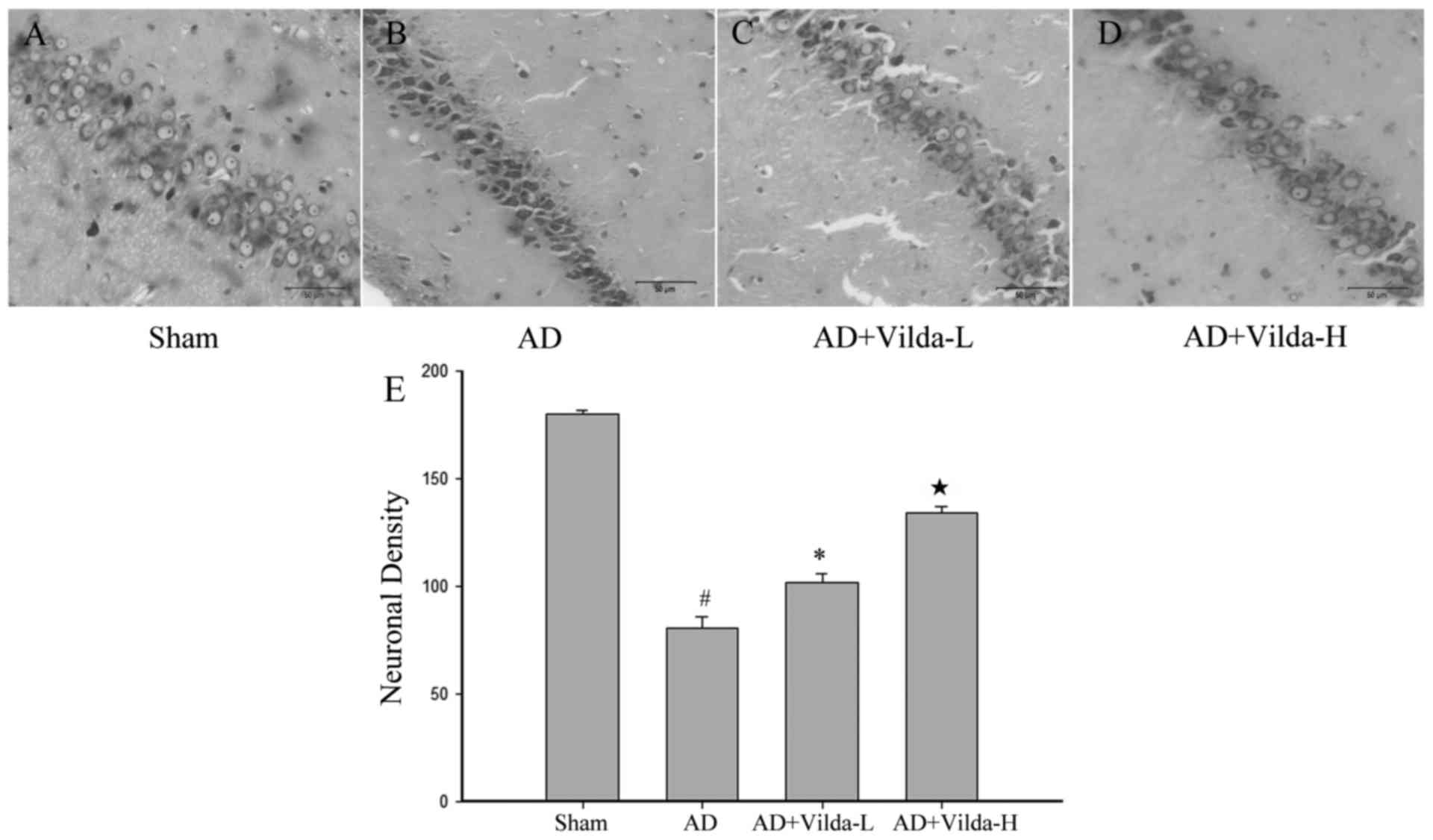
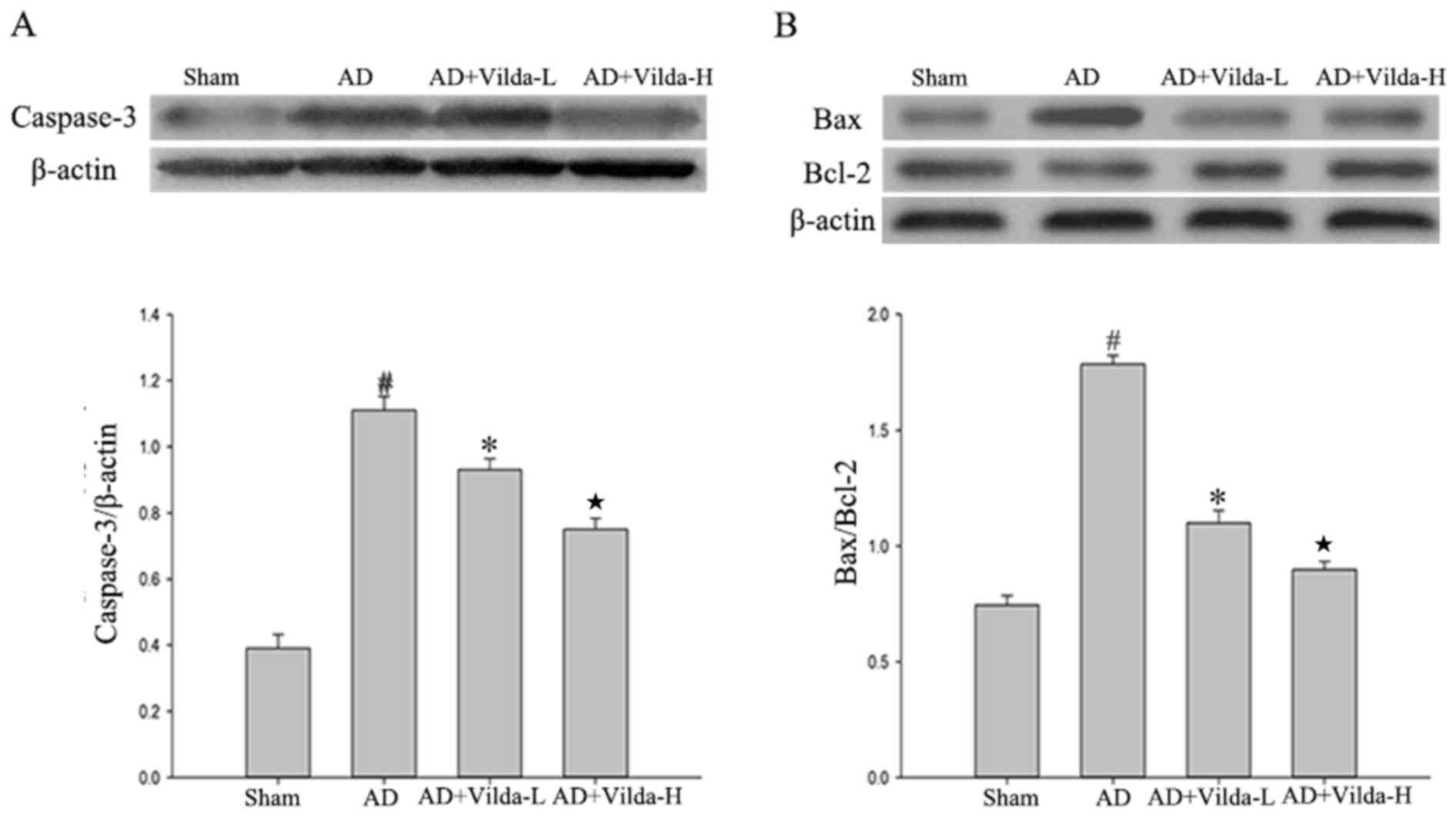
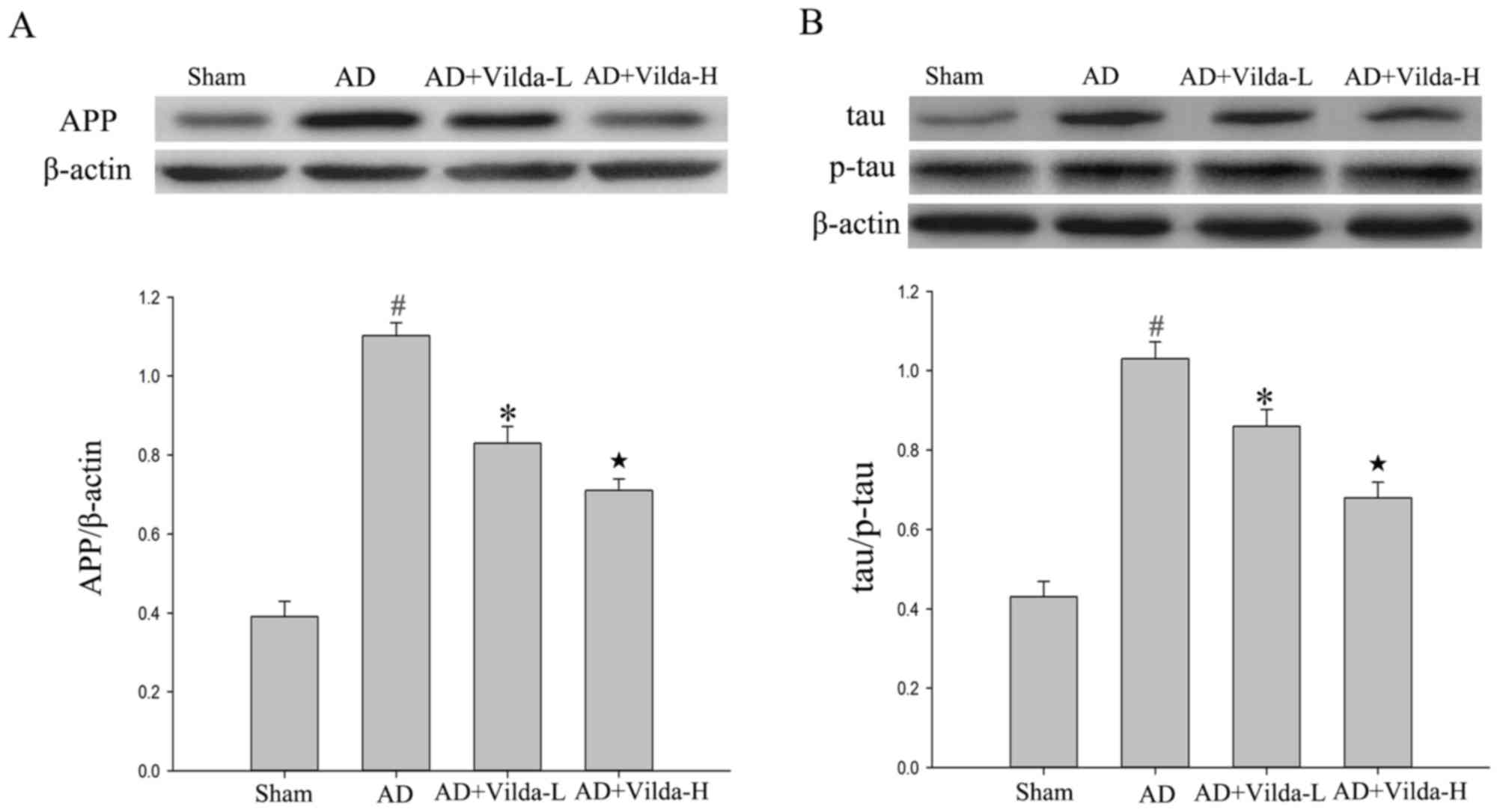
|
1
|
Scheltens P, Blennow K, Breteler MM, de
Strooper B, Frisoni GB, Salloway S and Van der Flier WM:
Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 388:505–517. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prince M, Bryce R, Albanese E, Wimo A,
Ribeiro W and Ferri CP: The global prevalence of dementia: A
systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimers Dement. 9:63–75.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li X, Bao X and Wang R: Neurogenesis-based
epigenetic therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease. Mol Med Rep.
14:1043–1053. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen PY, Tsai CT, Ou CY, Hsu WT, Jhuo MD,
Wu CH, Shih TC, Cheng TH and Chung JG: Computational analysis of
novel drugs designed for use as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and
histamine H3 receptor antagonists for Alzheimer's disease by
docking, scoring and de novo evolution. Mol Med Rep. 5:1043–1048.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Henry W, Querfurth HW and LaFerla FM:
Mechanisms of disease Alzheimer's disease. New Engl J Med.
362:329–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zuroff L, Daley D, Black KL and
Koronyo-Hamaoui M: Clearance of cerebral Aβ in Alzheimer's disease:
Reassessing the role of microglia and monocytes. Cell Mol Life Sci.
74:2167–2201. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kepp KP: Bioinorganic chemistry of
Alzheimer's disease. Chem Rev. 112:5193–5239. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Patrone C, Eriksson O and Lindholm D:
Diabetes drugs and neurological disorders: New views and
therapeutic possibilities. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2:256–262.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Palleria C, Leporini C, Maida F, Succurro
E, De Sarro G, Arturi F and Russo E: Potential effects of current
drug therapies on cognitive impairment in patients with type 2
diabetes. Front Neuroendocrinol. 42:76–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Darsalia V, Olverling A, Larsson M,
Mansouri S, Nathanson D, Nyström T, Klein T, Sjöholm Å and Patrone
C: Linagliptin enhances neural stem cell proliferation after stroke
in type 2 diabetic mice. Regul Pept 190–191. 1–31. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Nassar NN, Al-Shorbagy MY, Arab HH and
Abdallah DM: Saxagliptin: A novel antiparkinsonian approach.
Neuropharmacology. 89:308–317. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matteucci E and Giampietro O: Mechanisms
of Neurodegeration in Type 2 diabetes and the neuroprotective
potential of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors. Curr Med Chem.
22:1573–1581. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng T, Qin L, Chen B, Hu X, Zhang X, Liu
Y, Liu H, Qin S, Li G and Li Q: Association of plasma DPP4 activity
with mild cognitive impairment in elderly patients with type 2
diabetes: results from the GDMD study in China. Diabetes Care.
39:1594–1601. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kosaraju J, Murthy V, Khatwal RB, Dubala
A, Chinni S, Muthureddy Nataraj SK and Basavan D: Vildagliptin: An
anti-diabetes agent ameliorates cognitive deficits and pathology
observed in streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer's disease. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 65:1773–1784. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brion JP, Fraser H, Flament-Durand J and
Dickinson AG: Amyloid scrapie plaques in mice and Alzheimer senile
plaques, share common antigens with tau, a microtubule-associated
protein. Neurosci Lett. 78:113–118. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gonzalez B, Abud EM, Abud AM, Poon WW and
Gylys KH: Tau spread, apolipoprotein E, inflammation and more:
Rapidly evolving basic science in alzheimer disease. Neurol Clin.
35:175–190. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Storr T: Ligand design in medicinal
inorganic chemistry. John Wiley & Sons; New York, NY: 2014,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jakobroetne R and Jacobsen H: Alzheimer's
disease: From pathology to therapeutic approaches. Angew Chem Int
Ed Enge. 48:3030–3059. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pintana H, Apaijai N, Chattipakorn N and
Chattipakorn SC: DPP-4 inhibitors improve cognition and brain
mitochondrial function of insulin-resistant rats. J Endocrinol.
218:1–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gault VA, Lennox R and Flatt PR:
Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, improves
recognition memory, oxidative stress and hippocampal neurogenesis
and upregulates key genes involved in cognitive decline. Diabetes
Obes Metab. 17:403–413. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
D'Amico M, Di Filippo C, Marfella R,
Abbatecola AM, Ferraraccio F, Rossi F and Paolisso G: Long-term
inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 in Alzheimer's prone mice. Exp
Gerontol. 45:202–207. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pintana H, Tanajak P, Pratchayasakul W,
Sa-Nguanmoo P, Chunchai T, Satjaritanun P, Leelarphat L,
Chattipakorn N and Chattipakorn SC: Energy restriction combined
with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor exerts neuroprotection in
obese male rats. Br J Nutr. 1–9. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
El Batsh MM, El Batch MM, Shafik NM and
Younos IH: Favorable effects of vildagliptin on metabolic and
cognitive dysfunctions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur
J Pharmacol. 769:297–305. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao C, Hölscher C, Liu Y and Li L: GSK3: A
key target for the development of novel treatments for type 2
diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer disease. Rev Neurosci. 23:1–11.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu T and Lin W: Small-molecule GSK-3
inhibitor rescued apoptosis and neurodegeneration in
anesthetics-injured dorsal root ganglion neurons. Biomed
Pharmacother. 84:395–402. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fan R, Li X, Gu X, Chan JC and Xu G:
Exendin-4 protects pancreatic beta cells from human islet amyloid
polypeptide-induced cell damage: Potential involvement of AKT and
mitochondria biogenesis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 12:815–824. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Savelieff MG, Lee S, Liu Y and Lim MH:
Untangling amyloid-β, tau, and metals in Alzheimer's disease. Acs
Chem Biol. 8:856–865. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nadezhdin KD, Bocharova OV, Bocharov EV
and Arseniev AS: Structural and dynamic study of the transmembrane
domain of the amyloid precursor protein. Acta Naturae. 3:69–76.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Köpke E, Tung YC, Shaikh S, Alonso AC,
Iqbal K and Grundke-Iqbal I: Microtubule-associated protein tau.
Abnormal phosphorylation of a non-paired helical filament pool in
Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 268:24374–24384. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Braak H, Thal DR, Ghebremedhin E and Del
Tredici K: Stages of the pathologic process in Alzheimer disease:
Age categories from 1 to 100 years. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
70:960–969. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Do Carmo S, Crynen G, Paradis T, Reed J,
Iulita MF, Ducatenzeiler A, Crawford F and Cuello AC: Hippocampal
proteomic analysis reveals distinct pathway deregulation profiles
at early and late stages in a rat model of alzheimer's-like amyloid
pathology. Mol Neurobiol. May 13–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pratley RE, Jauffret-Kamel S, Galbreath E
and Holmes D: Twelve-week monotherapy with the DPP-4 inhibitor
vildagliptin improves glycemic control in subjects with type 2
diabetes. Horm Metab Res. 38:423–428. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|