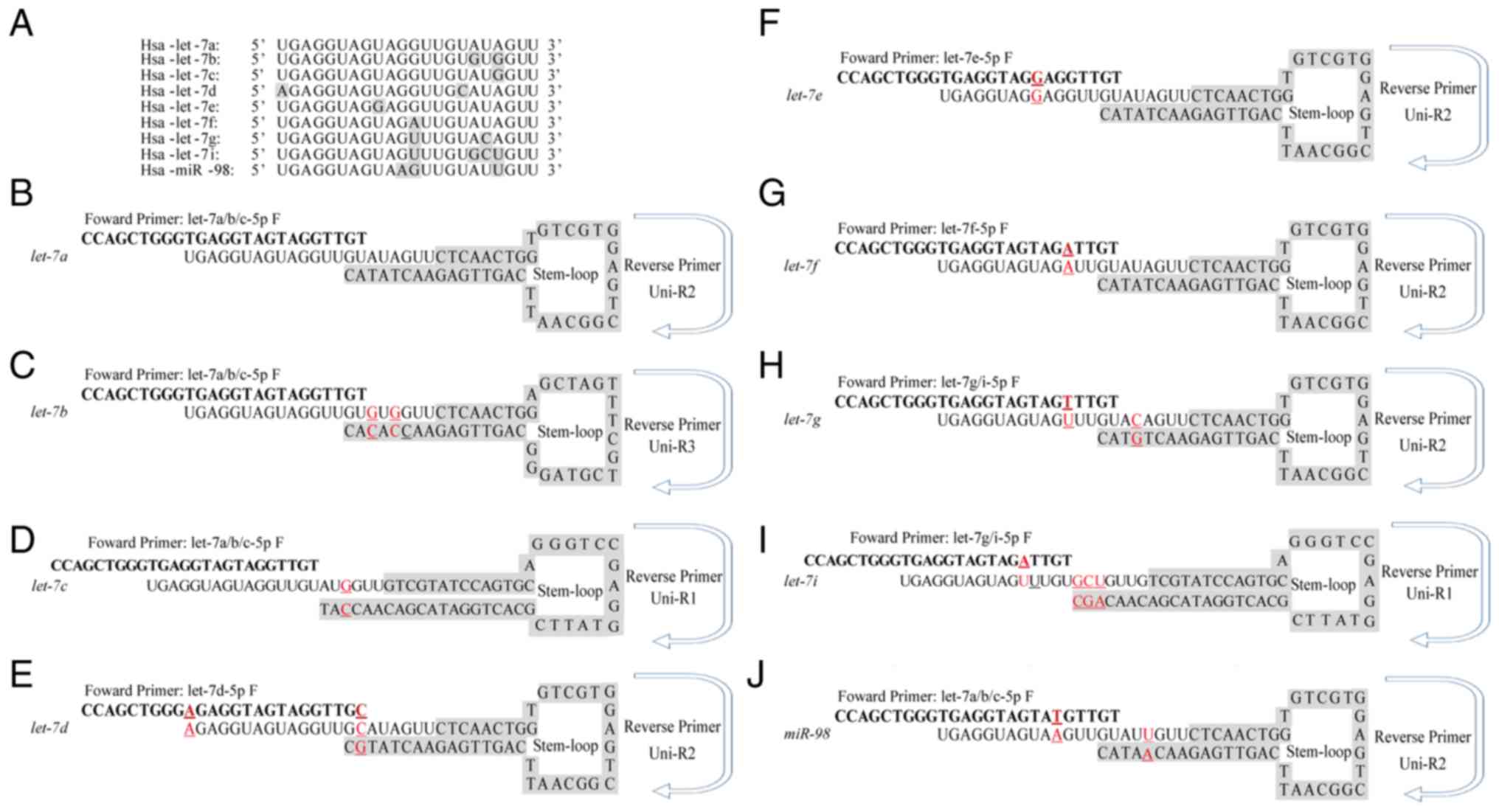
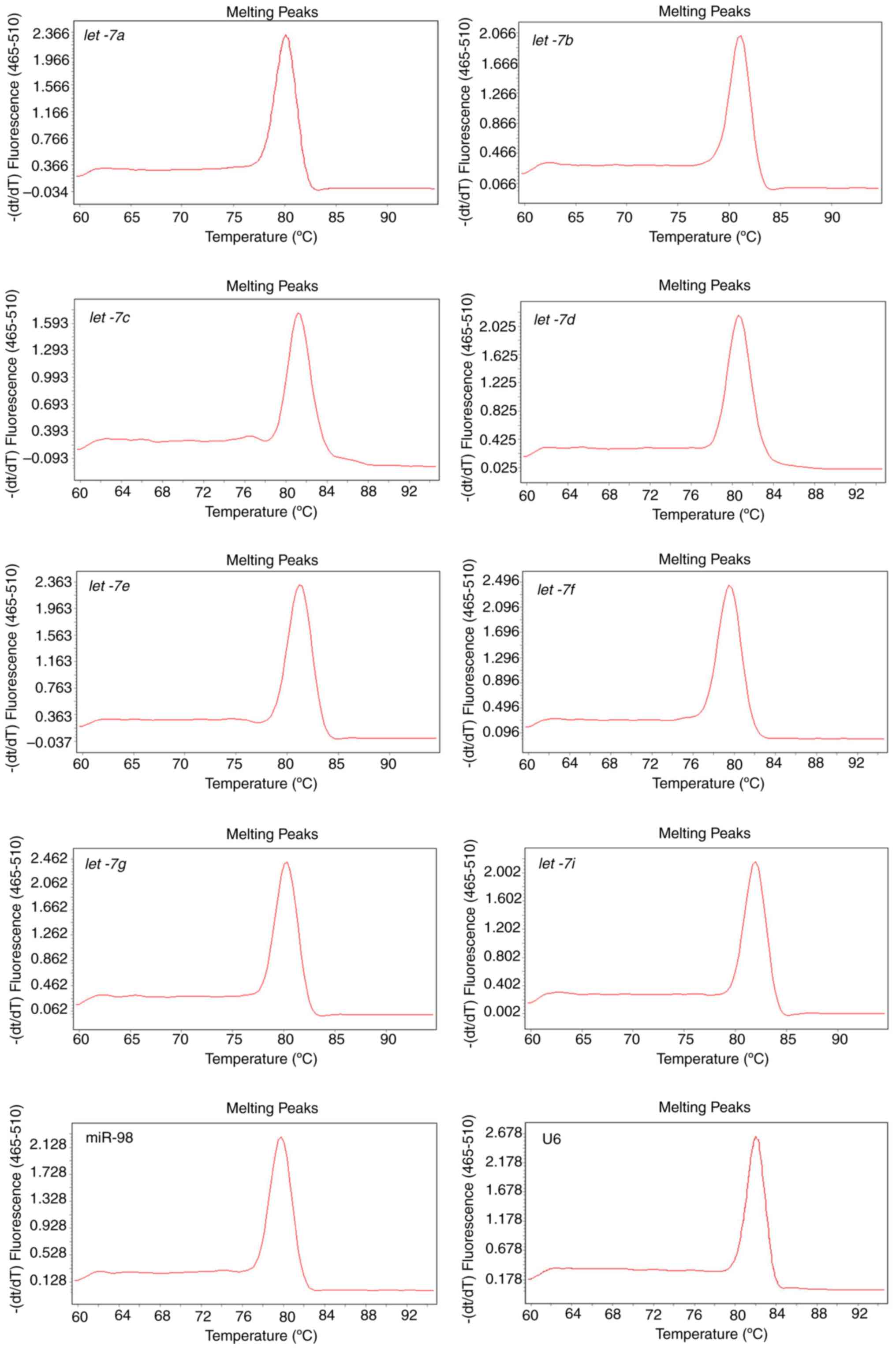
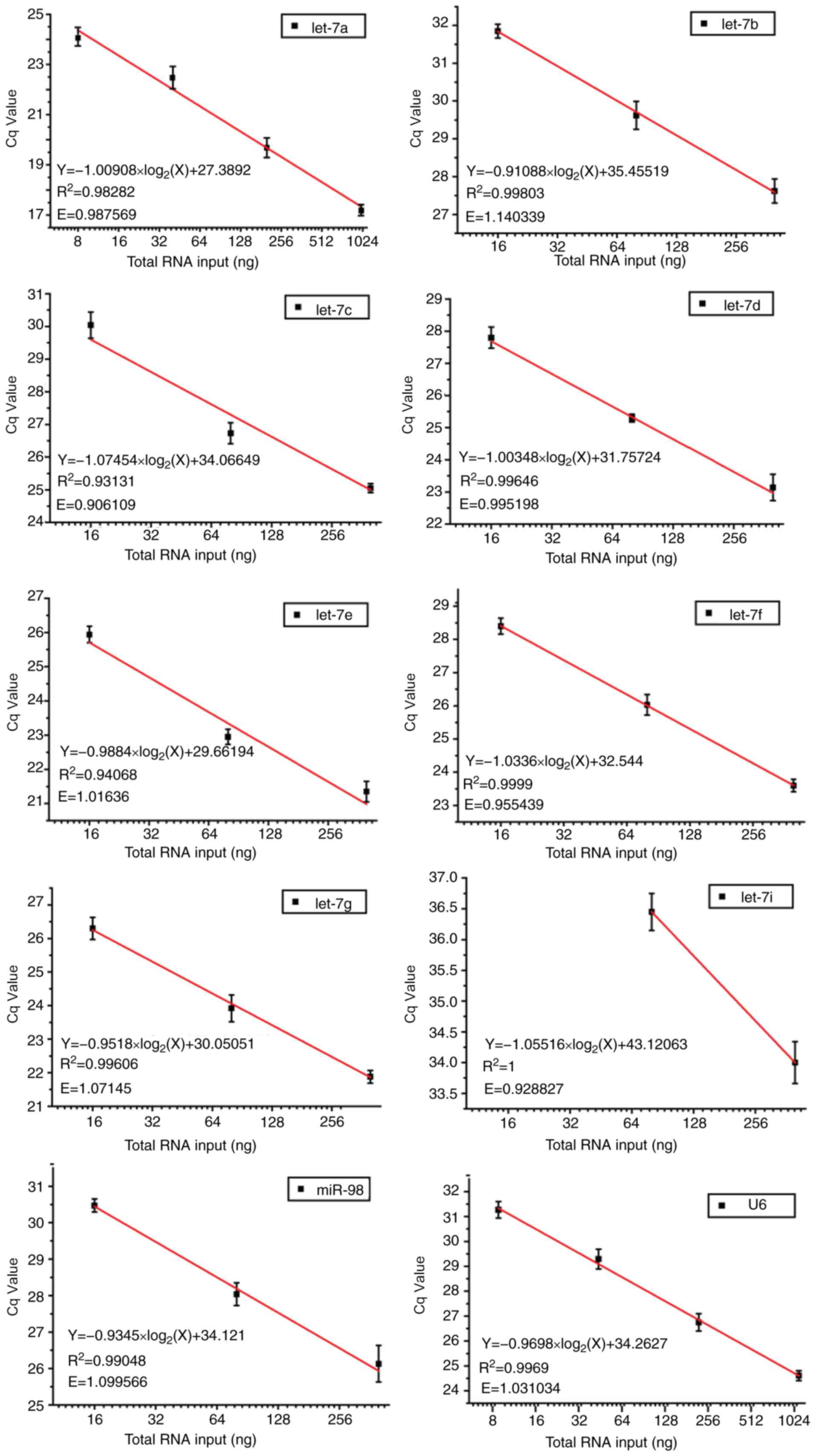
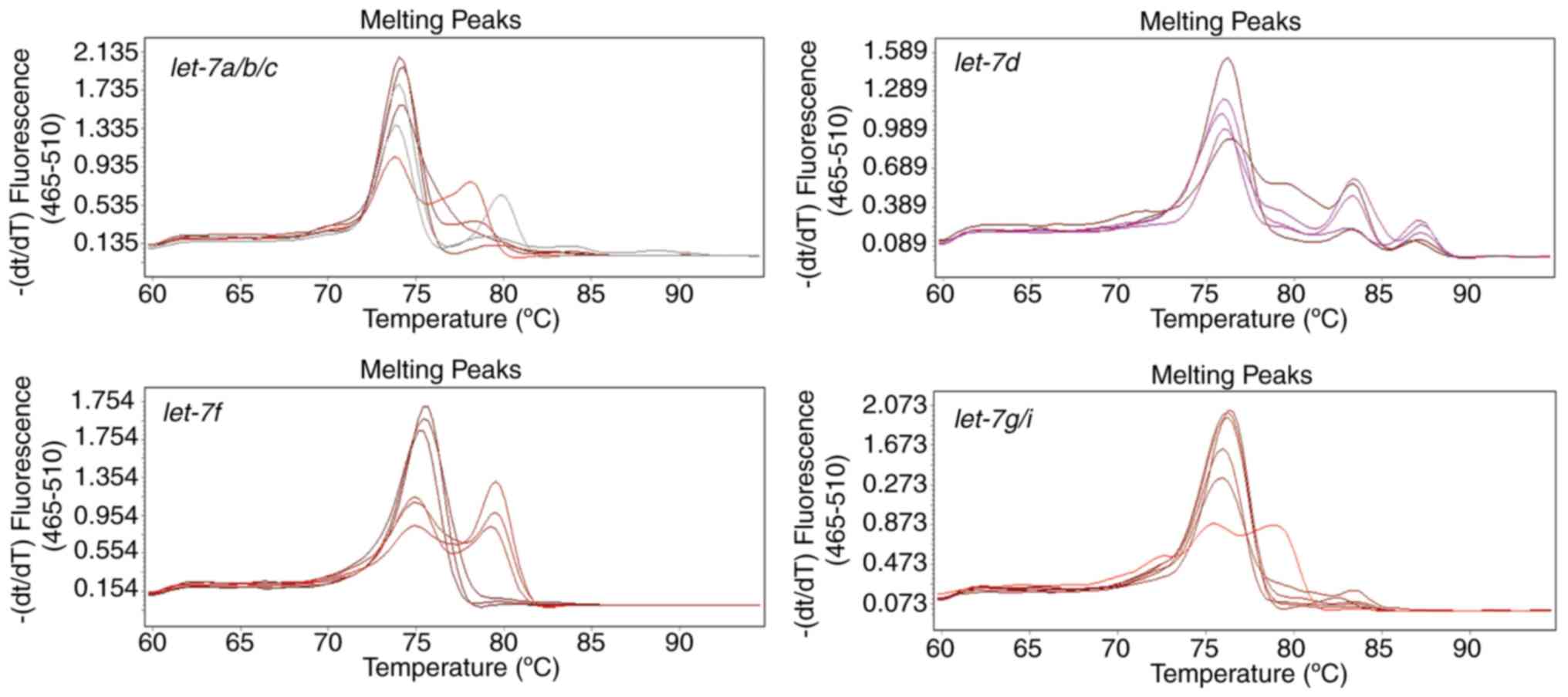
|
1
|
Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B and
Rigoutsos I: MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions
modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature.
455:1124–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Doench JG and Sharp PA: Specificity of
microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev.
18:504–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wightman B, Ha I and Ruvkun G:
Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by
lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell.
75:855–862. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Olsen PH and Ambros V: The lin-4
regulatory RNA controls developmental timing in Caenorhabditis
elegans by blocking LIN-14 protein synthesis after the initiation
of translation. Dev Biol. 216:671–680. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim VN, Han J and Siomi MC: Biogenesis of
small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:126–139. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bao N, Lye KW and Barton MK: MicroRNA
binding sites in Arabidopsis class III HD-ZIP mRNAs are required
for methylation of the template chromosome. Dev Cell. 7:653–662.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Michael MZ, O'Connor SM, van Holst
Pellekaan NG, Young GP and James RJ: Reduced Accumulation of
Specific MicroRNAs in Colorectal Neoplasia11Note: Susan M. O'Connor
and Nicholas G. van Holst Pellekaan contributed equally to this
work. Mol Cancer Res. 1:882–891. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M,
Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR and Ruvkun G:
The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 403:901–906. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rodini CO, Suzuki DE, Saba-Silva N,
Cappellano A, de Souza JE, Cavalheiro S, Toledo SR and Okamoto OK:
Expression analysis of stem cell-related genes reveal OCT4 as a
predictor of poor clinical outcome in medulloblastoma. J
Neurooncol. 106:71–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sakurai M, Miki Y, Masuda M, Hata S,
Shibahara Y, Hirakawa H, Suzuki T and Sasano H: LIN28: A regulator
of tumor-suppressing activity of let-7 microRNA in human breast
cancer. J Ster Biochem Mol Biol. 131:101–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhao C, Sun G, Li S, Lang MF, Yang S, Li W
and Shi Y: MicroRNA let-7b regulates neural stem cell proliferation
and differentiation by targeting nuclear receptor TLX signaling.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp. 1876–1881. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G,
Byrom M, Kelnar K, Ovcharenko D, Wilson M, Wang X, Shelton J,
Shingara J, et al: The let-7 MicroRNA represses cell proliferation
pathways in human cells. Cancer Res. 67:7713–7722. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong Q, Meng P, Wang T, Qin W, Qin W, Wang
F, Yuan J, Chen Z, Yang A and Wang H: MicroRNA let-7a inhibits
proliferation of human prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
by targeting E2F2 and CCND2. PLoS One. 5:e101472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shell S, Park SM, Radjabi AR, Schickel R,
Kistner EO, Jewell DA, Feig C, Lengyel E and Peter ME: Let-7
expression defines two differentiation stages of cancer. P Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:11400–11405. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee
DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K,
Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y,
et al: Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung
cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival.
Cancer Res. 64:3753–3756. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y and Naoe T: let-7
microRNA functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon
cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:903–906. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schultz J, Lorenz P, Gross G, Ibrahim S
and Kunz M: MicroRNA let-7b targets important cell cycle molecules
in malignant melanoma cells and interferes with
anchorage-independent growth. Cell Res. 18:549–557. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong
C, Huang Y, Hu X, Su F, Lieberman J and Song E: let-7 regulates
self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell.
131:1109–1123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumar MS, Erkeland SJ, Pester RE, Chen CY,
Ebert MS, Sharp PA and Jacks T: Suppression of non-small cell lung
tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:pp. 3903–3908. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu L, Schwartz P, Scarampi L, Rutherford
T, Canuto EM, Yu H and Katsaros D: MicroRNA let-7a: a potential
marker for selection of paclitaxel in ovarian cancer management.
Gynecol Oncol. 122:366–371. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zovoilis A, Agbemenyah HY, Agis-Balboa RC,
Stilling RM, Edbauer D, Rao P, Farinelli L, Delalle I, Schmitt A,
Falkai P, et al: microRNA-34c is a novel target to treat dementias.
Embo J. 30:4299–4308. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|