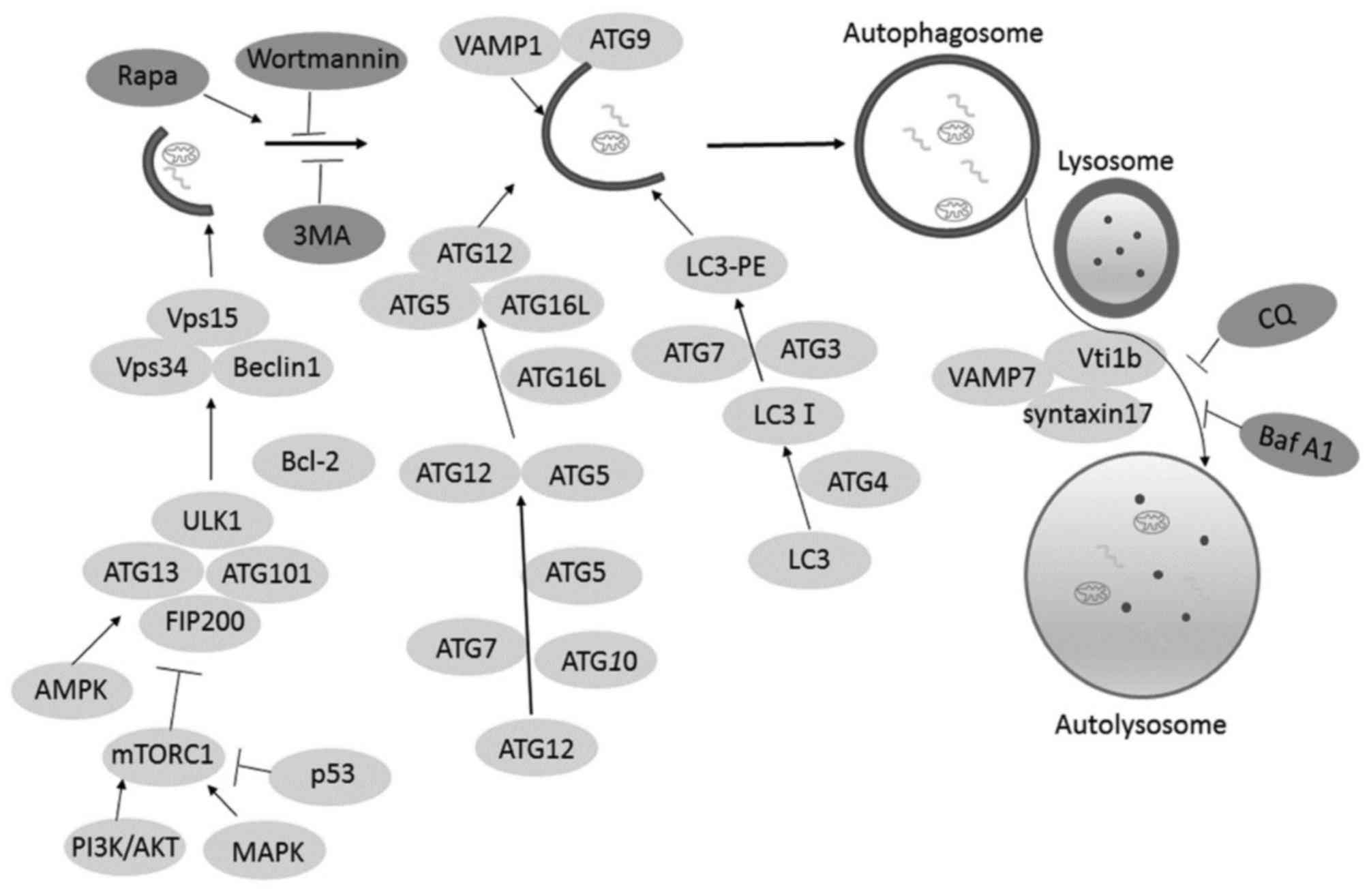
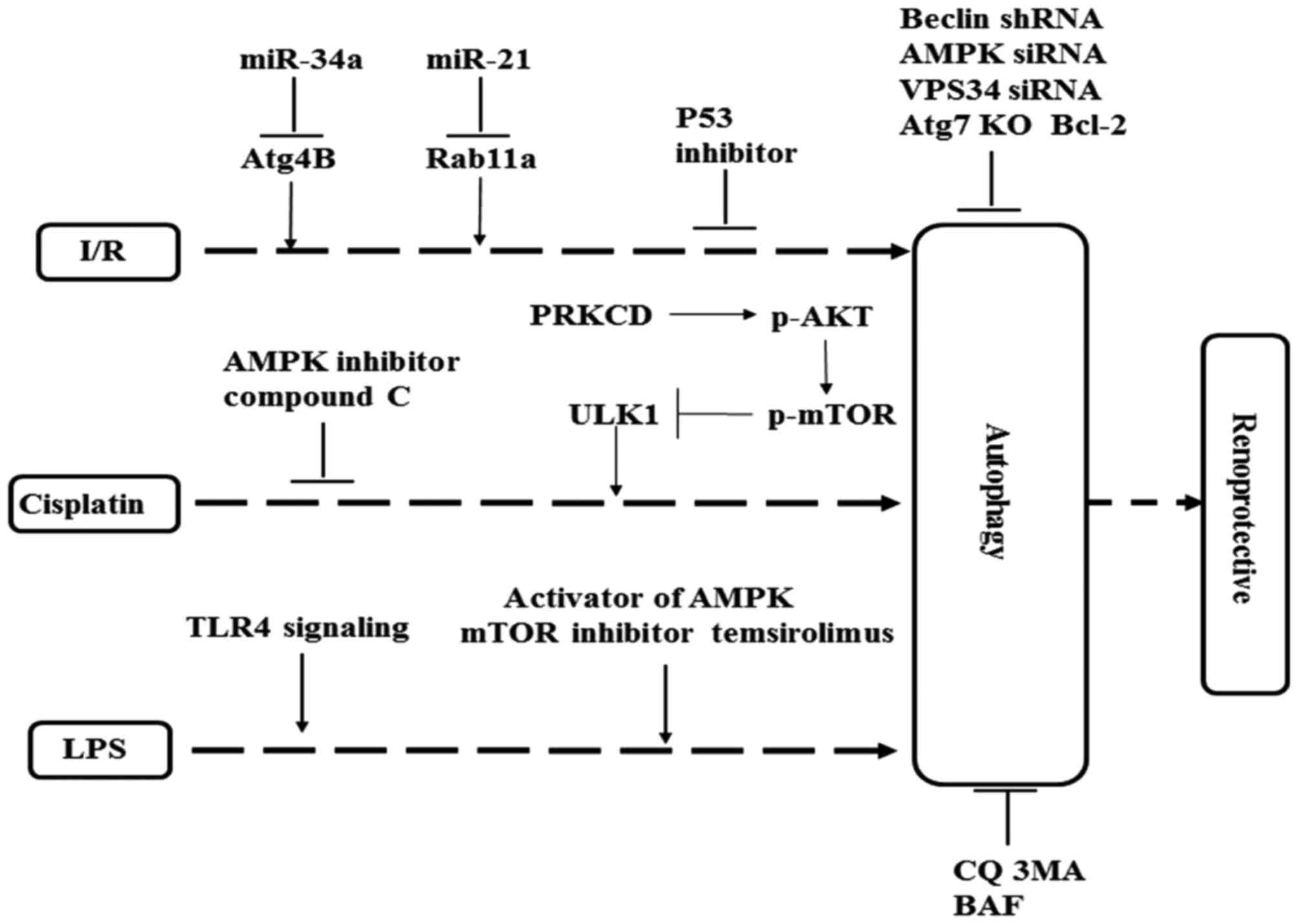
|
1
|
Qian M, Fang X and Wang X: Autophagy and
inflammation. Clin Transl Med. 6:242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tomiyama R, Takakura K, Takatou S, Le TM,
Nishiuchi T, Nakamura Y, Konishi T, Matsugo S and Hori O:
3,4-dihydroxybenzalacetone and caffeic acid phenethyl ester induce
preconditioning ER stress and autophagy in SH-SY5Y cells. J Cell
Physiol. 233:1671–1684. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Antikainen H, Driscoll M, Haspel G and
Dobrowolski R: TOR-mediated regulation of metabolism in aging.
Aging Cell. 16:1219–1233. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Germic N, Stojkov D, Oberson K, Yousefi S
and Simon HU: Neither eosinophils nor neutrophils require
ATG5-dependent autophagy for extracellular DNA trap formation.
Immunology. 152:517–525. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Long M, Li X, Li L, Dodson M, Zhang DD and
Zheng H: Multifunctional p62 effects underlie diverse metabolic
diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 28:818–830. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu ZY, Chen B, Zhang JP and Ma YY:
Up-regulation of autophagy-related gene 5 (ATG5) protects
dopaminergic neurons in a zebrafish model of Parkinson's disease. J
Biol Chem. 292:18062–18074. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Choi HS, Jeong EH, Lee TG, Kim SY, Kim HR
and Kim CH: Autophagy inhibition with monensin enhances cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis induced by mTOR or epidermal growth factor
receptor inhibitors in lung cancer cells. Tuberc Respir Dis
(Seoul). 75:9–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Z and Choi ME: Autophagy in kidney
health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:519–537. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huber TB, Edelstein CL, Hartleben B, Inoki
K, Jiang M, Koya D, Kume S, Lieberthal W, Pallet N, Quiroga A, et
al: Emerging role of autophagy in kidney function, diseases and
aging. Autophagy. 8:1009–1031. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He L, Wei Q, Liu J, Yi M, Liu Y, Liu H,
Sun L, Peng Y, Liu F, Venkatachalam MA and Dong Z: AKI on CKD:
Heightened injury, suppressed repair and the underlying mechanisms.
Kidney Int. 92:1071–1083. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Trongtrakul K, Sawawiboon C, Wang AY,
Chitsomkasem A, Limphunudom P, Kurathong S, Prommoon S,
Trakarnvanich T and Srisawat N: Acute kidney injury in critically
Ill surgical patients: Epidemiology, risk factors and outcomes.
Nephrology (Carlton). 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deng X, Xie Y and Zhang A: Advance of
autophagy in chronic kidney diseases. Ren Fail. 39:306–313. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ravikumar B, Sarkar S, Davies JE, Futter
M, Garcia-Arencibia M, Green-Thompson ZW, Jimenez-Sanchez M,
Korolchuk VI, Lichtenberg M, Luo S, et al: Regulation of mammalian
autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev.
90:1383–1435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sekito T, Kawamata T, Ichikawa R, Suzuki K
and Ohsumi Y: Atg17 recruits Atg9 to organize the
pre-autophagosomal structure. Genes Cells. 14:525–538. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livingston MJ and Dong Z: Autophagy in
acute kidney injury. Semin Nephrol. 34:17–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mi N, Chen Y, Wang S, Chen M, Zhao M, Yang
G, Ma M, Su Q, Luo S, Shi J, et al: CapZ regulates autophagosomal
membrane shaping by promoting actin assembly inside the isolation
membrane. Nat Cell Biol. 17:1112–1123. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sureshbabu A, Ryter SW and Choi ME:
Oxidative stress and autophagy: Crucial modulators of kidney
injury. Redox Biol. 4:208–214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ravanan P, Srikumar IF and Talwar P:
Autophagy: The spotlight for cellular stress responses. Life Sci.
188:53–67. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang JC, Feng YL, Liang X and Cai XJ:
Autophagy in 5-fluorouracil therapy in gastrointestinal cancer:
Trends and challenges. Chin Med J (Engl). 129:456–463. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Degenhardt K, Mathew R, Beaudoin B, Bray
K, Anderson D, Chen G, Mukherjee C, Shi Y, Gélinas C, Fan Y, et al:
Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis,
inflammation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 10:51–64. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pla A, Pascual M and Guerri C: Autophagy
constitutes a protective mechanism against ethanol toxicity in
mouse astrocytes and neurons. PLoS One. 11:e01530972016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shirakabe A, Ikeda Y, Sciarretta S,
Zablocki DK and Sadoshima J: Aging and autophagy in the heart. Circ
Res. 118:1563–1576. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang XY, Yang H, Wang MG, Yang DB, Wang ZY
and Wang L: Trehalose protects against cadmium-induced cytotoxicity
in primary rat proximal tubular cells via inhibiting apoptosis and
restoring autophagic flux. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
de Almeida DC, Donizetti-Oliveira C,
Barbosa-Costa P, Origassa CS and Câmara NO: In search of mechanisms
associated with mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies for acute
kidney injury. Clin Biochem Rev. 34:131–144. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang YL, Zhang J, Cui LY and Yang S:
Autophagy activation attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
in rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:1590–1598. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guan X, Qian Y, Shen Y, Zhang L, Du Y, Dai
H, Qian J and Yan Y: Autophagy protects renal tubular cells against
ischemia/reperfusion injury in a time-dependent manner. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 36:285–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ling H, Chen H, Wei M, Meng X, Yu Y and
Xie K: The effect of autophagy on inflammation cytokines in renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Inflammation. 39:347–356. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang M, Liu K, Luo J and Dong Z:
Autophagy is a renoprotective mechanism during in vitro hypoxia and
in vivo ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol. 176:1181–1192.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang M, Wei Q, Dong G, Komatsu M, Su Y
and Dong Z: Autophagy in proximal tubules protects against acute
kidney injury. Kidney Int. 82:1271–1283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chandrika BB, Yang C, Ou Y, Feng X, Muhoza
D, Holmes AF, Theus S, Deshmukh S, Haun RS and Kaushal GP:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced autophagy provides
cytoprotection from chemical hypoxia and oxidant injury and
ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One.
10:e01400252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A,
Kaimori JY, Matsui I, Namba T, Kitamura H, Niimura F, Matsusaka T,
Soga T, et al: Autophagy protects the proximal tubule from
degeneration and acute ischemic injury. J Am Soc Nephrol.
22:902–913. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu S, Hartleben B, Kretz O, Wiech T,
Igarashi P, Mizushima N, Walz G and Huber TB: Autophagy plays a
critical role in kidney tubule maintenance, aging and
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Autophagy. 8:826–837. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Matsumoto T, Urushido M, Ide H, Ishihara
M, Hamada-Ode K, Shimamura Y, Ogata K, Inoue K, Taniguchi Y,
Taguchi T, et al: Small heat shock protein beta-1 (HSPB1) is
upregulated and regulates autophagy and apoptosis of renal tubular
cells in acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 10:e01262292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang LT, Chen BL, Wu CT, Huang KH, Chiang
CK and Hwa Liu S: Protective role of AMP-activated protein
kinase-evoked autophagy on an in vitro model of
ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal tubular cell injury. PLoS One.
8:e798142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Decuypere JP, Ceulemans LJ, Agostinis P,
Monbaliu D, Naesens M, Pirenne J and Jochmans I: Autophagy and the
kidney: Implications for ischemia-reperfusion injury and therapy.
Am J Kidney Dis. 66:699–709. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Isaka Y, Suzuki C, Abe T, Okumi M,
Ichimaru N, Imamura R, Kakuta Y, Matsui I, Takabatake Y, Rakugi H,
et al: Bcl-2 protects tubular epithelial cells from
ischemia/reperfusion injury by dual mechanisms. Transplant Proc.
41:pp. 52–54. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chien CT, Shyue SK and Lai MK: Bcl-xL
augmentation potentially reduces ischemia/reperfusion induced
proximal and distal tubular apoptosis and autophagy.
Transplantation. 84:1183–1190. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suzuki C, Isaka Y, Takabatake Y, Tanaka H,
Koike M, Shibata M, Uchiyama Y, Takahara S and Imai E:
Participation of autophagy in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 368:100–106. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Turkmen K, Martin J, Akcay A, Nguyen Q,
Ravichandran K, Faubel S, Pacic A, Ljubanović D, Edelstein CL and
Jani A: Apoptosis and autophagy in cold preservation ischemia.
Transplantation. 91:1192–1197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu SY, Dong B, Zhou SH and Tang L: LncRNA
MALAT1: A potential regulator of autophagy in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 247:252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu XJ, Hong Q, Wang Z, Yu YY, Zou X and
Xu LH: MicroRNA-34a suppresses autophagy in tubular epithelial
cells in acute kidney injury. Am J Nephrol. 42:168–175. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu X, Hong Q, Wang Z, Yu Y, Zou X and Xu
L: MiR-21 inhibits autophagy by targeting Rab11a in renal
ischemia/reperfusion. Exp Cell Res. 338:64–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Arany I and Safirstein RL: Cisplatin
nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol. 23:460–464. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pabla N and Dong Z: Cisplatin
nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney
Int. 73:994–1007. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Levine B and Yuan J: Autophagy in cell
death: An innocent convict? J Clin Invest. 115:2679–2688. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu H, Gu LB, Tu Y, Hu H, Huang YR and Sun
W: Emodin ameliorates cisplatin-induced apoptosis of rat renal
tubular cells in vitro by activating autophagy. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
37:235–245. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Periyasamy-Thandavan S, Jiang M, Wei Q,
Smith R, Yin XM and Dong Z: Autophagy is cytoprotective during
cisplatin injury of renal proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int.
74:631–640. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fang B and Xiao H: Rapamycin alleviates
cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
448:443–447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sprowl JA, Lancaster CS, Pabla N, Hermann
E, Kosloske AM, Gibson AA, Li L, Zeeh D, Schlatter E, Janke LJ, et
al: Cisplatin-induced renal injury is independently mediated by
OCT2 and p53. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4026–4035. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cummings BS and Schnellmann RG:
Cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis: Caspase 3-dependent and
-independent pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 302:8–17. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jiang M, Wei Q, Wang J, Du Q, Yu J, Zhang
L and Dong Z: Regulation of PUMA-alpha by p53 in cisplatin-induced
renal cell apoptosis. Oncogene. 25:4056–4066. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jiang M, Yi X, Hsu S, Wang CY and Dong Z:
Role of p53 in cisplatin-induced tubular cell apoptosis: Dependence
on p53 transcriptional activity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
287:F1140–F1147. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Seth R, Yang C, Kaushal V, Shah SV and
Kaushal GP: p53-Dependent caspase-2 activation in mitochondrial
release of apoptosis-inducing factor and its role in renal tubular
epithelial cell injury. J Biol Chem. 280:31230–31239. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wei Q, Dong G, Franklin J and Dong Z: The
pathological role of Bax in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int.
72:53–62. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wei Q, Dong G, Yang T, Megyesi J, Price PM
and Dong Z: Activation and involvement of p53 in cisplatin-induced
nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 293:F1282–F1291. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Feng Z, Zhang H, Levine AJ and Jin S: The
coordinate regulation of the p53 and mTOR pathways in cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:pp. 8204–8209. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wei L, Chen W, Zou Y, Huang H, Pan B, Jin
S, Huang R, Nie S and Kong G: AMP-activated protein kinase
regulates autophagic protection against cisplatin-induced tissue
injury in the kidney. Genet Mol Res. 14:12006–12015. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim TW, Kim YJ, Kim HT, Park SR, Lee MY,
Park YD, Lee CH and Jung JY: NQO1 deficiency leads enhanced
autophagy in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through the
AMPK/TSC2/mTOR signaling pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal.
24:867–883. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Herzog C, Yang C, Holmes A and Kaushal GP:
zVAD-fmk prevents cisplatin-induced cleavage of autophagy proteins
but impairs autophagic flux and worsens renal function. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 303:F1239–F1250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Scaringi L, Cornacchione P, Ayroldi E,
Corazzi L, Capodicasa E, Rossi R and Marconi P: Omeprazole induces
apoptosis in jurkat cells. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
17:331–342. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bizat N, Galas MC, Jacquard C, Boyer F,
Hermel JM, Schiffmann SN, Hantraye P, Blum D and Brouillet E:
Neuroprotective effect of zVAD against the neurotoxin
3-nitropropionic acid involves inhibition of calpain.
Neuropharmacology. 49:695–702. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Madden DT, Egger L and Bredesen DE: A
calpain-like protease inhibits autophagic cell death. Autophagy.
3:519–522. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rovetta F, Stacchiotti A, Consiglio A,
Cadei M, Grigolato PG, Lavazza A, Rezzani R and Aleo MF: ER
signaling regulation drives the switch between autophagy and
apoptosis in NRK-52E cells exposed to cisplatin. Exp Cell Res.
318:238–250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xu QX, Qiu XY, Jiao Z, Zhang M and Zhong
MK: FOXP3 rs3761549 polymorphism predicts long-term renal allograft
function in patients receiving cyclosporine-based immunosuppressive
regimen. Gene. 2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
68
|
Lim SW, Hyoung BJ, Piao SG, Doh KC, Chung
BH and Yang CW: Chronic cyclosporine nephropathy is characterized
by excessive autophagosome formation and decreased autophagic
clearance. Transplantation. 94:218–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yadav RK, Lee GH, Lee HY, Li B, Jung HE,
Rashid HO, Choi MK, Yadav BK, Kim WH, Kim KW, et al: TMBIM6
(transmembrane BAX inhibitor motif containing 6) enhances autophagy
and reduces renal dysfunction in a Cyclosporine A-induced
nephrotoxicity model. Autophagy. 11:1760–1774. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yegenaga I, Tuglular S, Ari E, Etiler N,
Baykara N, Torlak S, Acar S, Akbas T, Toker K and Solak ZM:
Evaluation of sepsis/systemic inflammatory response syndrome, acute
kidney injury and RIFLE criteria in two tertiary hospital intensive
care units in Turkey. Nephron Clin Pract. 115:c276–c282. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Schrier RW and Wang W: Acute renal failure
and sepsis. N Engl J Med. 351:159–169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Leventhal JS, Ni J, Osmond M, Lee K,
Gusella GL, Salem F and Ross MJ: Autophagy limits endotoxemic acute
kidney injury and alters renal tubular epithelial cell cytokine
expression. PLoS One. 11:e01500012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hsiao HW, Tsai KL, Wang LF, Chen YH,
Chiang PC, Chuang SM and Hsu C: The decline of autophagy
contributes to proximal tubular dysfunction during sepsis. Shock.
37:289–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Mei S, Livingston M, Hao J, Li L, Mei C
and Dong Z: Autophagy is activated to protect against endotoxic
acute kidney injury. Sci Rep. 6:221712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Howell GM, Gomez H, Collage RD, Loughran
P, Zhang X, Escobar DA, Billiar TR, Zuckerbraun BS and Rosengart
MR: Augmenting autophagy to treat acute kidney injury during
endotoxemia in mice. PLoS One. 8:e695202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, Klüter H and
Bieback K: Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone
marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells.
24:1294–1301. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Caplan AI: Mesenchymal stem cells. J
Orthop Res. 9:641–650. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Golpanian S, Wolf A, Hatzistergos KE and
Hare JM: Rebuilding the damaged heart: Mesenchymal stem cells,
cell-based therapy and engineered heart tissue. Physiol Rev.
96:1127–1168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Gazdic M, Arsenijevic A, Markovic BS,
Volarevic A, Dimova I, Djonov V, Arsenijevic N, Stojkovic M and
Volarevic V: Mesenchymal stem cell-dependent modulation of liver
diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 13:1109–1117. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen C and Hou J: Mesenchymal stem
cell-based therapy in kidney transplantation. Stem Cell Res Ther.
7:162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li T, Yan Y, Wang B, Qian H, Zhang X, Shen
L, Wang M, Zhou Y, Zhu W, Li W and Xu W: Exosomes derived from
human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver
fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 22:845–854. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhang B, Wang M, Gong A, Zhang X, Wu X,
Zhu Y, Shi H, Wu L, Zhu W, Qian H and Xu W: HucMSC-exosome
mediated-Wnt4 signaling is required for cutaneous wound healing.
Stem Cells. 33:2158–2168. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhao Y, Sun X, Cao W, Ma J, Sun L, Qian H,
Zhu W and Xu W: Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells relieve acute myocardial ischemic injury.
Stem Cells Int. 2015:7616432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Meirelles Lda S, Fontes AM, Covas DT and
Caplan AI: Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic properties of
mesenchymal stem cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 20:419–427.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Tögel F, Zhang P, Hu Z and Westenfelder C:
VEGF is a mediator of the renoprotective effects of multipotent
marrow stromal cells in acute kidney injury. J Cell Mol Med.
13:2109–2114. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Bruno S, Grange C, Collino F, Deregibus
MC, Cantaluppi V, Biancone L, Tetta C and Camussi G: Microvesicles
derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal
model of acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 7:e331152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
da Costa MR, Pizzatti L, Lindoso RS,
Sant'Anna JF, DuRocher B, Abdelhay E and Vieyra A: Mechanisms of
kidney repair by human mesenchymal stromal cells after ischemia: A
comprehensive view using label-free MS(E). Proteomics.
14:1480–1493. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Xing L, Cui R, Peng L, Ma J, Chen X, Xie
RJ and Li B: Mesenchymal stem cells, not conditioned medium,
contribute to kidney repair after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 5:1012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhang G, Zou X, Huang Y, Wang F, Miao S,
Liu G, Chen M and Zhu Y: Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived
extracellular vesicles protect against acute kidney injury through
anti-oxidation by enhancing Nrf2/ARE activation in rats. Kidney
Blood Press Res. 41:119–128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Moghadasali R, Azarnia M, Hajinasrollah M,
Arghani H, Nassiri SM, Molazem M, Vosough A, Mohitmafi S, Najarasl
M, Ajdari Z, et al: Intra-renal arterial injection of autologous
bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorates cisplatin-induced
acute kidney injury in a rhesus Macaque mulatta monkey model.
Cytotherapy. 16:734–749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhou Y, Xu H, Xu W, Wang B, Wu H, Tao Y,
Zhang B, Wang M, Mao F, Yan Y, et al: Exosomes released by human
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against
cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress and apoptosis in vivo and
in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yao W, Hu Q, Ma Y, Xiong W, Wu T, Cao J
and Wu D: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair
cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through antiapoptotic
pathways. Exp Ther Med. 10:468–476. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang W, Liu L, Huo Y, Yang Y and Wang Y:
Hypoxia-pretreated human MSCs attenuate acute kidney injury through
enhanced angiogenic and antioxidative capacities. Biomed Res Int.
2014:4624722014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Qiao PF, Yao L, Zhang XC, Li GD and Wu DQ:
Heat shock pretreatment improves stem cell repair following
ischemia-reperfusion injury via autophagy. World J Gastroenterol.
21:12822–12834. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhao K, Hao H, Liu J, Tong C, Cheng Y, Xie
Z, Zang L, Mu Y and Han W: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells ameliorate chronic high glucose-induced β-cell injury through
modulation of autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 6:e18852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Li J, Zhou J, Zhang D, Song Y, She J and
Bai C: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance autophagy
via PI3K/AKT signaling to reduce the severity of
ischaemia/reperfusion-induced lung injury. J Cell Mol Med.
19:2341–2351. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Shin JY, Park HJ, Kim HN, Oh SH, Bae JS,
Ha HJ and Lee PH: Mesenchymal stem cells enhance autophagy and
increase β-amyloid clearance in Alzheimer disease models.
Autophagy. 10:32–44. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Park HJ, Shin JY, Kim HN, Oh SH and Lee
PH: Neuroprotective effects of mesenchymal stem cells through
autophagy modulation in a parkinsonian model. Neurobiol Aging.
35:1920–1928. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Park M, Kim YH, Woo SY, Lee HJ, Yu Y, Kim
HS, Park YS, Jo I, Park JW, Jung SC, et al: Tonsil-derived
mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in
mice via autophagy activation. Sci Rep. 5:86162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wang B, Jia H, Zhang B, Wang J, Ji C, Zhu
X, Yan Y, Yin L, Yu J, Qian H and Xu W: Pre-incubated with
hucMSC-Exosomes prevent cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by
activating autophagy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Fougeray S and Pallet N: Mechanisms and
biological functions of autophagy in diseased and ageing kidneys.
Nat Rev Nephrol. 11:34–45. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhang D, Xu X and Dong Z: PRKCD/PKCσ
contributes to nephrotoxicity during cisplatin chemotherapy by
suppressing autophagy. Autophagy. 13:631–632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|