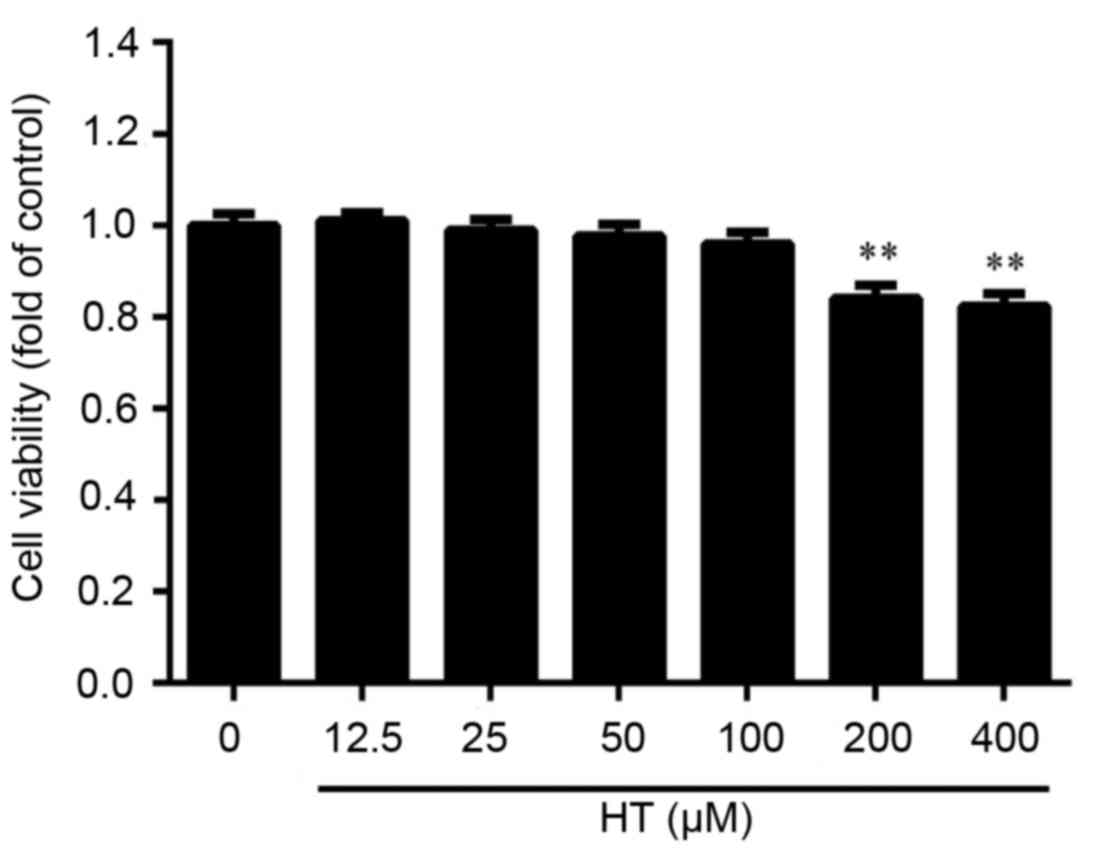
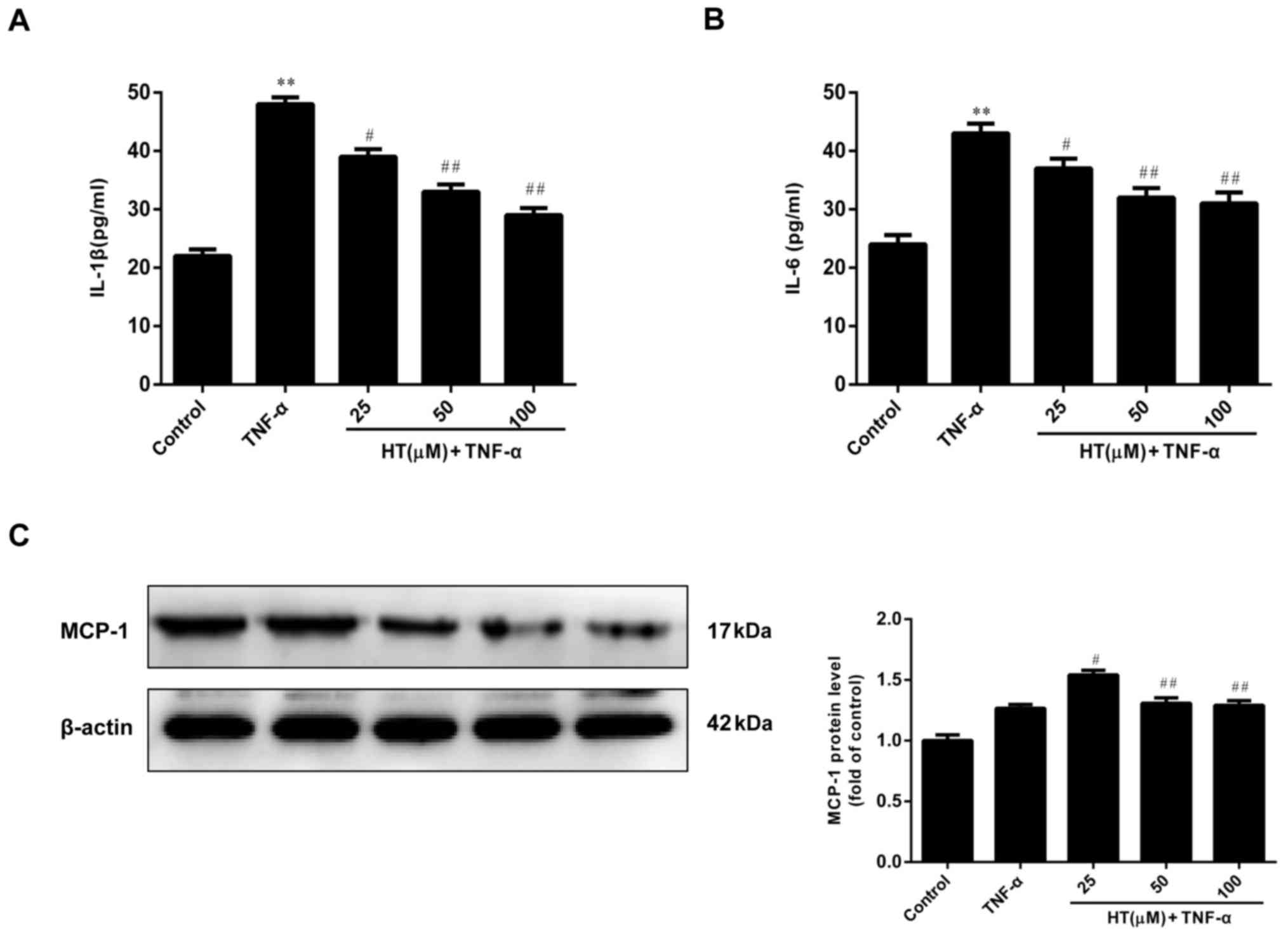
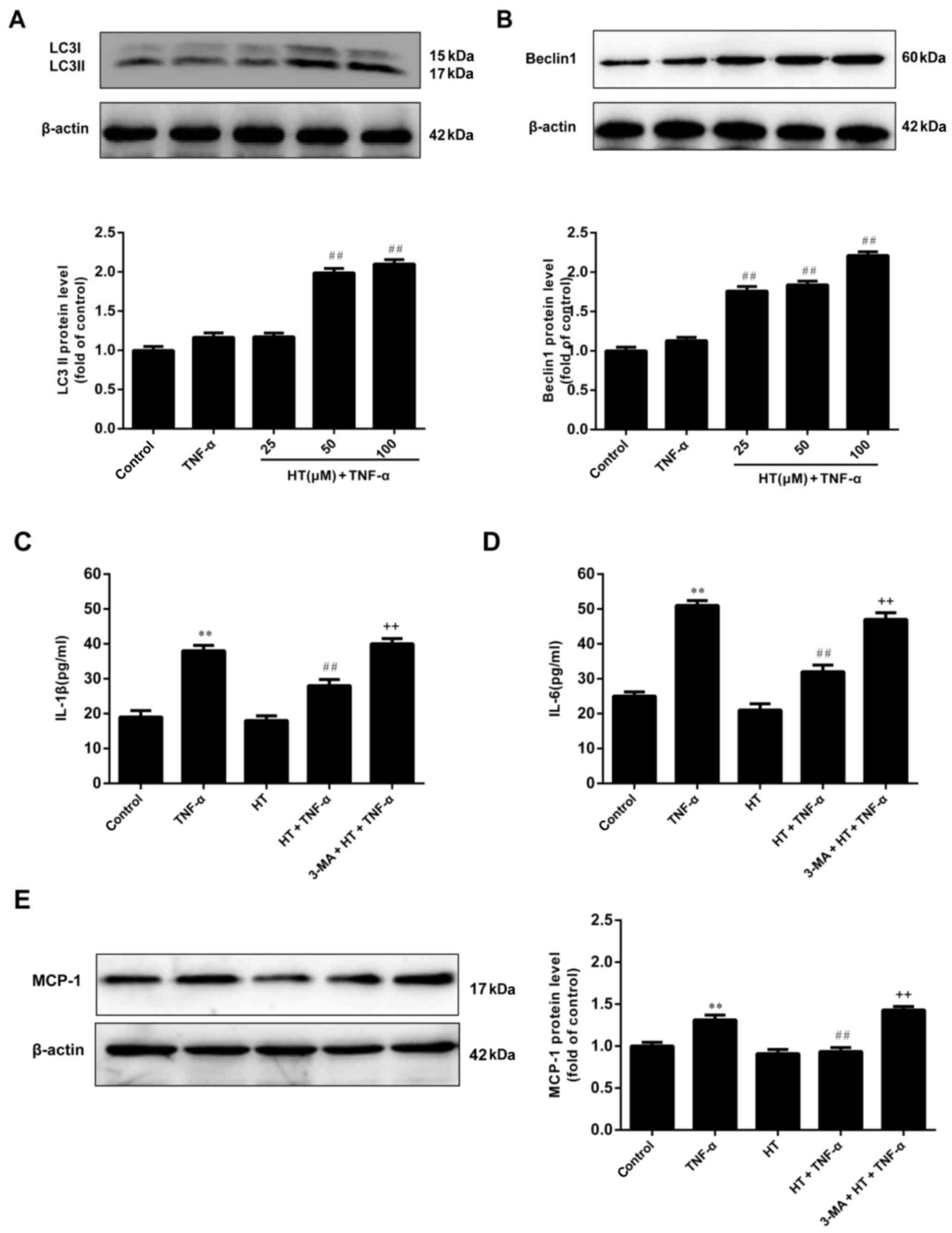
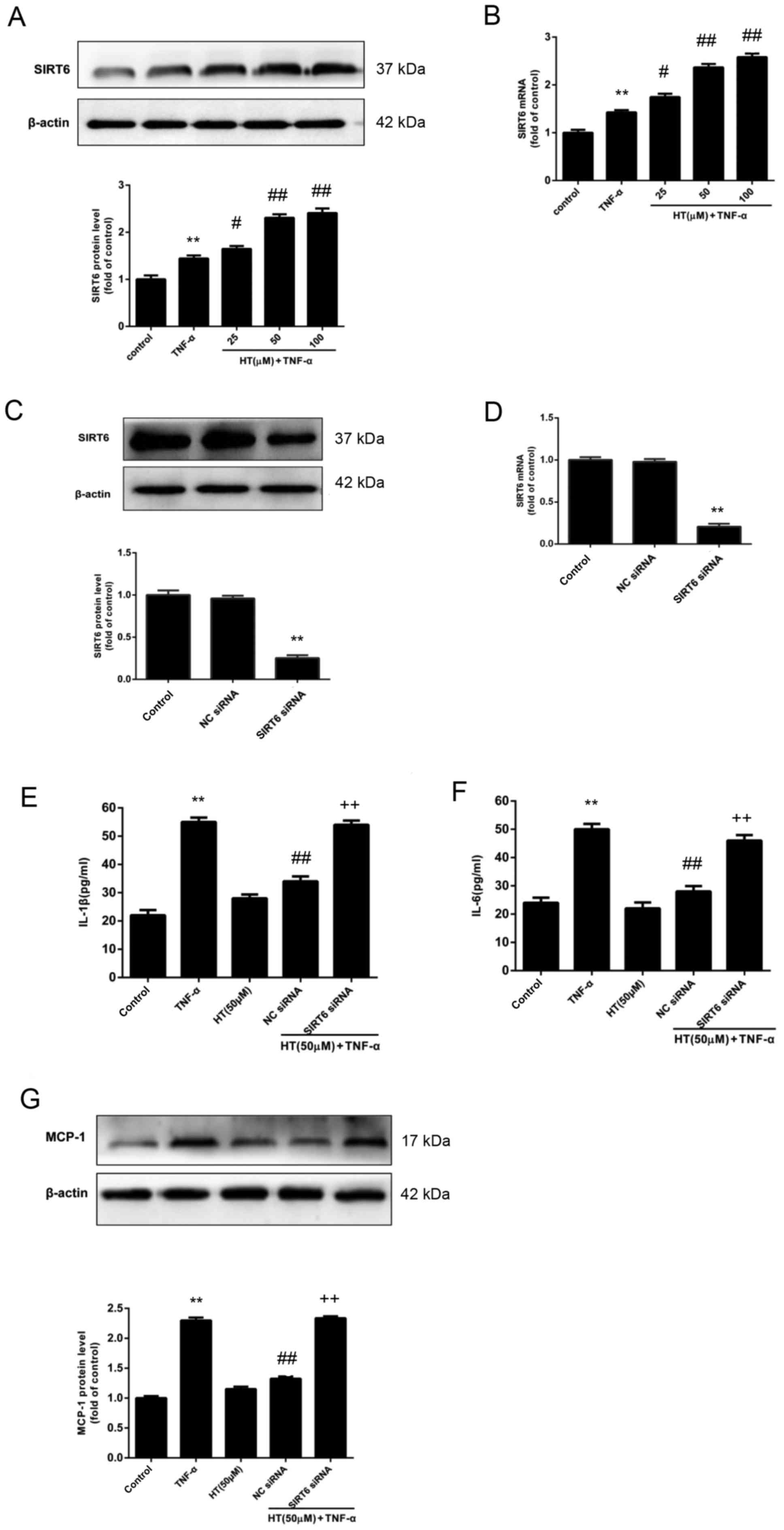
|
1
|
Roos EM and Arden NK: Strategies for the
prevention of knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 12:92–101.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang MC, Egan B and Wang JX: Epigenetic
mechanisms underlying the aberrant catabolic and anabolic
activities of osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
67:101–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Honorati MC, Cattini L and Facchini A:
IL-17, IL-1beta and TNF-alpha stimulate VEGF production by
dedifferentiated chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
12:683–691. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lianxu C, Hongti J and Changlong Y:
NF-kappa Bp65-specific siRNA inhibits expression of genes of COX-2,
NOS-2 and MMP-9 in rat IL-1 beta-induced and TNF-alpha-induced
chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 14:367–376. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tetlow LC, Adlam DJ and Woolley DE: Matrix
metalloproteinase and proinflammatory cytokine production by
chondrocytes of human osteoarthritic cartilage: Associations with
degenerative changes. Arthritis Rheum. 44:585–594. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Doria A, Gatto M and Punzi L: Autophagy in
human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 368:18452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Netea-Maier RT, Plantinga TS, van de
Veerdonk FL, Smit JW and Netea MG: Modulation of inflammation by
autophagy: Consequences for human disease. Autophagy. 12:245–260.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen ML, Yi L, Jin X, Liang XY, Zhou Y,
Zhang T, Xie Q, Zhou X, Chang H, Fu YJ, et al: Resveratrol
attenuates vascular endothelial inflammation by inducing autophagy
through the cAMP signaling pathway. Autophagy. 9:2033–2045. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kawahara TL, Michishita E, Adler AS,
Damian M, Berber E, Lin M, McCord RA, Ongaigui KC, Boxer LD, Chang
HY and Chua KF: SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to
NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression and organismal life span.
Cell. 136:62–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Michishita E, Park JY, Burneskis JM,
Barrett JC and Horikawa I: Evolutionarily conserved and
nonconserved cellular localizations and functions of human SIRT
proteins. Mol Biol Cell. 16:4623–4635. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang J, Cheng Y, Gu J, Wang S, Zhou S,
Wang Y, Tan Y, Feng W, Fu Y, Mellen N, et al: Fenofibrate increases
cardiac autophagy via FGF21/SIRT1 and prevents fibrosis and
inflammation in the hearts of Type 1 diabetic mice. Clin Sci
(Lond). 130:625–641. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takasaka N, Araya J, Hara H, Ito S,
Kobayashi K, Kurita Y, Wakui H, Yoshii Y, Yumino Y, Fujii S, et al:
Autophagy Induction by SIRT6 through attenuation of insulin-like
growth factor signaling is involved in the regulation of human
bronchial epithelial cell senescence. J Immunol. 192:958–968. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu Y, Chen L, Wang Y, Li W, Lin Y, Yu D,
Zhang L, Li F and Pan Z: Overexpression of Sirtuin 6 suppresses
cellular senescence and NF-κB mediated inflammatory responses in
osteoarthritis development. Sci Rep. 5:176022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nagai K, Matsushita T, Matsuzaki T,
Takayama K, Matsumoto T, Kuroda R and Kurosaka M: Depletion of
SIRT6 causes cellular senescence, DNA damage, and telomere
dysfunction in human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
23:1412–1420. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Granados-Principal S, Quiles JL,
Ramirez-Tortosa CL, Sanchez-Rovira P and Ramirez-Tortosa MC:
Hydroxytyrosol: From laboratory investigations to future clinical
trials. Nutr Rev. 68:191–206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bulotta S, Celano M, Lepore SM, Montalcini
T, Pujia A and Russo D: Beneficial effects of the olive oil
phenolic components oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol: Focus on
protection against cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J Transl
Med. 12:2192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo C, Li Y, Wang H, Cui Y, Feng ZH, Li H,
Li Y, Wang Y, Wurtz K, Weber P, et al: Hydroxytyrosol promotes
superoxide production and defects in autophagy leading to
anti-proliferation and apoptosis on human prostate cancer cells.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 13:625–639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cetrullo S, D'Adamo S, Guidotti S, Borzì
RM and Flamigni F: Hydroxytyrosol prevents chondrocyte death under
oxidative stress by inducing autophagy through sirtuin 1-dependent
and -independent mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1860:1181–1191.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao J, Zou X, Yang L, Feng Z and Liu J:
Hydroxytyrosol protects against acrolein induced preosteoblast cell
toxicity: Involvement of Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. J Funct Foods.
19:28–38. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Aparicio-Soto M, Sánchez-Fidalgo S,
González-Benjumea A, Maya I, Fernández-Bolaños JG and
Alarcón-de-la-Lastra C: Naturally occurring hydroxytyrosol
derivatives: Hydroxytyrosyl acetate and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol
modulate inflammatory response in murine peritoneal macrophages.
Potential utility as new dietary supplements. J Agric Food Chem.
63:836–846. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feng G, Wan Y, Balian G, Laurencin C and
Li X: Adenovirus-mediated expression of growth and differentiation
factor-5 promotes chondrogenesis of adipose stem cells. Growth
Factors. 26:132–142. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin J, Sun B, Jiang C, Hong H and Zheng Y:
Sirt2 suppresses inflammatory responses in collagen-induced
arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:897–903. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sasaki H, Takayama K, Matsushita T, Ishida
K, Kubo S, Matsumoto T, Fujita N, Oka S, Kurosaka M and Kuroda R:
Autophagy modulates osteoarthritis-related gene expression in human
chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 64:1920–1928. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shen C, Cai GQ, Peng JP and Chen XD:
Autophagy protects chondrocytes fromglucocorticoids-induced
apoptosis via ROS/Akt/FOXO3 signaling. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
23:2279–2287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Caramés B, Olmer M, Kiosses WB and Lotz
MK: The relationship of autophagy defects to cartilage damage
during joint aging in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheumatol.
67:1568–1576. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu N, Wang WB, Zhao Z, Zhang T and Song
YW: Autophagy in human articular chondrocytes is cytoprotective
following glucocorticoid stimulation. Mol Med Rep. 9:2166–2172.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|