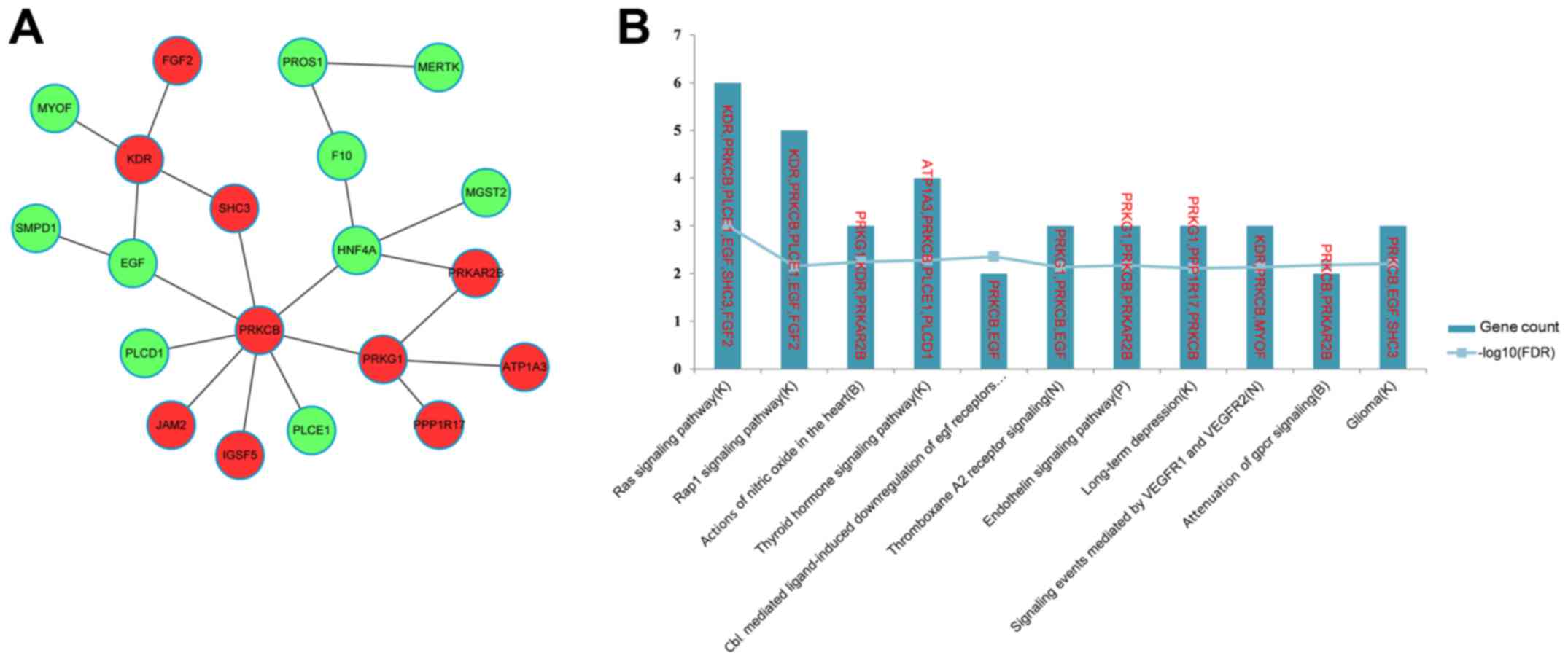
|
1
|
Kim K, Doi A, Wen B, Ng K, Zhao R, Cahan
P, Kim J, Aryee MJ, Ji H, Ehrlich LI, et al: Epigenetic memory in
induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 467:285–290. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K,
Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, Nie J, Jonsdottir GA,
Ruotti V, Stewart R, et al: Induced pluripotent stem cell lines
derived from human somatic cells. Science. 318:1917–1920. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park IH, Zhao R, West JA, Yabuuchi A, Huo
H, Ince TA, Lerou PH, Lensch MW and Daley GQ: Reprogramming of
human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors. Nature.
451:141–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng YW, Ohkohchi N and Taniguchi H:
Quantitative evaluation of long-term liver repopulation and the
reconstitution of bile ductules after hepatocellular
transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 11:6176–6181. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen YF, Tseng CY, Wang HW, Kuo HC, Yang
VW and Lee OK: Rapid generation of mature hepatocyte-like cells
from human induced pluripotent stem cells by an efficient
three-step protocol. Hepatology. 55:1193–1203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu H, Kim Y, Sharkis S, Marchionni L and
Jang YY: In vivo liver regeneration potential of human induced
pluripotent stem cells from diverse origins. Sci Transl Med.
3:82ra392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Si-Tayeb K, Noto FK, Nagaoka M, Li J,
Battle MA, Duris C, North PE, Dalton S and Duncan SA: Highly
efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced
pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology. 51:297–305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Di Bernardini E, Campagnolo P, Margariti
A, Zampetaki A, Karamariti E, Hu Y and Xu Q: Endothelial lineage
differentiation from induced pluripotent stem cells is regulated by
microRNA-21 and transforming growth factor β2 (TGF-β2) pathways. J
Biol Chem. 289:3383–3393. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li L, Bennett SA and Wang L: Role of
E-cadherin and other cell adhesion molecules in survival and
differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Adh Migr.
6:59–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen HF, Chuang CY, Lee WC, Huang HP, Wu
HC, Ho HN, Chen YJ and Kuo HC: Surface marker epithelial cell
adhesion molecule and E-cadherin facilitate the identification and
selection of induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rev.
7:722–735. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takayama K, Inamura M, Kawabata K,
Katayama K, Higuchi M, Tashiro K, Nonaka A, Sakurai F, Hayakawa T,
Furue MK and Mizuguchi H: Efficient generation of functional
hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent
stem cells by HNF4α transduction. Mol Ther. 20:127–137. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bernardo AS, Faial T, Gardner L, Niakan
KK, Ortmann D, Senner CE, Callery EM, Trotter MW, Hemberger M,
Smith JC, et al: BRACHYURY and CDX2 mediate BMP-induced
differentiation of human and mouse pluripotent stem cells into
embryonic and extraembryonic lineages. Cell Stem Cell. 9:144–155.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wilson AA, Ying L, Liesa M, Segeritz CP,
Mills JA, Shen SS, Jean J, Lonza GC, Liberti DC, Lang AH, et al:
Emergence of a stage-dependent human liver disease signature with
directed differentiation of alpha-1 antitrypsin-deficient iPS
cells. Stem Cell Reports. 4:873–885. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Carlson M, Falcon S, Pages H and Li N:
org. Hs. eg. db: Genome wide annotation for Human. R package
version. 2013.
|
|
17
|
MacDonald JW:
hugene10sttranscriptcluster.db: Affymetrix hugene10 annotation data
(chip hugene10sttranscriptcluster). R package version 8.4.0.
2016.
|
|
18
|
Smyth GK: Limma: linear models for
microarray dataBioinformatics and computational biology solutions
using R and Bioconductor. Springer; New York, NY: pp. 397–420.
2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. Journal of the royal statistical society. Series
B (Methodological). 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
20
|
Chen J, Bardes EE, Aronow BJ and Jegga AG:
ToppGene Suite for gene list enrichment analysis and candidate gene
prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Web Server issue): W305–W311.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Harris MA, Clark J, Ireland A, Lomax J,
Ashburner M, Foulger R, Eilbeck K, Lewis S, Marshall B, Mungall C,
et al: The gene ontology (GO) database and informatics resource.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32(Database issue): D258–D261. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M,
Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T
and Yamanishi Y: KEGG for linking genomes to life and the
environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36(Database issue): D480–D484.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39(Database issue): D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saito R, Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J,
Wang PL, Lotia S, Pico AR, Bader GD and Ideker T: A travel guide to
Cytoscape plugins. Nat Methods. 9:1069–1076. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu G, Dawson E, Duong A, Haw R and Stein
L: ReactomeFIViz: A Cytoscape app for pathway and network-based
data analysis. Version 2. F1000Res. 3:1462014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eiselleova L, Matulka K, Kriz V, Kunova M,
Schmidtova Z, Neradil J, Tichy B, Dvorakova D, Pospisilova S, Hampl
A and Dvorak P: A complex role for FGF-2 in self-renewal, survival,
and adhesion of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells.
27:1847–1857. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Diecke S, Quiroga-Negreira A, Redmer T and
Besser D: FGF2 signaling in mouse embryonic fibroblasts is crucial
for self-renewal of embryonic stem cells. Cells Tissues Organs.
188:52–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu P, Pan G, Yu J and Thomson JA: FGF2
sustains NANOG and switches the outcome of BMP4-induced human
embryonic stem cell differentiation. Cell Stem Cell. 8:326–334.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pera MF, Andrade J, Houssami S, Reubinoff
B, Trounson A, Stanley EG, Ward-van Oostwaard D and Mummery C:
Regulation of human embryonic stem cell differentiation by BMP-2
and its antagonist noggin. J Cell Sci. 117:1269–1280. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Valera E, Isaacs MJ, Kawakami Y, Izpisúa
Belmonte JC and Choe S: BMP-2/6 heterodimer is more effective than
BMP-2 or BMP-6 homodimers as inductor of differentiation of human
embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 5:e111672010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sudheer S, Bhushan R, Fauler B, Lehrach H
and Adjaye J: FGF inhibition directs BMP4-mediated differentiation
of human embryonic stem cells to syncytiotrophoblast. Stem Cells
Dev. 21:2987–3000. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wei Y, Chen YH, Li LY, Lang J, Yeh SP, Shi
B, Yang CC, Yang JY, Lin CY, Lai CC and Hung MC: CDK1-dependent
phosphorylation of EZH2 suppresses methylation of H3K27 and
promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem
cells. Nat Cell Biol. 13:87–94. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li L, Wang J, Hou J, Wu Z, Zhuang Y, Lu M,
Zhang Y, Zhou X, Li Z, Xiao W and Zhang W: Cdk1 interplays with
Oct4 to repress differentiation of embryonic stem cells into
trophectoderm. FEBS Lett. 586:4100–4107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ullah Z, Kohn MJ, Yagi R, Vassilev LT and
DePamphilis ML: Differentiation of trophoblast stem cells into
giant cells is triggered by p57/Kip2 inhibition of CDK1 activity.
Genes Dev. 22:3024–3036. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Van Hoof D, Muñoz J, Braam SR, Pinkse MW,
Linding R, Heck AJ, Mummery CL and Krijgsveld J: Phosphorylation
dynamics during early differentiation of human embryonic stem
cells. Cell Stem Cell. 5:214–226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang WW, Zhang XJ, Liu HX, Chen J, Ren
YH, Huang DG, Zou XH and Xiao W: Cdk1 is required for the
self-renewal of mouse embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biochem.
112:942–948. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
DeLaForest A, Nagaoka M, Si-Tayeb K, Noto
FK, Konopka G, Battle MA and Duncan SA: HNF4A is essential for
specification of hepatic progenitors from human pluripotent stem
cells. Development. 138:4143–4153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Deng XG, Qiu RL, Wu YH, Li ZX, Xie P,
Zhang J, Zhou JJ, Zeng LX, Tang J, Maharjan A and Deng JM:
Overexpression of miR-122 promotes the hepatic differentiation and
maturation of mouse ESCs through a miR-122/FoxA1/HNF4a-positive
feedback loop. Liver Int. 34:281–295. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu T, Zhang S, Xiang D and Wang Y:
Induction of hepatocyte-like cells from mouse embryonic stem cells
by lentivirus-mediated constitutive expression of Foxa2/Hnf4a. J
Cell Biochem. 114:2531–2541. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Heo JS, Lee YJ and Han HJ: EGF stimulates
proliferation of mouse embryonic stem cells: Involvement of Ca2+
influx and p44/42 MAPKs. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 290:C123–C133.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Park JH and Han HJ: Caveolin-1 plays
important role in EGF-induced migration and proliferation of mouse
embryonic stem cells: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and ERK. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 297:C935–C944. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Krampera M, Pasini A, Rigo A, Scupoli MT,
Tecchio C, Malpeli G, Scarpa A, Dazzi F, Pizzolo G and Vinante F:
HB-EGF/HER-1 signaling in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells:
Inducing cell expansion and reversibly preventing multilineage
differentiation. Blood. 106:59–66. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|