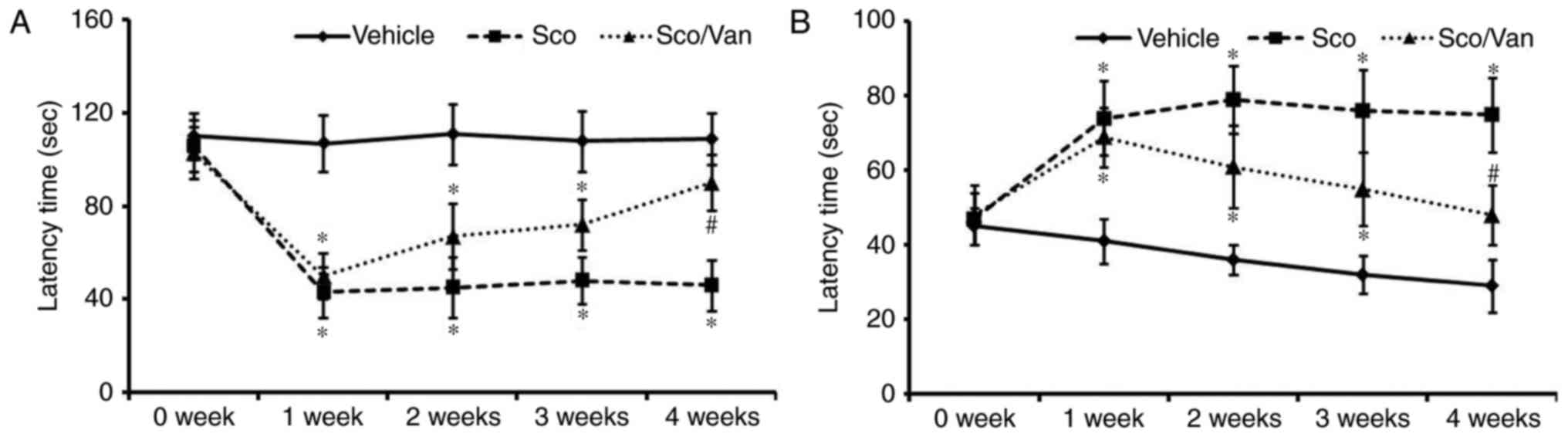
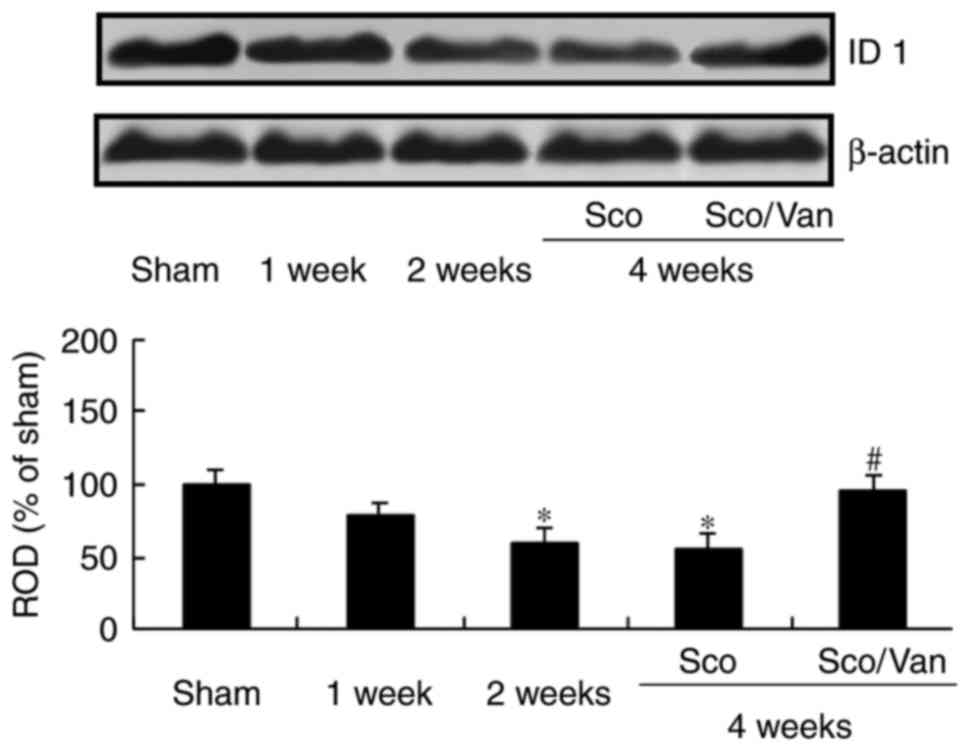
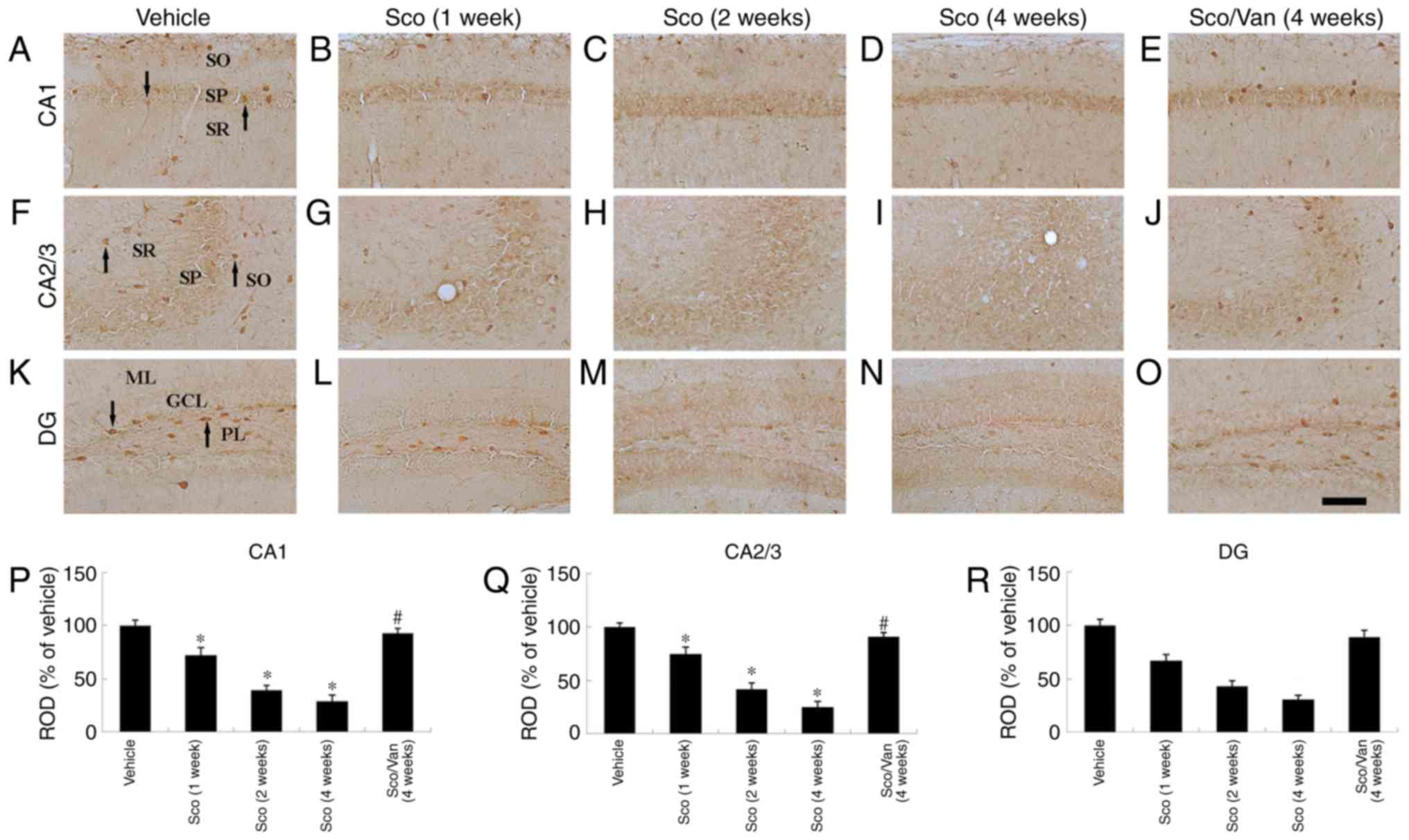
|
1
|
Hami J, Kheradmand H and Haghir H: Sex
differences and laterality of insulin receptor distribution in
developing rat hippocampus: An immunohistochemical study. J Mol
Neurosci. 54:100–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang W, Cao J, Liu X, Meng F, Li M, Chen
B and Zhang J: AMPK Plays a dual role in regulation of CREB/BDNF
pathway in mouse primary hippocampal cells. J Mol Neurosci.
56:782–788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kong Y, Bai PS, Sun H and Nan KJ:
Expression of the newly identified gene CAC1 in the hippocampus of
Alzheimer's disease patients. J Mol Neurosci. 47:207–218. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao L, Sun C, Xiong L, Yang Y, Gao Y,
Wang L, Zuo H, Xu X, Dong J, Zhou H and Peng R: MicroRNAs: Novel
mechanism involved in the pathogenesis of microwave exposure on
Rats' Hippocampus. J Mol Neurosci. 53:222–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lippa AS, Critchett DJ, Ehlert F, Yamamura
HI, Enna SJ and Bartus RT: Age-related alterations in
neurotransmitter receptors: An electrophysiological and biochemical
analysis. Neurobiol Aging. 2:3–8. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vijayan VK: Cholinergic enzymes in the
cerebellum and the hippocampus of the senescent mouse. Exp
Gerontol. 12:7–11. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartus RT, Dean RL III, Beer B and Lippa
AS: The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction.
Science. 217:408–414. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grasby PM, Frith CD, Paulesu E, Friston
KJ, Frackowiak RS and Dolan RJ: The effect of the muscarinic
antagonist scopolamine on regional cerebral blood flow during the
performance of a memory task. Exp Brain Res. 104:337–348. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee B, Sur B, Shim J, Hahm DH and Lee H:
Acupuncture stimulation improves scopolamine-induced cognitive
impairment via activation of cholinergic system and regulation of
BDNF and CREB expressions in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med.
14:3382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoo DY, Choi JH, Kim W, Nam SM, Jung HY,
Kim JH, Won MH, Yoon YS and Hwang IK: Effects of luteolin on
spatial memory, cell proliferation, and neuroblast differentiation
in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in a scopolamine-induced amnesia
model. Neurol Res. 35:813–820. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ebert U and Kirch W: Scopolamine model of
dementia: Electroencephalogram findings and cognitive performance.
Eur J Clin Invest. 28:944–949. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klinkenberg I and Blokland A: The validity
of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment:
A review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
34:1307–1350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu H, You Z, Wu Z, Zhou L, Shen J and Gu
Z: WY14643 attenuates the scopolamine-induced memory impairments in
mice. Neurochem Res. 41:2868–2879. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jung JW, Yoon BH, Oh HR, Ahn JH, Kim SY,
Park SY and Ryu JH: Anxiolytic-like effects of Gastrodia elata and
its phenolic constituents in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:261–265.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee YS, Ha JH, Yong CS, Lee DU, Huh K,
Kang YS, Lee SH, Jung MW and Kim JA: Inhibitory effects of
constituents of Gastrodia elata Bl. On glutamate-induced apoptosis
in IMR-32 human neuroblastoma cells. Arch Pharm Res. 22:404–409.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lirdprapamongkol K, Sakurai H, Kawasaki N,
Choo MK, Saitoh Y, Aozuka Y, Singhirunnusorn P, Ruchirawat S,
Svasti J and Saiki I: Vanillin suppresses in vitro invasion and in
vivo metastasis of mouse breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharm Sci.
25:57–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Murakami Y, Hirata A, Ito S, Shoji M,
Tanaka S, Yasui T, Machino M and Fujisawa S: Re-evaluation of
cyclooxygenase-2-inhibiting activity of vanillin and guaiacol in
macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Anticancer Res.
27:801–807. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu SL, Chen JC, Li CC, Lo HY, Ho TY and
Hsiang CY: Vanillin improves and prevents trinitrobenzene sulfonic
acid-induced colitis in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 330:370–376.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tai A, Sawano T, Yazama F and Ito H:
Evaluation of antioxidant activity of vanillin by using multiple
antioxidant assays. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1810:170–177. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim HJ, Hwang IK and Won MH: Vanillin,
4-hydroxybenzyl aldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol prevent
hippocampal CA1 cell death following global ischemia. Brain Res.
1181:130–141. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kee Y and Bronner-Fraser M: To proliferate
or to die: Role of Id3 in cell cycle progression and survival of
neural crest progenitors. Genes Dev. 19:744–755. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Massari ME and Murre C: Helix-loop-helix
proteins: Regulators of transcription in eucaryotic organisms. Mol
Cell Biol. 20:429–440. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Perk J, Iavarone A and Benezra R: Id
family of helix-loop-helix proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:603–614. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ruzinova MB and Benezra R: Id proteins in
development, cell cycle and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 13:410–418.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nair R, Teo WS, Mittal V and Swarbrick A:
ID proteins regulate diverse aspects of cancer progression and
provide novel therapeutic opportunities. Mol Ther. 22:1407–1415.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lasorella A, Benezra R and Iavarone A: The
ID proteins: Master regulators of cancer stem cells and tumour
aggressiveness. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:77–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ling F, Kang B and Sun XH: Id proteins:
Small molecules, mighty regulators. Curr Top Dev Biol. 110:189–216.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee JC, Chen BH, Cho JH, Kim IH, Ahn JH,
Park JH, Tae HJ, Cho GS, Yan BC, Kim DW, et al: Changes in the
expression of DNA-binding/differentiation protein inhibitors in
neurons and glial cells of the gerbil hippocampus following
transient global cerebral ischemia. Mol Med Rep. 11:2477–2485.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Andrews-Zwilling Y, Gillespie AK, Kravitz
AV, Nelson AB, Devidze N, Lo I, Yoon SY, Bien-Ly N, Ring K,
Zwilling D, et al: Hilar GABAergic interneuron activity controls
spatial learning and memory retrieval. PLoS One. 7:e405552012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McQuail JA, Frazier CJ and Bizon JL:
Molecular aspects of age-related cognitive decline: The role of
GABA signaling. Trends Mol Med. 21:450–460. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Palop JJ, Chin J, Roberson ED, Wang J,
Thwin MT, Bien-Ly N, Yoo J, Ho KO, Yu GQ, Kreitzer A, et al:
Aberrant excitatory neuronal activity and compensatory remodeling
of inhibitory hippocampal circuits in mouse models of Alzheimer's
disease. Neuron. 55:697–711. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang X, Wang ZH, Wu YY, Tang H, Tan L,
Wang X, Gao XY, Xiong YS, Liu D, Wang JZ and Zhu LQ: Melatonin
attenuates scopolamine-induced memory/synaptic disorder by rescuing
EPACs/miR-124/Egr1 pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 47:373–381. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan BC, Park JH, Chen BH, Cho JH, Kim IH,
Ahn JH, Lee JC, Hwang IK, Cho JH, Lee YL, et al: Long-term
administration of scopolamine interferes with nerve cell
proliferation, differentiation and migration in adult mouse
hippocampal dentate gyrus, but it does not induce cell death.
Neural Regen Res. 9:1731–1739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Horisawa T, Ishibashi T, Nishikawa H,
Enomoto T, Toma S, Ishiyama T and Taiji M: The effects of selective
antagonists of serotonin 5-HT7 and 5-HT1A receptors on
MK-801-induced impairment of learning and memory in the passive
avoidance and Morris water maze tests in rats: Mechanistic
implications for the beneficial effects of the novel atypical
antipsychotic lurasidone. Behav Brain Res. 220:83–90. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Z, Li J, Wang Z, Xue L, Zhang Y, Chen
Y, Su J and Li Z: L-tyrosine improves neuroendocrine function in a
mouse model of chronic stress. Neural Regen Res. 7:1413–1419.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Candelario-Jalil E, Alvarez D, Merino N
and León OS: Delayed treatment with nimesulide reduces measures of
oxidative stress following global ischemic brain injury in gerbils.
Neurosci Res. 47:245–253. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee JC, Kim IH, Cho GS, Park JH, Ahn JH,
Yan BC, Kwon HM, Kim YM, Cheon SH, Cho JH, et al: Ischemic
preconditioning-induced neuroprotection against transient cerebral
ischemic damage via attenuating ubiquitin aggregation. J Neurol
Sci. 336:74–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Romanski LM and LeDoux JE: Information
cascade from primary auditory cortex to the amygdala:
Corticocortical and corticoamygdaloid projections of temporal
cortex in the rat. Cereb Cortex. 3:515–532. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Morris R: Developments of a water-maze
procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci
Methods. 11:47–60. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
D'Hooge R and De Deyn PP: Applications of
the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain
Res Brain Res Rev. 36:60–90. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gupta S and Sharma B: Pharmacological
benefits of agomelatine and vanillin in experimental model of
Huntington's disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 122:122–135. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Blake MG, Boccia MM, Krawczyk MC and
Baratti CM: Scopolamine prevents retrograde memory interference
between two different learning tasks. Physiol Behav. 102:332–337.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Souza AC, Bruning CA, Acker CI, Neto JS
and Nogueira CW: 2-Phenylethynyl-butyltellurium enhances learning
and memory impaired by scopolamine in mice. Behav Pharmacol.
24:249–254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ohno M and Watanabe S: Interactive
processing between glutamatergic and cholinergic systems involved
in inhibitory avoidance learning of rats. Eur J Pharmacol.
312:145–147. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shi Z, Chen L, Li S, Chen S, Sun X, Sun L,
Li Y, Zeng J, He Y and Liu X: Chronic scopolamine-injection-induced
cognitive deficit on reward-directed instrumental learning in rat
is associated with CREB signaling activity in the cerebral cortex
and dorsal hippocampus. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 230:245–260.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kim YH and Park JH: Vanillin and
4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol attenuate cognitive impairment and the
reduction of cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in
the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of scopolamine-induced amnesia.
Anat Cell Biol. 50:143–151. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao C, Deng W and Gage FH: Mechanisms and
functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell. 132:645–660.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jen Y, Manova K and Benezra R: Each member
of the Id gene family exhibits a unique expression pattern in mouse
gastrulation and neurogenesis. Dev Dyn. 208:92–106. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jung S, Park RH, Kim S, Jeon YJ, Ham DS,
Jung MY, Kim SS, Lee YD, Park CH and Suh-Kim H: Id proteins
facilitate self-renewal and proliferation of neural stem cells.
Stem Cells Dev. 19:831–841. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lyden D, Young AZ, Zagzag D, Yan W, Gerald
W, O'Reilly R, Bader BL, Hynes RO, Zhuang Y, Manova K and Benezra
R: Id1 and Id3 are required for neurogenesis, angiogenesis and
vascularization of tumour xenografts. Nature. 401:670–677. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nam HS and Benezra R: High levels of Id1
expression define B1 type adult neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell.
5:515–526. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bai G, Sheng N, Xie Z, Bian W, Yokota Y,
Benezra R, Kageyama R, Guillemot F and Jing N: Id sustains Hes1
expression to inhibit precocious neurogenesis by releasing negative
autoregulation of Hes1. Dev Cell. 13:283–297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Owens DF and Kriegstein AR: Is there more
to GABA than synaptic inhibition? Nat Rev Neurosci. 3:715–727.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Pang KC, Jiao X, Sinha S, Beck KD and
Servatius RJ: Damage of GABAergic neurons in the medial septum
impairs spatial working memory and extinction of active avoidance:
Effects on proactive interference. Hippocampus. 21:835–846.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Roland JJ, Stewart AL, Janke KL, Gielow
MR, Kostek JA, Savage LM, Servatius RJ and Pang KC: Medial
septum-diagonal band of Broca (MSDB) GABAergic regulation of
hippocampal acetylcholine efflux is dependent on cognitive demands.
J Neurosci. 34:506–514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Van der Zee EA and Luiten PG: GABAergic
neurons of the rat dorsal hippocampus express muscarinic
acetylcholine receptors. Brain Res Bull. 32:601–609. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Navarria A, Wohleb ES, Voleti B, Ota KT,
Dutheil S, Lepack AE, Dwyer JM, Fuchikami M, Becker A, Drago F and
Duman RS: Rapid antidepressant actions of scopolamine: Role of
medial prefrontal cortex and M1-subtype muscarinic acetylcholine
receptors. Neurobiol Dis. 82:254–261. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Voleti B, Navarria A, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Li
N, Terwilliger R, Sanacora G, Eid T, Aghajanian G and Duman RS:
Scopolamine rapidly increases mammalian target of rapamycin complex
1 signaling, synaptogenesis, and antidepressant behavioral
responses. Biol Psychiatry. 74:742–749. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li G, Bien-Ly N, Andrews-Zwilling Y, Xu Q,
Bernardo A, Ring K, Halabisky B, Deng C, Mahley RW and Huang Y:
GABAergic interneuron dysfunction impairs hippocampal neurogenesis
in adult apolipoprotein E4 knockin mice. Cell Stem Cell. 5:634–645.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|