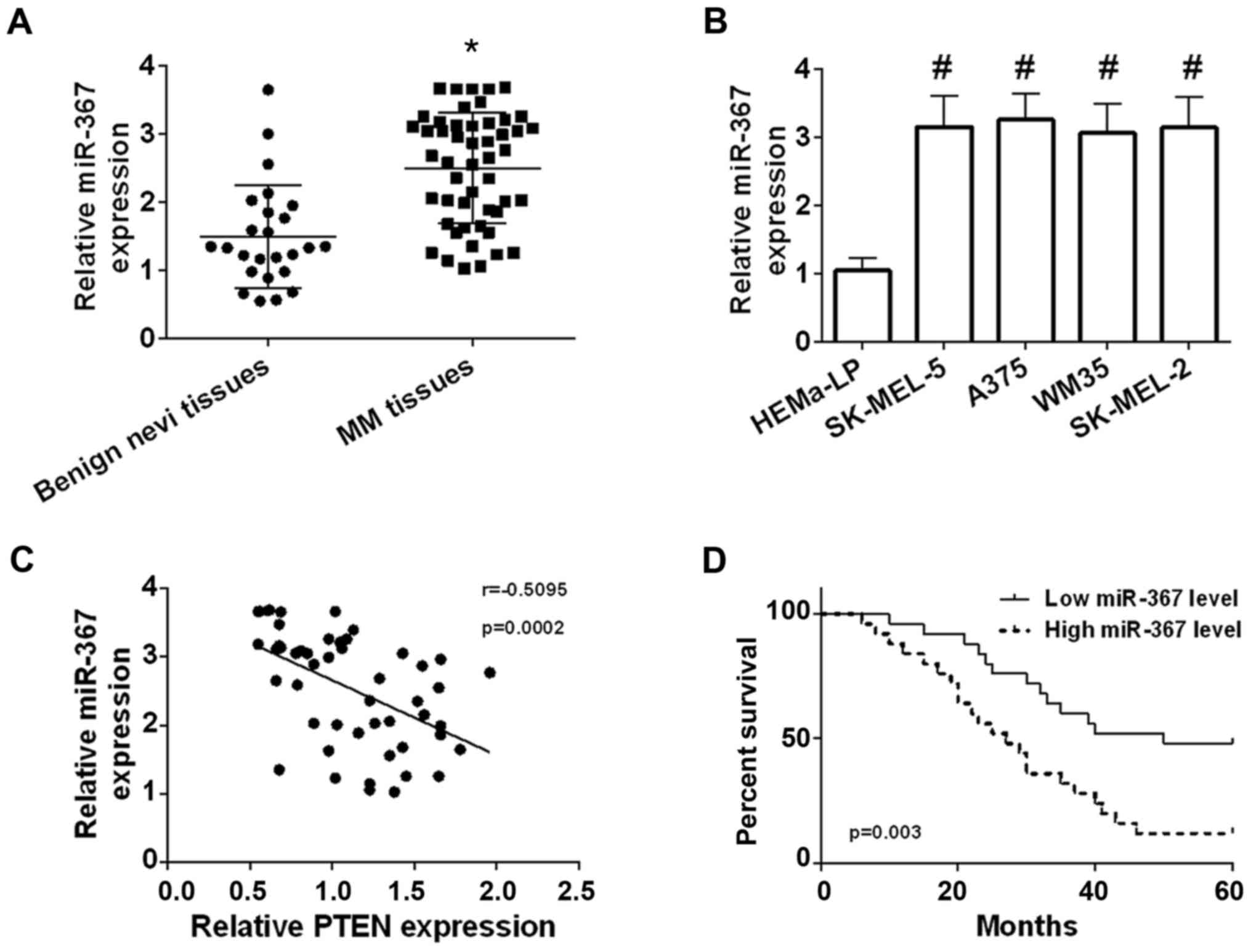
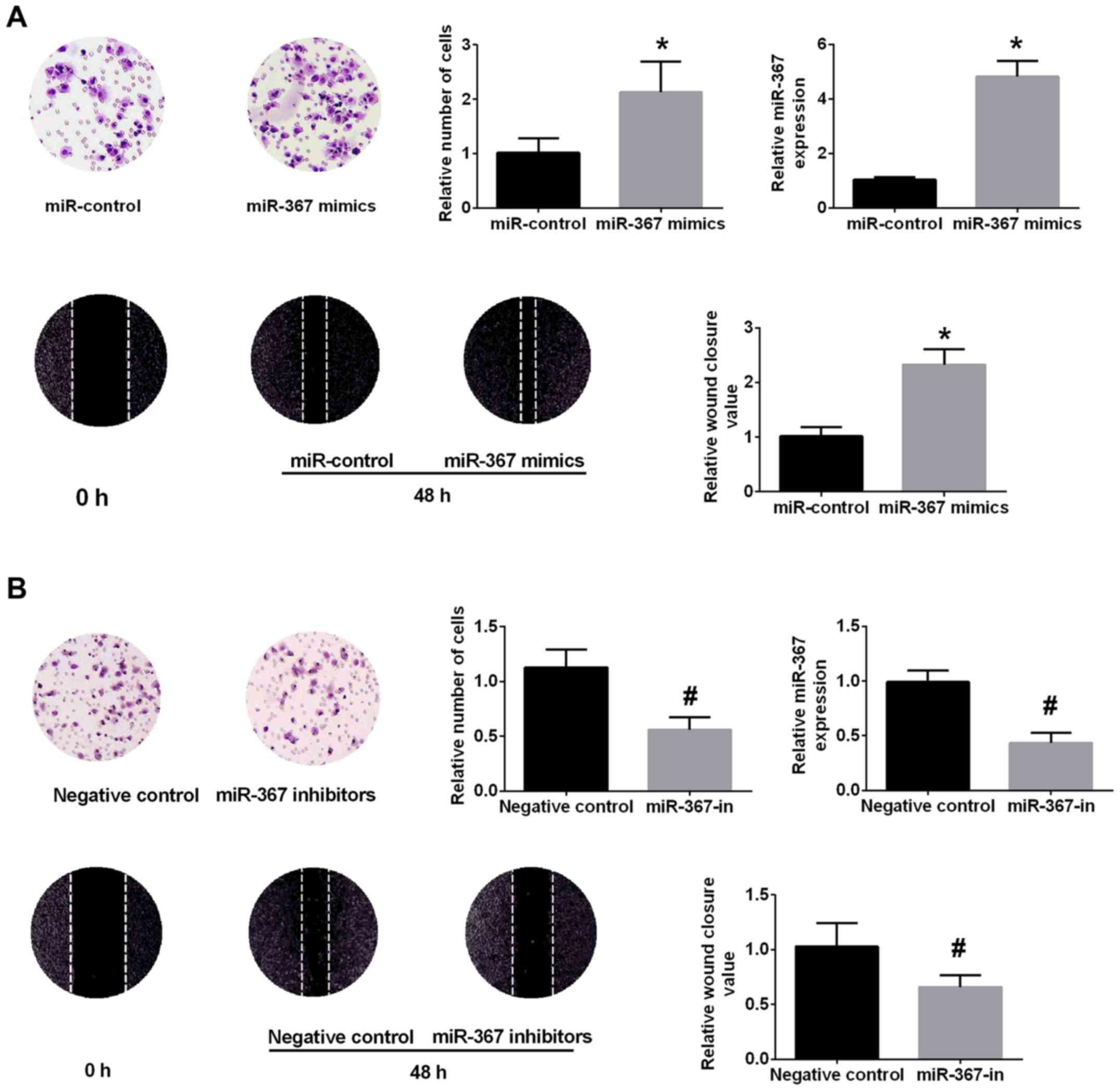
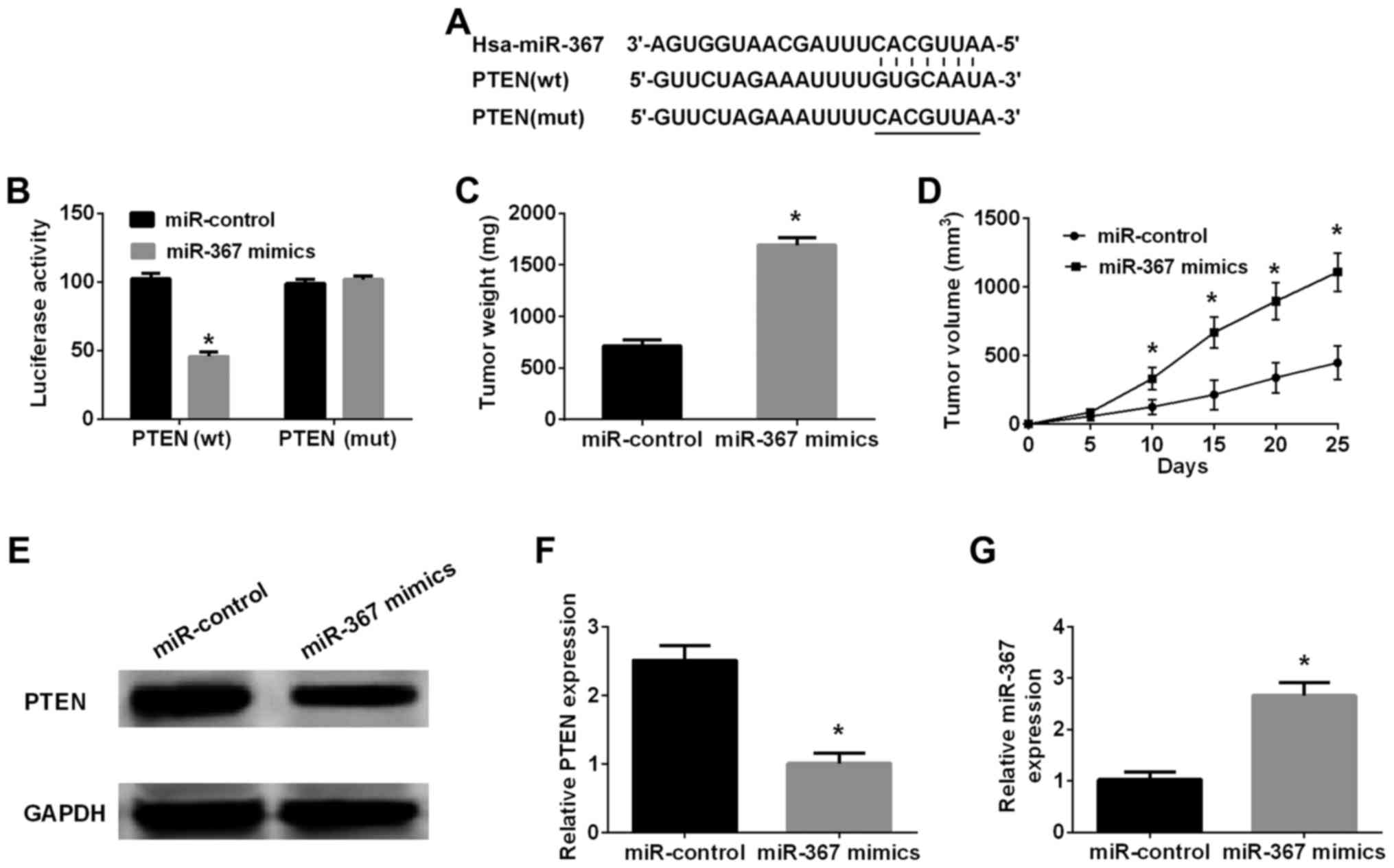
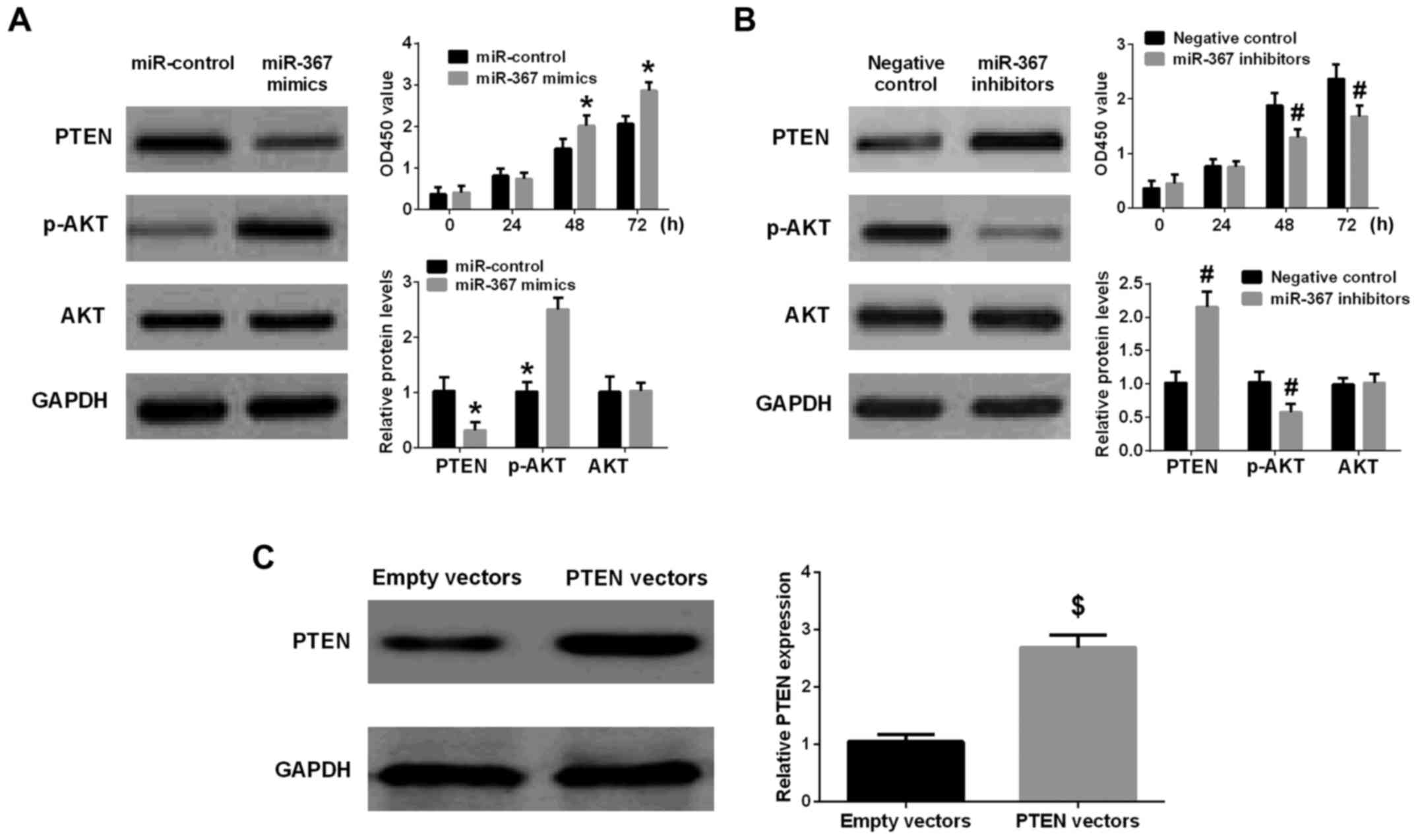
|
1
|
Isola AL, Eddy K and Chen S: Biology,
therapy and implications of tumor exosomes in the progression of
melanoma. Cancers. 8:E1102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Giblin AV and Thomas JM: Incidence,
mortality and survival in cutaneous melanoma. J Plast Reconstr
Aesthet Surg. 60:32–40. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peterson M, Albertini MR and Remington P:
Incidence, survival and mortality of malignant Cutaneous melanoma
in Wisconsin, 1995–2011. WMJ. 114:196–201. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Downing A, Newton-Bishop JA and Forman D:
Recent trends in cutaneous malignant melanoma in the Yorkshire
region of England; incidence, mortality and survival in relation to
stage of disease, 1993–2003. Br J Cancer. 95:91–95. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Leiter U, Meier F, Schittek B and Garbe C:
The natural course of cutaneous melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 86:172–178.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luo C, Weber CE, Osen W, Bosserhoff AK and
Eichmuller SB: The role of microRNAs in melanoma. Eur J Cell Biol.
93:11–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kashani-Sabet M: Molecular markers in
melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 170:31–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mannucci C, Casciaro M, Minciullo PL,
Calapai G, Navarra M and Gangemi S: Involvement of microRNAs in
skin disorders: A literature review. Allergy Asthma Proc. 38:pp.
9–15. 2017; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Greenberg E, Nemlich Y and Markel G:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Lessons from melanoma. Curr Pharm Des.
20:5246–5259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carthew RW: Gene regulation by microRNAs.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 16:203–208. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakahara K and Carthew RW: Expanding roles
for miRNAs and siRNAs in cell regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:127–133. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Long J, Menggen Q, Wuren Q, Shi Q and Pi
X: miR-219-5p inhibits the growth and metastasis of malignant
melanoma by targeting BCL-2. Biomed Res Int. 2017:90325022017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He J, Zhao J, Zhu W, Qi D, Wang L, Sun J,
Wang B, Ma X, Dai Q and Yu X: MicroRNA biogenesis pathway genes
polymorphisms and cancer risk: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Peer J. 4:e27062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fattore L, Costantini S, Malpicci D,
Ruggiero CF, Ascierto PA, Croce CM, Mancini R and Ciliberto G:
MicroRNAs in melanoma development and resistance to target therapy.
Oncotarget. 8:22262–22278. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stahl JM, Cheung M, Sharma A, Trivedi NR,
Shanmugam S and Robertson GP: Loss of PTEN promotes tumor
development in malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 63:2881–2890.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao Y and Wang Y and Wang Y: Up-regulated
microRNA-500a enhances hepatocarcinoma metastasis by repressing
PTEN expression. Biosci Rep. 37:BSR201708372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo J, Xiao Z, Yu X and Cao R: miR-20b
promotes cellular proliferation and migration by directly
regulating phosphatase and tensin homolog in prostate cancer. Oncol
Lett. 14:6895–6900. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guan Y, Chen L, Bao Y, Qiu B, Pang C, Cui
R and Wang Y: High miR-196a and low miR-367 cooperatively correlate
with unfavorable prognosis of high-grade glioma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:6576–6588. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun J, Song K, Feng X and Gao S:
MicroRNA-367 is a potential diagnostic biomarker for patients with
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
473:363–369. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu J, Wu W, Wang J, Huang C, Wen W, Zhao
F, Xu X, Pan X, Wang W, Zhu Q and Chen L: miR-367 promotes the
proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer via
targeting FBXW7. Oncol Rep. 37:1052–1058. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bin Z, Dedong H, Xiangjie F, Hongwei X and
Qinghui Y: The microRNA-367 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of
gastric cancer by directly repressing Rab23. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 19:69–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Campayo M, Navarro A, Vinolas N, Diaz T,
Tejero R, Gimferrer JM, Molins L and Cabanas ML: Low miR-145 and
high miR-367 are associated with unfavourable prognosis in resected
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur Respir J. 41:1172–1178. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kaid C, Silva PB, Cortez BA, Rodini CO,
Semedo-Kuriki P and Okamoto OK: miR-367 promotes proliferation and
stem-like traits in medulloblastoma cells. Cancer Sci.
106:1188–1195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Milella M, Falcone I, Conciatori F, Cesta
Incani U, Del Curatolo A, Inzerilli N, Nuzzo CM, Vaccaro V, Vari S,
Cognetti F and Ciuffreda L: PTEN: Multiple functions in human
malignant tumors. Front Oncol. 5:242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang H, Kircher DA, Kim KH, Grossmann AH,
VanBrocklin MW, Holmen SL and Robinson JP: Activated MEK cooperates
with Cdkn2a and Pten loss to promote the development and
maintenance of melanoma. Oncogene. 36:3842–3851. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song MS, Salmena L and Pandolfi PP: The
functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:283–296. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carnero A, Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O,
Link W and Leal JF: The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer,
therapeutic implications. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:187–198.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|