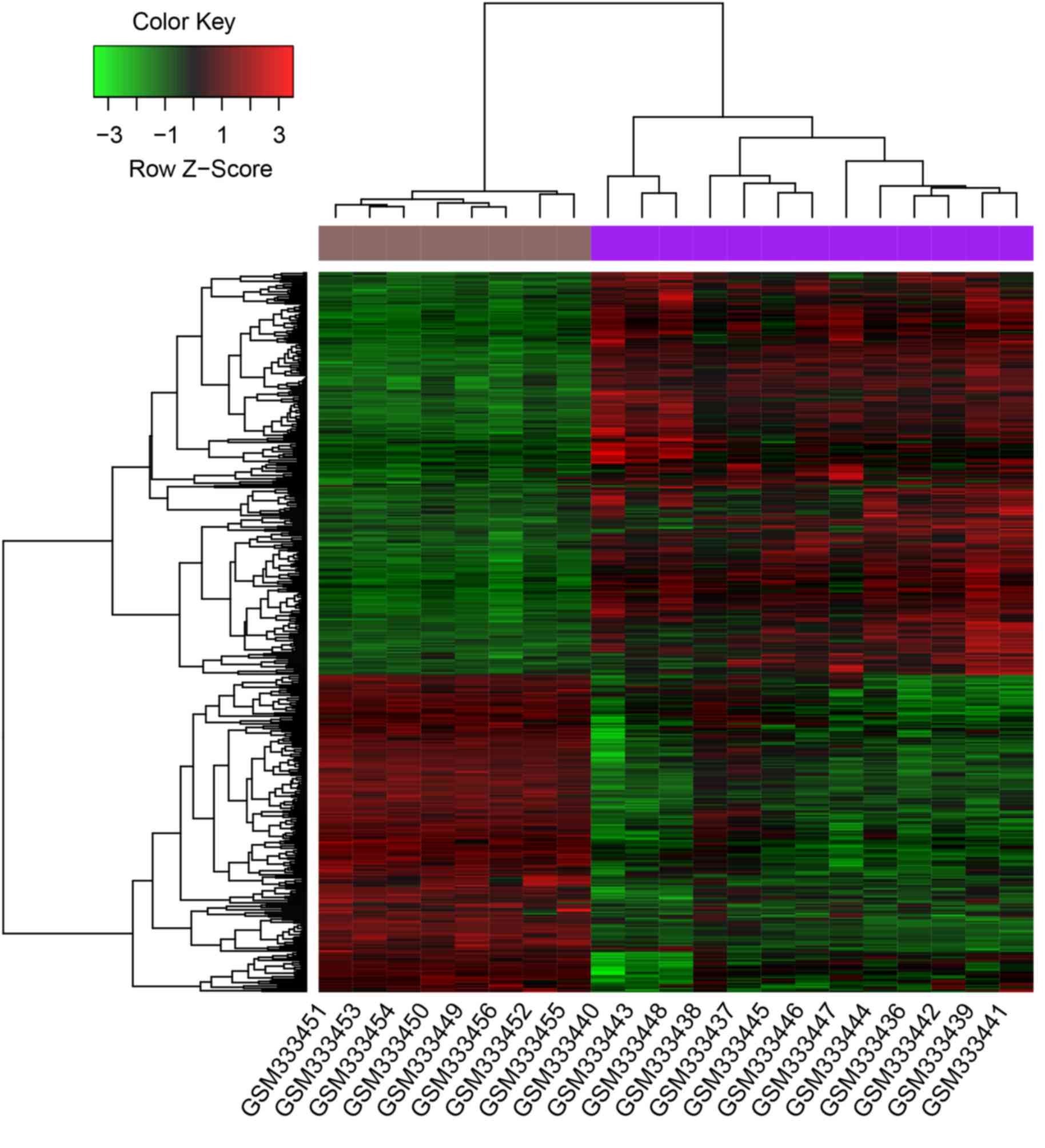
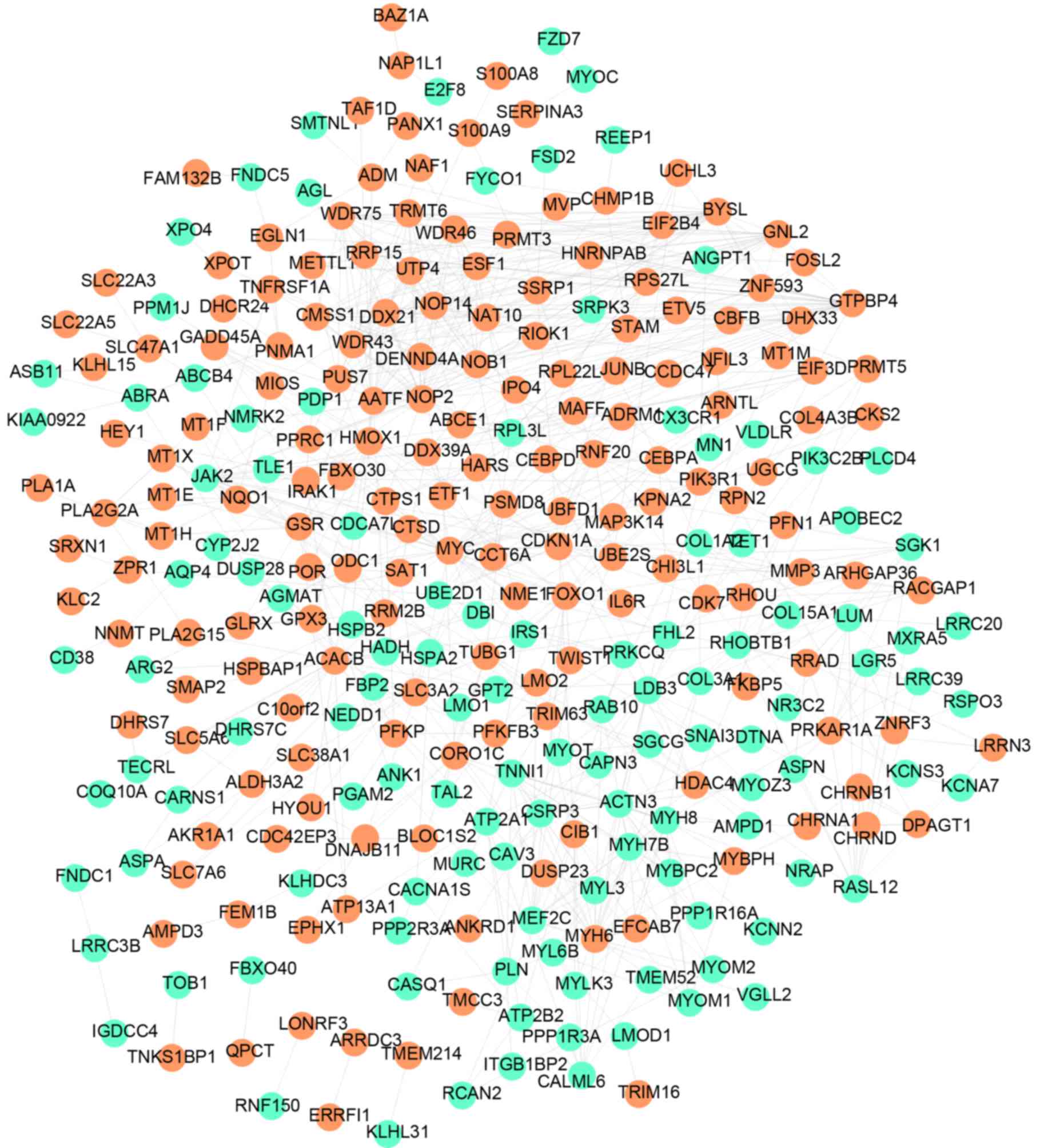
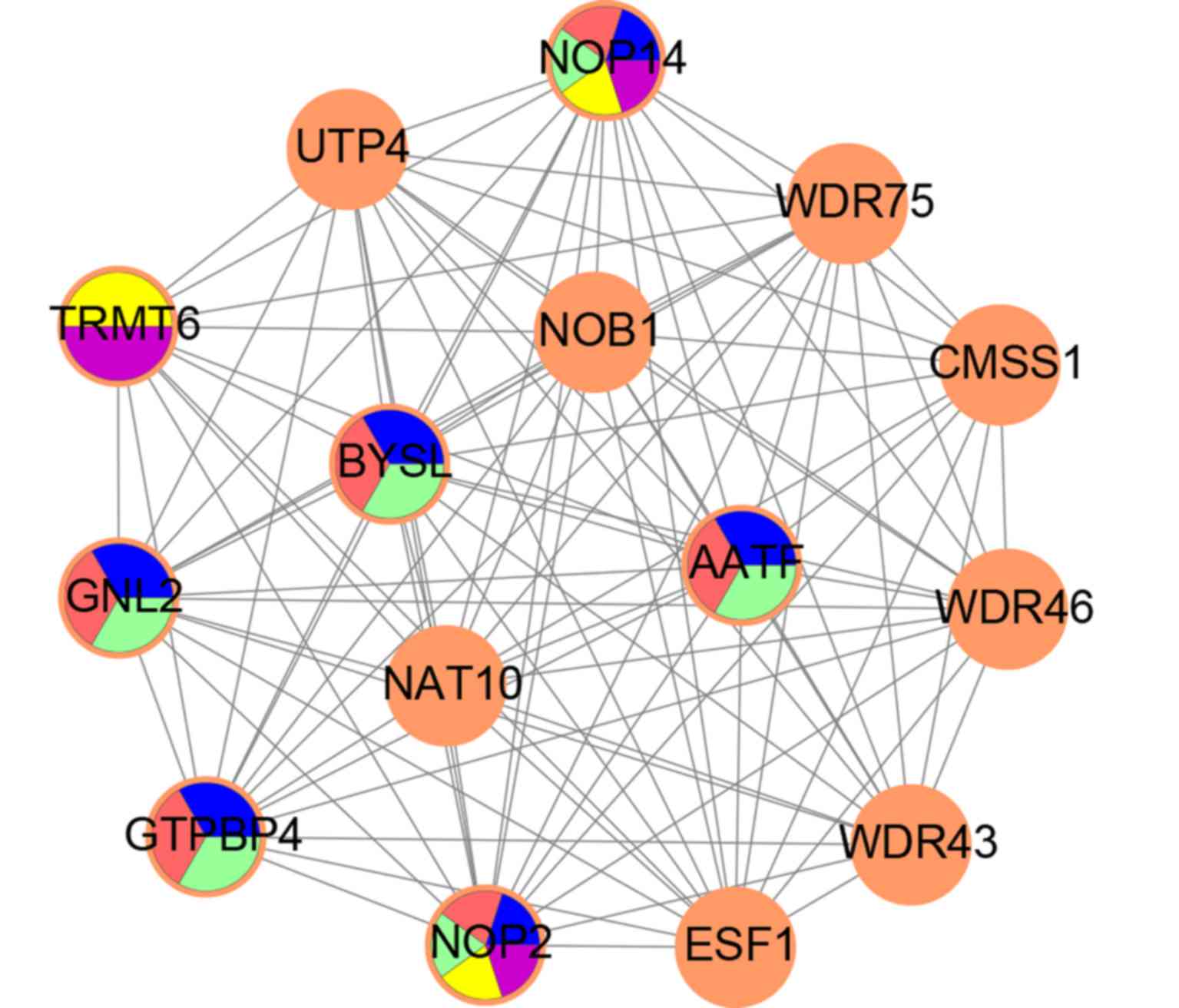
|
1
|
Tsai D, Stewart P, Goud R, Gourley S,
Hewagama S, Krishnaswamy S, Wallis SC, Lipman J and Roberts JA:
Total and unbound ceftriaxone pharmacokinetics in critically ill
Australian Indigenous patients with severe sepsis. Int J Antimicrob
Agents. 48:748–752. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK,
Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC and Reinhart K:
International Forum of Acute Care Trialists: Assessment of Global
incidence and mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current
estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:259–272.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cheng B, Xie G, Yao S, Wu X, Guo Q, Gu M,
Fang Q, Xu Q, Wang D, Jin Y, et al: Epidemiology of severe sepsis
in critically ill surgical patients in ten university hospitals in
China. Crit Care Med. 35:2538–2546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wallisch JS, Pang D, Carcillo JA and Aneja
RK: Implementation of guidelines to treat pediatric sepsis:
Cookbook medicine or the force awakens! Pediatr Crit Care Med.
17:884–885. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baghel K, Srivastava RN, Chandra A, Goel
SK, Agrawal J, Kazmi HR and Raj S: TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 cytokines
and their association with TNF-α-308 G/A polymorphism and
postoperative sepsis. J Gastrointest Surg. 18:1486–1494. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thimmulappa RK, Lee H, Rangasamy T, Reddy
SP, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW and Biswal S: Nrf2 is a critical
regulator of the innate immune response and survival during
experimental sepsis. J Clin Invest. 116:984–995. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Coquerel D, Neviere R, Delile E, Mulder P,
Marechal X, Montaigne D, Renet S, Remy-Jouet I, Gomez E, Henry JP,
et al: Gene deletion of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B protects
against sepsis-induced cardiovascular dysfunction and mortality.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1032–1044. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kloosterman WP, Wienholds E, de Bruijn E,
Kauppinen S and Plasterk RH: In situ detection of miRNAs in animal
embryos using LNA-modified oligonucleotide probes. Nat Methods.
3:27–29. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cifuentes D, Xue H, Taylor DW, Patnode H,
Mishima Y, Cheloufi S, Ma E, Mane S, Hannon GJ, Lawson ND, et al: A
Novel miRNA processing pathway independent of dicer requires
Argonaute2 catalytic activity. Science. 328:1694–1698. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goodwin AJ, Guo C, Cook JA, Wolf B,
Halushka PV and Fan H: Plasma levels of microRNA are altered with
the development of shock in human sepsis: An observational study.
Crit Care. 19:4402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao X, Wang Y and Chen Z: The predict
value of serum miRNA150 on sepsis prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Med.
9:18367–18372. 2016.
|
|
12
|
Fredriksson K, Tjäder I, Keller P,
Petrovic N, Ahlman B, Schéele C, Wernerman J, Timmons JA and
Rooyackers O: Dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics and the
muscle transcriptome in ICU patients suffering from sepsis induced
multiple organ failure. PLoS One. 3:e36862008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fredriksson K, Tjäder I, Keller P,
Petrovic N, Ahlman B, Schéele C, Wernerman J, Timmons JA and
Rooyackers O: Dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics and the
muscle transcriptome in ICU patients suffering from sepsis induced
multiple organ failure. PLoS One. 3:e36862008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Diboun I, Wernisch L, Orengo CA and
Koltzenburg M: Microarray analysis after RNA amplification can
detect pronounced differences in gene expression using limma. BMC
Genomics. 7:2522006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono
H and Kanehisa M: KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:29–34. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt
S, Bork P and Snel B: STRING: A database of predicted functional
associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:258–261. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y and Wu FX:
CytoNCA: A cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation
of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 127:67–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garcia O, Saveanu C, Cline M,
Fromont-Racine M, Jacquier A, Schwikowski B and Aittokallio T:
GOlorize: A cytoscape plug-in for network visualization with Gene
Ontology-based layout and coloring. Bioinformatics. 23:394–396.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng G, Tu K, Yang Q, Xiong Y, Wei C, Xie
L, Zhu Y and Li Y: ITFP: An integrated platform of mammalian
transcription factors. Bioinformatics. 24:2416–2417. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E,
Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A, Reuter I, Chekmenev D, Krull M,
Hornischer K, et al: TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel:
Transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res.
34:(Database Issue). D108–D110. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koh CM, Sabò A and Guccione E: Targeting
MYC in cancer therapy: RNA processing offers new opportunities.
Bioessays. 38:266–275. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roderburg C, Benz F, Schüller F, Pombeiro
I, Hippe HJ, Frey N, Trautwein C, Luedde T, Koch A, Tacke F and
Luedde M: Serum levels of TNF receptor ligands are dysregulated in
sepsis and predict mortality in critically Ill patients. PLoS One.
11:e01537652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G and Payen D:
Immunosuppression in sepsis: A novel understanding of the disorder
and a new therapeutic approach. Lancet Infect Dis. 13:260–268.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang Y, Li X, Zhang X, Li Z, Wang L, Sun
Y, Liu Z and Ma X: Elevated levels of plasma TNF-α are associated
with microvascular endothelial dysfunction in patients with sepsis
through activating the NF-κB and p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase in endothelial cells. Shock. 41:275–281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu T, Zhou Y, Ko KS and Yang H:
Interactions between Myc and mediators of inflammation in chronic
liver diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2015:2768502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qiao X, Zhu S, Zhang S and Dong H:
Disrupted pathways associated with neonatal sepsis: Combination of
protein-protein interactions and pathway data. BioChip J. 11:1–7.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu M, Wang D and Li N: Che-1 gene
silencing induces osteosarcoma cell apoptosis by inhibiting mutant
p53 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 473:168–173. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smigiel R, Marcelis C, Patkowski D, de
Leeuw N, Bednarczyk D, Barg E, Mascianica K, Maria Sasiadek M and
Brunner H: Oesophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula and
anal atresia in a patient with a de novo microduplication in 17q12.
Eur J Med Genet. 57:40–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
De Nicola F, Bruno T, Iezzi S, Di Padova
M, Floridi A, Passananti C, Del Sal G and Fanciulli M: The prolyl
isomerase Pin1 affects Che-1 stability in response to apoptotic DNA
damage. J Biol Chem. 282:19685–19691. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Baker ST, Opperman KJ, Tulgren ED, Turgeon
SM, Bienvenut W and Grill B: RPM-1 uses both ubiquitin ligase and
phosphatase-based mechanisms to regulate DLK-1 during neuronal
development. PLoSGenet. 10:e10042972014.
|
|
37
|
Sharma S, Singh D and Kaul D: AATF RNome
has the potential to define post mortem interval. Forensic Sci Int.
247:e21–e24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee SJ, Lee EJ, Kim SK, Jeong P, Cho YH,
Yun SJ, Kim S, Kim GY, Choi YH, Cha EJ, et al: Identification of
pro-Inflammatory cytokines associated with muscle invasive bladder
cancer; the roles of IL-5, IL-20, and IL-28A. PLoS One.
7:e402672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hashimoto M, Sato T, Muroyama Y, Fujimura
L, Hatano M and Saito T: Nepro is localized in the nucleolus and
essential for preimplantation development in mice. Dev Growth
Differ. 57:529–538. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Carron C, O'Donohue MF, Choesmel V,
Faubladier M and Gleizes PE: Analysis of two human pre-ribosomal
factors, bystin and hTsr1, highlights differences in evolution of
ribosome biogenesis between yeast and mammals. Nucleic Acids Res.
39:280–291. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu PC and Thiele DJ: Novel
stress-responsive genes EMG1 and NOP14 encode conserved,
interacting proteins required for 40S ribosome biogenesis. Mol Biol
Cell. 12:3644–3657. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang J, McCann KL, Chen Q, Gonzalez LE,
Baserga SJ and Hall TM: Nop9 is a PUF-like protein that prevents
premature cleavage to correctly process pre-18S rRNA. Nat Commun.
7:130852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
El Gawhary S, El-Anany M, Hassan R, Ali D
and El Gameel el Q: The role of 16S rRNA gene sequencing in
confirmation of suspected neonatal sepsis. J Trop Pediatr.
62:75–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mithal LB, Malczynski M, Green SJ, Qi C,
Yogev R and Mestan K: Deep sequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons to
screen umbilical cord blood of preterm infants. Open Forum
Infectious Dis. 3:22342016.
|
|
45
|
Midan DA, Abo El Fotoh WMM and El
Shalakany AH: The potential role of incorporating real-time PCR and
DNA sequencing for amplification and detection of 16S rRNA gene
signatures in neonatal sepsis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med.
30:1476–1483. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ticlea M, Bratu LM, Bodog F, Bedreag OH,
Rogobete AF and Crainiceanu ZP: The use of exosomes as biomarkers
for evaluating and monitoring critically Ill polytrauma patients
with sepsis. Biochem Genet. 55:1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu H, Yu X, Yu S and Kou J: Molecular
mechanisms in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary endothelial
barrier dysfunction. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:937–946. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Adyshev DM, Moldobaeva N, Mapes B,
Elangovan V and Garcia JG: MicroRNA regulation of nonmuscle myosin
light chain kinase expression in human lung endothelium. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 49:58–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|