|
1
|
Baggio LL and Drucker DJ: Biology of
incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 132:2131–2157. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chiang YT, Ip W and Jin T: The role of the
Wnt signaling pathway in incretin hormone production and function.
Front Physiol. 3:2732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Salehi M, Aulinger B, Prigeon RL and
D'Alessio DA: Effect of endogenous GLP-1 on insulin secretion in
type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 59:1330–1337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
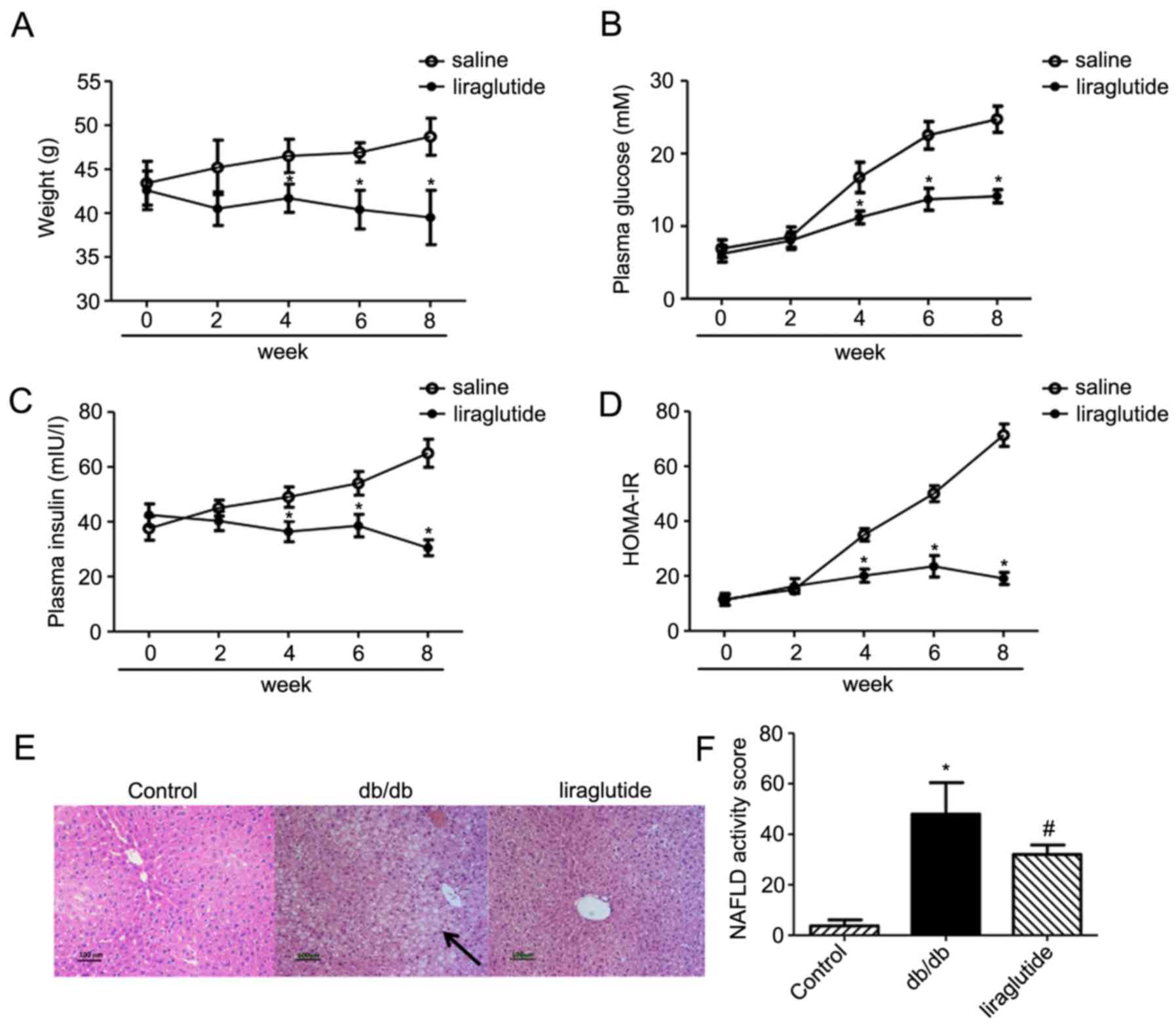
4
|
Zander M, Madsbad S, Madsen JL and Holst
JJ: Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide 1 on glycaemic
control, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function in type 2
diabetes: A parallel-group study. Lancet. 359:824–830. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ding X, Saxena NK, Lin S, Gupta NA and
Anania FA: Exendin-4, a glucagon-like protein-1 (GLP-1) receptor
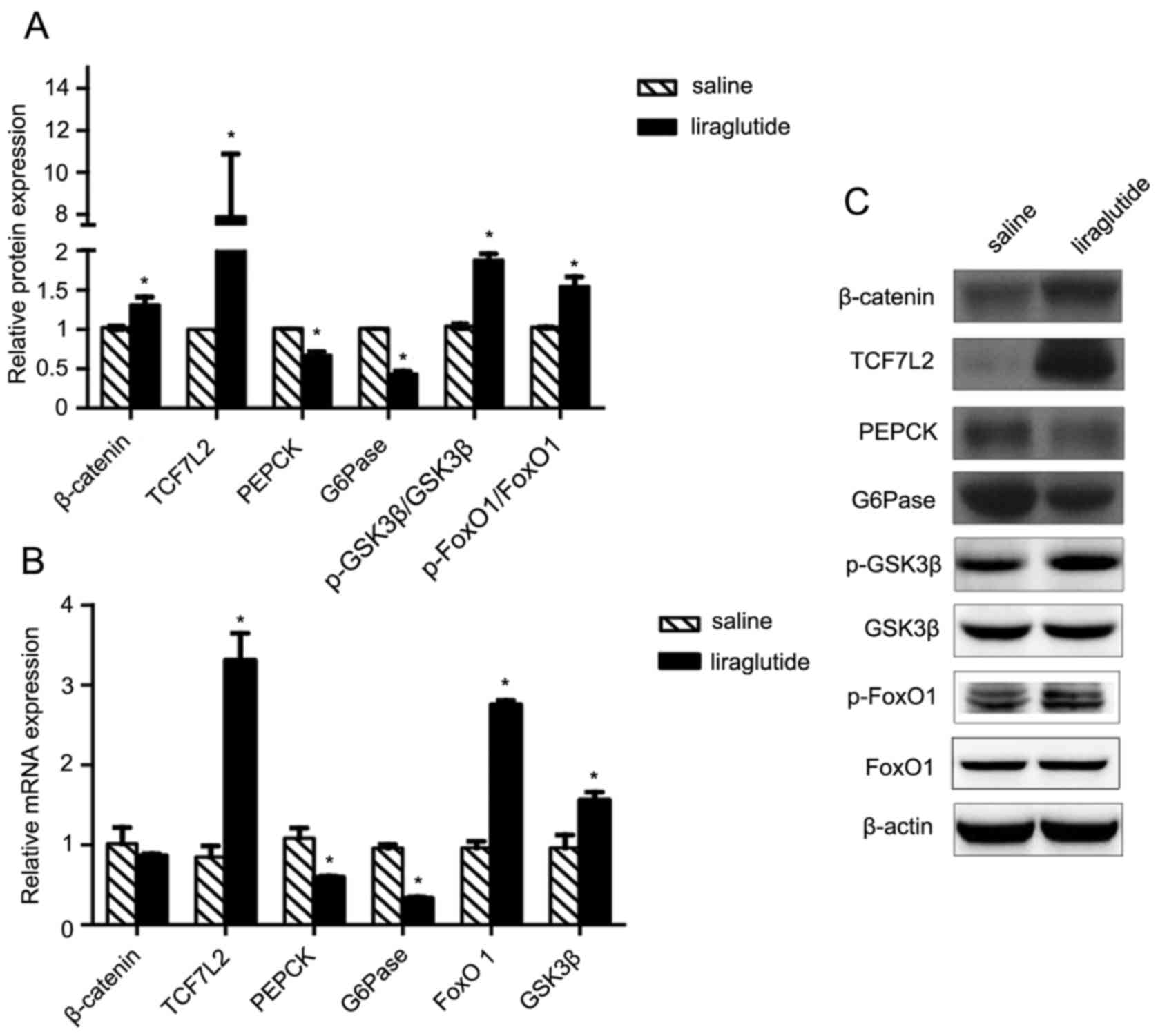
agonist, reverses hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. Hepatology.
43:173–181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fan R, Kang Z, He L, Chan J and Xu G:
Exendin-4 improves blood glucose control in both young and aging
normal non-diabetic mice, possible contribution of beta cell
independent effects. PLoS One. 6:e204432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gupta NA, Mells J, Dunham RM, Grakoui A,
Handy J, Saxena NK and Anania FA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
is present on human hepatocytes and has a direct role in decreasing
hepatic steatosis in vitro by modulating elements of the
insulin signaling pathway. Hepatology. 51:1584–1592. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee J, Hong SW, Chae SW, Kim DH, Choi JH,
Bae JC, Park SE, Rhee EJ, Park CY, Oh KW, et al: Exendin-4 improves
steatohepatitis by increasing Sirt1 expression in high-fat
diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice. PLoS One. 7:e313942012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thompson MD and Monga SP: WNT/beta-catenin
signaling in liver health and disease. Hepatology. 45:1298–1305.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ackers I and Malgor R: Interrelationship
of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways in chronic
metabolic diseases. Diab Vasc Dis Res. Nov 1–2017.(Epub ahead of
print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shao W, Wang D, Chiang YT, Ip W, Zhu L, Xu
F, Columbus J, Belsham DD, Irwin DM, Zhang H, et al: The Wnt
signaling pathway effector TCF7L2 controls gut and brain
proglucagon gene expression and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes.
62:789–800. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jin T and Liu L: The Wnt signaling pathway
effector TCF7L2 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol Endocrinol.
22:2383–2392. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Akiyama T: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11:273–282. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiong X, Shao W and Jin T: New insight
into the mechanisms underlying the function of the incretin hormone
glucagon-like peptide-1 in pancreatic β-cells: The involvement of
the Wnt signaling pathway effector β-catenin. Islets. 4:359–365.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I,
Benediktsson R, Manolescu A, Sainz J, Helgason A, Stefansson H,
Emilsson V, Helgadottir A, et al: Variant of transcription factor
7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet.
38:320–323. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
da Silva Xavier G, Mondragon A, Sun G,
Chen L, McGinty JA, French PM and Rutter GA: Abnormal glucose
tolerance and insulin secretion in pancreas-specific Tcf7l2-null
mice. Diabetologia. 55:2667–2676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Boj SF, van Es JH, Huch M, Li VS, José A,
Hatzis P, Mokry M, Haegebarth A, van den Born M, Chambon P, et al:
Diabetes risk gene and Wnt effector Tcf7l2/TCF4 controls hepatic
response to perinatal and adult metabolic demand. Cell.
151:1595–1607. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaur K, Vig S, Srivastava R, Mishra A,
Singh VP, Srivastava AK and Datta M: Elevated hepatic miR-22-3p
expression impairs gluconeogenesis by silencing the Wnt-responsive
transcription factor Tcf7. Diabetes. 64:3659–3669. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ip W, Shao W, Song Z, Chen Z, Wheeler MB
and Jin T: Liver-specific expression of dominant-negative
transcription factor 7-like 2 causes progressive impairment in
glucose homeostasis. Diabetes. 64:1923–1932. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gustafson B and Smith U: WNT signalling is
both an inducer and effector of glucagon-like peptide-1.
Diabetologia. 51:1768–1770. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Z and Habener JF: Glucagon-like
peptide-1 activation of TCF7L2-dependent Wnt signaling enhances
pancreatic beta cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 283:8723–8735.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS,
Naylor BA, Treacher DF and Turner RC: Homeostasis model assessment:
Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma
glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia.
28:412–419. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Li B, Meng X, Yao S, Jin L, Yang
J, Wang J, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Cai D, et al: Berberine prevents
progression from hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis and fibrosis
by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Sci Rep. 6:208482016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yin J, Hu R, Chen M, Tang J, Li F, Yang Y
and Chen J: Effects of berberine on glucose metabolism in
vitro. Metabolism. 51:1439–1443. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tikhanovich I, Cox J and Weinman SA:
Forkhead box class O transcription factors in liver function and
disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28 Suppl 1:S125–S131. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Desouza CV, Gupta N and Patel A:
Cardiometabolic effects of a new class of antidiabetic agents. Clin
Ther. 37:1178–1194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van Can J, Sloth B, Jensen CB, Flint A,
Blaak EE and Saris WH: Effects of the once-daily GLP-1 analog
liraglutide on gastric emptying, glycemic parameters, appetite and
energy metabolism in obese, non-diabetic adults. Int J Obes (Lond).
38:784–793. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nyström T, Gutniak MK, Zhang Q, Zhang F,
Holst JJ, Ahrén B and Sjöholm A: Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1
on endothelial function in type 2 diabetes patients with stable
coronary artery disease. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
287:E1209–E1215. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alcántara AI, Morales M, Delgado E,
López-Delgado MI, Clemente F, Luque MA, Malaisse WJ, Valverde I and
Villanueva-Peñacarrillo ML: Exendin-4 agonist and
exendin(9–39)amide antagonist of the GLP-1(7–36)amide effects in
liver and muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 341:1–7. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Su H, He M, Li H, Liu Q, Wang J, Wang Y,
Gao W, Zhou L, Liao J, Young AA and Wang MW: Boc5, a non-peptidic
glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonist, invokes sustained
glycemic control and weight loss in diabetic mice. PLoS One.
3:e28922008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cho YM, Fujita Y and Kieffer TJ:
Glucagon-like peptide-1: Glucose homeostasis and beyond. Annu Rev
Physiol. 76:535–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Redondo A, Trigo MV, Acitores A, Valverde
I and Villanueva-Peñacarrillo ML: Cell signalling of the GLP-1
action in rat liver. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 204:43–50. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nerurkar PV, Nishioka A, Eck PO, Johns LM,
Volper E and Nerurkar VR: Regulation of glucose metabolism via
hepatic forkhead transcription factor 1 (FoxO1) by Morinda
citrifolia (noni) in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Br J Nutr.
108:218–228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ip W, Shao W, Chiang YT and Jin T: The Wnt
signaling pathway effector TCF7L2 is upregulated by insulin and
represses hepatic gluconeogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
303:E1166–E1176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu H, Fergusson MM, Wu JJ, Rovira II, Liu
J, Gavrilova O, Lu T, Bao J, Han D, Sack MN and Finkel T: Wnt
signaling regulates hepatic metabolism. Sci Signal. 4:ra62011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hino S, Tanji C, Nakayama KI and Kikuchi
A: Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by cyclic AMP-dependent protein
kinase stabilizes beta-catenin through inhibition of its
ubiquitination. Mol Cell Biol. 25:9063–9072. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Norton L, Fourcaudot M, Abdul-Ghani MA,
Winnier D, Mehta FF, Jenkinson CP and Defronzo RA: Chromatin
occupancy of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) and its role in
hepatic glucose metabolism. Diabetologia. 54:3132–3142. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hoogeboom D, Essers MA, Polderman PE,
Voets E, Smits LM and Burgering BM: Interaction of FOXO with
beta-catenin inhibits beta-catenin/T cell factor activity. J Biol
Chem. 283:9224–9230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Arai T, Kano F and Murata M: Translocation
of forkhead box O1 to the nuclear periphery induces histone
modifications that regulate transcriptional repression of PCK1 in
HepG2 cells. Genes Cells. 20:340–357. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Patel V, Joharapurkar A, Gandhi T, Patel
K, Dhanesha N, Kshirsagar S, Dhote V, Detroja J, Bahekar R and Jain
M: Omeprazole improves the anti-obesity and antidiabetic effects of
exendin-4 in db/db mice (−4 db/db)*. J Diabetes. 5:163–171. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yi F, Sun J, Lim GE, Fantus IG, Brubaker
PL and Jin T: Cross talk between the insulin and Wnt signaling
pathways: Evidence from intestinal endocrine L cells.
Endocrinology. 149:2341–2351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun J, Wang D and Jin T: Insulin alters
the expression of components of the Wnt signaling pathway including
TCF-4 in the intestinal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1800:344–351.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|