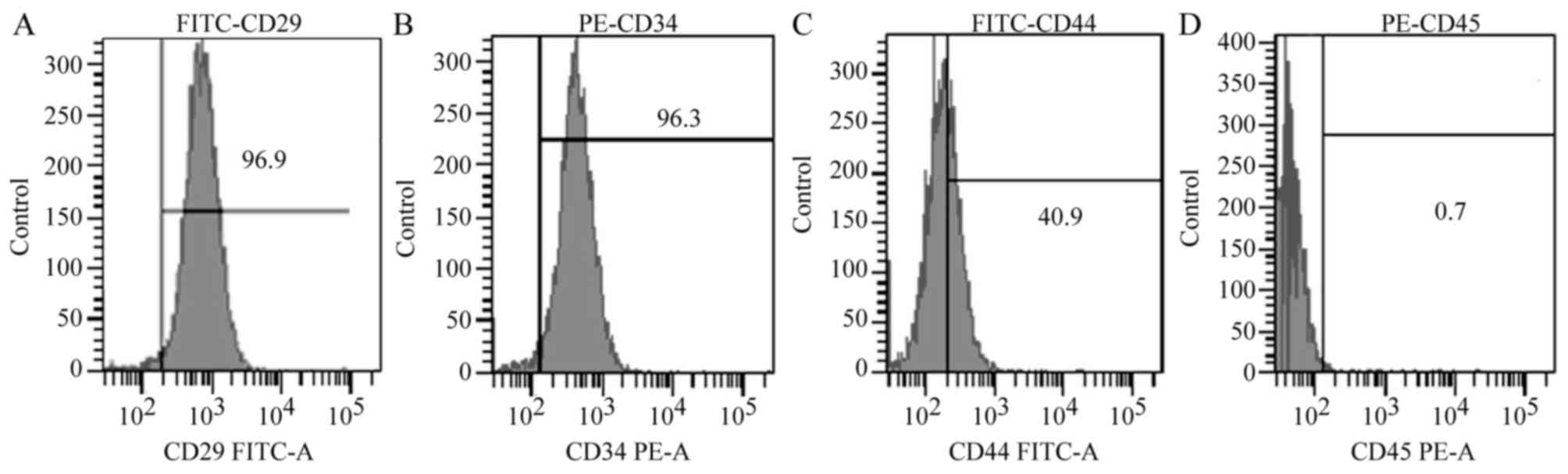
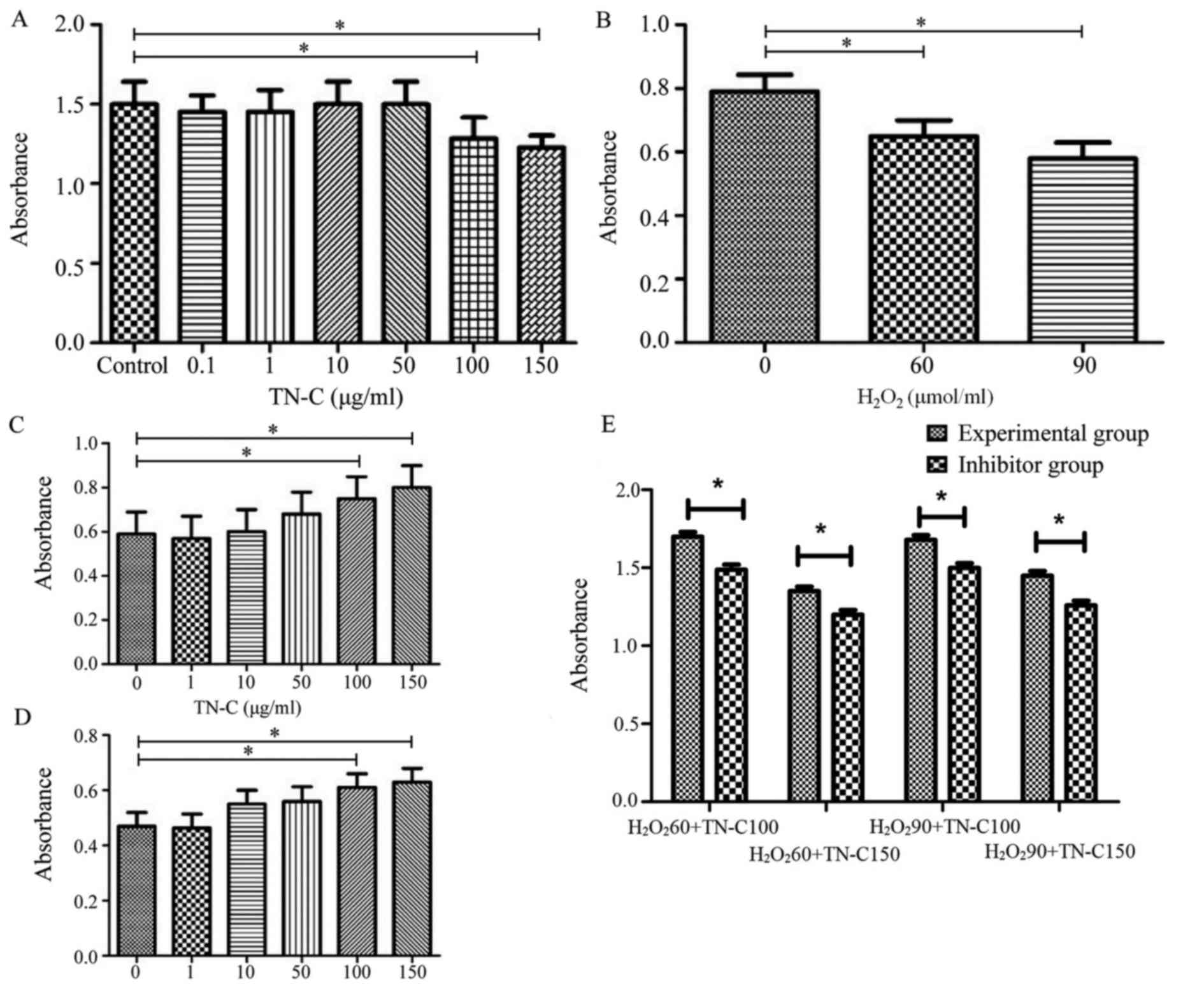
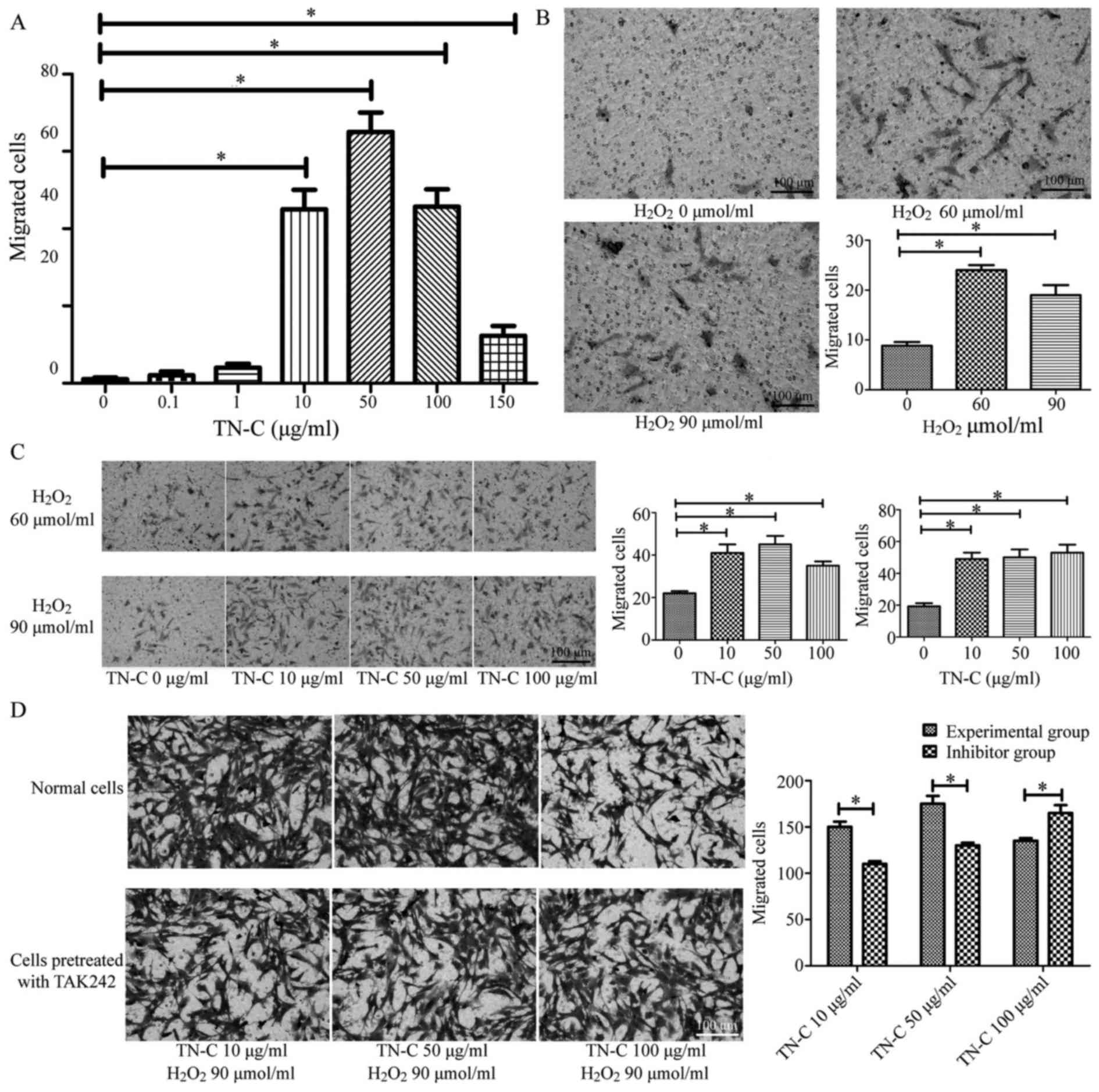
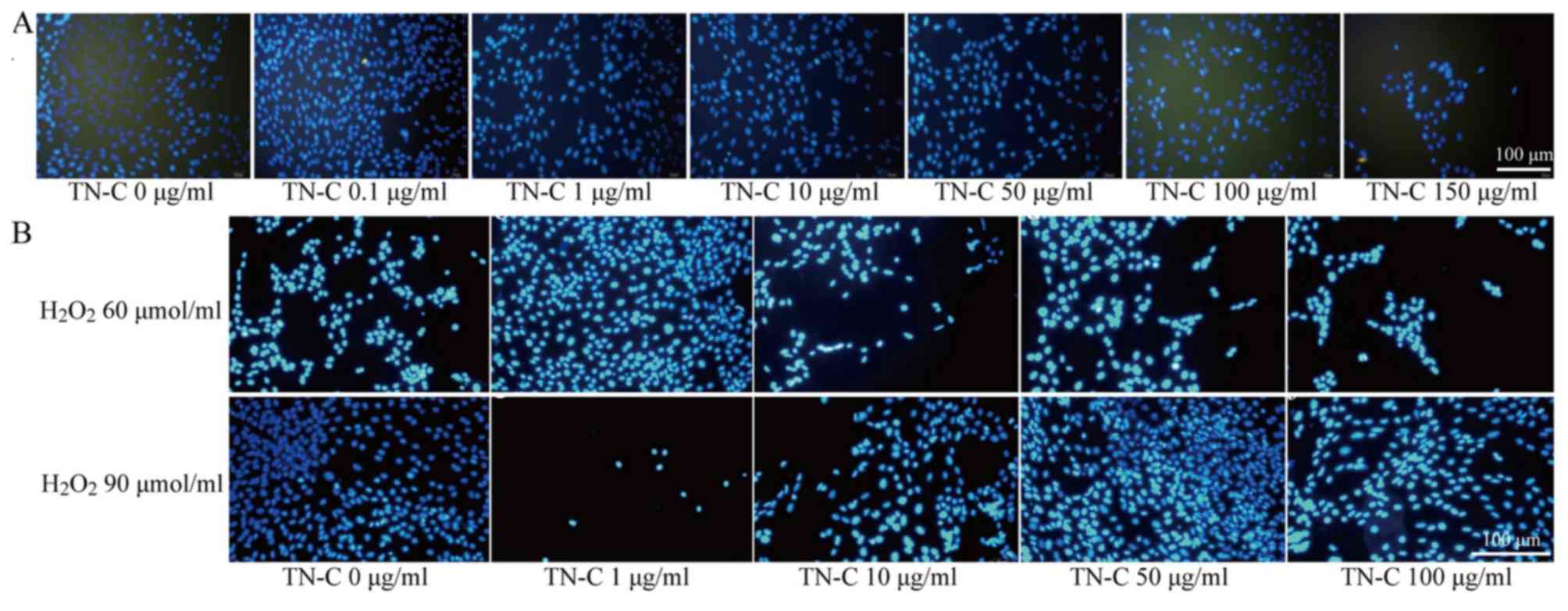
|
1
|
Tomita S, Li RK, Weisel RD, Mickle DA, Kim
EJ, Sakai T and Jia ZQ: Autologous transplantation of bone marrow
cells improves damaged heart function. Circulation. 100 19
Suppl:II247–II256. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Geng YJ: Molecular mechanisms for
cardiovascular stem cell apoptosis and growth in the hearts with
atherosclerotic coronary disease and ischemic heart failure. Ann N
Y Acad Sci. 1010:687–697. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Przybyt E and Harmsen MC: Mesenchymal stem
cells: Promising for myocardial regeneration? Curr Stem Cell Res
Ther. 8:270–277. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sato A, Aonuma K, Imanaka-Yoshida K,
Yoshida T, Isobe M, Kawase D, Kinoshita N, Yazaki Y and Hiroe M:
Serum tenascin-C might be a novel predictor of left ventricular
remodeling and prognosis after acute myocardial infarction. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 47:2319–2325. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jones FS and Jones PL: The tenascin family
of ECM glycoproteins: Structure, function, and regulation during
embryonic development and tissue remodeling. Dev Dyn. 218:235–259.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Niebroj-Dobosz I: Tenascin-C in human
cardiac pathology. Clin Chim Acta. 413:1516–1518. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sato A, Hiroe M, Akiyama D, Hikita H,
Nozato T, Hoshi T, Kimura T, Wang Z, Sakai S, Imanaka-Yoshida K, et
al: Prognostic value of serum tenascin-C levels on long-term
outcome after acute myocardial infarction. J Card Fail. 18:480–486.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Loreto C, Musumeci G and Leonardi R:
Chondrocyte-like apoptosis in temporomandibular joint disc internal
derangement as a repair-limiting mechanism. Histol Histopathol.
24:293–298. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Musumeci G, Castrogiovanni P, Loreto C,
Castorina S, Pichler K and Weinberg AM: Post-traumatic caspase-3
expression in the adjacent areas of growth plate injury site: A
morphological study. Int J Mol Sci. 14:15767–15784. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Puzzo D, Loreto C, Giunta S, Musumeci G,
Frasca G, Podda MV, Arancio O and Palmeri A: Effect of
phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition on apoptosis and beta amyloid load
in aged mice. Neurobiol Aging. 35:520–531. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pevsner-Fischer M, Morad V, Cohen-Sfady M,
Rousso-Noori L, Zanin-Zhorov A, Cohen S, Cohen IR and Zipori D:
Toll-like receptors and their ligands control mesenchymal stem cell
functions. Blood. 109:1422–1432. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gutiérrez-Uzquiza Á, Arechederra M,
Bragado P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA and Porras A: p38α mediates cell
survival in response to oxidative stress via induction of
antioxidant genes: Effect on the p70S6K pathway. J Biol Chem.
287:2632–2642. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peti W and Page R: Molecular basis of MAP
kinase regulation. Protein Sci. 22:1698–1710. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wee KB and Aguda BD: Akt versus p53 in a
network of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes regulating cell
survival and death. Biophys J. 91:857–865. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pillai VB, Sundaresan NR and Gupta MP:
Regulation of Akt signaling by sirtuins: Its implication in cardiac
hypertrophy and aging. Circ Res. 114:368–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ling L, Nurcombe V and Cool SM: Wnt
signaling controls the fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene.
433:1–7. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim W, Kim M and Jho EH: Wnt/β-catenin
signalling: From plasma membrane to nucleus. Biochem J. 450:9–21.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wakitani S, Saito T and Caplan AI:
Myogenic cells derived from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
exposed to 5-azacytidine. Muscle Nerve. 18:1417–1426. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng W, Bivalacqua TJ, Chattergoon NN,
Jeter JR Jr and Kadowitz PJ: Engineering ex vivo-expanded marrow
stromal cells to secrete calcitonin gene-related peptide using
adenoviral vector. Stem Cells. 22:1279–1291. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hussey SE, Liang H, Costford SR, Klip A,
DeFronzo RA, Sanchez-Avila A, Ely B and Musi N: TAK-242, a
small-molecule inhibitor of Toll-like receptor 4 signalling,
unveils similarities and differences in lipopolysaccharide- and
lipid-induced inflammation and insulin resistance in muscle cells.
Biosci Rep. 33:37–47. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
He PP, Ouyang XP, Tang YY, Liao L, Wang
ZB, Lv YC, Tian GP, Zhao GJ, Huang L, Yao F, et al: MicroRNA-590
attenuates lipid accumulation and pro-inflammatory cytokine
secretion by targeting lipoprotein lipase gene in human THP-1
macrophages. Biochimie. 106:81–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen T, Li Z, Tu J, Zhu W, Ge J, Zheng X,
Yang L, Pan X, Yan H and Zhu J: MicroRNA-29a regulates
pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion and scavenger receptor
expression by targeting LPL in oxLDL-stimulated dendritic cells.
FEBS Lett. 585:657–663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Abbott JD, Huang Y, Liu D, Hickey R,
Krause DS and Giordano FJ: Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha plays
a critical role in stem cell recruitment to the heart after
myocardial infarction but is not sufficient to induce homing in the
absence of injury. Circulation. 110:3300–3305. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sterlacci W, Saker S, Huber B, Fiegl M and
Tzankov A: Expression of the CXCR4 ligand SDF-1/CXCL12 is
prognostically important for adenocarcinoma and large cell
carcinoma of the lung. Virchows Arch. 468:463–471. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bi J, Li P, Li C, He J, Wang Y, Zhang H,
Fan X, Jia R and Ge S: The SDF-1/CXCR4 chemokine axis in uveal
melanoma cell proliferation and migration. Tumour Biol.
37:4175–4182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Raicevic G, Rouas R, Najar M, Stordeur P,
Boufker HI, Bron D, Martiat P, Goldman M, Nevessignsky MT and
Lagneaux L: Inflammation modifies the pattern and the function of
Toll-like receptors expressed by human mesenchymal stromal cells.
Hum Immunol. 71:235–244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liotta F, Angeli R, Cosmi L, Filì L,
Manuelli C, Frosali F, Mazzinghi B, Maggi L, Pasini A, Lisi V, et
al: Toll-like receptors 3 and 4 are expressed by human bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and can inhibit their T-cell
modulatory activity by impairing Notch signaling. Stem Cells.
26:279–289. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang ZJ, Zhang FM, Wang LS, Yao YW, Zhao Q
and Gao X: Lipopolysaccharides can protect mesenchymal stem cells
(MSCs) from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and enhance
proliferation of MSCs via Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 and PI3K/Akt.
Cell Biol Int. 33:665–674. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Brewster BD, Rouch JD, Wang M and Meldrum
DR: Toll-like receptor 4 ablation improves stem cell survival after
hypoxic injury. J Surg Res. 177:330–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Raicevic G, Najar M, Pieters K, De Bruyn
C, Meuleman N, Bron D, Toungouz M and Lagneaux L: Inflammation and
Toll-like receptor ligation differentially affect the osteogenic
potential of human mesenchymal stromal cells depending on their
tissue origin. Tissue Eng Part A. 18:1410–1418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fiedler T, Salamon A, Adam S, Herzmann N,
Taubenheim J and Peters K: Impact of bacteria and bacterial
components on osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res.
319:2883–2892. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alvarado AG, Thiagarajan PS,
Mulkearns-Hubert EE, Silver DJ, Hale JS, Alban TJ, Turaga SM,
Jarrar A, Reizes O, Longworth MS, et al: Glioblastoma cancer stem
cells evade innate immune suppression of self-Renewal through
reduced TLR4 expression. Cell Stem Cell. 20:450–461.e4. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Goloviznina NA, Verghese SC, Yoon YM,
Taratula O, Marks DL and Kurre P: Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived
extracellular vesicles promote myeloid-biased multipotent
hematopoietic progenitor expansion via toll-like receptor
engagement. J Biol Chem. 291:24607–24617. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yao Y, Zhang F, Wang L, Zhang G, Wang Z,
Chen J and Gao X: Lipopolysaccharide preconditioning enhances the
efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in a rat model
of acute myocardial infarction. J Biomed Sci. 16:742009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang C, Pan L, Lin F, Dai H and Fu R:
Monoclonal antibody against Toll-like receptor 4 attenuates
ventilator-induced lung injury in rats by inhibiting MyD88- and
NF-κB-dependent signaling. Int J Mol Med. 39:693–700. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sindhu S, Al-Roub A, Koshy M, Thomas R and
Ahmad R: Palmitate-induced MMP-9 expression in the human monocytic
cells is mediated through the TLR4-MyD88 dependent mechanism. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 39:889–900. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|