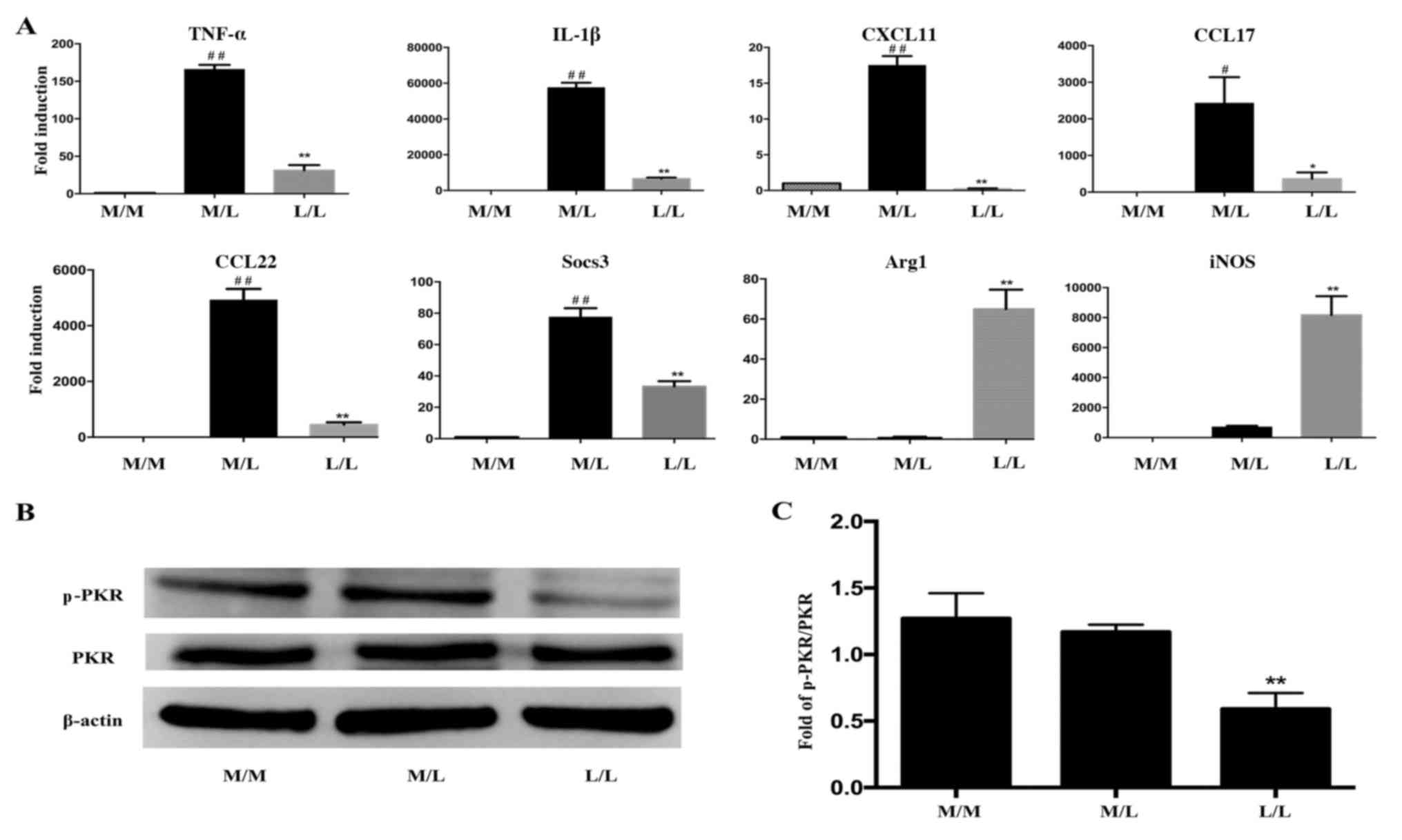
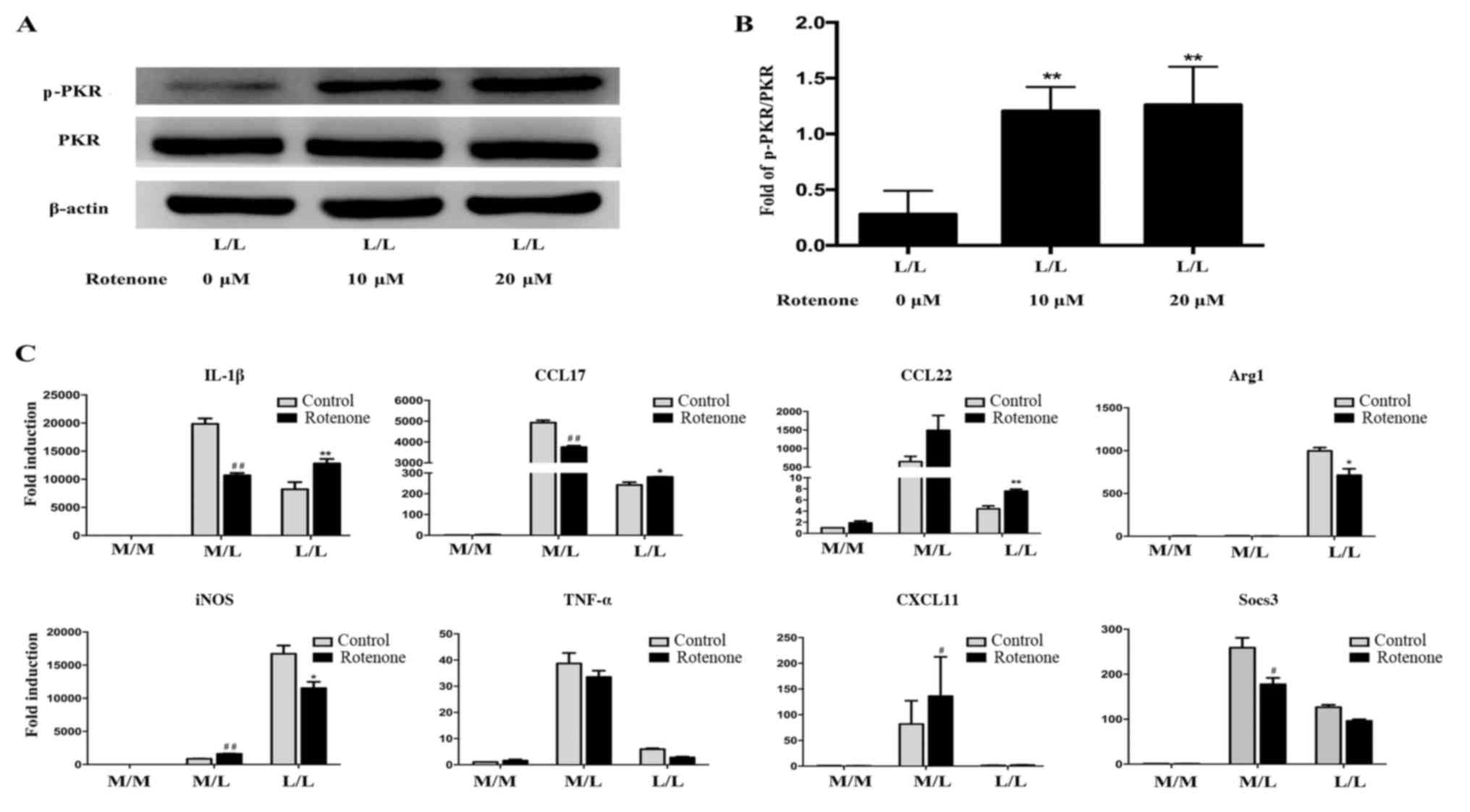
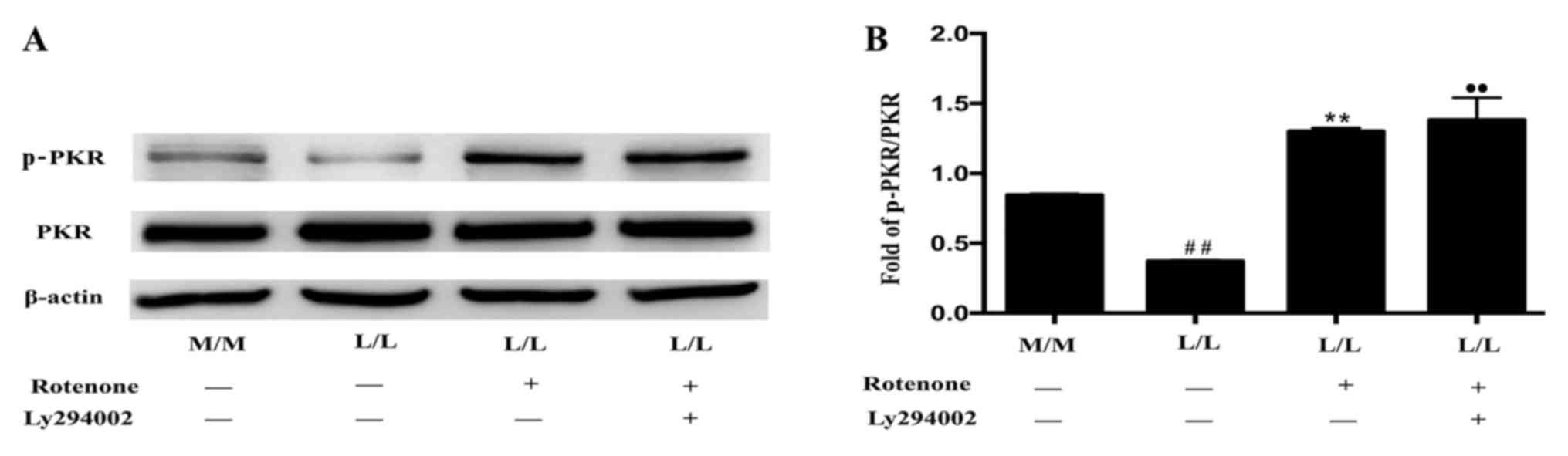
|
1
|
Gordon S and Taylor PR: Monocyte and
macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:953–964. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lawrence T and Natoli G: Transcriptional
regulation of macrophage polarization: Enabling diversity with
identity. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:750–761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Beutler B: SHIP, TGF-beta, and endotoxin
tolerance. Immunity. 21:134–135. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O'Neill LA and Bowie AG: The family of
five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor
signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:353–364. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cavaillon JM and Adib-Conquy M:
Bench-to-bedside review: Endotoxin tolerance as a model of
leukocyte reprogramming in sepsis. Crit Care. 10:2332006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fan H and Cook JA: Molecular mechanisms of
endotoxin tolerance. J Endotoxin Res. 10:71–84. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
del Fresno C, García-Rio F, Gómez-Piña V,
Soares-Schanoski A, Fernández-Ruíz I, Jurado T, Kajiji T, Shu C,
Marín E, del Arroyo Gutierrez A, et al: Potent phagocytic activity
with impaired antigen presentation identifying
lipopolysaccharide-tolerant human monocytes: Demonstration in
isolated monocytes from cystic fibrosis patients. J Immunol.
182:6494–6507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zuckerman SH and Evans GF: Endotoxin
tolerance: In vivo regulation of tumor necrosis factor and
interleukin-1 synthesis is at the transcriptional level. Cell
Immunol. 140:513–519. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rajaiah R, Perkins DJ, Polumuri SK, Zhao
A, Keegan AD and Vogel SN: Dissociation of endotoxin tolerance and
differentiation of alternatively activated macrophages. J Immunol.
190:4763–4772. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Piao W, Song C, Chen H, Diaz MA, Wahl LM,
Fitzgerald KA, Li L and Medvedev AE: Endotoxin tolerance
dysregulates MyD88- and Toll/IL-1R domain-containing adapter
inducing IFN-beta-dependent pathways and increases expression of
negative regulators of TLR signaling. J Leukoc Biol. 86:863–875.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rackov G, Hernández-Jiménez E, Shokri R,
Carmona-Rodríguez L, Mañes S, Álvarez-Mon M, López-Collazo E,
Martínez-A C and Balomenos D: p21 mediates macrophage reprogramming
through regulation of p50-p50 NF-κB and IFN-β. J Clin Invest.
126:3089–3103. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Foster SL and Medzhitov R: Gene-specific
control of the TLR-induced inflammatory response. Clin Immunol.
130:7–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Foster SL, Hargreaves DC and Medzhitov R:
Gene-specific control of inflammation by TLR-induced chromatin
modifications. Nature. 447:972–978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shalova IN, Lim JY, Chittezhath M,
Zinkernagel AS, Beasley F, Hernández-Jiménez E, Toledano V,
Cubillos-Zapata C, Rapisarda A, Chen J, et al: Human monocytes
undergo functional re-programming during sepsis mediated by
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Immunity. 42:484–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pena OM, Hancock DG, Lyle NH, Linder A,
Russell JA, Xia J, Fjell CD, Boyd JH and Hancock RE: An endotoxin
tolerance signature predicts sepsis and organ dysfunction at
initial clinical presentation. EBioMedicine. 1:64–71. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hotchkiss RS, Levy JH and Levi M:
Sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation, symmetrical
peripheral gangrene, and amputations. Crit Care Med. 41:e290–e291.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moller K: Of cells and men: Ex vivo and in
vivo tolerance to lipopolysaccharide. Crit Care Med. 39:1997–1998.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Angus DC and van der Poll T: Severe sepsis
and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 369:20632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Delano MJ and Ward PA: Sepsis-induced
immune dysfunction: Can immune therapies reduce mortality? J Clin
Invest. 126:23–31. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lopez-Collazo E and del Fresno C:
Pathophysiology of endotoxin tolerance: Mechanisms and clinical
consequences. Crit Care. 17:2422013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sly LM, Rauh MJ, Kalesnikoff J, Song CH
and Krystal G: LPS-induced upregulation of SHIP is essential for
endotoxin tolerance. Immunity. 21:227–239. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiong Y and Medvedev AE: Induction of
endotoxin tolerance in vivo inhibits activation of IRAK4 and
increases negative regulators IRAK-M, SHIP-1, and A20. J Leukoc
Biol. 90:1141–1148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meurs E, Chong K, Galabru J, Thomas NS,
Kerr IM, Williams BR and Hovanessian AG: Molecular cloning and
characterization of the human double-stranded RNA-activated protein
kinase induced by interferon. Cell. 62:379–390. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shen SJ, Zhang YH, Gu XX, Jiang SJ and Xu
LJ: Yangfei Kongliu Formula, a compound Chinese herbal medicine,
combined with cisplatin, inhibits growth of lung cancer cells
through transforming growth factor-β1 signaling pathway. J Integr
Med. 15:242–251. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Balachandran S and Barber GN: PKR in
innate immunity, cancer, and viral oncolysis. Methods Mol Biol.
383:277–301. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Williams BR: Signal integration via PKR.
Sci STKE. 2001:re22001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
García MA, Gil J, Ventoso I, Guerra S,
Domingo E, Rivas C and Esteban M: Impact of protein kinase PKR in
cell biology: From antiviral to antiproliferative action. Microbiol
Mol Biol Rev. 70:1032–1060. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang P and Samuel CE: Induction of
protein kinase PKR-dependent activation of interferon regulatory
factor 3 by vaccinia virus occurs through adapter IPS-1 signaling.
J Biol Chem. 283:34580–34587. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zamanian-Daryoush M, Mogensen TH, DiDonato
JA and Williams BR: NF-kappaB activation by
double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) is mediated
through NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and IkappaB kinase. Mol Cell
Biol. 20:1278–1290. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han BH, Lee YJ, Yoon JJ, Choi ES, Namgung
S, Jin XJ, Jeong DH, Kang DG and Lee HS: Hwangryunhaedoktang exerts
anti-inflammation on LPS-induced NO production by suppressing MAPK
and NF-κB activation in RAW264.7 macrophages. J Integr Med.
15:326–336. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Porta C, Rimoldi M, Raes G, Brys L, Ghezzi
P, Di Liberto D, Dieli F, Ghisletti S, Natoli G, De Baetselier P,
et al: Tolerance and M2 (alternative) macrophage polarization are
related processes orchestrated by p50 nuclear factor kappaB. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:14978–14983. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu B, Nakamura T, Inouye K, Li J, Tang Y,
Lundbäck P, Valdes-Ferrer SI, Olofsson PS, Kalb T, Roth J, et al:
Novel role of PKR in inflammasome activation and HMGB1 release.
Nature. 488:670–674. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cavaillon JM, Adrie C, Fitting C and
Adib-Conquy M: Endotoxin tolerance: Is there a clinical relevance?
J Endotoxin Res. 9:101–107. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
del Fresno C, Gómez-Piña V, Lores V,
Soares-Schanoski A, Fernández-Ruiz I, Rojo B, Alvarez-Sala R,
Caballero-Garrido E, García F, Veliz T, et al: Monocytes from
cystic fibrosis patients are locked in an LPS tolerance state:
Down-regulation of TREM-1 as putative underlying mechanism. PLoS
One. 3:e26672008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Escoll P, del Fresno C, García L, Vallés
G, Lendínez MJ, Arnalich F and López-Collazo E: Rapid up-regulation
of IRAK-M expression following a second endotoxin challenge in
human monocytes and in monocytes isolated from septic patients.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 311:465–472. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G and Payen D:
Immunosuppression in sepsis: A novel understanding of the disorder
and a new therapeutic approach. Lancet Infect Dis. 13:260–268.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hotchkiss RS and Karl IE: The
pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 348:138–150.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hotchkiss RS and Opal S: Immunotherapy for
sepsis-a new approach against an ancient foe. N Engl J Med.
363:87–89. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nahid MA, Satoh M and Chan EK: MicroRNA in
TLR signaling and endotoxin tolerance. Cell Mol Immunol. 8:388–403.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
West MA and Koons A: Endotoxin tolerance
in sepsis: Concentration-dependent augmentation or inhibition of
LPS-stimulated macrophage TNF secretion by LPS pretreatment. J
Trauma. 65:893–898. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Biswas SK and Lopez-Collazo E: Endotoxin
tolerance: New mechanisms, molecules and clinical significance.
Trends Immunol. 30:475–487. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena
P and Sica A: Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages
as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends
Immunol. 23:549–555. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mosser DM: The many faces of macrophage
activation. J Leukoc Biol. 73:209–212. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shirey KA, Pletneva LM, Puche AC, Keegan
AD, Prince GA, Blanco JC and Vogel SN: Control of RSV-induced lung
injury by alternatively activated macrophages is IL-4R alpha-,
TLR4-, and IFN-beta-dependent. Mucosal Immunol. 3:291–300. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gordon S: Alternative activation of
macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:23–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Castegren M, Skorup P, Lipcsey M, Larsson
A and Sjolin J: Endotoxin tolerance variation over 24 h during
porcine endotoxemia: Association with changes in circulation and
organ dysfunction. PLoS One. 8:e532212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dias MB, Almeida MC, Carnio EC and Branco
LG: Role of nitric oxide in tolerance to lipopolysaccharide in
mice. J Appl Physiol (1985). 98:1322–1327. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Perkins DJ, Qureshi N and Vogel SN: A
Toll-like receptor-responsive kinase, protein kinase R, is
inactivated in endotoxin tolerance through differential K63/K48
ubiquitination. MBio. 1:e00239–e002310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Goh KC, deVeer MJ and Williams BR: The
protein kinase PKR is required for p38 MAPK activation and the
innate immune response to bacterial endotoxin. EMBO J.
19:4292–4297. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nakamura T, Furuhashi M, Li P, Cao H,
Tuncman G, Sonenberg N, Gorgun CZ and Hotamisligil GS:
Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase links pathogen sensing
with stress and metabolic homeostasis. Cell. 140:338–348. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bonnet MC, Weil R, Dam E, Hovanessian AG
and Meurs EF: PKR stimulates NF-kappaB irrespective of its kinase
function by interacting with the IkappaB kinase complex. Mol Cell
Biol. 20:4532–4542. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Alisi A, Spaziani A, Anticoli S,
Ghidinelli M and Balsano C: PKR is a novel functional direct player
that coordinates skeletal muscle differentiation via p38MAPK/AKT
pathways. Cell Signal. 20:534–542. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhu M, Liu X, Wang S, Miao J, Wu L, Yang
X, Wang Y, Kang L, Li W, Cui C, et al: PKR promotes choroidal
neovascularization via upregulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
in VEGF expression. Mol Vis. 22:1361–1374. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|