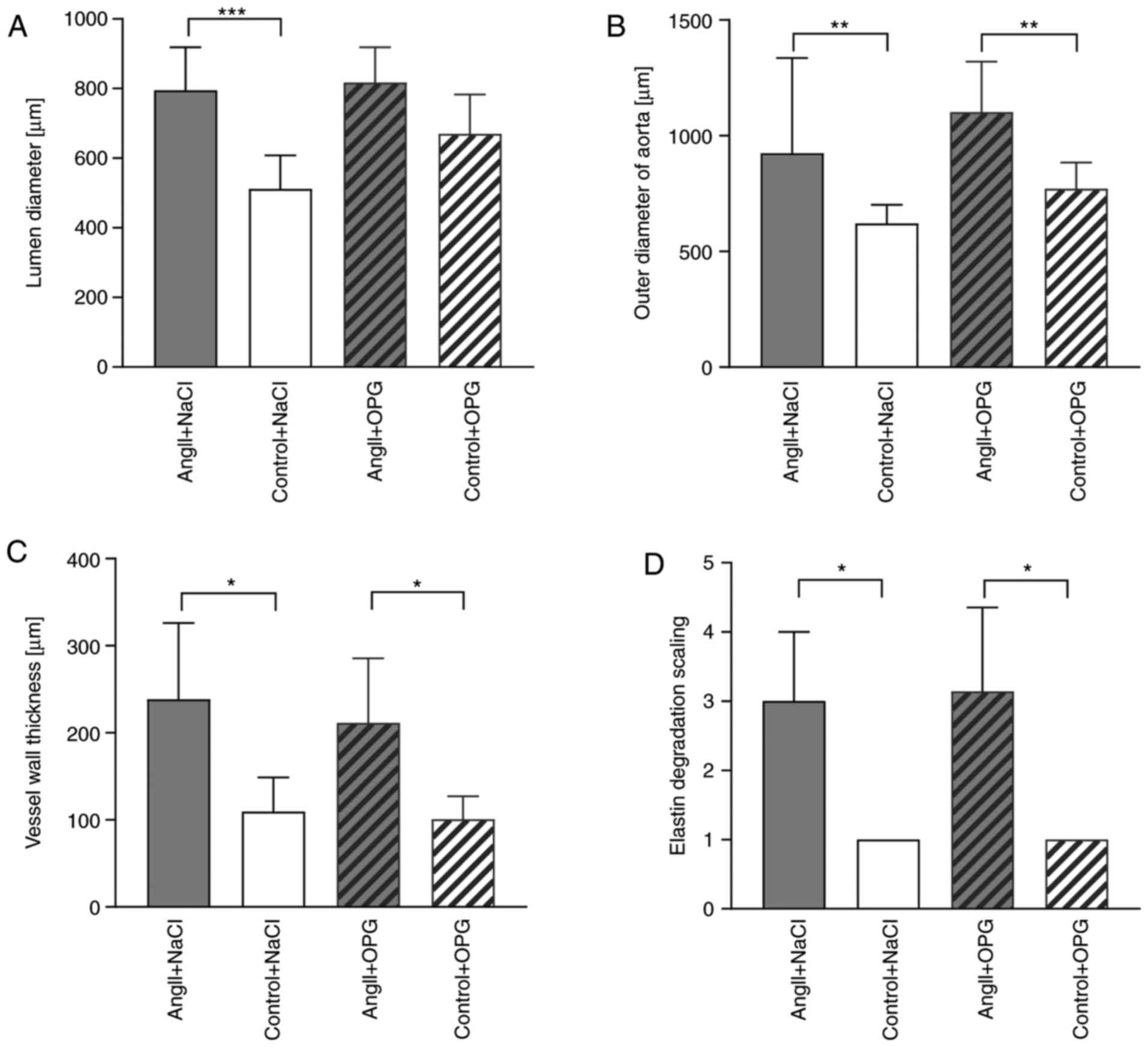
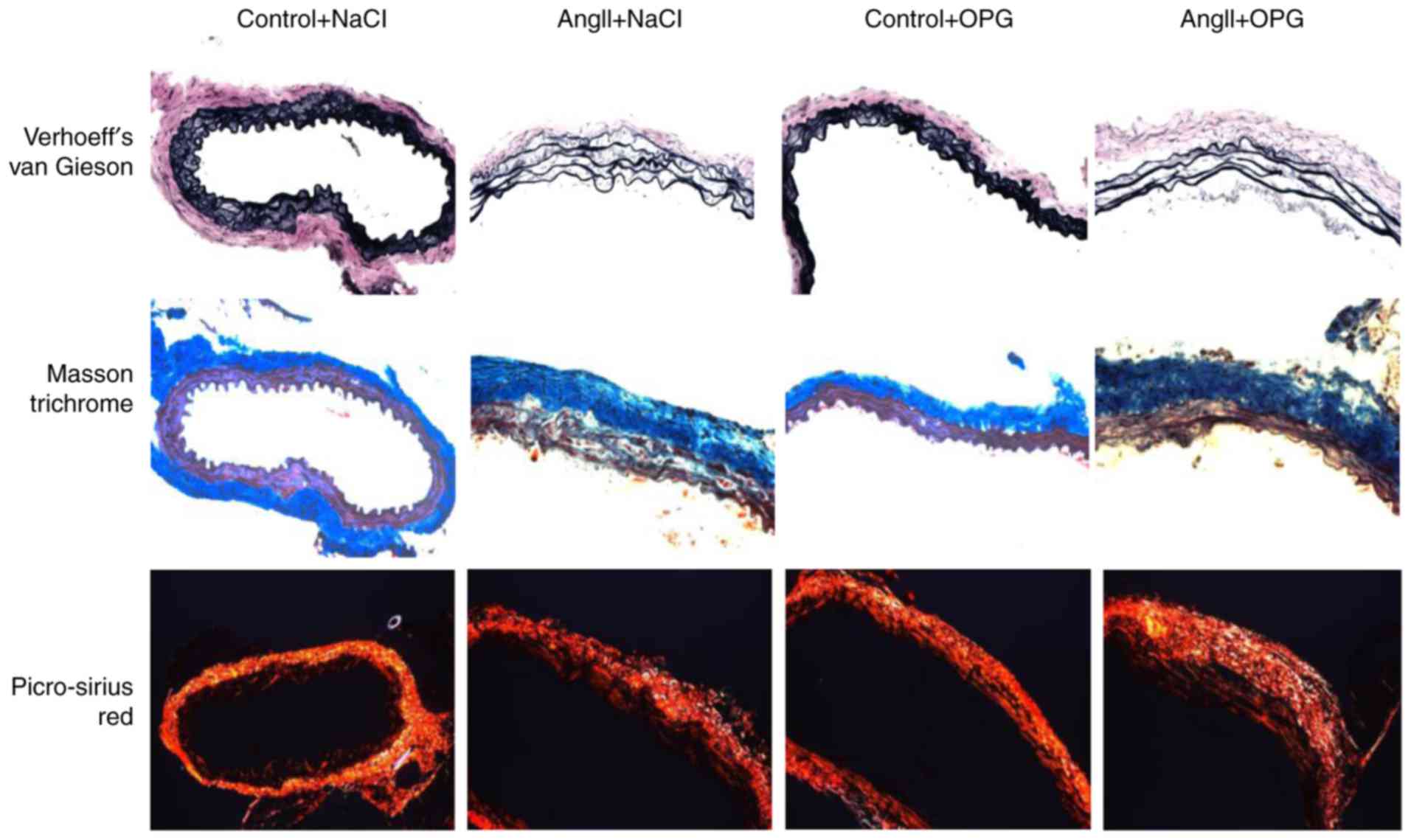
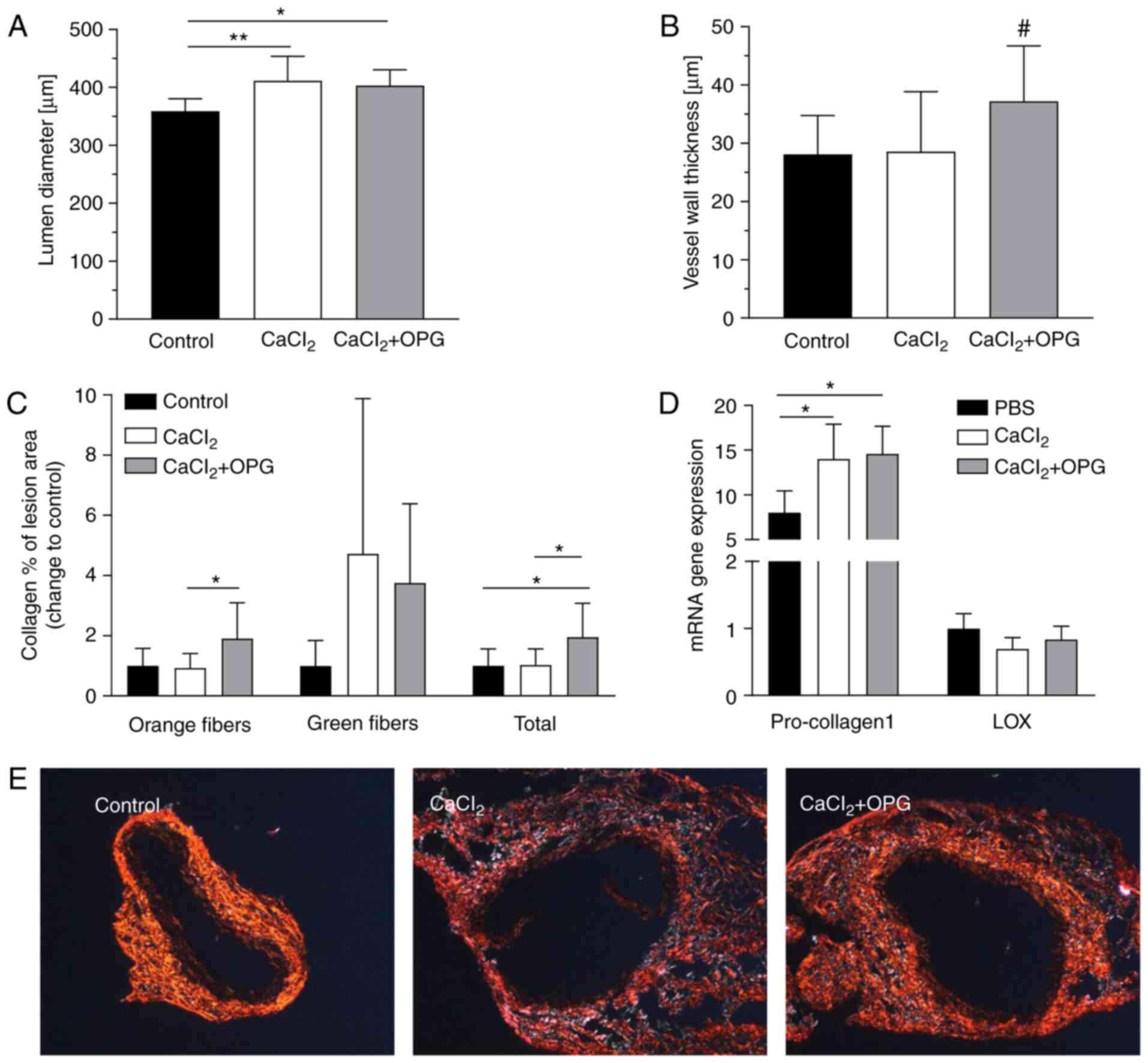
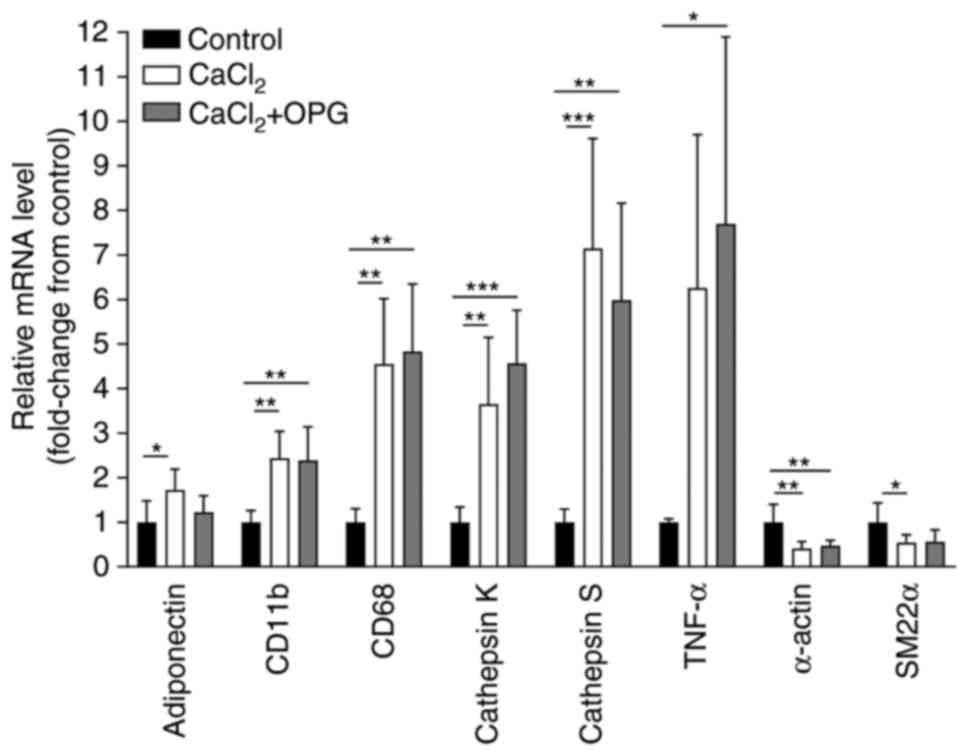
|
1
|
Assar AN and Zarins CK: Ruptured abdominal
aortic aneurysm: A surgical emergency with many clinical
presentations. Postgrad Med J. 85:268–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Toghill BJ, Saratzis A and Bown MJ:
Abdominal aortic aneurysm-an independent disease to
atherosclerosis? Cardiovasc Pathol. 27:71–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shimizu K, Libby P and Mitchell RN: Local
cytokine environments drive aneurysm formation in allografted
aortas. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 15:142–148. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moran CS, McCann M, Karan M, Norman P,
Ketheesan N and Golledge J: Association of osteoprotegerin with
human abdominal aortic aneurysm progression. Circulation.
111:3119–3125. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moran CS, Clancy P, Biros E, Blanco-Martin
B, McCaskie P, Palmer LJ, Coomans D, Norman PE and Golledge J:
Association of PPARgamma allelic variation, osteoprotegerin and
abdominal aortic aneurysm. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).
72:128–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Emery JG, McDonnell P, Burke MB, Deen KC,
Lyn S, Silverman C, Dul E, Appelbaum ER, Eichman C, DiPrinzio R, et
al: Osteoprotegerin is a receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. J
Biol Chem. 273:14363–14367. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley
M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, et
al: Osteoprotegerin: A novel secreted protein involved in the
regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pan G: An antagonist decoy receptor and a
death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science. 277:815–818.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Ciriza Pérez C, Lawrie A and Varo N:
Osteoprotegerin in cardiometabolic disorders. Int J Endocrinol.
2015:5649342015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ,
Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S,
et al: Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates
osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hofbauer LC and Schoppet M: Clinical
implications of the osteoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK system for bone and
vascular diseases. JAMA. 292:490–495. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, Tan HL,
Timms E, Capparelli C, Morony S, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Van G,
Itie A, et al: OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis,
lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature.
397:315–323. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hofbauer LC, Shui C, Riggs BL, Dunstan CR,
Spelsberg TC, O'Brien T and Khosla S: Effects of immunosuppressants
on receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin
production by human osteoblastic and coronary artery smooth muscle
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 280:334–339. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lieb W, Gona P, Larson MG, Massaro JM,
Lipinska I, Keaney JF Jr, Rong J, Corey D, Hoffmann U, Fox CS, et
al: Biomarkers of the osteoprotegerin pathway: Clinical correlates,
subclinical disease, incident cardiovascular disease, and
mortality. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:1849–1854. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Abedin M, Omland T, Ueland T, Khera A,
Aukrust P, Murphy SA, Jain T, Gruntmanis U, McGuire DK and de Lemos
JA: Relation of osteoprotegerin to coronary calcium and aortic
plaque (from the Dallas Heart Study). Am J Cardiol. 99:513–518.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kiechl S, Schett G, Wenning G, Redlich K,
Oberhollenzer M, Mayr A, Santer P, Smolen J, Poewe W and Willeit J:
Osteoprotegerin is a risk factor for progressive atherosclerosis
and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 109:2175–2180. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Koole D, Hurks R, Schoneveld A, Vink A,
Golledge J, Moran CS, de Kleijn DP, van Herwaarden JA, de Vries JP,
Laman JD, et al: Osteoprotegerin is associated with aneurysm
diameter and proteolysis in abdominal aortic aneurysm disease.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:1497–1504. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schoppet M, Preissner KT and Hofbauer LC:
RANK ligand and osteoprotegerin: Paracrine regulators of bone
metabolism and vascular function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
22:549–553. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Collin-Osdoby P: Regulation of vascular
calcification by osteoclast regulatory factors RANKL and
osteoprotegerin. Circ Res. 95:1046–1057. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Venuraju SM, Yerramasu A, Corder R and
Lahiri A: Osteoprotegerin as a predictor of coronary artery disease
and cardiovascular mortality and morbidity. J Am Coll Cardiol.
55:2049–2061. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bennett BJ, Scatena M, Kirk EA, Rattazzi
M, Varon RM, Averill M, Schwartz SM, Giachelli CM and Rosenfeld ME:
Osteoprotegerin inactivation accelerates advanced atherosclerotic
lesion progression and calcification in older ApoE-/- mice.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:2117–2124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bucay N, Sarosi I, Dunstan CR, Morony S,
Tarpley J, Capparelli C, Scully S, Tan HL, Xu W, Lacey DL, et al:
Osteoprotegerin-deficient mice develop early onset osteoporosis and
arterial calcification. Genes Dev. 12:1260–1268. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Min H, Morony S, Sarosi I, Dunstan CR,
Capparelli C, Scully S, Van G, Kaufman S, Kostenuik PJ, Lacey DL,
et al: Osteoprotegerin reverses osteoporosis by inhibiting
endosteal osteoclasts and prevents vascular calcification by
blocking a process resembling osteoclastogenesis. J Exp Med.
192:463–474. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ovchinnikova O, Gylfe A, Bailey L,
Nordström A, Rudling M, Jung C, Bergström S, Waldenström A, Hansson
GK and Nordström P: Osteoprotegerin promotes fibrous cap formation
in atherosclerotic lesions of ApoE-deficient mice-brief report.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:1478–1480. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Candido R, Toffoli B, Corallini F,
Bernardi S, Zella D, Voltan R, Grill V, Celeghini C and Fabris B:
Human full-length osteoprotegerin induces the proliferation of
rodent vascular smooth muscle cells both in vitro and in vivo. J
Vasc Res. 47:252–261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moran CS, Jose RJ, Biros E and Golledge J:
Osteoprotegerin deficiency limits angiotensin II-induced aortic
dilatation and rupture in the apolipoprotein E-knockout mouse.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:2609–2616. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bumdelger B, Kokubo H, Kamata R, Fujii M,
Yoshimura K, Aoki H, Orita Y, Ishida T, Ohtaki M, Nagao M, et al:
Osteoprotegerin prevents development of abdominal aortic aneurysms.
PLoS One. 11:e01470882016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morony S, Tintut Y, Zhang Z, Cattley RC,
Van G, Dwyer D, Stolina M, Kostenuik PJ and Demer LL:
Osteoprotegerin inhibits vascular calcification without affecting
atherosclerosis in ldlr(−/-) mice. Circulation. 117:411–420. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mäki JM, Räsänen J, Tikkanen H, Sormunen
R, Mäkikallio K, Kivirikko KI and Soininen R: Inactivation of the
lysyl oxidase gene Lox leads to aortic aneurysms, cardiovascular
dysfunction, and perinatal death in mice. Circulation.
106:2503–2509. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Callegari A, Coons ML, Ricks JL, Rosenfeld
ME and Scatena M: Increased calcification in
osteoprotegerin-deficient smooth muscle cells: Dependence on
receptor activator of NF-κB ligand and interleukin 6. J Vasc Res.
51:118–131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Olesen P, Ledet T and Rasmussen LM:
Arterial osteoprotegerin: Increased amounts in diabetes and
modifiable synthesis from vascular smooth muscle cells by insulin
and TNF-alpha. Diabetologia. 48:561–568. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Fu M, Myles D, Zhu X, Du J, Cao X
and Chen YE: PDGF induces osteoprotegerin expression in vascular
smooth muscle cells by multiple signal pathways. FEBS Lett.
521:180–184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|