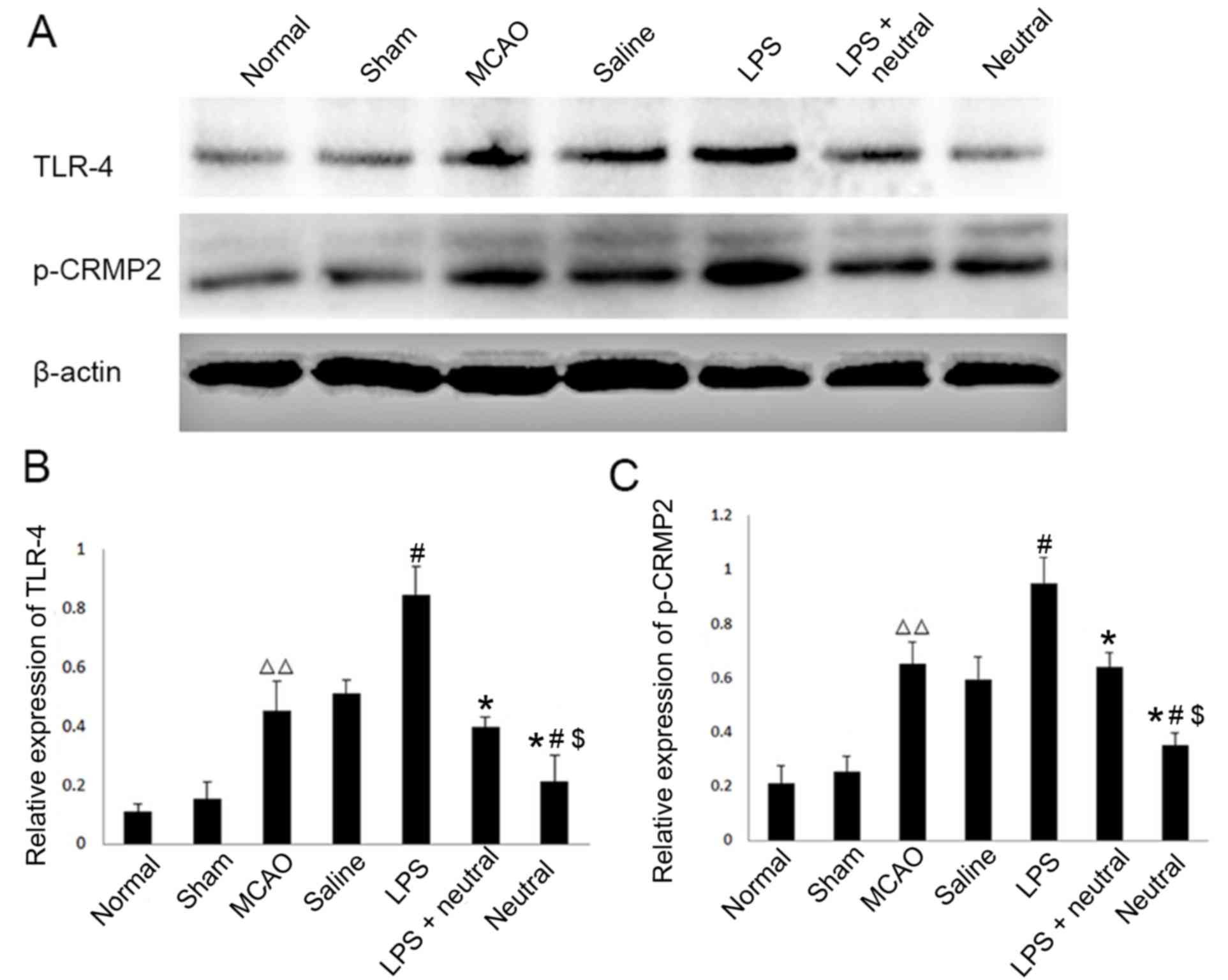
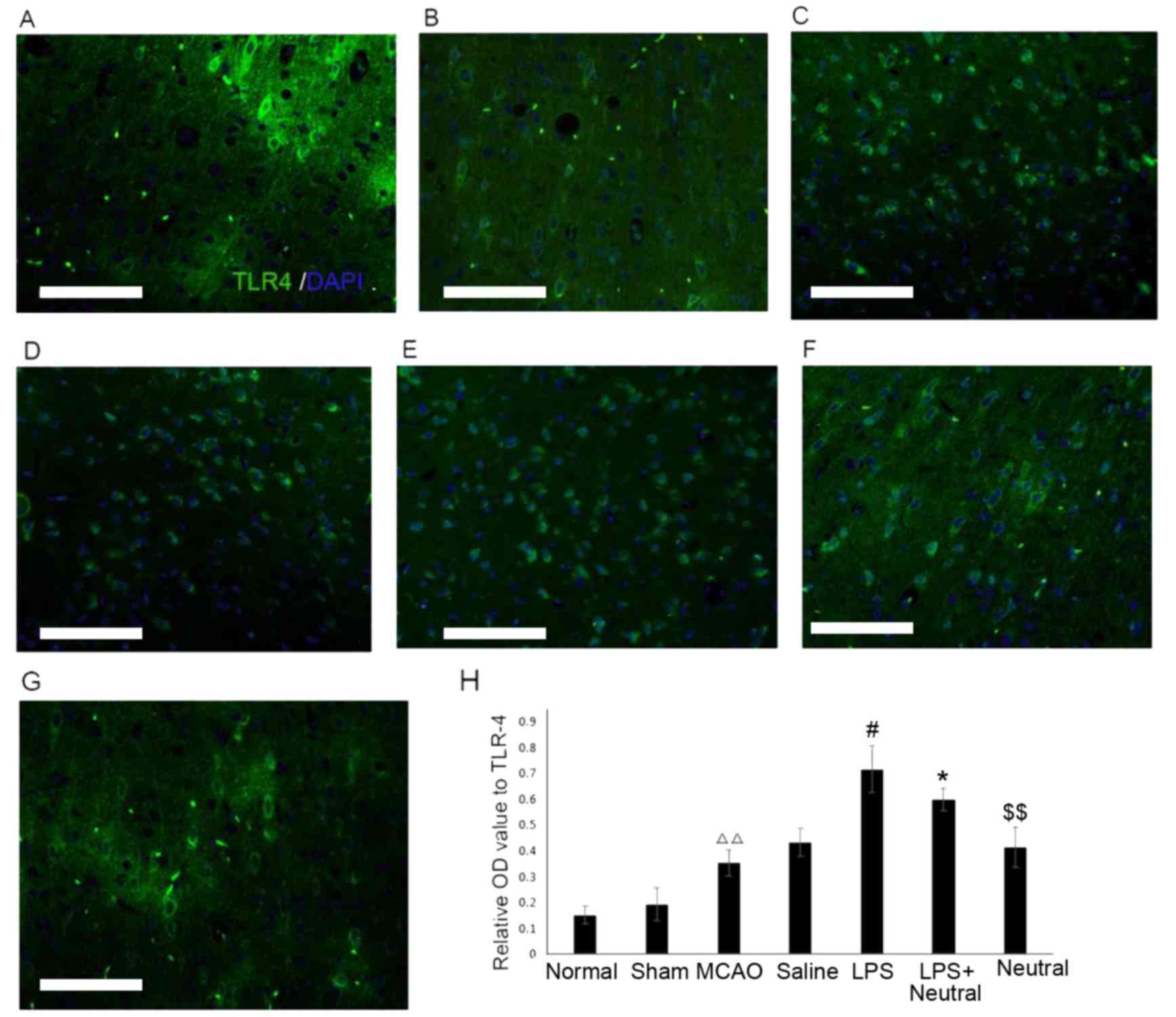
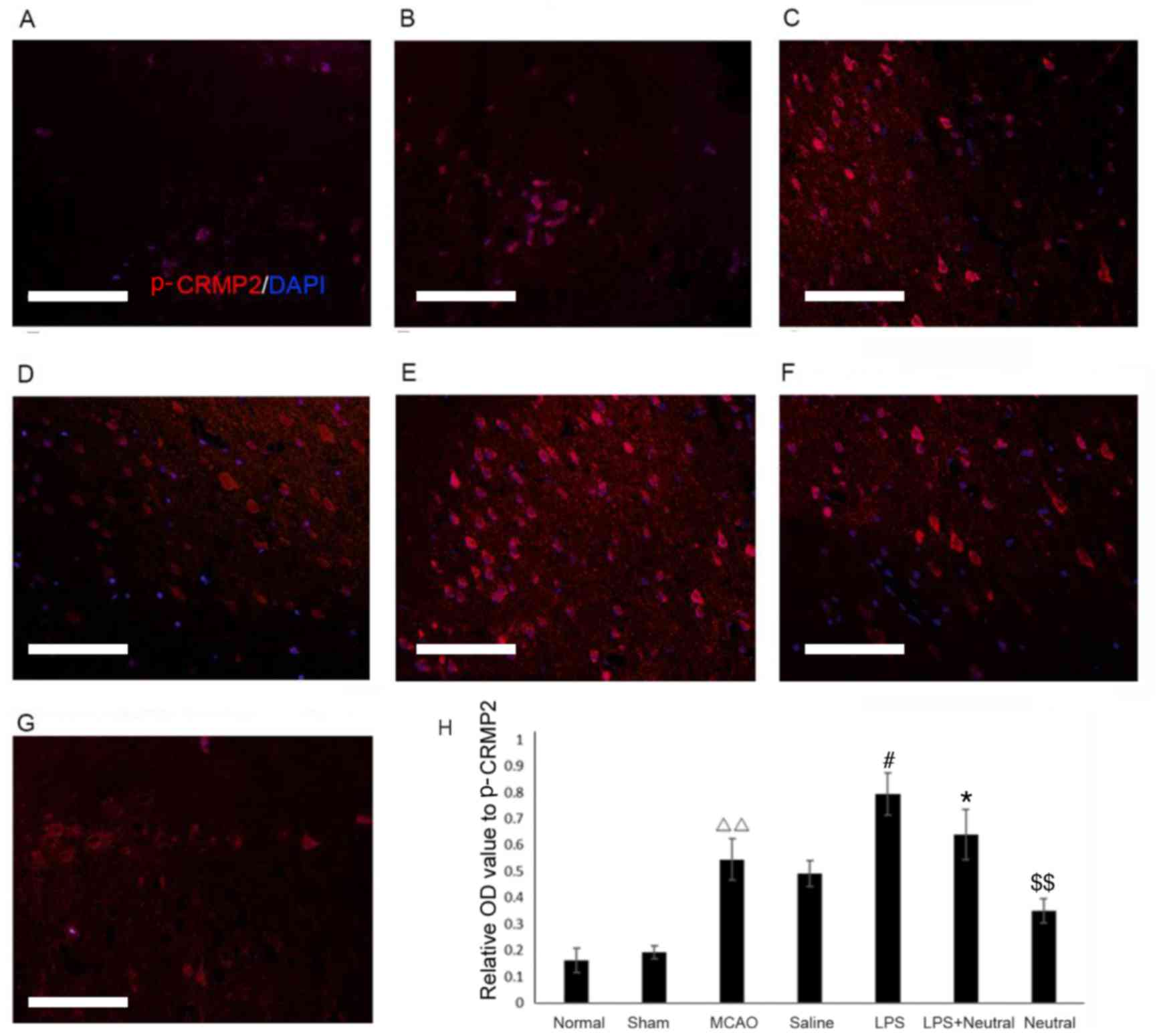
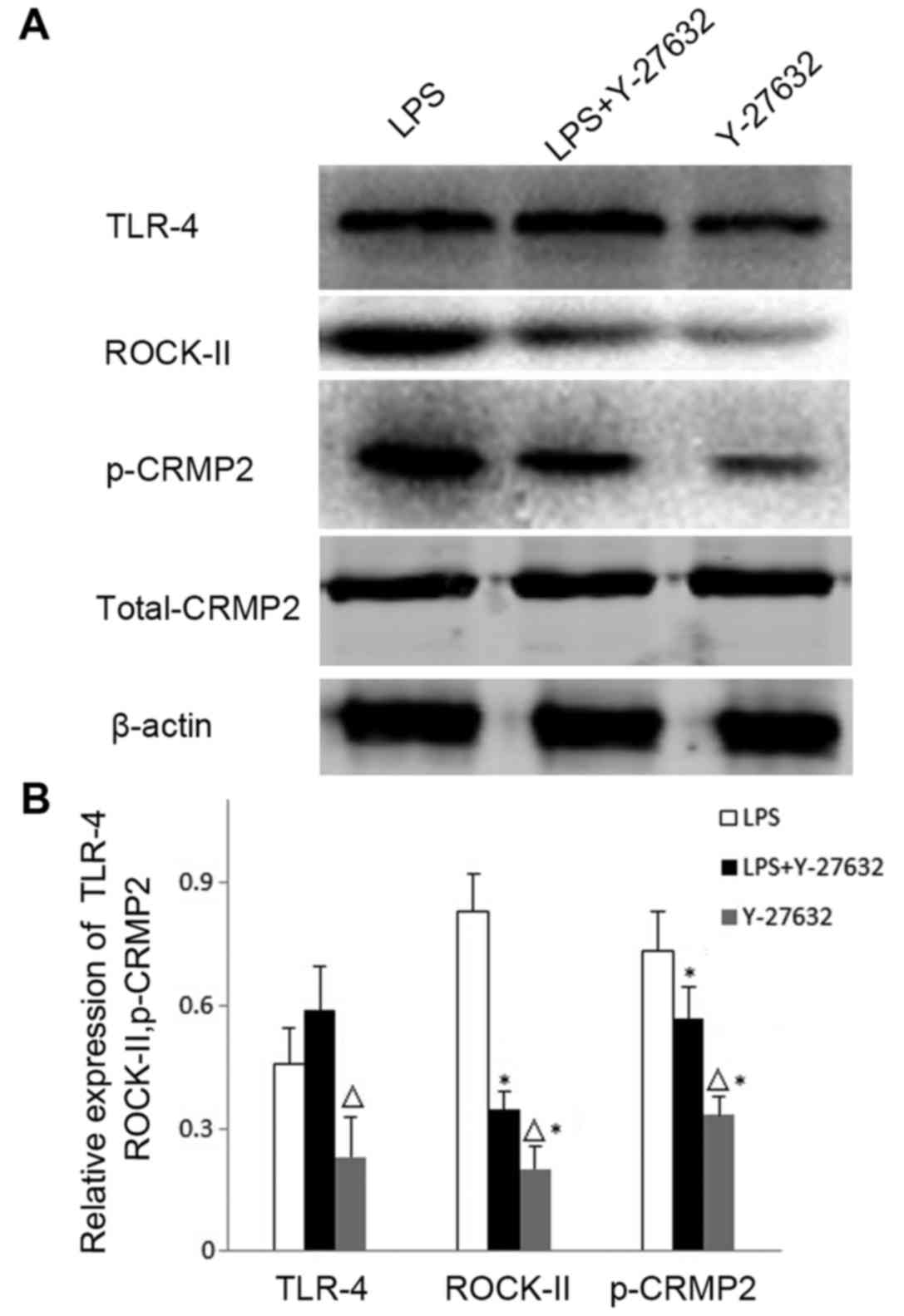
|
1
|
Mensah GA, Norrving B and Feigin VL: The
global burden of stroke. Neuroepidemiology. 45:143–145. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herson PS and Traystman RJ: Animal models
of stroke: Translational potential at present and in 2050. Future
Neurol. 9:541–551. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sierra C, Coca A and Schiffrin EL:
Vascular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of stroke. Curr Hypertens
Rep. 13:200–207. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu X, Wen Z, Zhao N, Xu X, Wang F, Gao J,
Jiang Y and Liu X: MicroRNA-1906, a Novel regulator of toll-like
receptor 4, ameliorates ischemic injury after experimental stroke
in mice. J Neurosci. 37:10498–10515. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang SC, Arumugam TV, Xu X, Cheng A,
Mughal MR, Jo DG, Lathia JD, Siler DA, Chigurupati S, Ouyang X, et
al: Pivotal role for neuronal Toll-like receptors in ischemic brain
injury and functional deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:13798–13803. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tang SC, Yeh SJ, Li YI, Wang YC, Baik SH,
Santro T, Widiapradja A, Manzanero S, Sobey CG, Jo DG, et al:
Evidence for a detrimental role of TLR8 in ischemic stroke. Exp
Neurol. 250:341–347. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Olson JK and Miller SD: Microglia initiate
central nervous system innate and adaptive immune responses through
multiple TLRs. J Immunol. 173:3916–3924. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lehnardt S, Lehmann S, Kaul D, Tschimmel
K, Hoffmann O, Cho S, Krueger C, Nitsch R, Meisel A and Weber JR:
Toll-like receptor 2 mediates CNS injury in focal cerebral
ischemia. J Neuroimmunol. 190:28–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fukata Y, Itoh TJ, Kimura T, Ménager C,
Nishimura T, Shiromizu T, Watanabe H, Inagaki N, Iwamatsu A, Hotani
H and Kaibuchi K: CRMP-2 binds to tubulin heterodimers to promote
microtubule assembly. Nat Cell Biol. 4:583–591. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoshimura T, Kawano Y, Arimura N, Kawabata
S, Kikuchi A and Kaibuchi K: GSK-3beta regulates phosphorylation of
CRMP-2 and neuronal polarity. Cell. 120:137–149. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gim SA, Sung JH, Shah FA, Kim MO and Koh
PO: Ferulic acid regulates the AKT/GSK-3β/CRMP-2 signaling pathway
in a middle cerebral artery occlusion animal model. Lab Anim Res.
29:63–69. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ye Y, Xu H, Zhang X, Li Z, Jia Y, He X and
Huang JH: Association between toll-like receptor 4 expression and
neural stem cell proliferation in the hippocampus following
traumatic brain injury in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 15:12651–12664.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Julian L and Olson MF: Rho-associated
coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): Structure, regulation, and
functions. Small GTPases. 5:e298462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yoneda A, Multhaupt HA and Couchman JR:
The rho kinases I and II regulate different aspects of myosin II
activity. J Cell Biol. 170:443–453. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
National Research Council, . Guide for the
care and use of laboratory animals. 8th edition. National Academy
Press; Washington, DC: 2011, https://grants.nih.gov/grants/olaw/guide-for-the-care-and-use-of-laboratory-animals.pdfPubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Arumugam TV, Salter JW, Chidlow JH,
Ballantyne CM, Kevil CG and Granger DN: Contributions of LFA-1 and
Mac-1 to brain injury and microvascular dysfunction induced by
transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 287:H2555–H2560. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiong X, Barreto GE, Xu L, Ouyang YB, Xie
X and Giffard RG: Increased brain injury and worsened neurological
outcome in interleukin-4 knockout mice after transient focal
cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 42:2026–2032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwasa T, Matsuzaki T, Tungalagsuvd A,
Munkhzaya M, Kawami T, Kato T, Kuwahara A, Yasui T and Irahara M:
Effects of ovariectomy on the inflammatory responses of female rats
to the central injection of lipopolysaccharide. J Neuroimmunol.
277:50–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma Y, Zhang X, Bao H, Mi S, Cai W, Yan H,
Wang Q, Wang Z, Yan J, Fan GC, et al: Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2
and TLR4 differentially regulate doxorubicin induced cardiomyopathy
in mice. PLoS One. 7:e407632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gong G, Bai S, Wu W, Hu L, Liu Y, Niu J,
Dai X, Yin L and Wang X: Lrg participates in lipopolysaccharide
preconditioning-induced brain ischemia injury via TLR4 signaling
pathway. J Mol Neurosci. 54:20–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rikitake Y, Kim HH, Huang Z, Seto M, Yano
K, Asano T, Moskowitz MA and Liao JK: Inhibition of rho kinase
(ROCK) leads to increased cerebral blood flow and stroke
protection. Stroke. 36:2251–2257. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sugawara T, Ayer R, Jadhav V and Zhang JH:
A new grading system evaluating bleeding scale in filament
perforation subarachnoid hemorrhage rat model. J Neurosci Methods.
167:327–334. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kawai T and Akira S: The role of
pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on
toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 11:373–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Medzhitov R and Janeway CA Jr: Innate
immunity: The virtues of a nonclonal system of recognition. Cell.
91:295–298. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Doi Y, Mizuno T, Maki Y, Jin S, Mizoguchi
H, Ikeyama M, Doi M, Michikawa M, Takeuchi H and Suzumura A:
Microglia activated with the toll-like receptor 9 ligand CpG
attenuate oligomeric amyloid {beta} neurotoxicity in in vitro and
in vivo models of Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 175:2121–2132.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hensley K, Venkova K, Christov A, Gunning
W and Park J: Collapsin response mediator protein-2: An emerging
pathologic feature and therapeutic target for neurodisease
indications. Mol Neurobiol. 43:180–191. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brown M, Jacobs T, Eickholt B, Ferrari G,
Teo M, Monfries C, Qi RZ, Leung T, Lim L and Hall C:
Alpha2-chimaerin, cyclin-dependent Kinase 5/p35, and its target
collapsin response mediator protein-2 are essential components in
semaphorin 3A-induced growth-cone collapse. J Neurosci.
24:8994–9004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arimura N, Ménager C, Kawano Y, Yoshimura
T, Kawabata S, Hattori A, Fukata Y, Amano M, Goshima Y, Inagaki M,
et al: Phosphorylation by rho kinase regulates CRMP-2 activity in
growth cones. Mol Cell Biol. 25:9973–9984. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang T, Wu X, Yin C, Klebe D, Zhang JH and
Qin X: CRMP-2 is involved in axon growth inhibition induced by RGMa
in vitro and in vivo. Mol Neurobiol. 47:903–913. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|