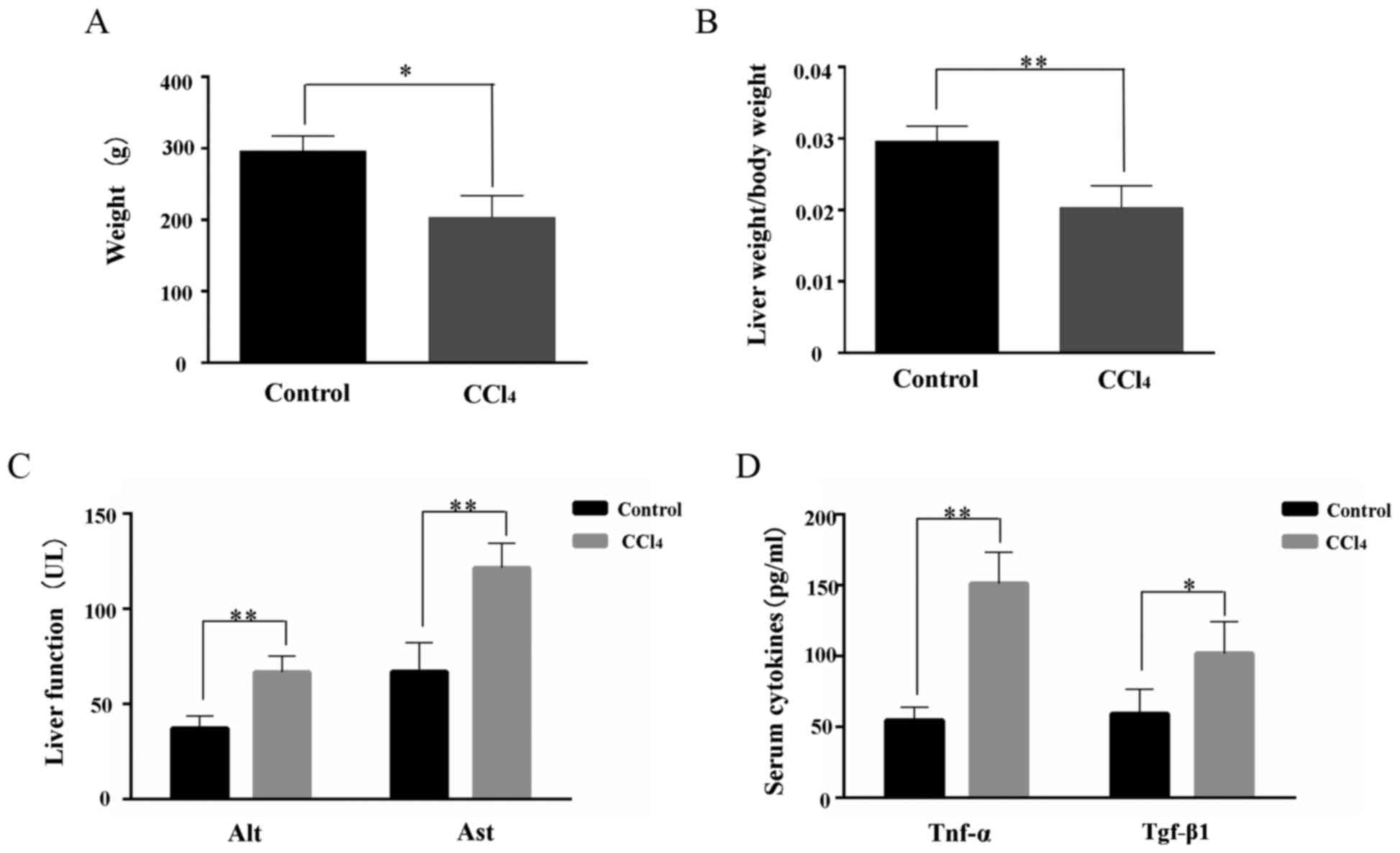
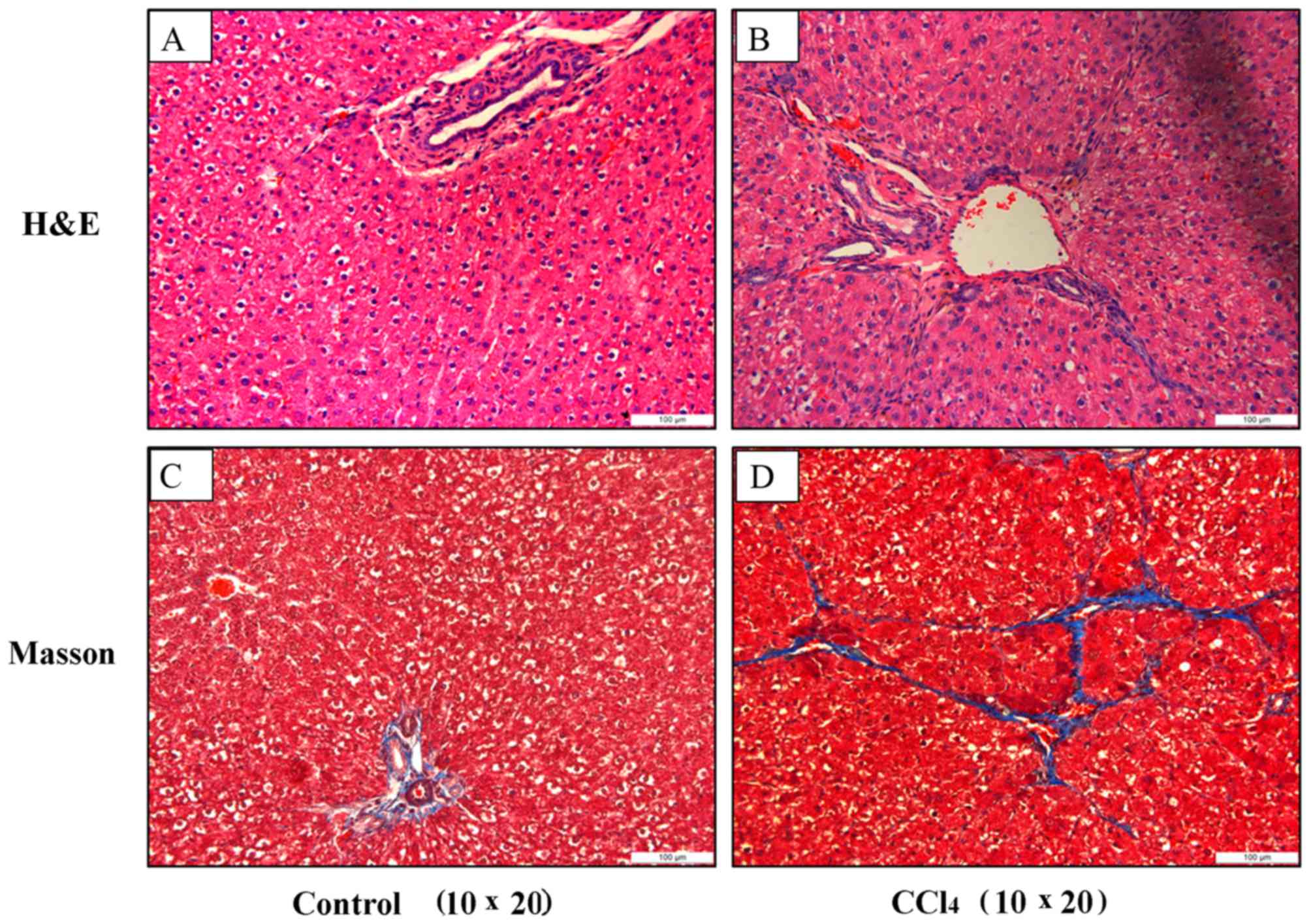
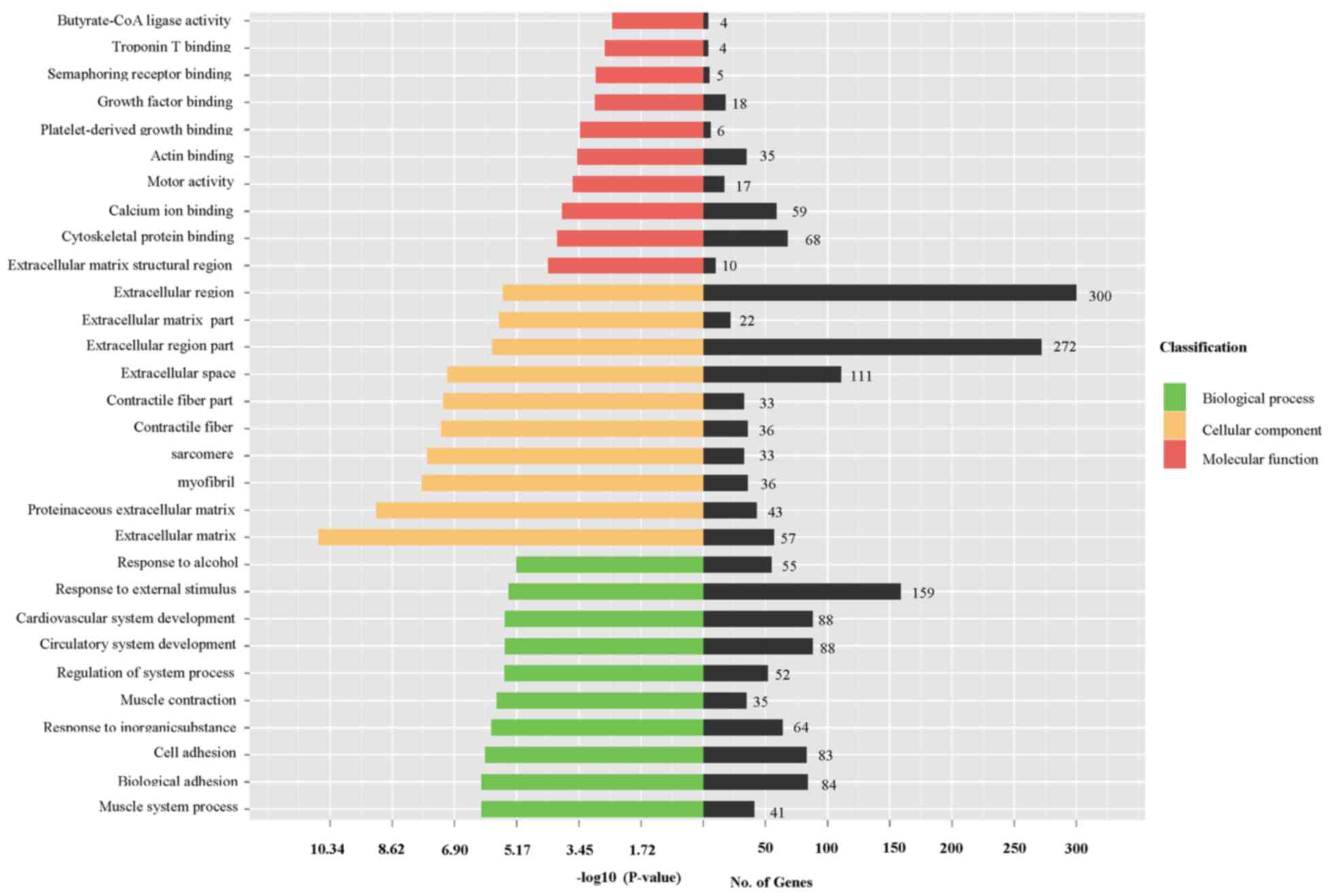
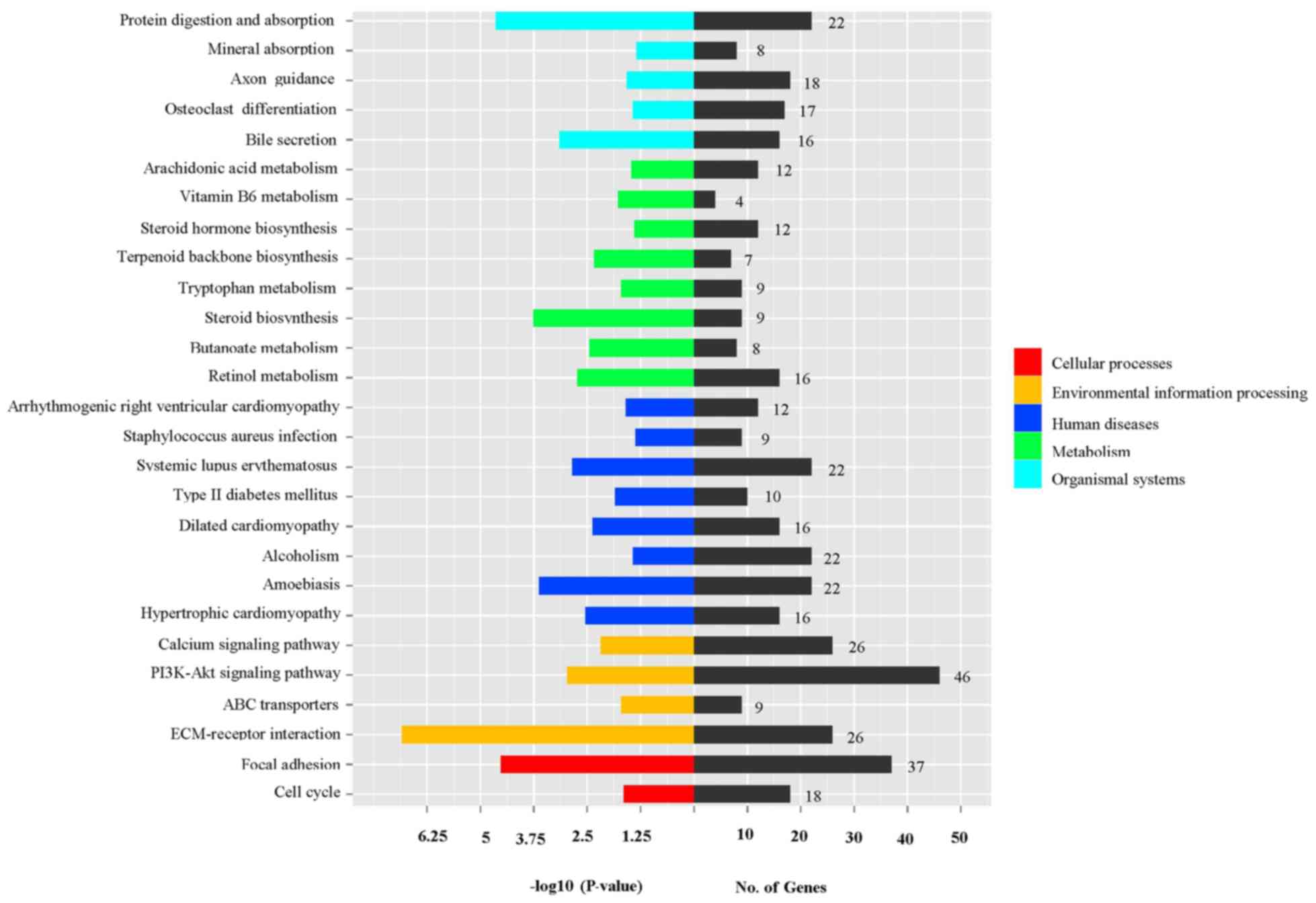
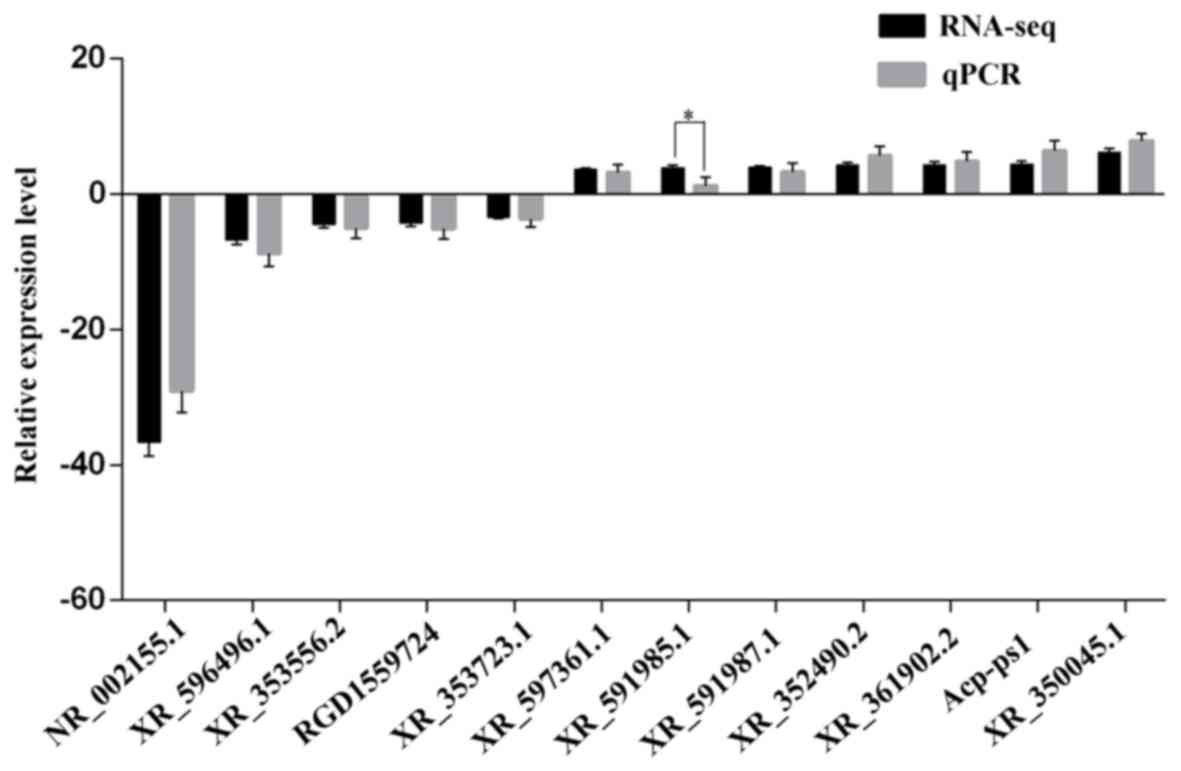
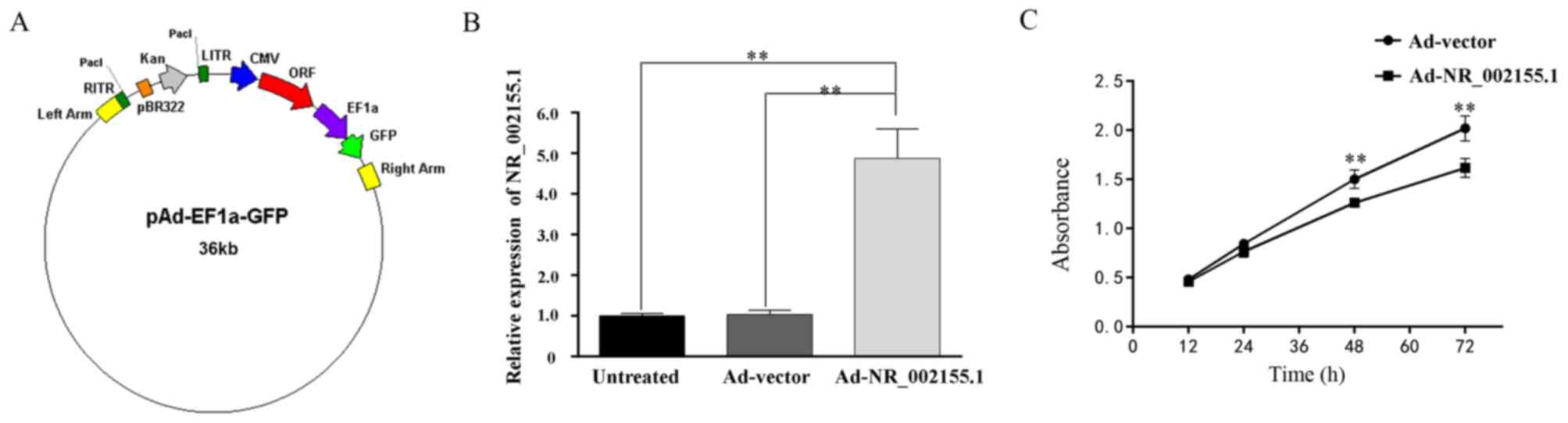
|
1
|
Duval F, Moreno-Cuevas JE, Gonzalez-Garza
MT, Maldonado-Bernal C and Cruz-Vega DE: Liver fibrosis and
mechanisms of the protective action of medicinal plants targeting
inflammation and the immune response. Int J Inflam.
2015:9434972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Enomoto M, Morikawa H, Tamori A and Kawada
N: Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with
chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 20:12031–12038. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xuan J, Chen S, Ning B, Tolleson WH and
Guo L: Development of HepG2-derived cells expressing cytochrome
P450s for assessing metabolism-associated drug-induced liver
toxicity. Chem Biol Interact. 255:63–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang ZG, Zhai WR, Zhang YE and Zhang XR:
Study of heteroserum-induced rat liver fibrosis model and its
mechanism. World J Gastroenterol. 4:206–209. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Novikova IV, Hennelly SP and Sanbonmatsu
KY: Sizing up long non-coding RNAs: Do lncRNAs have secondary and
tertiary structure? Bioarchitecture. 2:189–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Geisler S and Coller J: RNA in unexpected
places: Long non-coding RNA functions in diverse cellular contexts.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:699–712. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gibb EA, Brown CJ and Lam WL: The
functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol
Cancer. 10:382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li J, Tian H, Yang J and Gong Z: Long
noncoding RNAs regulate cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis.
DNA Cell Biol. 35:459–470. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Briggs JA, Wolvetang EJ, Mattick JS, Rinn
JL and Barry G: Mechanisms of long Non-coding RNAs in mammalian
nervous system development, plasticity, disease, and evolution.
Neuron. 88:861–877. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roberts TC, Morris KV and Weinberg MS:
Perspectives on the mechanism of transcriptional regulation by long
non-coding RNAs. Epigenetics. 9:13–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu F, Zheng J, Mao Y, Dong P, Li G, Lu Z,
Guo C, Liu Z and Fan X: Long non-coding RNA APTR promotes the
activation of hepatic stellate cells and the progression of liver
fibrosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:679–685. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu Y, Liu X, Zhou Q, Huang C, Meng X, Xu F
and Li J: Silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) ameliorates liver
fibrosis via promoting activated stellate cell apoptosis and
reversion. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 289:163–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He Y, Wu YT, Huang C, Meng XM, Ma TT, Wu
BM, Xu FY, Zhang L, Lv XW and Li J: Inhibitory effects of long
noncoding RNA MEG3 on hepatic stellate cells activation and liver
fibrogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1842:2204–2215. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu F, Zheng J, Mao Y, Dong P, Lu Z, Li G,
Guo C, Liu Z and Fan X: Long Non-coding RNA growth Arrest-specific
transcript 5 (GAS5) inhibits liver fibrogenesis through a mechanism
of competing endogenous RNA. J Biol Chem. 290:28286–28298. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kong X, Zhou W, Wan JB, Zhang Q, Ni J and
Hu Y: An integrative thrombosis network: Visualization and
topological analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2015:2653032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
National Research Council, . Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The National Academies Press;
Washington, DC: 1996, https://www.nap.edu/catalog/5140/guide-for-the-care-and-use-of-laboratory-animals
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Trapnell C, Pachter L and Salzberg SL:
TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics.
25:1105–1111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feng J, Meyer CA, Wang Q, Liu JS, Liu
Shirley X and Zhang Y: GFOLD: A generalized fold-change for ranking
differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics.
28:2782–2788. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G,
Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL and Pachter L:
Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 7:562–578. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dong S, Chen QL, Song YN, Sun Y, Wei B, Li
XY, Hu YY, Liu P and Su SB: Mechanisms of CCl4-induced liver
fibrosis with combined transcriptomic and proteomic analysis. J
Toxicol Sci. 41:561–572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marques TG, Chaib E, da Fonseca JH,
Lourenço AC, Silva FD, Ribeiro MA Jr, Galvão FH and D'Albuquerque
LA: Review of experimental models for inducing hepatic cirrhosis by
bile duct ligation and carbon tetrachloride injection. Acta Cir
Bras. 27:589–594. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sancheti S, Sancheti S and Seo SY:
Ameliorative effects of 7-methylcoumarin and 7-methoxycoumarin
against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol.
36:42–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li S, Tan HY, Wang N, Zhang ZJ, Lao L,
Wong CW and Feng Y: The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants
in liver diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 16:26087–26124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heeba GH and Mahmoud ME: Therapeutic
potential of morin against liver fibrosis in rats: Modulation of
oxidative stress, cytokine production and nuclear factor kappa B.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 37:662–671. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Duval F, Moreno-Cuevas JE, Gonzalez-Garza
MT, Rodriguez-Montalvo C and Cruz-Vega DE: Protective mechanisms of
medicinal plants targeting hepatic stellate cell activation and
extracellular matrix deposition in liver fibrosis. Chin Med.
9:272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Roy S, Benz F, Cardenas Vargas D, Vucur M,
Gautheron J, Schneider A, Hellerbrand C, Pottier N, Alder J, Tacke
F, et al: miR-30c and miR-193 are a part of the TGF-β-dependent
regulatory network controlling extracellular matrix genes in liver
fibrosis. J Dig Dis. 16:513–524. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karsdal MA, Manon-Jensen T, Genovese F,
Kristensen JH, Nielsen MJ, Sand JM, Hansen NU, Bay-Jensen AC, Bager
CL, Krag A, et al: Novel insights into the function and dynamics of
extracellular matrix in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 308:G807–G830. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Carloni V, Romanelli RG, Pinzani M, Laffi
G and Gentilini P: Focal adhesion kinase and phospholipase C gamma
involvement in adhesion and migration of human hepatic stellate
cells. Gastroenterology. 112:522–531. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Renshaw MW, Price LS and Schwartz MA:
Focal adhesion kinase mediates the integrin signaling requirement
for growth factor activation of MAP kinase. J Cell Biol.
147:611–618. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Ma J, Chen L, Xie XL and Jiang H:
Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase on hepatic Stellate-cell
adhesion and migration. Am J Med Sci. 353:41–48. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Reif S, Lang A, Lindquist JN, Yata Y,
Gabele E, Scanga A, Brenner DA and Rippe RA: The role of focal
adhesion kinase-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt signaling in
hepatic stellate cell proliferation and type I collagen expression.
J Biol Chem. 278:8083–8090. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Novo E, Cannito S, Paternostro C, Bocca C,
Miglietta A and Parola M: Cellular and molecular mechanisms in
liver fibrogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 548:20–37. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin X, Bai F, Nie J, Lu S, Lu C, Zhu X,
Wei J, Lu Z and Huang Q: Didymin alleviates hepatic fibrosis
through inhibiting ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways via regulation of raf
kinase inhibitor protein. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:1422–1432. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim AH, Khursigara G, Sun X, Franke TF and
Chao MV: Akt phosphorylates and negatively regulates apoptosis
signal-regulating kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol. 21:893–901. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Coffer PJ, Jin J and Woodgett JR: Protein
kinase B (c-Akt): A multifunctional mediator of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. Biochem J. 335:1–13.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ricupero DA, Poliks CF, Rishikof DC,
Cuttle KA, Kuang PP and Goldstein RH: Phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-dependent stabilization of alpha1(I) collagen mRNA in
human lung fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 281:C99–C105.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|