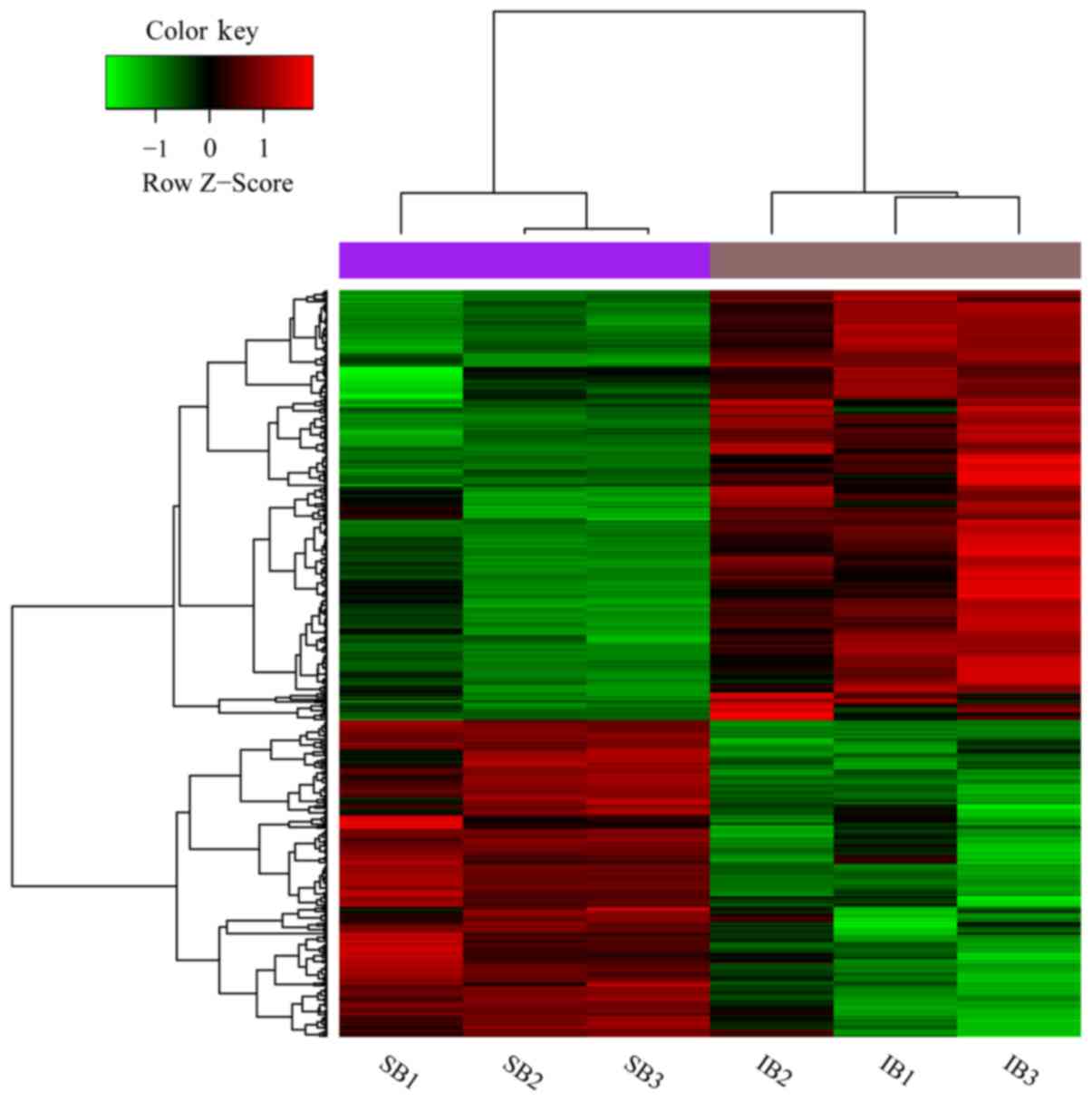
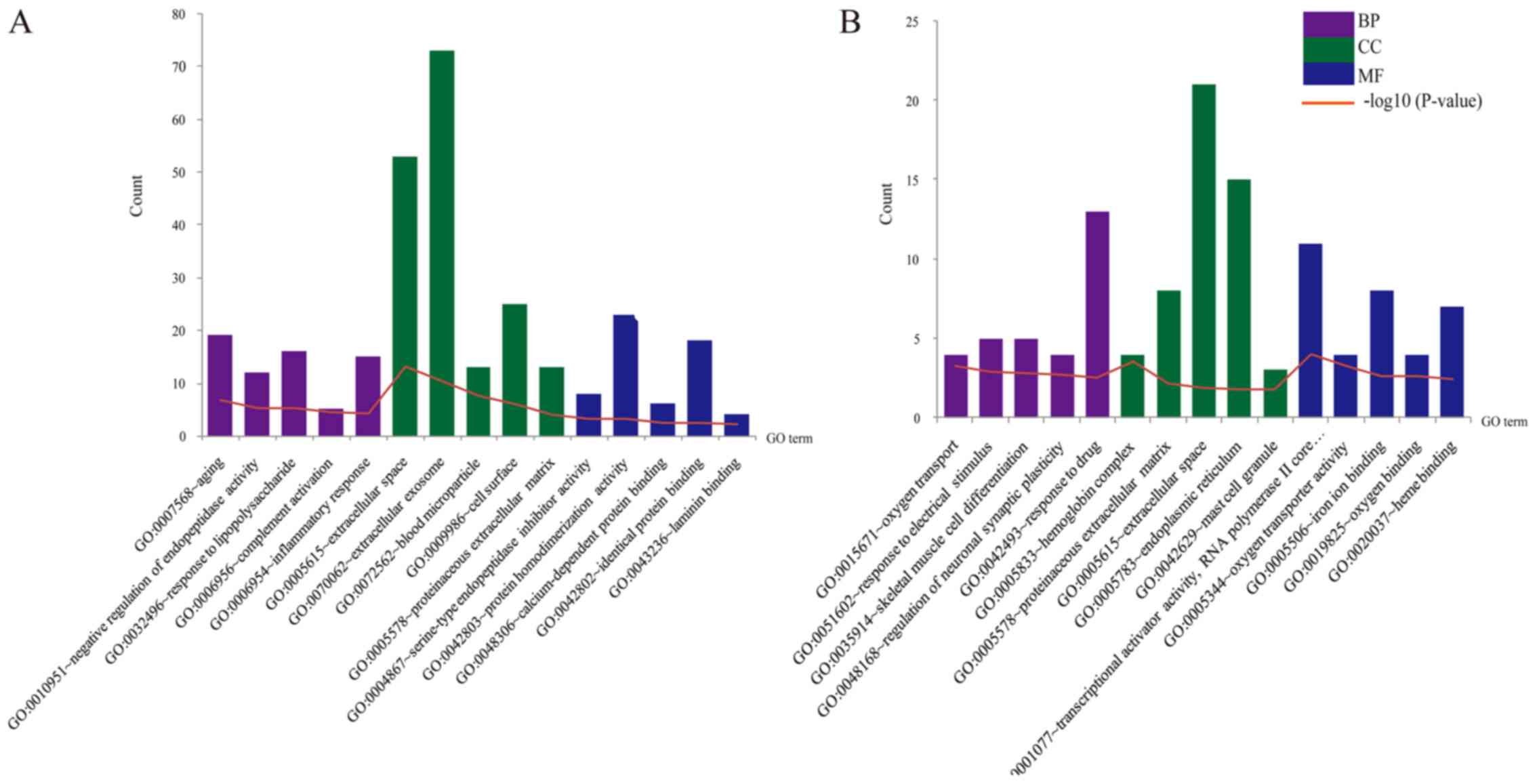
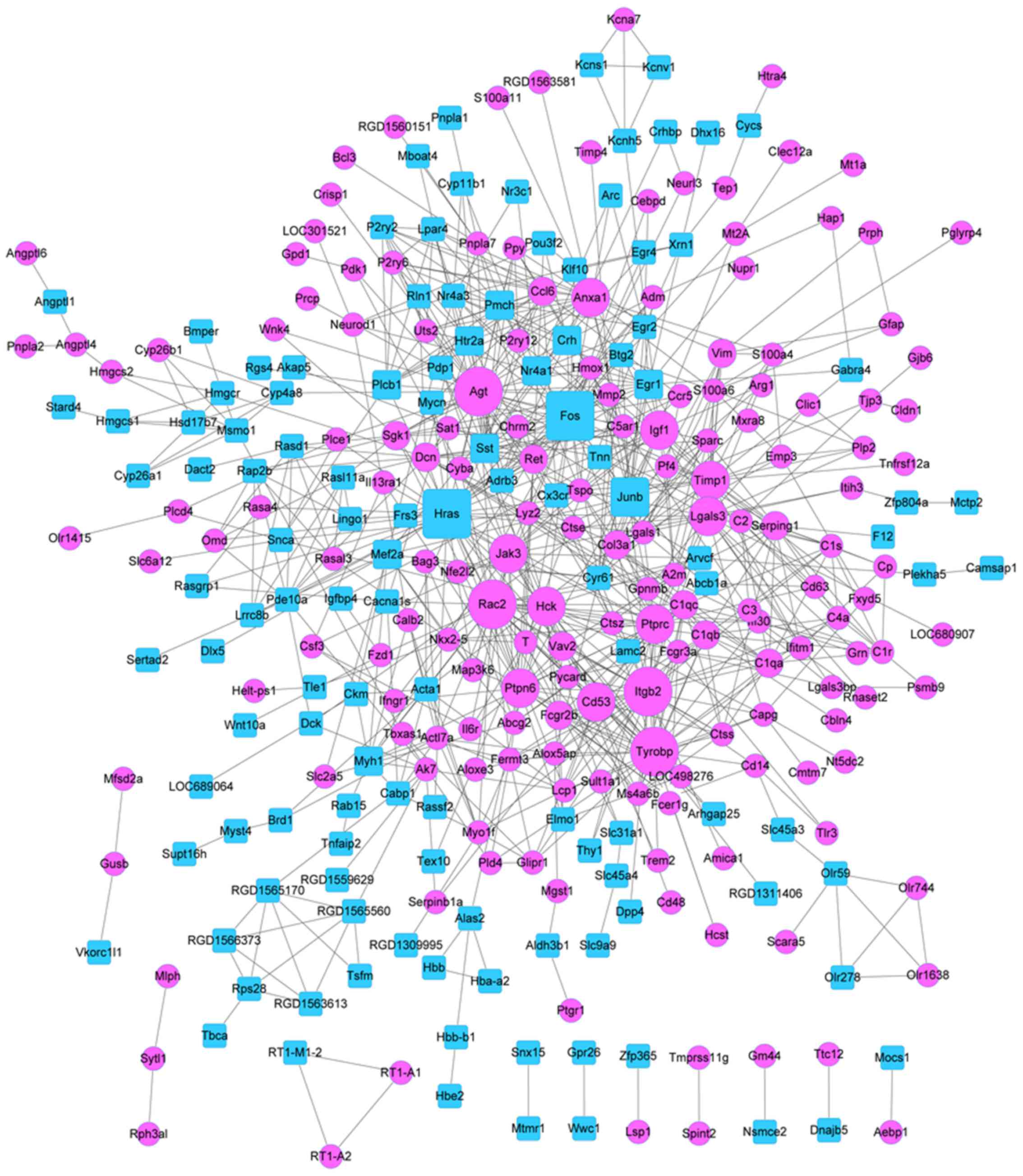
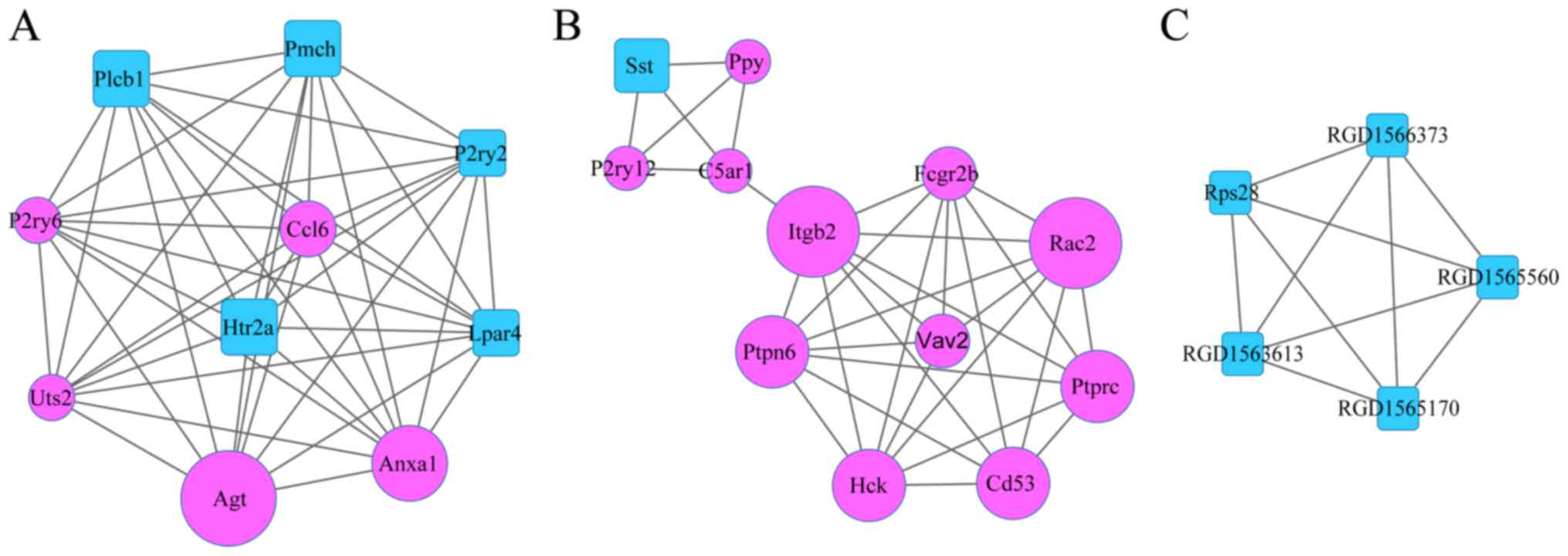
|
1
|
Muresanu DF, Buzoianu A, Florian SI and
von Wild T: Towards a roadmap in brain protection and recovery. J
Cell Mol Med. 16:2861–2871. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hankey GJ: Anticoagulant therapy for
patients with ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Neurol. 8:319–328. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klimkiewicz P, Kubsik A and
Woldańska-Okońska M: NDT-Bobath method used in the rehabilitation
of patients with a history of ischemic stroke. Wiad Lek.
65:102–107. 2012.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Malki N, Koupil I, Eloranta S, Weibull CE,
Tiikkaja S, Ingelsson E and Sparén P: Temporal trends in incidence
of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke by socioeconomic
position in Sweden 1987–2010. PLoS One. 9:e1052792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sherzai AZ, Ma H, Hornross P, Canchola AJ,
Voutsinas J, Willey JZ, Gu Y, Scarmeas N, Sherzai D, Bernstein L,
et al: Abstract MP85: Mediterranean diet and incidence of stroke in
the California teachers study. Circulation. 131:AMP85. 2015.
|
|
6
|
Khoury JC, Kissela B, Sucharew H, Alwell
K, Moomaw C, Woo D, Flaherty M, Adeoye O, Khatri P, Ferioli S, et
al: Abstract 145: Is the rate of ischemic stroke incidence changing
differentially over time for women and men? In:
American-Heart-Association/American-Stroke-Association
International. Stroke. 44 Suppl 1:A1452013.
|
|
7
|
Tu XS: Epidemiological studies of acute
ischemic stroke. Chin J Clin Neurosci. 24:594–599. 2016.
|
|
8
|
Li L, Li H and Li M: Curcumin protects
against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:14985–14991. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yepes M, Roussel BD, Ali C and Vivien D:
Tissue-type plasminogen activator in the ischemic brain: More than
a thrombolytic. Trends Neurosci. 32:48–55. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang Y, Jiang S, Dong Y, Fan C, Zhao L,
Yang X, Li J, Di S, Yue L, Liang G, et al: Melatonin prevents cell
death and mitochondrial dysfunction via a SIRT1-dependent mechanism
during ischemic-stroke in mice. J Pineal Res. 58:61–70. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Palencia G, Medrano JÁ, Ortiz-Plata A,
Farfán DJ, Sotelo J, Sánchez A and Trejo-Solís C: Anti-apoptotic,
anti-oxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects of thalidomide on
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Neurol Sci.
351:78–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nicolas CS, Amici M, Bortolotto ZA,
Doherty A, Csaba Z, Fafouri A, Dournaud P, Gressens P, Collingridge
GL and Peineau S: The role of JAK-STAT signaling within the CNS.
JAKSTAT. 2:e229252013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang G, Zhou D, Wang C, Gao Y, Zhou Q,
Qian G and Decoster MA: Hypoxic preconditioning suppresses group
III secreted phospholipase A2-induced apoptosis via JAK2-STAT3
activation in cortical neurons. J Neurochem. 114:1039–1048.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou TF and Yu JG: Recombinant human
erythropoietin attenuates neuronal apoptosis and cognitive defects
via JAK2/STAT3 signaling in experimental endotoxemia. J Surg Res.
183:304–312. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feng Q, Wang YI and Yang Y:
Neuroprotective effect of interleukin-6 in a rat model of cerebral
ischemia. Exp Ther Med. 9:1695–1701. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu H, Zou L, Tian J, Du G and Gao Y:
SMND-309, a novel derivative of salvianolic acid B, protects rat
brains ischemia and reperfusion injury by targeting the JAK2/STAT3
pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 714:23–31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yasukawa H, Misawa H, Sakamoto H, Masuhara
M, Sasaki A, Wakioka T, Ohtsuka S, Imaizumi T, Matsuda T and Ihle
JN: The JAK-binding protein JAB inhibits Janus tyrosine kinase
activity through binding in the activation loop. EMBO J.
18:1309–1320. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pradip D, Peng X and Durden DL: Rac2
specificity in macrophage integrin signaling: Potential role for
Syk kinase. J Biol Chem. 278:41661–14669. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De P, Peng Q, Traktuev DO, Li W, Yoder MC,
March KL and Durden DL: Expression of RAC2 in endothelial cells is
required for the postnatal neovascular response. Exp Cell Res.
315:248–263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Joshi S, Singh AR, Zulcic M, Bao L, Messer
K, Ideker T, Dutkowski J and Durden DL: Rac2 controls tumor growth,
metastasis and M1-M2 macrophage differentiation in vivo. PLoS One.
9:e958932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saugstad JA: MicroRNAs as effectors of
brain function with roles in ischemia and injury, neuroprotection,
and neurodegeneration. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:1564–1576.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ouyang YB, Xu L, Lu Y, Sun X, Yue S, Xiong
XX and Giffard RG: Astrocyte-enriched miR-29a targets PUMA and
reduces neuronal vulnerability to forebrain ischemia. Glia.
61:1784–1794. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lai W, Zheng Z, Zhang X, Wei Y, Chu K,
Brown J, Hong G and Chen L: Salidroside-mediated neuroprotection is
associated with induction of early growth response genes (Egrs)
across a wide therapeutic window. Neurotox Res. 28:108–121. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barrett T, Suzek TO, Troup DB, Wilhite SE,
Ngau WC, Ledoux P, Rudnev D, Lash AE, Fujibuchi W and Edgar R: NCBI
GEO: Mining millions of expression profiles-database and tools.
Nucleic Acids Res. 33:D562–D566. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear Models for
Microarray DataBioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
Using R and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey VJ, Huber W, Irizarry
RA and Dudoit S: Springer; New York, NY: pp. 397–420. 2005,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kolde R: Pheatmap: Pretty HeatmapsR
Package. Version 0.7. 7. CRAN Repository; 2012
|
|
27
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Du J, Yuan Z, Ma Z, Song J, Xie X and Chen
Y: KEGG-PATH: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes-based pathway
analysis using a path analysis model. Mol Biosyst. 10:2441–2447.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: PRotein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:(Database Issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bandettini WP, Kellman P, Mancini C,
Booker OJ, Vasu S, Leung SW, Wilson JR, Shanbhag SM, Chen MY and
Arai AE: MultiContrast Delayed Enhancement (MCODE) improves
detection of subendocardial myocardial infarction by late
gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance: A
clinical validation study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 14:832012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Slezak-Prochazka I, Durmus S, Kroesen BJ
and van den Berg A: MicroRNAs, macrocontrol: Regulation of miRNA
processing. RNA. 16:1087–1095. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang J, Duncan D, Shi Z and Zhang B:
WEB-based GEne SeT AnaLysis Toolkit (WebGestalt): update 2013.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:W77–W83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang B, Kirov S and Snoddy J: WebGestalt:
An integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological
contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:W741–W748. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Didsbury J, Weber RF, Bokoch GM, Evans T
and Snyderman R: rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that
are botulinum toxin substrates. J Biol Chem. 264:16378–16382.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Haataja L, Groffen J and Heisterkamp N:
Characterization of RAC3, a novel member of the Rho family. J Biol
Chem. 272:20384–20388. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Diekmann D, Nobes CD, Burbelo PD, Abo A
and Hall A: Rac GTPase interacts with GAPs and target proteins
through multiple effector sites. EMBO J. 14:5297–5305.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ueyama T, Eto M, Kami K, Tatsuno T,
Kobayashi T, Shirai Y, Lennartz MR, Takeya R, Sumimoto H and Saito
N: Isoform-specific membrane targeting mechanism of Rac during Fc
gamma R-mediated phagocytosis: Positive charge-dependent and
independent targeting mechanism of Rac to the phagosome. J Immunol.
175:2381–2390. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yamauchi A, Li SJ, Marchal CC and Dinauer
MC: Rac2-null macrophages have defects in superoxide production and
Fc gamma-R-mediated phagocytosis. Blood. 100:17722002.
|
|
41
|
Patel JC, Hall A and Caron E: Vav
regulates activation of Rac but not Cdc42 during FcgammaR-mediated
phagocytosis. Mol Biol Cell. 13:1215–1226. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang YK, Lu XB, Wang YH, Yang MM and Jiang
DM: Identification crucial genes in peripheral neuropathic pain
induced by spared nerve injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
18:2152–2159. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kriegel AJ, Liu Y, Fang Y, Ding X and
Liang M: The miR-29 family: Genomics, cell biology, and relevance
to renal and cardiovascular injury. Physiol Genomics. 44:237–244.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Smirnova L, Gräfe A, Seiler A, Schumacher
S, Nitsch R and Wulczyn FG: Regulation of miRNA expression during
neural cell specification. Eur J Neurosci. 21:1469–1477. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dharap A, Bowen K, Place R, Li LC and
Vemuganti R: Transient focal ischemia induces extensive temporal
changes in rat cerebral microRNAome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
29:675–687. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yuan Y, Wang JY, Xu LY, Cai R, Chen Z and
Luo BY: MicroRNA expression changes in the hippocampi of rats
subjected to global ischemia. J Clin Neurosci. 17:774–778. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shioya M, Obayashi S, Tabunoki H, Arima K,
Saito Y, Ishida T and Satoh J: Aberrant microRNA expression in the
brains of neurodegenerative diseases: miR-29a decreased in
Alzheimer disease brains targets neurone navigator 3. Neuropathol
Appl Neurobiol. 36:320–330. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Khanna S, Rink C, Ghoorkhanian R, Gnyawali
S, Heigel M, Wijesinghe DS, Chalfant CE, Chan YC, Banerjee J, Huang
Y, et al: Loss of miR-29b following acute ischemic stroke
contributes to neural cell death and infarct size. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 33:1197–1206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pandi G, Nakka VP, Dharap A, Roopra A and
Vemuganti R: MicroRNA miR-29c downregulation leading to
de-repression of its target DNA methyltransferase 3a promotes
ischemic brain damage. PLoS One. 8:e580392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hand NJ, Horner AM, Master ZR, Boateng LA,
LeGuen C, Uvaydova M and Friedman JR: MicroRNA profiling identifies
miR-29 as a regulator of disease-associated pathways in
experimental biliary atresia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
54:186–192. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|