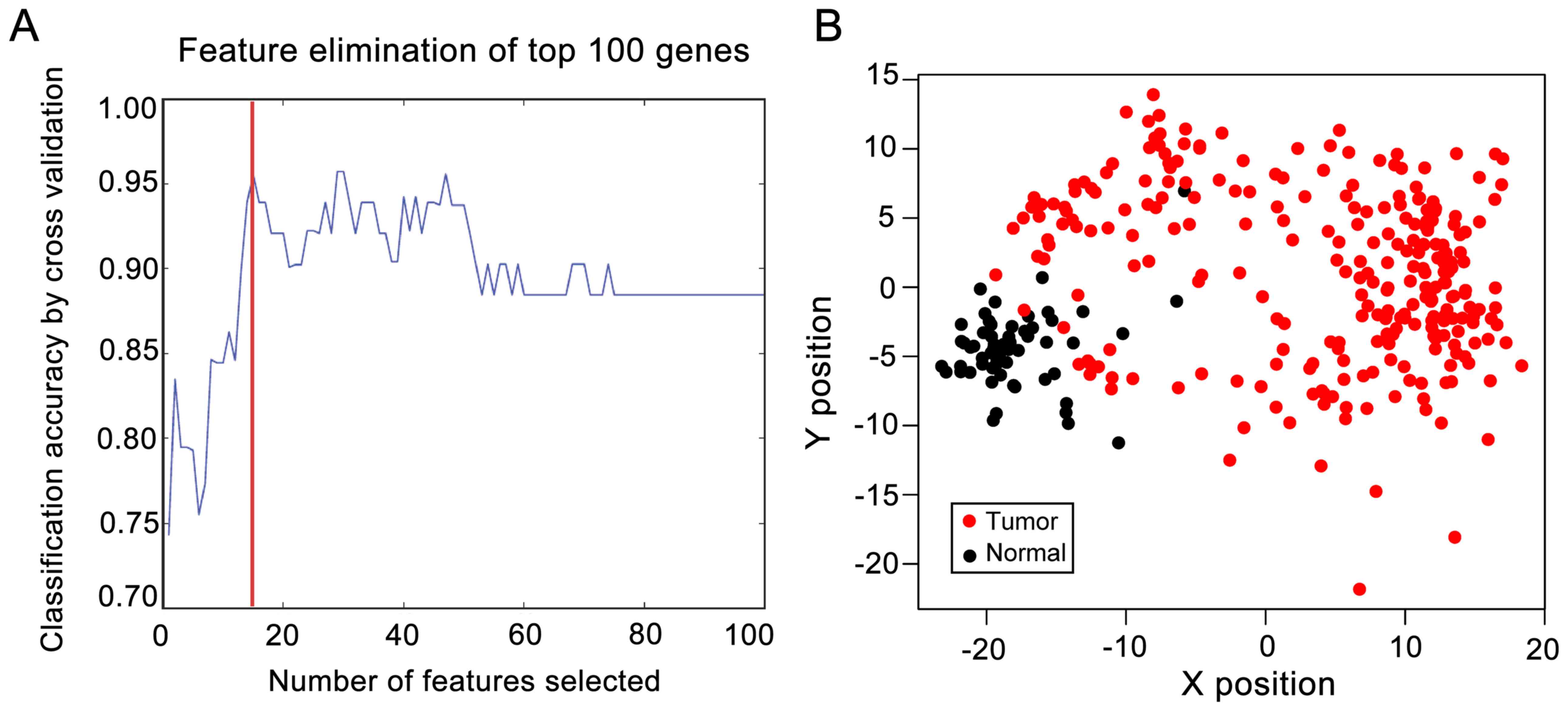
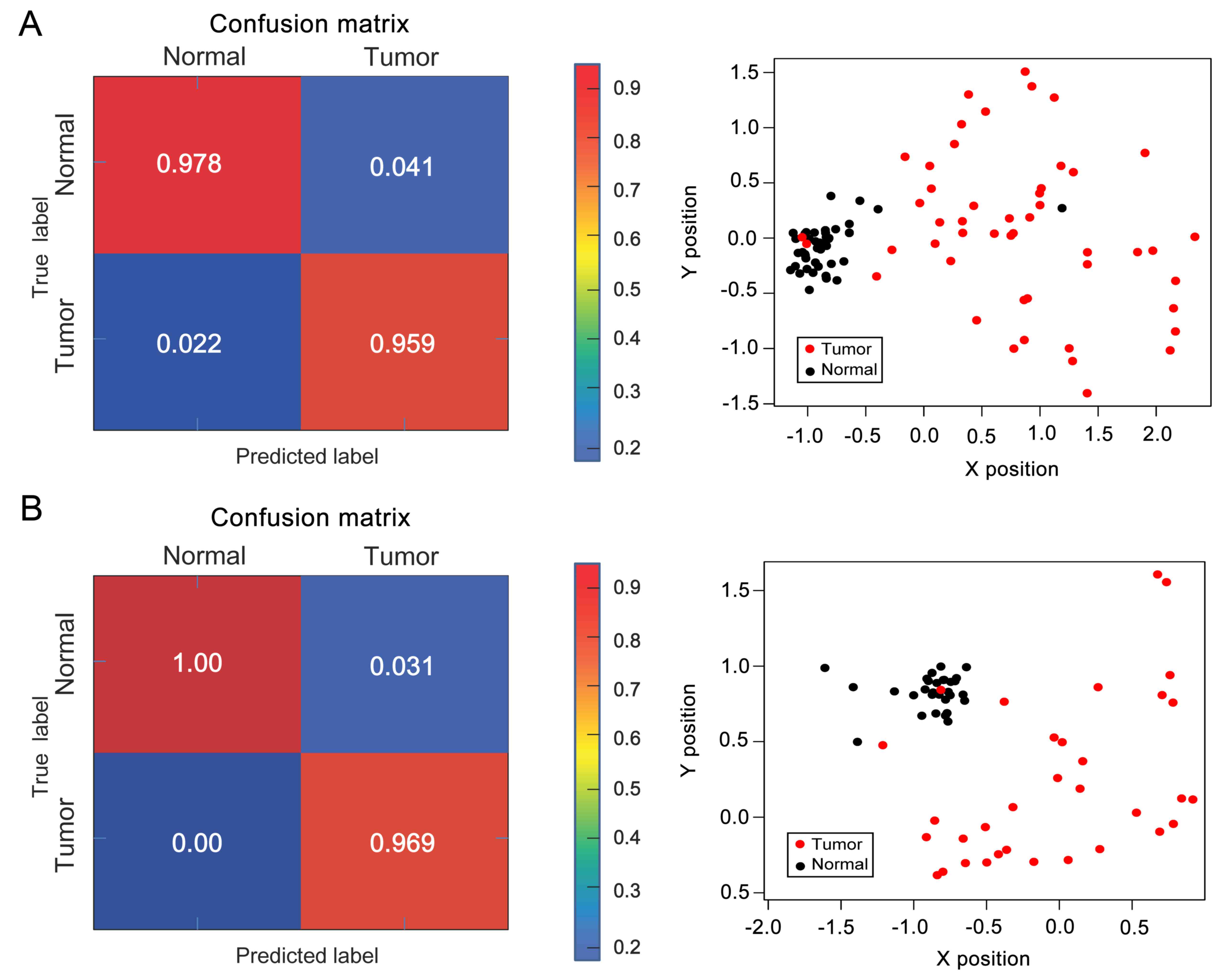
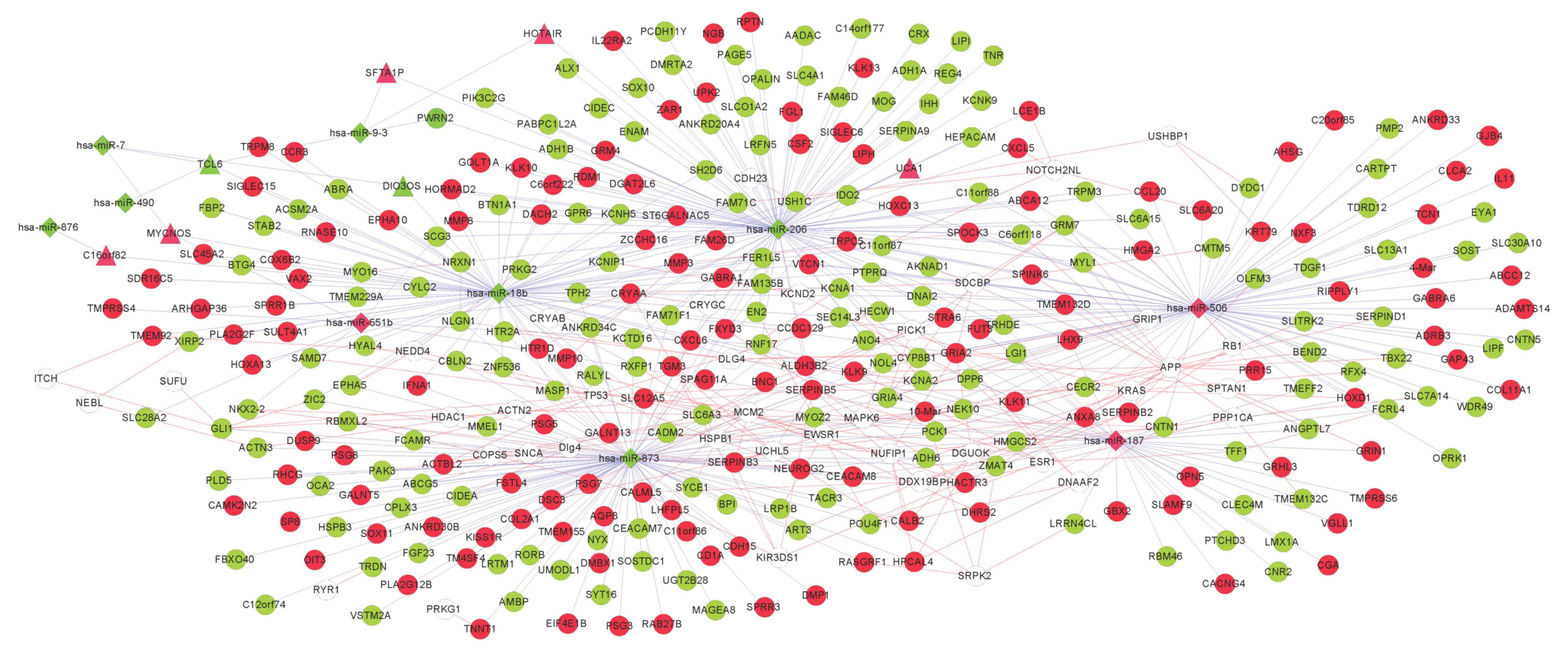
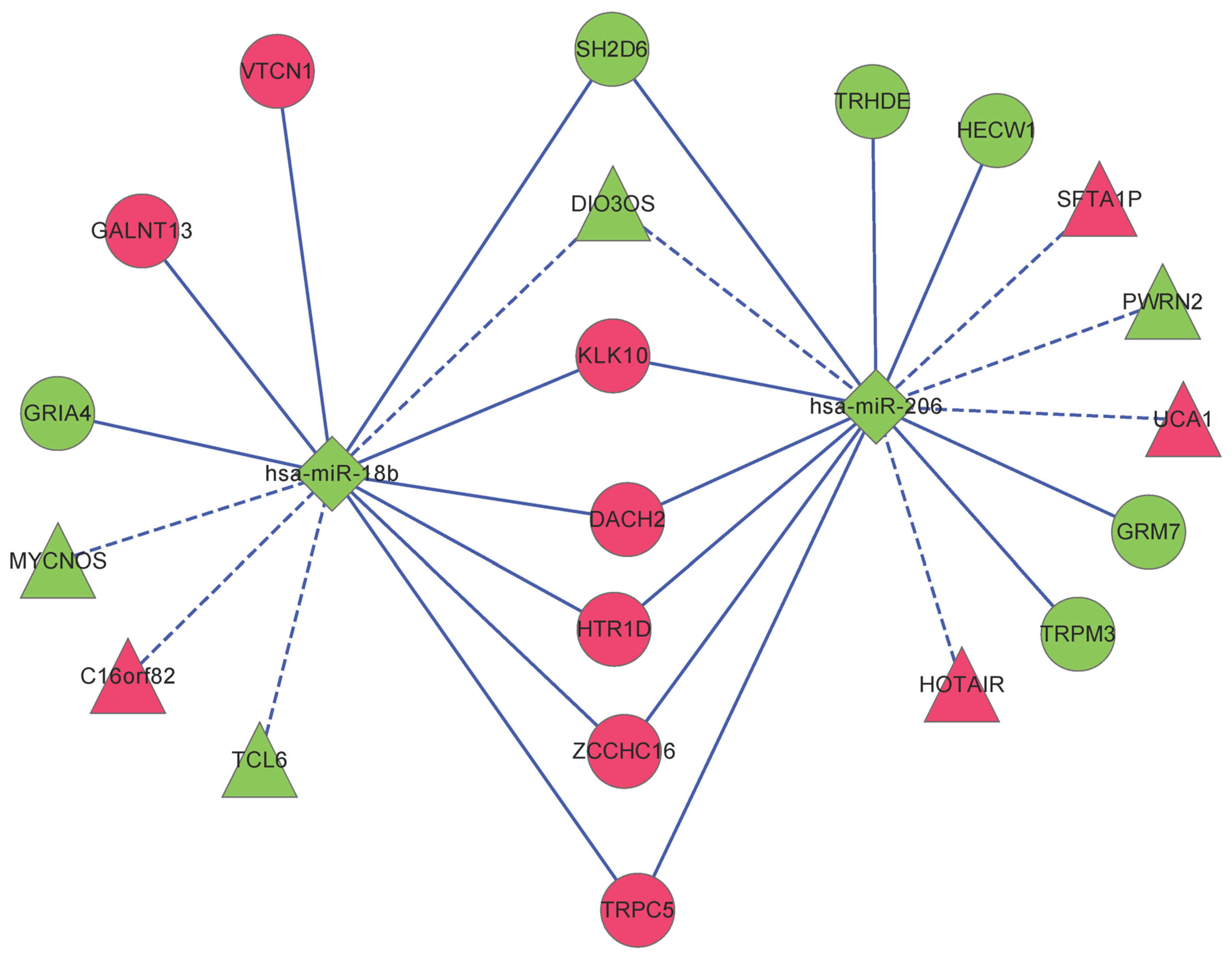
|
1
|
PDQ Cancer Information Summaries: Health
Professional VersionPDQ Cancer Information Summaries. Bethesda
(MD): 2002
|
|
2
|
Sosa JA and Udelsman R: Papillary thyroid
cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 15:585–601. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty
GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph GW, Sawka AM,
Schlumberger M, et al: 2015 American Thyroid Association Management
Guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and
differentiated thyroid cancer: The American Thyroid Association
Guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid
cancer. Thyroid. 26:1–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xing M, Haugen BR and Schlumberger M:
Progress in molecular-based management of differentiated thyroid
cancer. Lancet. 381:1058–1069. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song X, Wang B, Bromberg M, Hu Z,
Konigsberg W and Garen A: Retroviral-mediated transmission of a
mouse VL30 RNA to human melanoma cells promotes metastasis in an
immunodeficient mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:6269–6273.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yotsukura S, duVerle D, Hancock T,
Natsume-Kitatani Y and Mamitsuka H: Computational recognition for
long non-coding RNA (lncRNA): Software and databases. Brief
Bioinform. 18:9–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jeggari A, Marks DS and Larsson E:
miRcode: A map of putative microRNA target sites in the long
non-coding transcriptome. Bioinformatics. 28:2062–2063. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karreth FA, Tay Y, Perna D, Ala U, Tan SM,
Rust AG, DeNicola G, Webster KA, Weiss D, Perez-Mancera PA, et al:
In vivo identification of tumor-suppressive PTEN ceRNAs in an
oncogenic BRAF-induced mouse model of melanoma. Cell. 147:382–395.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, Ni P, Gu Z, Qiao Y,
Chen N, Sun F and Fan Q: CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA,
HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver
cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:5366–5383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang H, Niu L, Jiang S, Zhai J, Wang P,
Kong F and Jin X: Comprehensive analysis of aberrantly expressed
profiles of lncRNAs and miRNAs with associated ceRNA network in
muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 7:86174–86185. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Fan D, Jian Z, Chen GG and Lai
PB: Cancer specific long noncoding RNAs show differential
expression patterns and competing endogenous RNA potential in
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01410422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Troyanskaya O, Cantor M, Sherlock G, Brown
P, Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Botstein D and Altman RB: Missing value
estimation methods for DNA microarrays. Bioinformatics. 17:520–525.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rao Y, Lee Y, Jarjoura D, Ruppert AS, Liu
CG, Hsu JC and Hagan JP: A comparison of normalization techniques
for microRNA microarray data. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol.
7:Article222008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li D and Dye TD: Power and stability
properties of resampling-based multiple testing procedures with
applications to gene oncology studies. Comput Math Methods Med.
2013:6102972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kivimäki I, Lebichot B, Saramäki J and
Saerens M: Two betweenness centrality measures based on Randomized
Shortest Paths. Sci Rep. 6:196682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Breitkreutz D, Hlatky L, Rietman E and
Tuszynski JA: Molecular signaling network complexity is correlated
with cancer patient survivability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:9209–9212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van den Heuvel MP and Sporns O: Network
hubs in the human brain. Trends Cogn Sci. 17:683–696. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baur B and Bozdag S: A feature selection
algorithm to compute gene centric methylation from probe level
methylation data. PLoS One. 11:e01489772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Berrondo C, Flax J, Kucherov V, Siebert A,
Osinski T, Rosenberg A, Fucile C, Richheimer S and Beckham CJ:
Expression of the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR correlates with
disease progression in bladder cancer and is contained in bladder
cancer patient urinary exosomes. PLoS One. 11:e01472362016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Geng YJ, Xie SL, Li Q, Ma J and Wang GY:
Large intervening non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated with
hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J Int Med Res. 39:2119–2128.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ono H, Motoi N, Nagano H, Miyauchi E,
Ushijima M, Matsuura M, Okumura S, Nishio M, Hirose T, Inase N, et
al: Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR is relevant to cellular
proliferation, invasiveness, and clinical relapse in small-cell
lung cancer. Cancer Med. 3:632–642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang J, Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang XM, Yin DT,
Zheng LL, Zhang DY and Lu XB: Differential expression profiling and
functional analysis of microRNAs through stage I–III papillary
thyroid carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. 10:585–592. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suresh R, Sethi S, Ali S, Giorgadze T and
Sarkar FH: Differential expression of MicroRNAs in papillary
thyroid carcinoma and their role in racial disparity. J Cancer Sci
Ther. 7:145–154. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen YT, Kitabayashi N, Zhou XK, Fahey TJ
III and Scognamiglio T: MicroRNA analysis as a potential diagnostic
tool for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 21:1139–1146.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nikiforova MN, Tseng GC, Steward D, Diorio
D and Nikiforov YE: MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid
tumors: Biological significance and diagnostic utility. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 93:1600–1608. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McCarthy JJ: MicroRNA-206: The skeletal
muscle-specific myomiR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1779:682–691. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu X, He M, Hou Y, Liang B, Zhao L, Ma S,
Yu Y and Liu X: Expression profiles of microRNAs and their target
genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:1415–1420.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yip L, Kelly L, Shuai Y, Armstrong MJ,
Nikiforov YE, Carty SE and Nikiforova MN: MicroRNA signature
distinguishes the degree of aggressiveness of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2035–2041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leone V, D'Angelo D, Rubio I, de Freitas
PM, Federico A, Colamaio M, Pallante P, Medeiros-Neto G and Fusco
A: MiR-1 is a tumor suppressor in thyroid carcinogenesis targeting
CCND2, CXCR4, and SDF-1alpha. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
96:E1388–E1398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Borgoño CA, Michael IP and Diamandis EP:
Human tissue kallikreins: Physiologic roles and applications in
cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2:257–280. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu XL, Wazer DE, Watanabe K and Band V:
Identification of a novel serine protease-like gene, the expression
of which is down-regulated during breast cancer progression. Cancer
Res. 56:3371–3379. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Goyal J, Smith KM, Cowan JM, Wazer DE, Lee
SW and Band V: The role for NES1 serine protease as a novel tumor
suppressor. Cancer Res. 58:4782–4786. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mancikova V, Buj R, Castelblanco E,
Inglada-Pérez L, Diez A, de Cubas AA, Curras-Freixes M, Maravall
FX, Mauricio D, Matias-Guiu X, et al: DNA methylation profiling of
well-differentiated thyroid cancer uncovers markers of recurrence
free survival. Int J Cancer. 135:598–610. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|